Cloud services have been among the most popular platforms lately, with companies like Microsoft, Amazon, Google leading the way for technology growth. Instead of relying on their servers, companies prefer outsourcing their storage to trusted providers, passing over the responsibility for supporting the infrastructure and assuring security.
Let’s take a brief look at the statistics of the cloud computing market to see its latest trends:
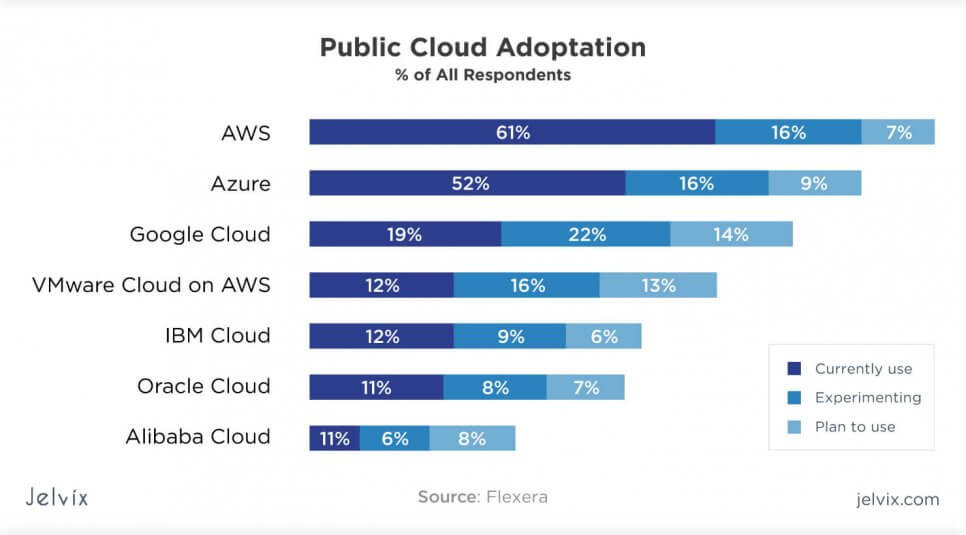
- Public cloud services are projected to account for a larger share of cloud infrastructure spending, reaching nearly 46% by 2024;
- 49% of data will be stored in public cloud environments by 2025;
- The global cloud computing market is projected to reach $791.48 billion worth in 2028, with a 17.9% CAGR.
The trust of the number of businesses in cloud service is rapidly increasing. We are looking at the future where the majority of companies will be using cloud providers regularly. If you are considering switching over to cloud infrastructure instead of maintaining the local network, this guide is for you.
We’ll talk about the benefits of using cloud, types of services, choice criteria, and examine the best cloud service providers.
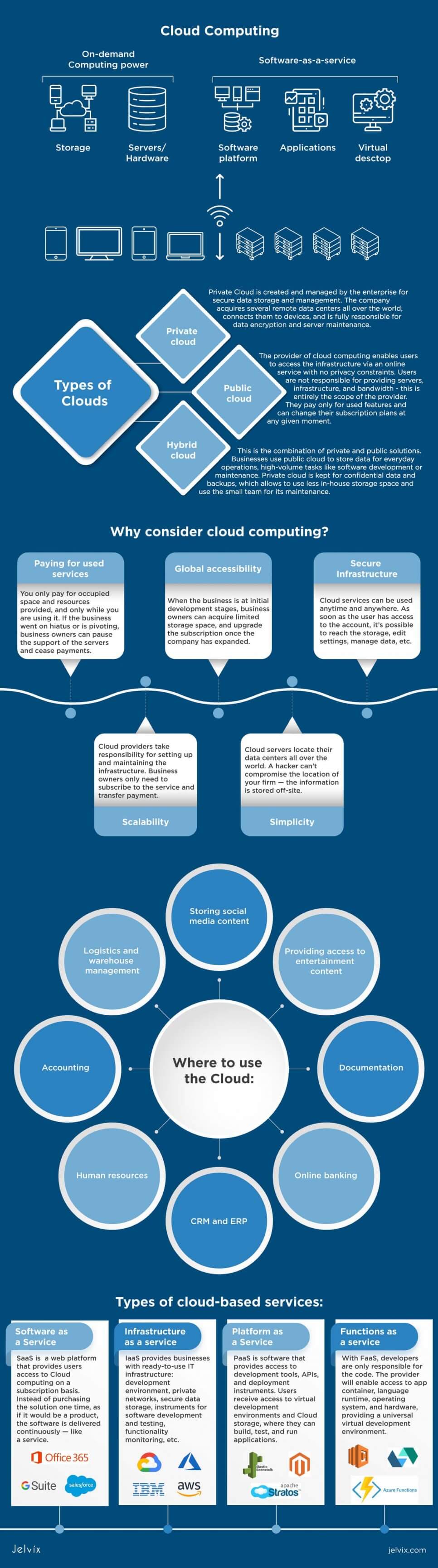
What is Cloud Computing?
