In the past years, we observed virtual & augmented reality technologies only in sci-fi films. By 2020, this has become our reality, and everyone can experience the AR/VR technologies via computer games. The industries such as healthcare, gaming, entertainment, and e-commerce are the main drivers of augmented reality market growth.
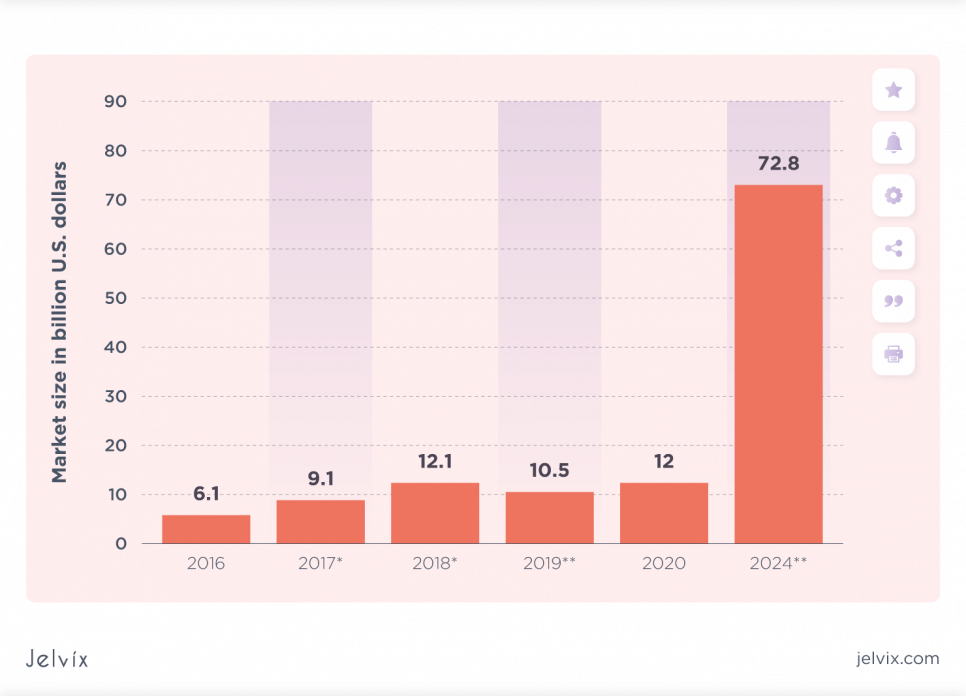
It is expected that in the nearest five years, the AR market will increase 5 times: from $15.3 billion in 2020 to $77 billion by 2025 with 38.1% of the annual growth rate. At the same time, the VR market will grow from $6.1 billion to $20.9 billion by 2025, with 27.9% of annual growth.
The unquestioned leaders in the AR/VR market are US-based companies such as Google, PTC, Microsoft, Oculus, and Apple. The growing use of smartphones and electronic devices is the main factor that boosts these companies’ growth and the entire North American market.
Let’s consider the AR/VR market’s actual state, the latest trends and discuss the future of virtual reality.
AR/VR Explained
Both augmented and virtual reality are immersive technologies that use digital means to create a physical environment. What’s the difference?
Augmented reality (AR) interacts with the environment surrounding you in real-life: rooms, streets, parks, and even people. With the help of digital instruments, the AR software transforms the environment and adds virtual details. For example:
- Instagram & Snapchat lenses change the appearance of a human;
- Pokémon Go video game adds virtual characters to the real environment for the player to find them;
- Ikea Place App will allow you to see how the piece of furniture will fit into your room;
- Enhanced navigation systems and military technologies can superimpose a route over the live scape.
Read more about how different brands are already using augmented reality in their business.
Virtual Reality (VR) devices create a seemingly-real but fully digital environment. You need special equipment to interact with it — helmets or glasses with screens, gloves with sensors, different types of simulators, etc. VR future technologies already exist in education, healthcare, science, and many other industries.
As to education & training, VR technologies can create situations where students can safely interact with complex or dangerous objects. For example, realistic training simulators are already used for training the racers and Air Force professionals.
