Backend-as-a-service is becoming a driver of app-based projects. This is supported by the growing mobile app development and expansion of MBaaS solutions. These platforms help companies reduce administrative, operational, and compliance costs and improve small and medium businesses’ efficiency in other ways.
Companies increasingly delegate backend development to external services, allowing them to concentrate on frontend functionality. That is why developers, product owners, and investors need to understand how BaaS works and the value it offers.
In this article, we’ll explore the key features of BaaS platforms, highlight common use cases, and review some of the most reliable providers available today.
BaaS Market Overview
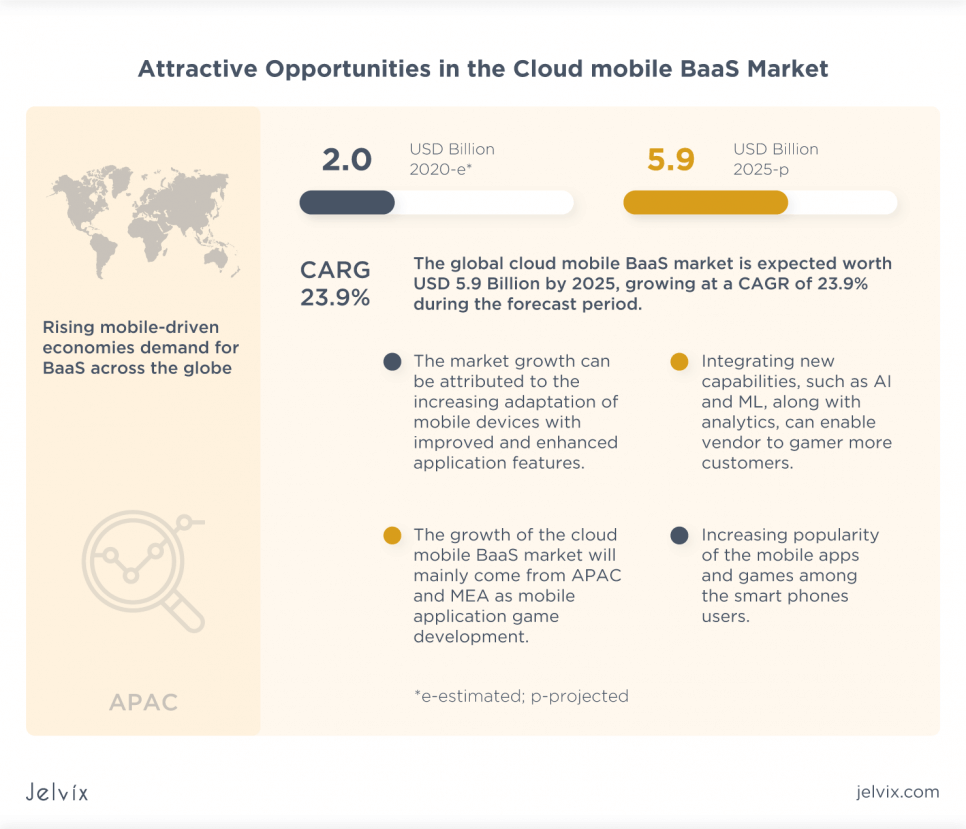
In 2024, the global Cloud Backend‑as‑a‑Service sector was valued at about USD 4.31 billion, and it’s expected to generate USD 10.53 billion by 2030.
Low-code and no-code development is expanding, with the global market projected to reach about USD 65 billion by 2027. As these tools make it easier to build the front end of applications, many teams still need a way to manage the backend without investing in complex infrastructure. BaaS meets that need by offering ready-to-use features like authentication, data storage, and system integrations, allowing teams to deliver quality custom enterprise solutions.
The market is also growing thanks to the rising adoption of cloud-based mobile applications. As of 2025, there are about 7.4 billion smartphone users in the world. This number will only grow, creating a massive user base and driving BaaS demand.
What is BaaS in Cloud Computing?