The definition of cloud computing is the system of computer resources, infrastructure, computing power, and data storage that are available on-demand without user involvement. The provider fully manages the technical aspects of the service. The data is made accessible to multiple users via an online service. To access the information, a user needs to log in to a personal account.
Why Consider Cloud Computing?
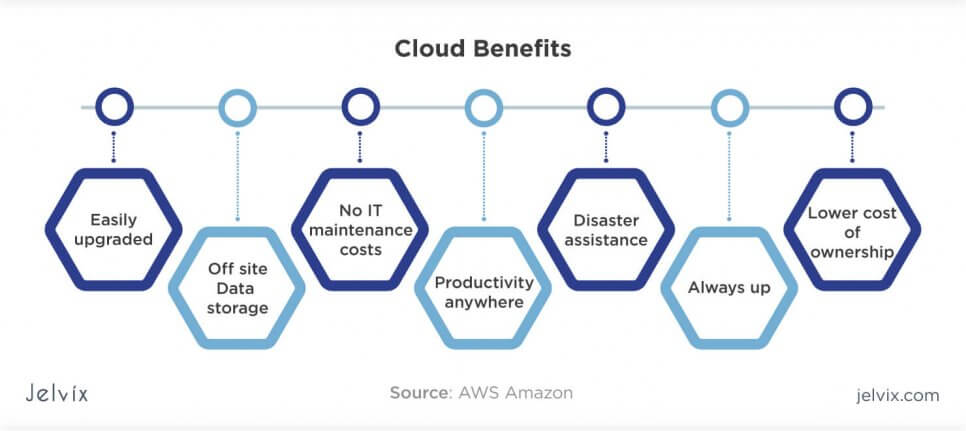
Over the years, business owners received tangible proof of cloud multiple benefits — and the statistics serve excellent evidence. Let’s see what these advantages that managed to attract millions of users all over the world are and how they apply to your business.
- Paying for used services. One of the defining qualities of cloud storage is that you only pay for occupied space, computing power, used traffic, and other resources when you were using them. If the business went on hiatus or is pivoting, business owners can pause the support of the cloud-based server and cease payments.
- Scalability. When the business is at initial development stages, business owners can acquire limited storage space, and upgrade the subscription once the company has expanded. With in-house infrastructure, you need to foresee your growth and implement massive systems from the very beginning. Otherwise, you’d have to consider reconfiguration, which is just as expensive as overpaying.
- Global accessibility. Cloud services can be used anytime and anywhere. As soon as the user has access to the account, it’s possible to reach the storage, edit settings, manage data, etc.
- Simplicity. Cloud providers take responsibility for setting up and maintaining the infrastructure. Business owners only need to subscribe to the service and transfer payment.
- Secure infrastructure. Cloud providers offer safe infrastructure, hundreds of customization instruments, versatile security and access settings.
