Due to our clients’ numerous requests and high demand for E-commerce websites among many quotes of business, we decided to discuss the key differences between E-Commerce and E-Business in this guide. The list of E-Commerce technologies and applications is growing every day, thereby adding considerable value to all businesses conducted online.
Savvy entrepreneurs looking for smart E-Business solutions use the terms interchangeably, which can be confusing for the development agencies providing such solutions. Moreover, unclear requirements often result in developing inaccurate business models and, thus, failed projects.
To prevent this, you must know the difference between E-Commerce and E-Business, so you can make your project’s success inevitable.
The next section will elaborate on the differences between the two commonly confused business terms and some of the basic knowledge critical for understanding and using the two popular networks, E-Commerce vs E-Business.
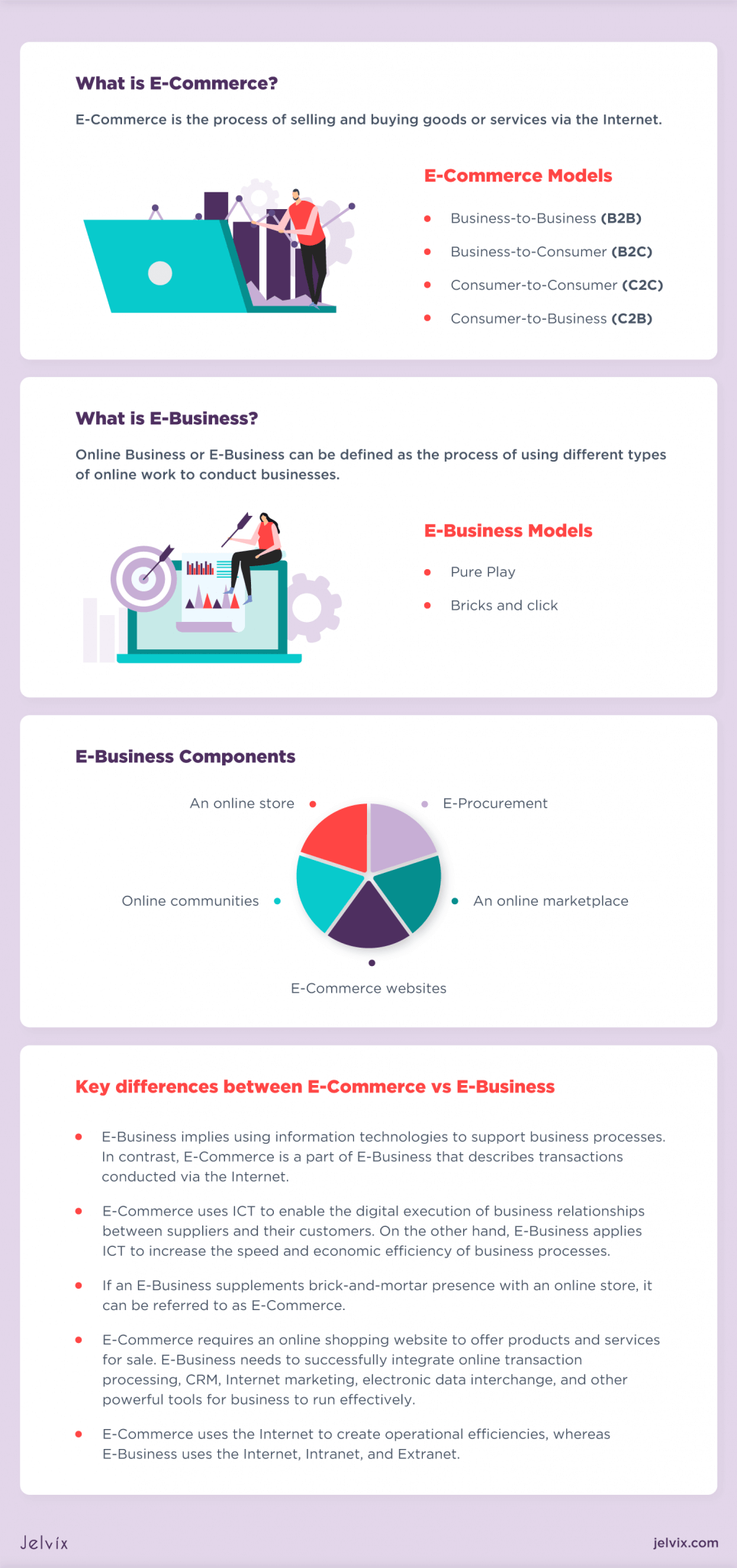
What is E-Commerce?
Although E-Commerce is often confused with E-Business, they aren’t synonymous. E-Commerce, also referred to as Internet Commerce, is the process of selling and buying goods or services via the Internet. The term can also be used to describe any commercial transaction that is facilitated through the web. Unlike physical commerce, it does not require any in-person meetings to do the whole selling and buying process.