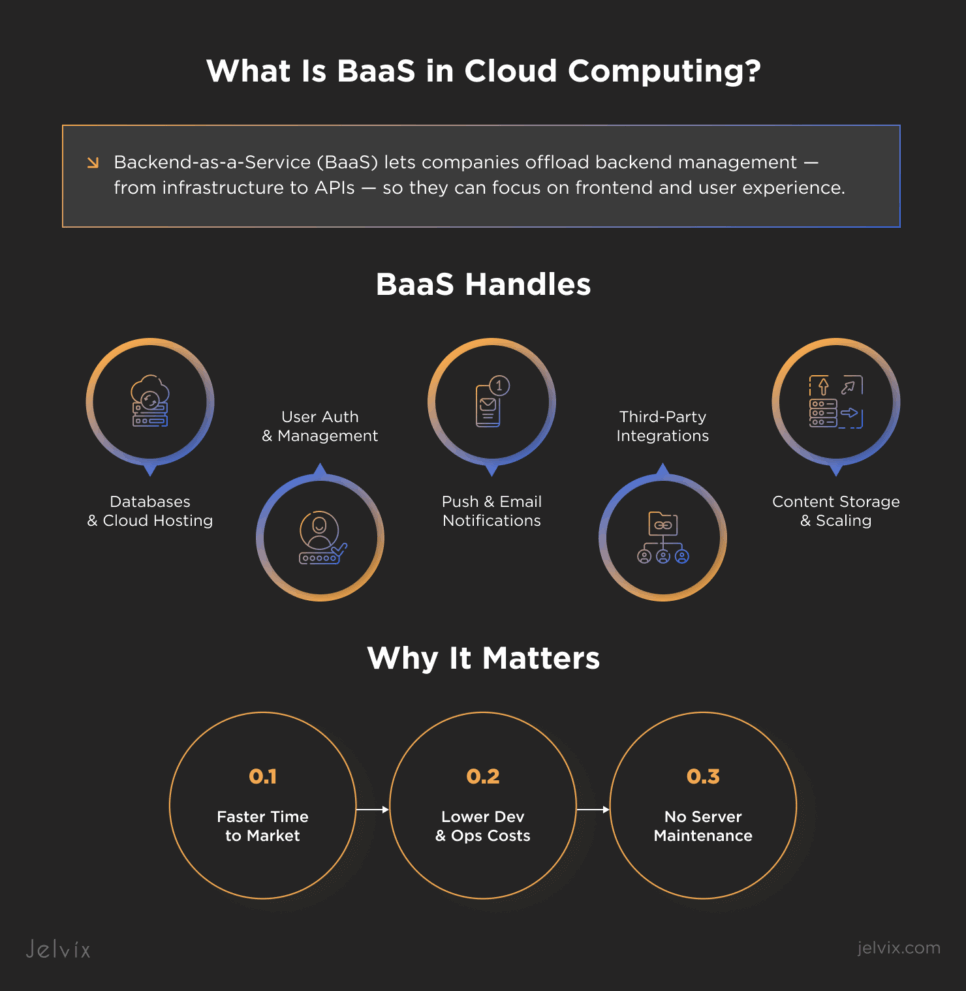
BaaS can be defined as a partnership model allowing companies to delegate backend and focus on the production and client-side. The backend providers offer APIs and SDKs to help integrate all backend services without writing them. You also don’t need to manage servers to maintain the work of the application.
By using BaaS, you hand over cloud infrastructure management to your provider. Managing it in-house would require significant investment in setup and ongoing maintenance. BaaS platforms give you access to ready-to-use infrastructure along with a team that handles it.
You can expect to get the following server-side features from a BaaS vendor:
- Database management and optimization
- Cloud storage and hosting
- User authentication, verification, and management
- Storage of user-generated content
- Push and email notifications
- Integrations with third-party services (e.g., Google Maps, social media)
- Infrastructure management, including scaling, data backup, and security settings
Key Benefits of Implementing BaaS Software
Backend SaaS development is often the most resource-intensive part of building an application. The more complex the project, the more time, budget, computing power, and developers it requires. With a BaaS provider, much of this can be outsourced and automated.
Instead of building everything from scratch, developers get auto-generated backend code tailored to the app’s needs. This allows them to focus on customizing features within a ready-made architecture.