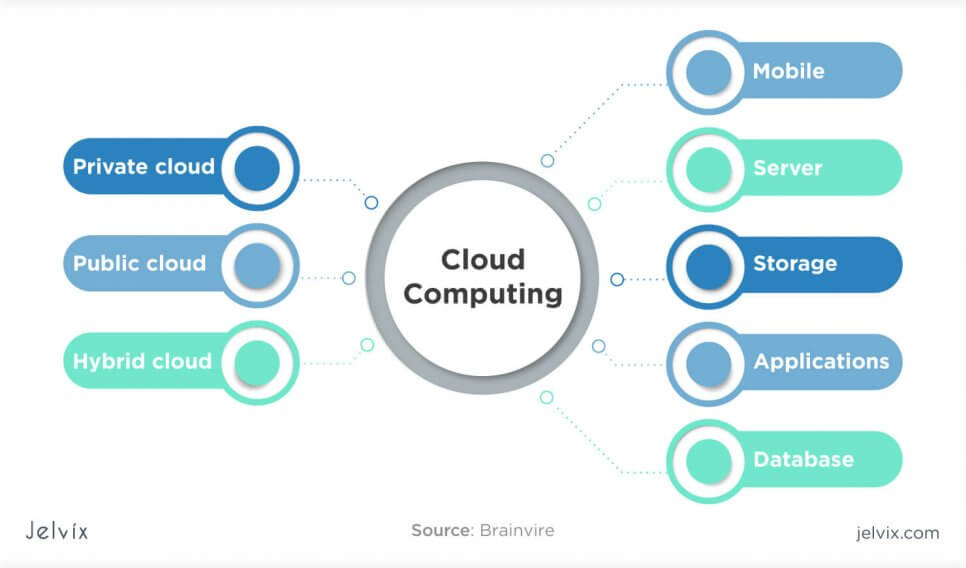
Types of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing offers three distinct deployment options. Cloud computing models are based on the availability of the data centers and the way these deployments relate to enterprise business needs.
What Is a Public Cloud?
The provider of cloud computing enables users to access the infrastructure via an online service with no privacy constraints. Users are not responsible for providing servers, infrastructure, and bandwidth – this is entirely the provider’s scope.
Users pay only for used features and can change their subscription plans at any time. Public cloud computing services are easy to use and navigate, highly scalable, and accessible.
However, business owners don’t sign SLA agreements with the provider; they must rely on general service guidelines and Terms of Use. If you store sensitive information, it’s impossible to negotiate the implementation of extra security levels or receive a personalized offer.
What Is a Private Cloud?
The enterprise creates and manages a private cloud for secure data storage and management. The company acquires several remote data centers worldwide, connects them to devices, and is fully responsible for data encryption and server maintenance.
In this scenario, the company doesn’t need to give data away to a third-party provider. An in-house team can manage asset security, increase operations speed, add new functionality, and scale according to the organization’s needs.
However, a private cloud requires a lot of initial investments: the company needs to acquire server space, hardware, employ a team of experienced cloud developers and testers and, and ensure data security. The main advantage of the method is that confidential data is stored within the company with no intermediaries.
What Is a Hybrid Cloud?
As the name suggests, this type is the combination of private and public solutions. Businesses use a public cloud to store data for everyday operations, high-volume tasks like software development or maintenance. A private cloud is kept for confidential data and backups, which allows you to use less in-house storage space and use the small team for its maintenance.
Companies can benefit from the expertise of the third-party provider while still keeping control over crucial data. However, the business still needs to invest in in-house infrastructure, since private cloud, even if it’s less scaled, has to be supported with local resources.
How to Pick a Cloud Service Model?
Cloud computing is a general term used to identify online delivery of data storage, processing, analytics, and other services, online without being dependent on local hardware. The businesses connect to the provider and use third-party services to enable their computing operations.
Further, cloud services can be distinguished based on their business model, functionality, and billing systems. Let’s take a look at the main types of cloud-based services and examine their features and differences.