The main difference between E-Commerce vs E-Business is that the latter refers to all aspects of conducting business over the Internet. In contrast, E-Commerce refers explicitly to the transactions processing goods and services.
E-Commerce models vary widely and can include different sales types. Since the 1990s, many street-side businesses have adjusted to E-Commerce and are now driving shoppers online. For example, in B2B E-Commerce, businesses sell products to consumers using their websites.
Many giant companies like Apple, Nike, Walmart, etc., also use popular visual marketplaces to increase online sales. This allows customers to buy their products at wholesale prices, and at the same time, provides the potential to generate more revenue. So, whether you buy Nike sneakers from retailers or Nike’s official website, the transaction is still an example of E-Commerce.
E-Commerce includes every element of a sale: product ordering, order payment, and delivery. It might also involve only part of the sales process. For example, customers can buy a product online and choose the local pick-up option from a convenient nearby location. To complete the purchase, they might use online or offline payment methods; either way, the transaction still involves an element of E-Commerce.
According to the most recent statistics, it is expected that by 2040, 95% of all purchases will be conducted via E-Commerce.
The next section discusses the most common E-Commerce models in detail, as well as provides popular eBusiness examples that make a dent in the E-Commerce market.
Types of E-Commerce Models
Listed below are four main types of E-Commerce models that describe any transaction conducted between business and consumer.
1. Business-to-Business (B2B)
This type of E-Commerce involves all kinds of electronic transaction processing services or products conducted between two businesses. The B2B model is often used to describe the relationship between the producer and the retail business, where the latter sells products to the end consumer.
One good example of the B2B market is the auto industry. The largest car companies cooperate with numerous manufacturers to buy parts for vehicles of their brand. When you buy a car from one company, you’re buying parts produced by dozens of suppliers from all around the world: therefore, they are B2B.
Best cases of a business-to-business e-commerce model
Amazon Business is a B2B e-commerce marketplace that targets companies, not individuals. While many are familiar with the success of the B2C Amazon, you might be surprised to find out that its B2B platform is also a market leader. By 2025, the value of products purchased on Amazon’s B2B is predicted to reach 59 billion U.S. dollars.
Another thing to consider here is that Amazon Business wasn’t even aiming at large international success until 2019. This means the platform’s growth is only starting – and it’s already reaching very impressive thresholds.
Features of B2B Amazon
- Versatile business-oriented admin panel: the platform allows companies to manage multiple invoices, keep track of inventories, generate documentation;
- The Business Prime subscription unlocks many offers & benefits in terms of costs and delivery fees and allows entering exclusive communities;
- Constant updates: Amazon Business constantly introduces new updates to its core functionality. They keep competitors on edge and attract clients with versatile features.
2. Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
This business model is considered the earliest and most common form of E-Commerce. According to the stats, the B2C E-Commerce market accounts for the largest share in the industry and is projected to reach $6.2 trillion by 2027. In B2C, the products/services are sold directly between a seller and an individual consumer.
B2C businesses sell various kinds of physical and electronic goods, from clothing to e-books, and allow consumers to experience the buying process without much waiting time. Popular examples of B2C businesses include Amazon, Google, Walmart, and other companies that sell their products to the end-user online.
Examples of B2C business models
Spotify is an example of an innovative B2C service that offers an innovative solution to well-known problems. Giving access to music, podcasts, and audio files directly to users is the platform’s main goal. The subscription-based business model encourages users to spend more time on the service rather than paying for every track or listening time.
According to Spotify’s 2022 Q3 highlights, the platform’s active users had grown to 456 million globally. Quarter by quarter, the platform demonstrates steady 20-30% growth, proving the business model’s sustainability.
Features of Spotify
- Simple user experience: in B2C platforms, the ease of user experience is a determining factor. If a visitor manages to get hooked on the functionality and interface, the business can build a long-term relationship. Shopify totally succeeds with that, offering very transparent functionality and a de-cluttered interface.
- Efficient personalization. The power of recommendation engines was shown by many B2C platforms, including Netflix, Amazon, and of course, Shopify. The platform tracks user listening preferences and offers new tracks – all to encourage prolonged page visits.
- Cooperation with artists. B2C businesses often have to cooperate with other individuals and companies to increase the versatility of their products. Shopify is not an exception. The platform launches programs that make it easier for artists to get noticed and offers a transparent payment system.
3. Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C).
The type of E-Commerce business model where consumers sell goods or personal services to other consumers using popular online market makers. The market maker’s role is to provide a catalog that matches search engine criteria, pricing, and sales transactions so that products can be easily discovered and paid for.