Using the VR simulator in training allows increasing its efficiency by involving muscular memory. That helps to cut the 12-month training program to 6 or even 4 months and make it fascinating. The flight simulator will also help focus on the students’ behavior in extreme and dangerous situations and interact with costly equipment that the company can’t afford to buy for training purposes.
The Impact of the Pandemic on the AR/VR Market
In 2020, the world faced the Covid-19 pandemic that changed how we work, rest, and communicate. It boosted the demand for technologies that facilitate remote interaction between people, including the AR\VR solutions. According to the Omdia research, in 2020, the users bought about 6.4 million consumer VR headsets and spent over $1 billion.
In the first half of the year, the VR headsets providers experienced manufacturing challenges caused by the pandemic. Yet, the November release of Xbox and PS5 consoles attracted the gamers’ audience. Omdia states that household penetration of VR devices is about 1.2% in top-32 countries.
Enterprise and Consumer VR
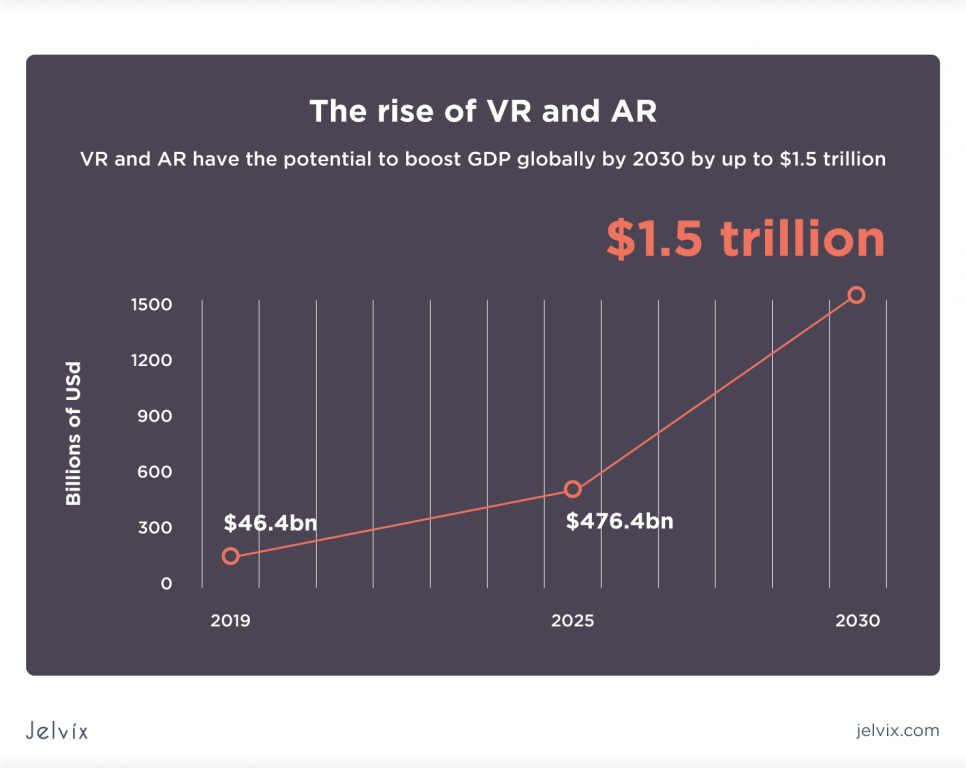
Neither AR nor VR is a new technology, but they are becoming wide-spread trends in business and tech society. According to the PwC report, AR/VR solutions had already delivered $46.4 billion to the global economy by 2019. By 2030, this value is expected to grow to $1.5 trillion.
Business and Tech Benefits of AR/VR
Introducing the full-dive virtual reality technology, companies can improve many aspects of their work. Although AR/VR technology is not yet commonly adopted, it is not new. This is its benefit — solutions are maturing, bugs get fixed, software and hardware are not as expensive as they used to be.
Any business’s goal is to deliver a product of the best possible quality and cut its initial cost. Let’s consider the options of using virtual reality in business.
- Improved training and reduced risks
Organizations can train their employees by simulating realistic working conditions. In case the work is connected with high-risk operations (work with the human body, complex equipment, military environment), AR/VR training is the only way of efficient and safe training.
- Optimization of product development
Working on any product, the design and development teams can test different hypotheses before implementing physical prototypes. This will help the organizations to reduce the costs and time to market. For example, the period between design and physical modeling can be reduced from weeks to days in the automotive industry.