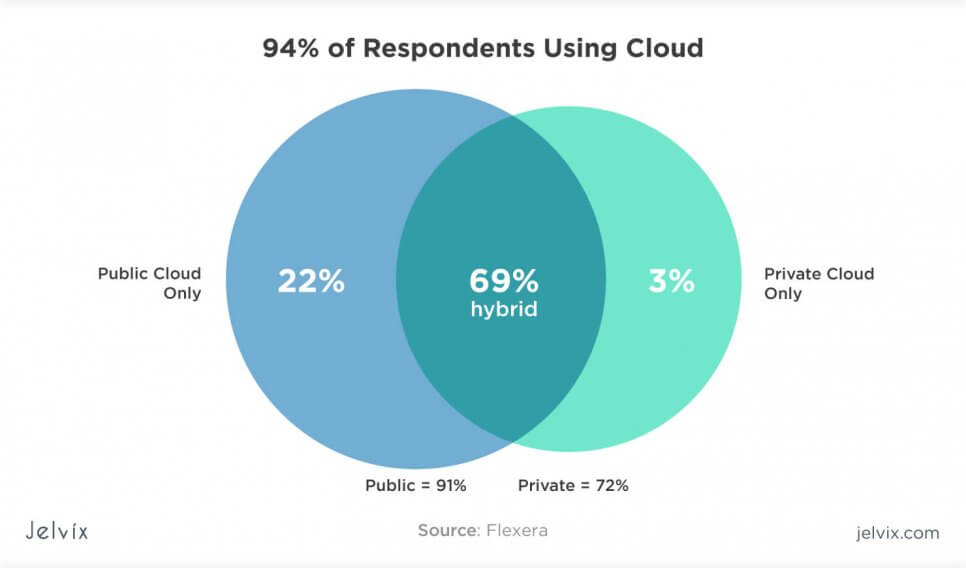
Compare public, private, and hybrid cloud solutions and find out which one supports your business strategy best.
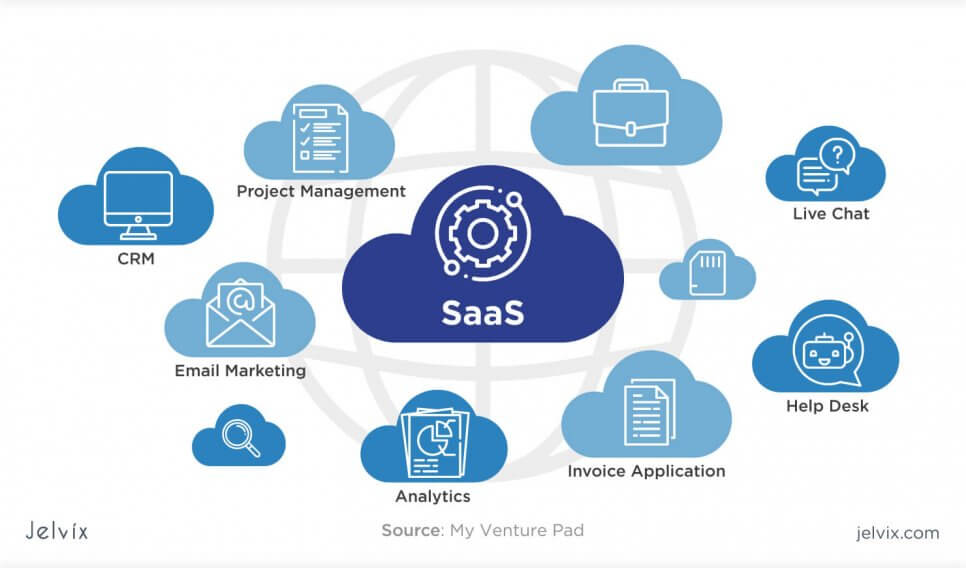
Software as a Service
Software as a Service, also known as SaaS, is essentially a web platform that provides users access to cloud computing on a subscription basis. Instead of purchasing the solution one time, as if it would be a product, the software is delivered continuously — like a service.