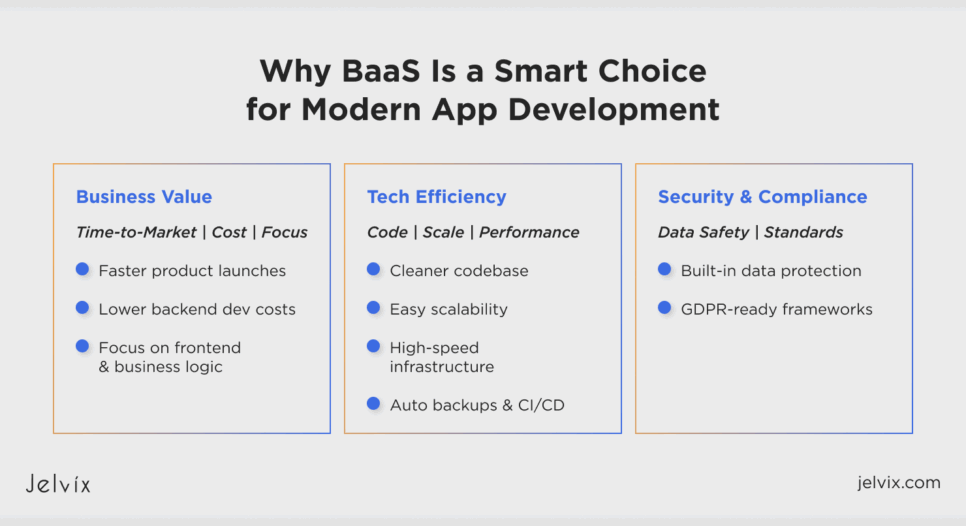
Business Benefits
From a business point of view, you need to cut time and money without affecting the quality of the final product. When you choose the BaaS model, you save your resources by automating the routine tasks.
Reduced Time-to-Market and Cost-Effectiveness
These two benefits go hand in hand. By outsourcing backend development, you gain extra time to refine features, streamline operations, and enhance customer experience. Faster development also means you can launch new products and updates faster than your competitors.
Focus on Business Logic
By using a BaaS provider, you can eliminate much of the routine backend coding. This frees up resources, allowing developers to focus on business-specific features and helping the team concentrate more on the strategic side of the app.
Focus on Frontend and UX
The frontend shapes how users interact with your mobile app. When backend development is outsourced, your team can focus more on designing a seamless and engaging user experience. Prioritizing frontend quality leads to higher user satisfaction and better retention.
Cross-Platform Development
Developing apps for web, desktop, and mobile platforms requires different approaches, tools, and codebases. This will take the corresponding amount of money and effort. Considering the BaaS/MBaaS vendors’ service, you will get the corresponding SDKs instead of duplicating the effort.
Tech Benefits
App development usually involves building architecture, handling security, backups, scaling, and ongoing maintenance. BaaS automates much of this work, saving time and resources. It’s especially useful in areas like AI software development, where teams benefit from faster deployment and fewer infrastructure distractions.
Code quality
As apps grow more complex, maintaining clean, efficient code becomes harder. Developers often prioritize new features over fixing bugs, leading to quick patches and mounting technical debt. With BaaS, much of the backend is handled through reliable, ready-made APIs and SDKs. This reduces boilerplate work and keeps your codebase leaner and easier to maintain.
Scalability
Most projects start small but need room to grow. BaaS makes it easy to scale up or down using your provider’s infrastructure without major investments or architectural changes. Instead of rebuilding your app, you simply request more resources or upgrade your plan.
Performance
App performance depends heavily on server capacity. BaaS providers offer robust infrastructure and expert DevOps support, delivering better performance than most in-house setups. By relying on their computing power, you ensure smoother, faster app performance as demand grows.
Out-of-the-box backup procedures
You can never predict exactly when a service outage or system failure may occur, and downtime can happen without warning. In 2024, Forbes Tech Council reported that the average cost of downtime for large organizations has escalated to approximately USD 9,000 per minute. That translates to over USD $540,000 per hour. Given these high stakes, it’s essential to rely on a BaaS provider that includes built-in backup and recovery features.
Continuous Delivery and Integration (CI/CD)
CI/CD is a development practice that imposes frequent implementation of small changes and continuous version control. When you use BaaS, you don’t have to spend much effort to deploy every minor update, as all changes are integrated into your app instantly.