- Enhanced working communication
Using VR, the companies can bring together team members from different locations in a shared virtual space. This will combine all the office and remote cooperation benefits — live communication and saving traveling time & costs.
- Routine optimization
Logistics and warehouse companies already use AR glasses for their employees to instantly see the information about cargos without the necessity to check it in the database manually.
- Creating a new customer experience
Engaging the customers and giving them live impressions is the key to increasing their loyalty and growing the business. Retail, hospitality, and automotive industries are just starting to explore AR/VR solutions’ potential, while gaming and entertainment are already actively using them.
Besides the benefits mentioned above, AR/VR technologies will also help build a solid reputation as a forward-looking and innovative company.
AR/VR Use Cases
We have already considered the benefits of using AR\VR technologies in different industries from the theoretical point of view. Now let’s move to the practical part.
Education and Training
The companies are introducing AR/VR systems for training their employees. VR-based education is expected to be a $700 million industry by 2025 and the 4th biggest sector of investing in virtual reality. Why is this method more effective than classical classroom/e-learning?
1. Increased speed of learning
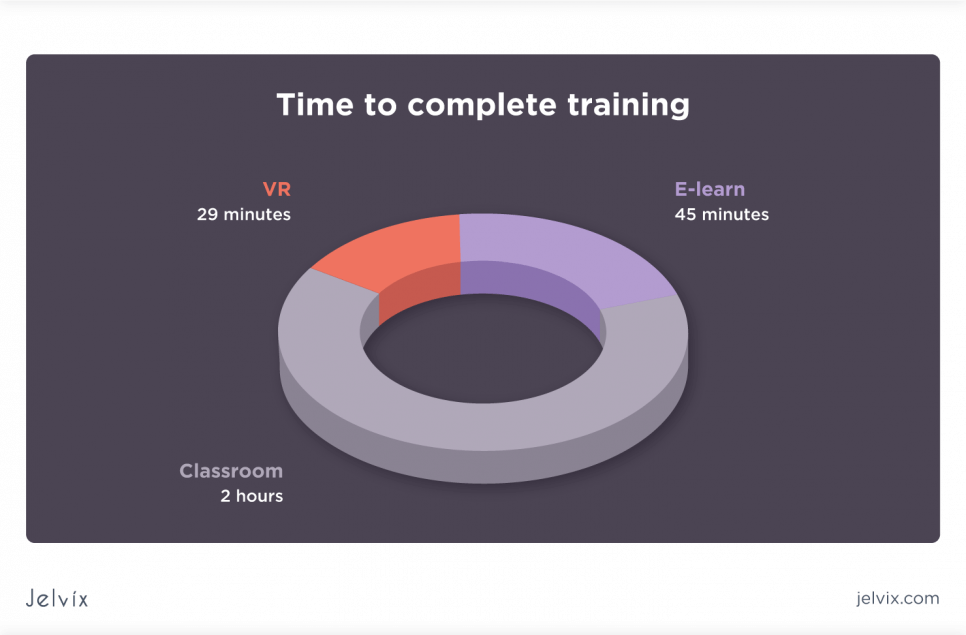
VR headsets make it possible to learn the material that usually takes two hours of classroom work in 30 minutes, which is four times more effective studying! And this is only the time of the actual learning process, without the time and money expenses for traveling to the classroom and organizing the process.