SaaS services provide companies with data storage and management features. Often, these are services for process automation, marketing, collaboration, and data organization. Development environments can also be done as SaaS — software developers receive access to the platform where they can build, test, and deploy a product, configure its functionality and interface with built-in tools and templates.
Examples of SaaS:
- Google’s G Suite: top cloud service provides businesses with access to management, communication, and organization tools and uses cloud for data computing. Gmail, Google Drive, Google Docs, Google Planner, Hangouts — these are all SaaS tools that can be accessed anytime and anywhere.
- Microsoft Office 365: the series of web services that provide business owners and individuals with access to Microsoft Office main tools directly from their browsers. Users can access Microsoft editing tools, business email, communication instruments, and documentation software.
- Salesforce: the most popular CRM on the market that unites marketing, communication, e-commerce. Salesforce uses cloud computing benefits to provide access to its services and internal data. Business owners can keep track of their sales, client relations, communications, and relevant tasks from any device. Salesforce can be integrated into the website — the information about incoming leads will be sent to the platform automatically.
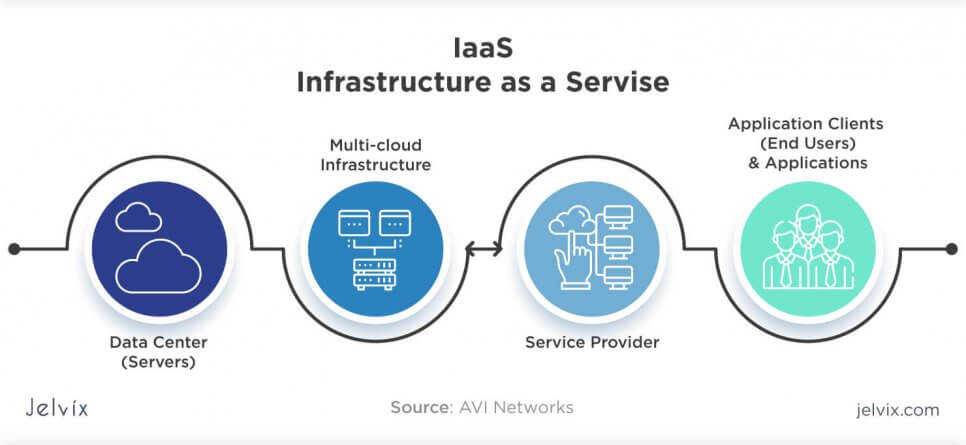
Infrastructure as a Service
IaaS provides businesses with ready-to-use IT infrastructure: development environment, private networks, secure data storage, instruments for software development and testing, functionality monitoring, etc. The enterprises don’t need to build and secure their own IT infrastructure — they fully power the development process with third-party servers and cloud backup storage.
Examples of IaaS:
- Amazon Web Services: a public cloud that offers subscribers access to virtual servers for product deployment, Cloud storage, tools for development, testing, and analytics. The application provides a ready-to-use environment to develop and test the product and offers the full cloud infrastructure for its deployment and maintenance.
- Microsoft Azure: the combination of IaaS and platform as a service, the software offers 100+ services for software development, administration, and deployment, provides tools for working with innovative technologies (big data, machine learning, Internet of Things), etc.
- IBM Infrastructure: IBM uses its in-house services to store the data of infrastructure users, enabling remote data access via Cloud computing. IBM servers support AI, blockchain, and the Internet of Things. The infrastructure also provides Cloud storage and virtual development environments, enabled on the subscription basis.
- Google Cloud Infrastructure: the large network of international servers that provides users access to remote Cloud data centers. Companies can store their information in Asia, Europe, Latin America, which minimizes the risk of a security breach.
Platform as a Service
Platform as a Service is software that provides access to development tools, APIs, and deployment instruments. Users receive access to virtual development environments and Cloud storage, where they can build, test, and run applications.