Many modern BaaS platforms provide built-in support for CI/CD out of the box. For example, GitHub Actions and GitLab CI templates are now available for platforms like Supabase and AWS Amplify, allowing developers to automate testing, deployment, and monitoring directly from their repositories. This reduces the setup overhead and speeds up the development lifecycle even further.
Security Benefits
Software projects must protect user data and comply with international regulations like GDPR. As cybersecurity threats are getting more severe, companies can face financial and reputational risks if customer data is exposed or lost.
BaaS platforms are equipped with the tools and expertise to strengthen security, meet compliance standards, block unauthorized access, and recover data in case of an incident.
Is BaaS a Good Choice for My Project?
BaaS can be helpful for the business and technical side of the project. In fact, it’s perfect for most projects, but still, there are areas where BaaS doesn’t fit.
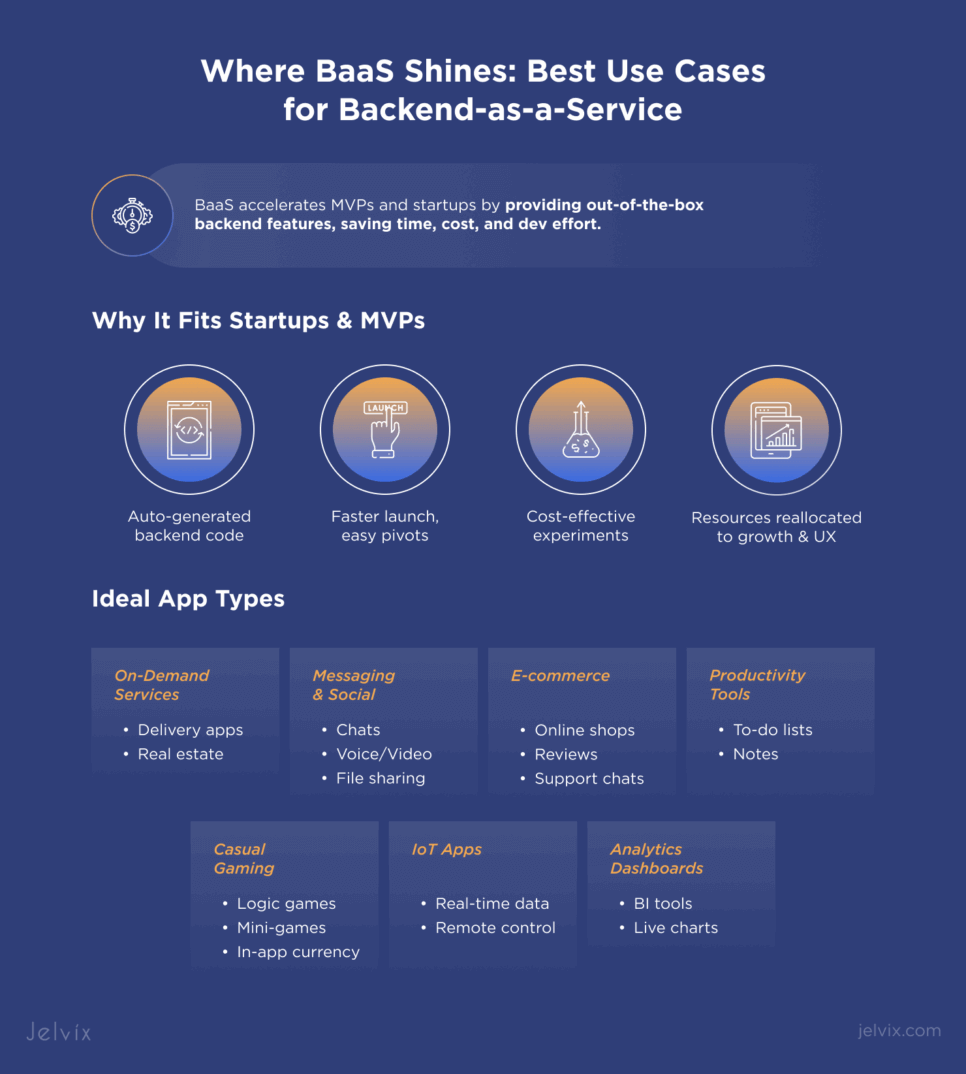
BaaS Perfect Fits
One of the biggest advantages of BaaS is access to ready-made APIs and SDKs. That makes it an ideal solution for startups and MVPs.