The most famous C2C company sites are eBay, Amazon, Etsy, and Craigslist, but there are many other terrific classified and auction-based sites. C2C platforms don’t have to be product-oriented; services can also be marketable.
An example of a C2C platform: iTalki
iTalki is an online platform for language learners that connects individuals who want to learn a foreign language with native speakers. Admins and moderators mediate the process, but there are no corporate entities involved. Users provide both demand and supply. The website receives revenue by getting a commission from transactions.
iTalki now has more than 3 million users, and some active users manage to give more than 172 lessons a week. Building such a dedicated community is a great way to ensure a constant revenue stream on a C2C platform.
Features of a C2C platform:
- Two types of user profiles: one for sellers, one for buyers. Buyers should see their orders and receipts and track engagement with the sellers. With iTalki, learners can track their upcoming lessons, look for new teachers, leave reviews, and approve the messages. Teachers, on the other hand, control their teaching schedule, communicate with moderators, and have special offers from the community.
- Profiles for moderators. The team has to constantly hire administrators and moderators who will keep track of fraudulent profiles, verify the offer’s quality, and resolve conflicts.
- A transparent system of ratings and reviews. With peer-to-peer platforms, trust is the key to building a successful community. Presenting buyers with reviews and ratings of sellers gives them a way to understand the quality of the offer – and that’s precisely what iTalki does.
4. Consumer-to-Business (C2B)
Consumer to Business refers to a business model that facilitates the transactions between a consumer and a business organization. The main goal of C2B is to help individuals sell a product or service to a company and create a win-win situation for both parties. In C2B, businesses profit from favorable prices, while consumers gain from the transaction flexibility the market creates.
There are many C2B sites where freelance developers get listed, and businesses can browse for what they need. Common examples of such sites include UpWork, Google, Commission Junction, and Fotolia.
In addition to the types mentioned above, E-Commerce includes G2C (Government-to-Consumer), C2G (Consumer-to-Government), and B2E (Business-to-Employer).
Crowdsourcing companies are a good example of a consumer-to-business model. Eyeka, the biggest crowdsourcing platform, connects large brands to creators, helping companies find ideas – and users get paid for their contributions.
Just like a C2C company, a C2B business needs administration – a team should oversee the quality of offers and make sure both parties fulfill their needs. On Eyeka, each submitted logo, idea, or naming project undergoes official moderation before being sent to the deliberation of a brand.
The features of a C2B company
- Dashboard: each user has a personalized dashboard with projects or offers that fit certain skills, interests, requirements. The dashboard provides a way to control activity on the platform and makes navigation much more effortless.
- Personal profile. Both users and companies should have a personal page that stores their personal information, history, and achievements on the platform. Talent-search, job-hunting, and crowdsourcing platforms all share this feature.
- Special offers for companies. Typically, attracting a business to join such a platform is harder than motivating individuals. Once businesses enter the platform, people will be inevitably motivated to join the community. So, C2B businesses usually have a dedicated partner program designed for companies. Between users and businesses, the latter usually are of a higher priority.
What is E-Business?
Online Business or E-Business can be defined as the process of using different types of online work to conduct businesses. Unlike e-Commerce, E-Business deals with online transactions and facilitates business processes such as manufacturing, logistics, customer service, marketing, sales, etc. Hence, e-Commerce is a part of E-Business.
E-Businesses use the power of online technology to extend organizations’ reach beyond their brick-and-mortar walls, thus boosting business operations’ efficiency. Modern corporations, non-profits, governments, and other institutions use information and communications technologies to increase productivity, cut costs, and enable fast business growth.
For example, digital communication tools (e.g., emails or social media) used as an alternative to face-to-face communication increase customer support efficiency by decreasing delays between inquiries and responses. To the point, e-Businesses often turn social media into collaborative tools to improve communication between employees and enable faster decision-making.
The E-Commerce payment systems that companies use to facilitate electronic transactions also reduce the time employees spend processing transactions. For example, e-invoicing allows businesses to speed up payments and frees employees from manual, repetitive work. As a result, employees can concentrate on more urgent, valuable tasks and improve workplace flexibility.
E-Business Models
The primary e-Business models cover two major categories: Pure Play and Bricks-and-Clicks. Both terms refer to a company with an online presence but differ in how this company uses the Internet for business. The Pure Play business model describes an e-Commerce company that operates solely on the Internet.
At the same time, Brick-and-Mortar refers to a traditional business with a physical store and uses the web as an exchange mechanism. Below we identify the characteristics and differences of Pure Plays vs Brick-and-Click.
Pure Play
An investor’s term that was originally used to describe companies that serve a specific product or industry. However, as more players are taking on the digital world, economic experts use it to refer to businesses completely carried out through an electronic medium.