In PaaS, users are billed only for the platforms they use for the time they use the services. Unlike desktop solutions, there is no need to pay for excessive functionality.
Examples of PaaS:
- AWS Elastic Beanstalk: a web platform for software deployment and management, powered by the AWS Cloud. Users upload their applications to the service, and it automatically monitors the performance, load capacity, and checks for deployment errors.
- Apache Stratos: the Cloud computing platform for arranging PHP and MySQL. The PaaS provides users with ready-to-use tools for database development and testing, performance monitoring, integration, and billing.
- Magento Commerce Cloud : Magento Cloud offers tools for e-commerce development, testing, deployment, and maintenance. The Cloud environment allows accessing the store settings anytime and anywhere as well as automates the key processes.
Functions as a Service
In FaaS, developers can break down their software’s functionality into individual features and edit them one by one. This additional abstraction level facilitates app development and maintenance.
Software engineers can isolate an individual feature and make changes without affecting the rest of the functionality. Narrowing the work scope down to functional code block makes development easier and faster, especially for complex projects.
With FaaS, developers are only responsible for the code. The provider will enable access to app container, language runtime, operating system, and hardware, providing a universal virtual development environment.
Examples of FaaS:
- AWS Lambda: the service allows accessing software code without server setting and management. Developers need only to upload the code, and the solution will automatically connect the app to servers, language runtimes, OS, and highlight the functional code fragments. From that point, developers only choose features for editing.
- Azure Functions: the platform uses trigger mechanisms to highlight functions. Developers can set events that will lead to changes in code — for instance, a particular user input (interaction with an app or provided data) can turn on a function (like showing a pop-up or opening a page). Developers set up these triggers and responses without building the software infrastructure.
- IBM OpenWhisk: similar to Lambda and Azure, IBM OpenWhisk reacts to trigger effects and produces a series of organized outputs. Developers only have to set up action sequences and describe possible trigger events. The action itself will be enabled by IBM’s infrastructure — users don’t have to control these aspects.
Let's discuss which IT outsourcing trends will change the industry.
Criteria for Choosing the Best Cloud Service Provider
The first step in switching to cloud computing is determining what kind of cloud services you could be interested in — we already reviewed the most common types and considered the most prominent real-life cloud services examples As you can see, many services offer similar functionality, so choosing a single one can be overwhelming.
Choosing a cloud computing service is a long-term investment. Your application will heavily rely on third-party capacities, and you need to make sure that the provider is legitimate and fits your needs. Here’s a short criteria checklist for choosing a trustworthy cloud provider.
- Financial stability. Your cloud provider should be well-financed and receive steady profits from the infrastructure. If the company shuts down due to monetary issues, your solutions will be in jeopardy, too. In the worst-case scenario, you will have to cease the support of your solutions, or, in a better case, migrate to a new provider, which is an expensive and time-consuming process.
- Industries that prefer the solution. Before committing to a cloud services company, take a look at its existing clients and examine their markets. Ideally, the provider should be popular among companies in your niche, or at least in the neighboring ones. Another road to take is asking competitors and partners about their favorite choices.
- Datacenter locations. To avoid safety risks, make sure that cloud providers can enable geographical distribution for your data. Ideally, you want to locate your data on servers in Asia, Europe, America, without betting on a single region. Also, pay attention to countries — some, like Japan or Germany, are known to be more secure, whereas Russia, for instance, is not the safest option.
- Security programs. Take a look at the security programs of your favorite cloud providers. The majority of companies have dedicated papers and e-books that discuss this matter in detail — take your time to go through them. Start with taking a look at security documentation of the top cloud providers — AWS, G Suite, Microsoft Azure, Salesforce. You can use these pages as references during your safety research.
- Encryption standards. Make sure the cloud provider specifies the use of encryption. The provider should encrypt the data both when it’s being transferred to the cloud and during the storage itself. No matter what is the stage of data storage, the information should be secured end-to-end, so there is no way even for developers of the service to access the file contents.