Early-stage companies focus on finding product-market fit—a process that often involves trial and error. Each failed experiment costs time and money, so keeping development costs low is critical. BaaS helps startups quickly launch MVPs, test ideas, and pivot without overspending on backend infrastructure.
With out-of-the-box backend solutions, startups can save numerous development hours and tens of thousands of dollars. These saved resources can be redirected toward market research, business growth, or attracting investors. And if a product attempt fails, the financial loss is much more manageable.
BaaS works best for apps with common, reusable features. You can build them using pre-made frameworks from BaaS providers, then customize them to match your specific business needs.
On-demand services: transportation (Uber), food delivery (Glovo), different types of marketplaces (freelance, real estate, services, e-commerce). Functionality:
- vendor and customer profiles
- listings of goods and services
- in-app search, shopping cart
- geolocation
- paying and delivery
Social networks and real-time messengers (Tinder, WhatsApp, Slack, Discord). Functionality:
- user account
- chat with file sharing, audio, and video calling
- in-app search with different criteria
E-commerce apps, online shops (eBay, brand shops). Functionality:
- advanced search
- in-app messenger (buyer-seller/buyer-support service)
- customer rates, reviews
- shopping cart, checkout, delivery options
Productivity apps (Trello, Todoist, OneNote). Functionality:
- to-do lists, ticket creation
- advanced search
- note sharing, attachments, comments
Gaming without complex gameplay (business, three-in-a-row, hidden objects, logical quizzes). Functionality:
- levels and mini-games
- in-app currency
IoT applications. Functionality:
- device registration and management
- real-time data collection and syncing
- remote control and automation
- push notifications and alerts
Data-heavy analytics dashboards. These are common for BaaS use cases, including Firebase Analytics and other analytics or BI systems. Functionality:
- integration with multiple data sources
- real-time and historical data visualization
- role-based access control
- export and reporting tools
Think Twice
While backend-as-a-service offers a powerful way to speed up development by replacing custom infrastructure with ready-made building blocks, it’s not the perfect fit for every scenario. Depending on your business model and technical needs, there are situations where BaaS might require extra caution or a hybrid approach.
Heavy Apps for Large Enterprises
Many BaaS providers now support enterprise-scale workloads. Firebase, for example, is used in apps with over 10 million daily active users. Supabase and AWS Amplify offer enterprise features like multi-region support, SLAs, and advanced access controls.
However, as applications grow more complex, teams may run into challenges related to scaling costs, vendor lock-in, or limited backend customization. BaaS is still a viable option in these cases, but it’s important to assess whether its convenience offsets long-term flexibility and operational control.
Apps with Strict Security and Compliance Requirements
Today’s BaaS vendors offer stronger compliance options than ever before, including HIPAA-eligible, ISO 27001-certified, and FedRAMP-ready hosting plans. This makes BaaS usable in industries like healthcare software development, finance, and government.
Still, if your app handles especially sensitive data or requires strict internal security policies, it may be safer to host your own backend. Open-source platforms like Appwrite or Hasura offer self-hosting options that give teams more control over data residency, access policies, and audit processes.
High-Performance Games with Complex Architecture
BaaS platforms are a solid fit for casual and mid-tier games, especially those needing real-time data, messaging, or user authentication. But when it comes to graphically intensive, multiplayer, or VR/AR games, BaaS can fall short.
These projects typically require deep control over server performance, low-latency networking, and resource management. In such cases, combining custom infrastructure with select BaaS features might offer the best results.
BaaS Use Case: 1001 Dubai and Back4App BaaS platform
You’ve already seen how BaaS can simplify development. No, let’s look at how one startup used it to build and grow a real-world SaaS platform.
1001 Dubai is an e-commerce startup that helps local supermarkets, pharmacies, and convenience stores serve their customers directly. The company provides both a mobile application and a backend order management system used internally by its clients.