2. Better self-confidence of VR learners
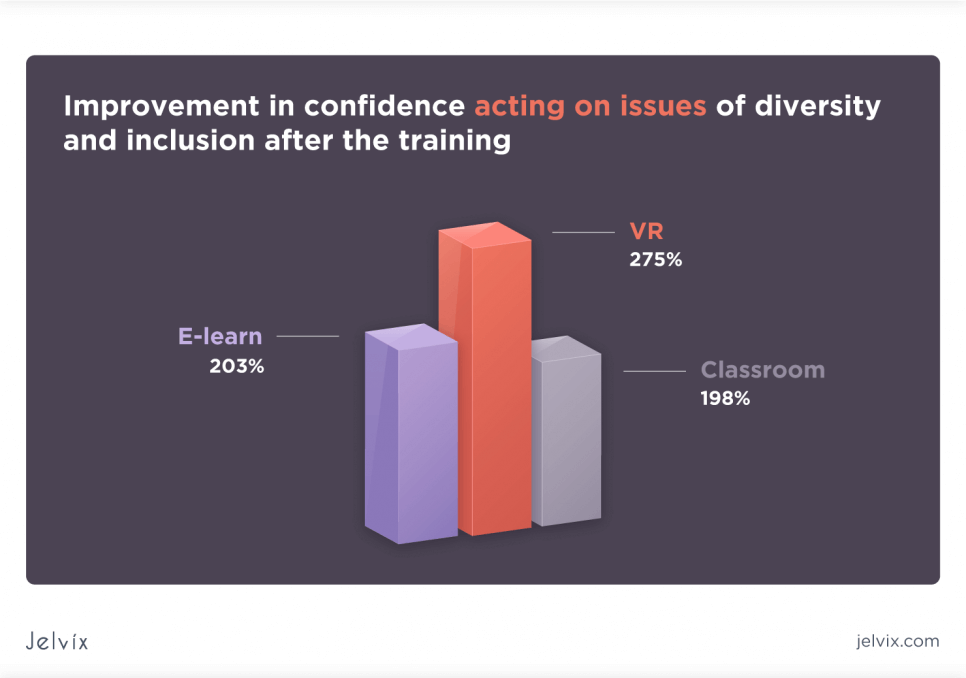
Self-confidence is a crucial factor of successful learning. With VR-based training, students can practice in a safe environment and make mistakes without the fear of harming something or someone. Such type of education demonstrates higher confidence levels and a better ability to apply the knowledge in a real job. The statistics show that VR learners are 35% more confident than e-learners and 40% more confident than their classroom peers.
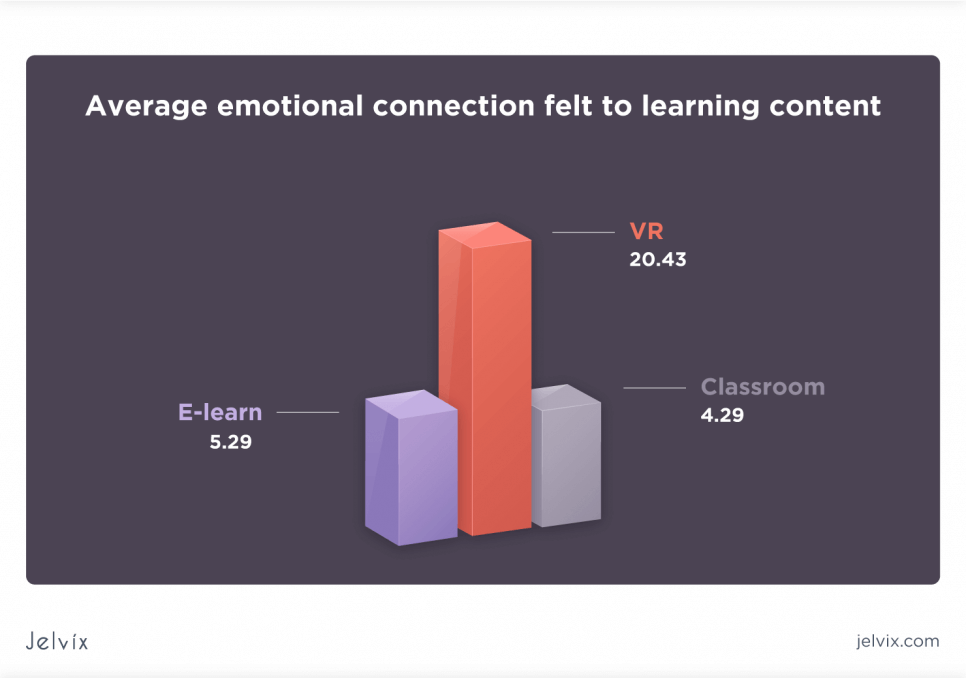
3. Emotional connection to learning material
It’s commonly known that learners understand the material better if emotions are involved. The studies demonstrate that VR learners have 3.75 times stronger emotional connection to the material than classroom ones. They perceive simulation as their own meaningful experience, not a mere learning situation.