- Check accreditation and auditing. The most common online auditing standard is SSAE — the procedure that verifies that the online service checked the safety of its data-storing practices. ISO 27001 certificate verified that a cloud provider complies with international safety standards for data storage.
- Look for solutions that offer free cloud backup. OneDrive, Google Drive, Dropbox, and Box offer free space to create cloud backup copies, both manually and automatically.
Where and How to Use the Cloud: Examples
We described how cloud computing could be used for software development and automation, but it’s not limited only to these applications. Here’s a short rundown of other fields where cloud computing can be applied to increase the efficiency of processes.
Providing access to entertainment content: entertainment companies quickly switch to the cloud to enable their users’ access to movies, TV shows, music, and other types of content. The most prominent examples of such cloud players are Netflix and Spotify. Users don’t have to download files to their hardware — instead, it can be accessed online via a personal account.
Storing social media content: website developers can use cloud to store online posts, comments, news updates, and profile information on social media platforms and online communities.
Documentation: cloud computing industry increases the safety of sensitive information. Files are no longer stored in a single location, but remote data centers all over the world. Getting access to multiple IPs that are encrypted and audited by professional providers is much harder than entering a single database. This is why companies often use the best cloud providers like Google Drive and Dropbox to store confidential files.
Online banking: fintech organizations and banks use cloud-based solutions to power money transfer, store personal information, provide real-time access to financial documentation, and power online purchases. Banks actively release APIs that allow connecting them to online stores, enabling card-to-card transfers from any device. Fargo, Bank of America, Morgan Chase have been among the earliest adopters of the cloud technology in their mobile applications.
CRMs and ERPs: customer relationship management and enterprise resource planning tools rely on cloud computing to synchronize data flow from multiple sources and enable secure data storage for successful organization management. Business owners can access data from any department (marketing, customer relationship, logistics, warehouse management) and coordinate their workflow with other team members.
The most powerful example of such cloud solutions is — a robust CRM used to track sales and customer engagement in websites and mobile apps that can even be connected directly to the site.
Human resources: businesses can use cloud to automate their recruitment, receive in-depth reports on their on-boarding, control the productivity of the personnel, and increase their team’s efficiency. The data access isn’t limited to local networks — users can access the company’s files from any device and anytime. An example of such applications is Hubstaff — popular team management and time tracking tool for digitally transformed businesses.
Accounting: business owners can use cloud tools to access their financial data remotely, keep track of tax reports and documentation, track revenue and spendings, and automate billing processes — popular platforms are Zoho Books and Wave Financial. Cloud applications, unlike the desktop ones, don’t require installation, and data is stored in remote data centers rather than on unreliable local networks.
Logistics and warehouse management: companies can automate their inventory management, order processing, ordering, selling, and delivering products with cloud tools. Online platforms connect team members, partners, vendors, retailers in a single solution, providing all participants with a bigger picture and better control. All participants of the supply chain know where products are real-time and can forecast their movements.
The Most Common Questions
What is cloud computing?
It’s the form of computing where digital infrastructure and online resources are available on-demand online by the third-party provider. The company takes full responsibility for enabling data storage, transfer, maintenance, and users only have to work with functionality. The software is delivered continuously, and users usually pay only for what they use — no overpaying for excessive features or inactive use.
What is the cloud?
The cloud is the term that describes a global server network where storage is distributed over multiple locations all over the world. These services are connected and operate together to enable smooth data storage, transfer, processing, deliver content, and power software development. Files aren’t located on personal hardware but removed from local networks for increased security and accessibility.
What is the best cloud service and the best cloud backup service?