By adopting a backend-as-a-service model, 1001 Dubai was able to run its entire cross-platform application through a single infrastructure, without building separate versions for Android, iOS, desktop, and web. This approach helped the startup save approximately $370,000 over four years by avoiding the need to hire full-time mobile developers.
Using BaaS also allowed 1001 Dubai to automate many backend tasks, such as scaling, load balancing, and security. When releasing updates, the team could easily add new server logic, enable features, and handle deployment with minimal effort—saving valuable time and resources.
Read more about the most common software development strategies and take a look at their benefits and drawbacks.
Leading BaaS Platforms To Consider in 2025-2026
The BaaS environment has matured into two clear categories based on how services are delivered:
- Hosted or Fully-Managed BaaS: perfect for fast deployment, minimal infrastructure overhead, and scalable support.
- Open-Source or Self-Hosted BaaS: favored by teams that need more control, customization, or data sovereignty.
Understanding these models helps businesses and developers choose the backend solution that fits their project goals and compliance needs.
Hosted or Fully-Managed BaaS
These platforms handle infrastructure, scalability, and maintenance, allowing teams to focus on the frontend and user experience.
Firebase (Google)
The best mobile backend-as-a-service and a long-time leader in mobile and web app development, Firebase offers a robust suite of tools:
- Development: Firestore database, hosting, serverless functions, cloud messaging, and ML integration.
- Monitoring: Performance tracking, crash reporting, A/B testing, and real-time analytics.
- Engagement: In-app messaging, predictive targeting, push notifications, and remote config.
Firebase is ideal for startups and cross-platform apps that need to scale quickly with minimal backend overhead.
AWS Amplify
Amazon’s solution for building full-stack apps with ease is now tightly integrated with popular frameworks like React, Flutter, and Next.js.
- Backend: GraphQL and REST APIs, Lambda functions, Amazon Cognito for auth, and storage via S3.
- Frontend Integration: Amplify Studio simplifies UI + backend deployment without deep BaaS cloud expertise.
- Engagement: Amazon Pinpoint for user behavior tracking, push notifications, and marketing automation.
Best suited for teams that want to leverage AWS infrastructure with a modern DevOps workflow.
MongoDB Atlas App Services
Previously known as Stitch, this managed BaaS offering from MongoDB includes:
- Data Access: Native connection to MongoDB Atlas with sync, triggers, and real-time queries.
- Authentication: Built-in identity providers, rules, and user roles.
- Edge Functions: Serverless backend functions for custom logic and workflows.
Ideal for applications that are already built around MongoDB or require flexible data models with global deployment.
Important! As of 2024, Azure Mobile Apps is in maintenance mode. Microsoft recommends migrating to a combination of Azure App Service + Azure Functions for serverless backend needs, along with Cosmos DB or Azure SQL for storage.
Open-Source or Self-Hosted BaaS
These platforms offer developer control, transparency, and flexibility for teams who prefer to host their infrastructure or meet strict compliance needs.
Supabase
Often dubbed the “open-source Firebase alternative,” Supabase is built on PostgreSQL and offers:
- Database: Instant PostgreSQL with real-time subscriptions.
- Auth: Magic links, OAuth, and third-party login support.
- Storage and Edge Functions: File storage, row-level security, and JS-based serverless functions.
- Self-hosting: Full Docker-based deployment for local or private cloud use.
Perfect for startups or enterprises that want Firebase-like speed but own their stack.
Appwrite
An all-in-one backend platform designed for frontend developers:
- APIs: REST APIs for authentication, databases, file storage, and real-time messaging.
- Multi-language SDKs: Native support for JavaScript, Flutter, Swift, Kotlin, and more.
- Security: Role-based access, data encryption, and custom permissions.
Offers full hosting flexibility — run it on your cloud or use Appwrite Cloud for managed hosting.
Hasura + Postgres
Hasura isn’t a full BaaS, but it powers real-time GraphQL APIs on top of PostgreSQL and is used as a lightweight backend layer.
- Instant GraphQL: Generate APIs automatically from your schema.
- Access control: Fine-grained rules, JWT integration, and remote schema support.
- Event triggers and actions: Connect with serverless functions or legacy systems.
Ideal for advanced teams needing low-latency GraphQL and tight control over data workflows.