Pure plays are normally free from the traditional boundaries of brick and mortar business, i.e., sophisticated supply chain services, expensive rentals, queues, etc. However, in the wake of hybrid success stories from Walmart and Barnes & Noble, consumers are much more in favor of digital shopping and stores supplying them with digital options.
To the point, the world’s biggest tech company Amazon struck a balance between traditional and electronic commerce and has turned the spotlight onto a checkout-free technology.
In January 2018, Amazon opened its first checkout-free store – the Amazon Go store. It offers a super convenient shopping experience – including no check-out operators. To make a purchase, you simply need to identify yourself on entering the store with the Amazon Go app, scan the QR code of the item you want to buy, and leave without stopping at a cashier register.
Once you’ve finished shopping, you are automatically charged by Amazon and receive an automatic receipt.
With the arrival of the COVID-19 pandemic, the checkout-free tech will probably be stuck in the stage of early adoption as online shopping is replacing traditional retailers.
Bricks-and-Clicks (also Click-and-Mortar)
Bricks-and-Clicks is a business model that focuses on the online-offline integration between e-commerce (clicks) and a physical retail store (bricks). “Click-and-mortar” companies leverage their physical and virtual presence in business, thereby staying afloat in both markets.
Face-to-face communication allows these businesses to build strong relationships with their customers, which consequently adds up to their digital presence. Because customers are familiar with the brand’s product, they naturally spend less time browsing websites to find the product they want.
Research shows that those retailers who launch Internet sales sites besides their physical retail outlets are more popular with consumers than premises-based retailers. For instance, to drive its business, Walmart invested billions in its e-Commerce sites to optimize the online shopping experience and provide better customer loyalty. Today, online sales account for around 11% of Walmart’s total revenue.
E-Business Components
There are three major components of E-Business: information, communication, and transaction. However, the primary focus lies on digital networks (information) that entrepreneurs use to improve e-commerce efficiency. Listed below are the key areas of these components.
- e-Procurement (a.k.a. supplier exchange) is a B2B or B2G process of sourcing goods and services through the web as well as other information systems like electronic data interchange. E-Procurement aims to automate procedures along the entire procurement cycle, reducing cost and manual effort.
E-Procurement offers the convenience of evaluating and selecting suppliers, i.e., eAuctions and eTenders, as well as what makes researching products easier, including electronic ordering and catalogs.
- An online store is an official website of a brick-and-mortar business that facilitates customer’s access to their preferred brand, and allows them to find, order, and pay for the product – without leaving the house.
- An online marketplace is an e-Commerce platform where third-party sellers can market their products to customers. Amazon and Alibaba are considered the world’s leading eCommerce companies.
- Online communities. These are either social networks or product review websites where customers can advise each other and share product experiences. Amazon Customer Reviews and Angie’s List are the most popular examples of community websites for collecting business and product reviews.
- E-Commerce websites. An e-commerce website is a multi-brand online store where third-party sellers market their products to customers. The only difference between online marketplaces and e-commerce websites is that in the latter, the inventory is owned by the website owner who can operate the online store for selling goods. The website owner also invoices the customer and pays the value-added tax.
Let’s review how the SaaS business model works and how users interact with SaaS.
Key Differences between E-Commerce vs E-Business
Now that you have learned key characteristics of e-Commerce vs e-Business, we can look at their differences. Below we have provided a list of e-Commerce vs e-Business business differentiation.
- Buying and selling through the web is not as easy as carrying out business activities. e-Business implies using information technologies to support business processes. In contrast, e-Commerce is a part of e-Business that describes transactions conducted via the Internet.
- e-Commerce uses ICT to enable the digital execution of business relationships between suppliers and their customers. On the other hand, e-Business applies ICT to increase the speed and economic efficiency of business processes.
- If an e-Business supplements brick-and-mortar presence with an online store, it can be referred to as e-Commerce.
- e-Commerce requires an online shopping website to offer products and services for sale. E-Business needs to successfully integrate online transaction processing, CRM, Internet marketing, electronic data interchange, and other powerful tools for business to run effectively.
- e-Commerce uses the Internet to create operational efficiencies, whereas e-Business uses the Internet, Intranet, and Extranet.
- The four main types of e-commerce are B2B, B2C, C2C, and C2B.
- Pure Play and Bricks-and-Clicks represent the two primary e-Business models.
- e-Commerce industries will continue to grow, and by 2027 the global e-commerce market will hit USD 27.15 trillion.
Final Thoughts
We have come to the end of our definitive guide and hope it has given you some insights into the eCommerce industry. If you have a business plan for the move, make sure you know the dos and don’ts for running a successful e-Commerce business. If you don’t have an exact idea or you are just starting, go to the Services page and see our retail software solutions.
We can help you automate your business operations and create disruptive retail technology that will revolutionize the way customers interact with your brand.
Need a qualified team?
Reach new business objectives with the dedicated team of professionals.