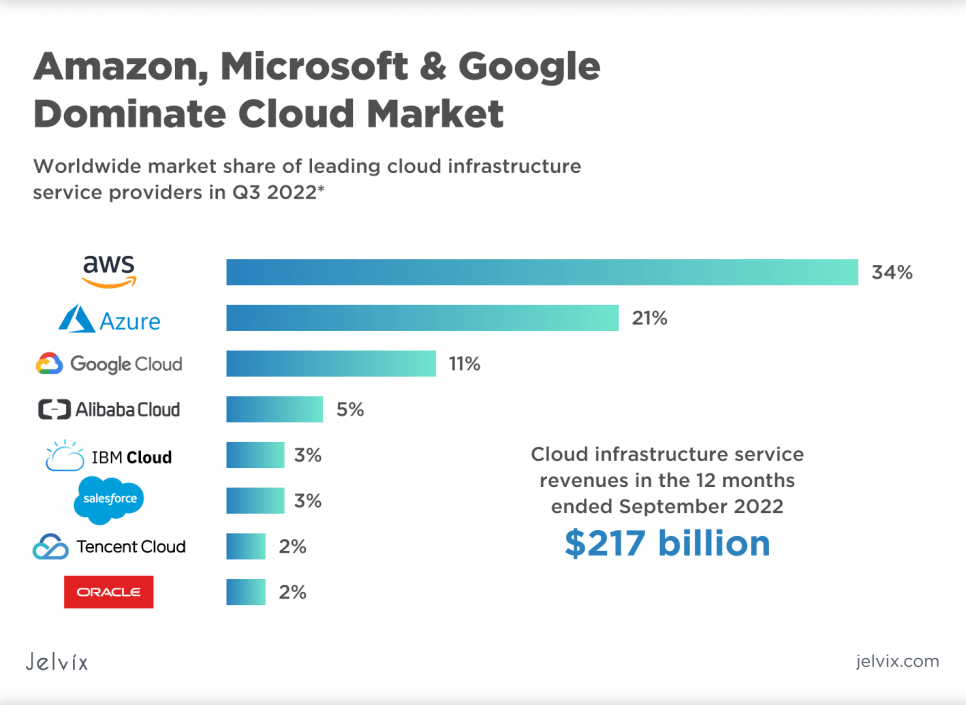
According to Statista, the most popular cloud providers are Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services, Rackspace, Google Cloud, Box, OpenDrive, and JustCloud. The most popular Cloud CRM is Salesforce, while Magento is the most used tool for e-commerce management.
What is cloud storage?
It’s a type of data storage where the data is stored across multiple servers located all over the world in several international data centers. These servers are united into the network that can be accessed from user’s profiles anytime and anywhere. Users aren’t limited to their hardware with their local servers.
However, they should be aware that the provider owns and manages the server space. The third-party has full responsibility for data security and availability, which is why it’s important to choose a trustworthy cloud provider.
How does cloud computing work?
For cloud computing to work, there should be at least one remote data center that a user can connect to via an online server. The user uploads files manually or automatically to the service.
It can be a file transfer from local to cloud network, or files can be created right away in the cloud, with no local copies (an example is creating a new document in Google Docs). The service assigns this data to the user’s profile, and it can be accessed from any device as long as the login credentials were entered correctly.
Conclusion
Cloud computing has been one of the most growing markets over the last five years, and this trend is sure to be relevant in the new decade. With top cloud computing companies like Amazon, Microsoft, Google, and IBM investing in the technology, it’s obvious that сloud will become increasingly more innovative with every new release.
At this point, сloud computing has multiple applications across different industries. It’s used for software development, testing, and maintenance, business management, client support, marketing, accounting, logistics.
Integrating сloud solutions into your website and organizational practices is the tried-and-proven method of automating your interactions with clients and team members, which leads to significant efficiency increases.
To get started with сloud computing, you need to look for top cloud service providers with certified security practices, versatile functionality, and a cost-efficient pricing model.
Also, you need an expert software development team that will help you make an educated choice and integrate the solution into your operations. If you’d like to integrate сloud into your custom software or third-party tools, drop a line to our сloud developers and testers.
We will analyze your business needs, determine the areas that could be improved by introducing сloud computing, help to choose a provider that fits your needs, and integrate the solution.
Need a qualified team?
Reach new business objectives with the dedicated team of professionals.