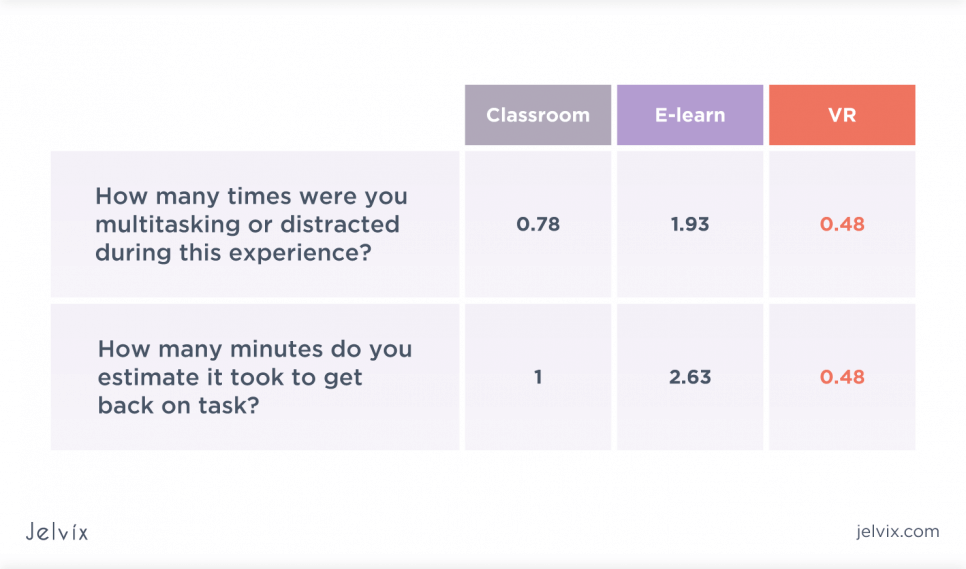
4. More focus, less distraction
Using a VR headset, learners dedicate all their vision and attention to the learning situation. There are no distracting factors like smartphones, classmates, or a breeze from the window. The VR-learners are 1.5 times more focused than classroom ones and 4 times more concentrated than e-learning students. Moreover, students don’t have an option to multitask, so they get about 100% information from training and demonstrate better results.
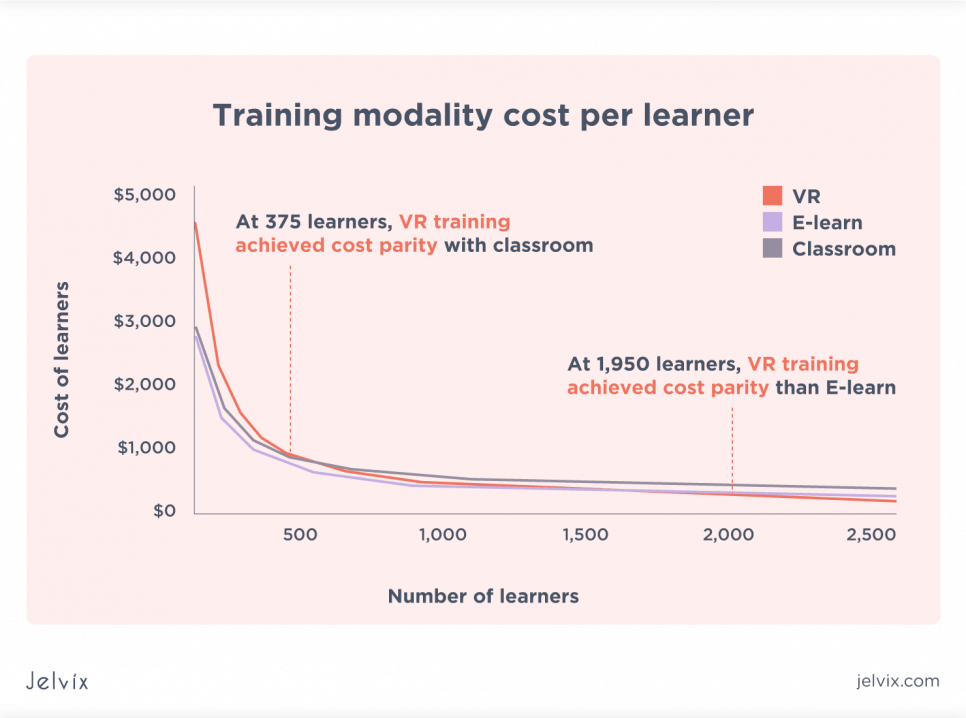
5. Cost-effectiveness in scaling
Currently, VR-based training requires 48% more investment than a similar classroom or e-learning course. But with 375 learners, the VR course achieves cost parity with classroom learning, and with 3,000 students becomes 52% more cost-effective than the classroom one.