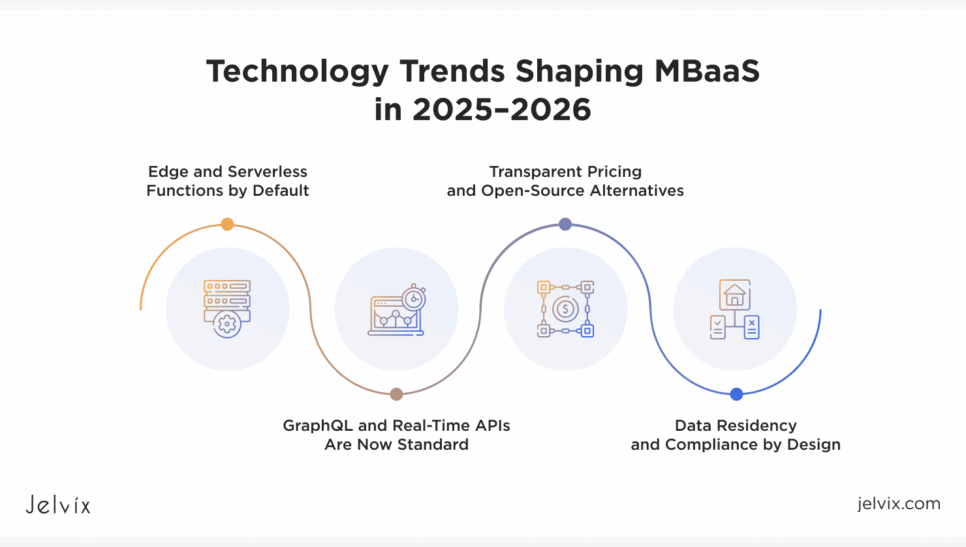
Technology Trends That Shape the Best MBaaS Solutions
As backend-as-a-service platforms continue to evolve, several technology shifts are shaping what developers and businesses expect from modern back-end solutions.
Edge and Serverless Functions by Default
Traditional BaaS platforms often relied on centralized data centers to execute backend logic, which introduced delays and performance issues, especially for global applications. In 2025, many vendors will provide edge-deployed serverless functions, such as Cloudflare Workers or Vercel Functions, allowing code to run closer to the end user. This reduces latency, supports regional execution, and improves application responsiveness across different geographies.
GraphQL and Real-Time APIs Are Now Standard
REST APIs, while still common, no longer meet the demands of modern, dynamic applications that require flexible data access and live updates. Platforms like Supabase, Hasura, and AWS AppSync have established GraphQL and real-time subscriptions as core components of their services. As a result, support for GraphQL has become a key checklist item for teams selecting a BaaS platform in 2025.
Data Residency and Compliance by Design
With increasing pressure from regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, FedRAMP, and CCPA/CPRA, enterprise organizations are demanding strict control over where data is stored and how it is accessed. In 2025, leading BaaS providers offer region-level data residency, detailed audit logs, and certifications like SOC 2 and FedRAMP. These features are now essential, particularly for industries handling sensitive or regulated data, and should be considered part of the security evaluation process.
Transparent Pricing and Open-Source Alternatives
Many proprietary BaaS platforms have unpredictable pricing models that make it difficult to plan costs at scale. In contrast, open-source and self-hosted alternatives like Supabase and Appwrite offer transparent pricing and full access to their codebases. This gives developers more control over deployment, compliance, and long-term flexibility. In 2025, the choice between closed SaaS and open-source BaaS often depends on how much ownership and customization a team requires.
Developing Custom Backend Solutions with a Tech Partner
As the IT industry continues to evolve, expectations for modern applications are rising. Users now expect reliable performance, strong functionality, and a smooth user experience, regardless of the industry. With competitors launching new products regularly, speeding up development has become a top priority for app-driven businesses. This is where the BaaS model proves valuable.
Backend-as-a-service offers clear advantages for both business and development teams. It fits most application types, though in some cases, it may not be the ideal choice. Choosing the right approach means carefully reviewing what different BaaS providers offer. If you’re considering building a custom backend instead, our experts are available to help. Contact us to discuss your project requirements and explore the most effective solution for your stage and growth plans.
Need a certain developer?
Access top talent pool to reach new business objectives.