Gaming
Gran Turismo Sport is a racing video game using VR for simulating real car driving. During their promotional campaign, they invited Alex Brundle, a racer, to try the game’s VR version and compare the sensation with real-life racing. He agreed that the dynamic camera and the 360-degree view gave him the possibility of looking around and feeling as if he were inside a car driving at a track.
But is it possible to train yourself as a racer using a VR racing simulator? Alex Brundle believes it is, as the simulator can actually help become a quicker racer. The simulation involves the work of muscles and emotional engagement that are the key factors of VR training success. Another benefit is that the simulation can help you know the track better and feel more confident when it will come to a real race.
Healthcare
According to the MarketsandMarkets healthcare analysis, the AR/VR part in the healthcare market is expected to reach $4.9 billion by 2023, with about 36.6% of annual growth.
The most obvious application of AR/VR in healthcare is education. Doctors have to know a lot about the human body’s anatomy and physiology and learn to perform medical manipulations of different complexity levels. The AR/VR equipment and software visualize the 3D representation of a human body, allowing students to see its real-time work and safely perform the intrusions.
It’s a way for surgeons to plan their surgeries and cut the chance to encounter surprises. The technologies can visualize the area of medical intrusion, display real-time digital information on a patient’s body, improve the operation’s accuracy, and simplify further rehabilitation.
There are many other interesting use cases for AR/VR futuristic technology in medicine. Let’s take a look.
Patient education
Patients often have difficulties describing the symptoms: they inaccurately identify the pain location, overreact to minor issues or diminish serious ones. The doctors can display the visualization of the organ and the disease or describe how he or she will fix the problem during the intrusion.
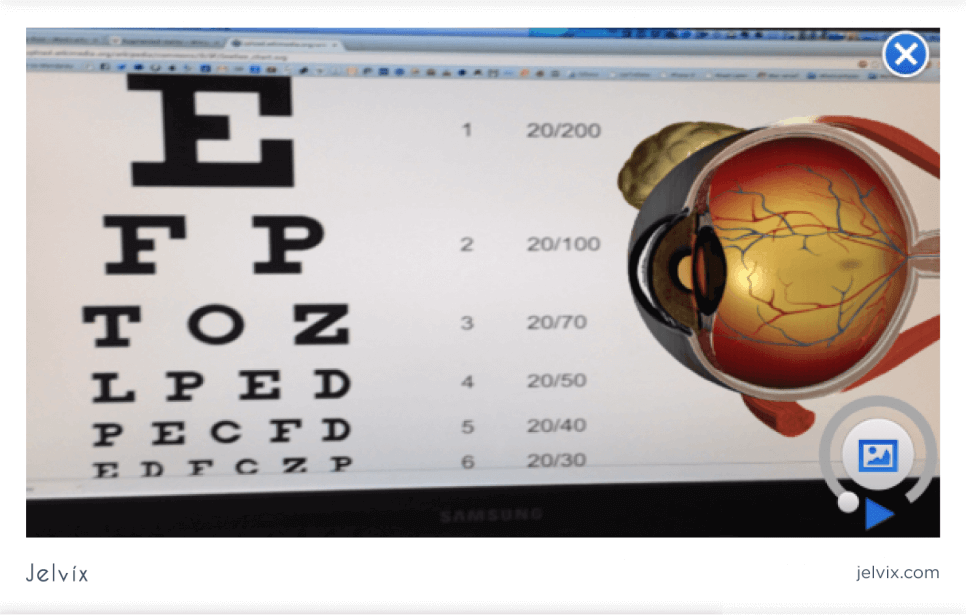
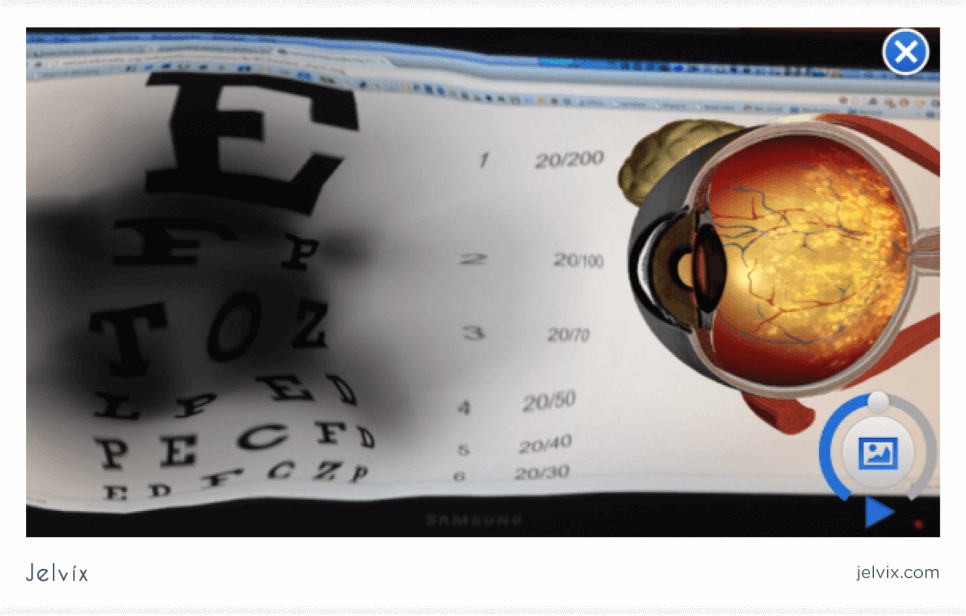
EyeDecide is a medical app designed for patient education. The app simulates a patient’s vision with a different eye disease and demonstrates how it’s progressing. Seeing the impact of the lifestyle on their health and possible consequences can motivate patients to take the treatment seriously. In the screenshots, the app demonstrates how AMD progression changes the vision.
Pharmacy
With AR, making a 3D visualization of how the drug works inside a body becomes possible. This can be useful for educating the patients and for safe experiments of pharmaceutical companies.
VR can also be useful in supplementing traditional pharmacotherapy. The trial demonstrated that the combination of VR and traditional analgesic was more effective in reducing the pain than the medication alone. It is unclear how exactly it worked, but scientists believe that the VR environment distracted the patients from unpleasant manipulation, limiting the brain’s capacity for processing pain.
Manufacturing
AR/VR technologies have matured enough to be used in business and manufacturing and have the potential to deliver $359.4 billion to the economy. As the Annual Manufacturing report demonstrates, 94% of manufacturers are adjusting their businesses to new technologies, but 43% encounter difficulties implementing digital transformation. Let’s see how AR/VR technologies can transform manufacturing.
Rapid prototyping and product design
Due to fierce competition, manufacturing companies face the pressure to deliver innovative solutions faster and more cost-effectively. AR/VR automatization will help enhance the product design bringing it to a physical prototype.
Automotive companies have already managed to cut the time between design and physical implementation from weeks to days. AR/VR solutions allow them to reduce or completely eliminate the most time-consuming stage — building a physical prototype and testing it under real-life conditions.
Virtual reality future solutions allow remote team members to cooperate as if they were in the same room and use virtual visualizations of products.
Driving process improvements for engineers and technicians
The engineers can use AR solutions for accessing information and instructions for details in real-time. They can also compare the object with its digital versions to identify the problem quickly. This will help them save time and fix the problem without checking all parts of the detail.
VR headsets can also replicate expensive or dangerous scenarios for training or crash testing purposes. This will also increase the safety and efficiency of work.
Industry Key Players
In 2013, Google released a prototype of Google Glass allowing to see digital information over natural surrounding. In 2015, Google stopped producing Google Glass only to continue in 2017. In 2017, Google released Google Glass Enterprise Edition, and in 2019 — its second version.
The first edition of Google Glass received a great deal of criticism and privacy concerns. Yet, the device started to be used in different industries, and other companies decided to make their own improved devices.
Now key companies on tech markets are merging, acquiring, or collaborating with the major players in AR/VR industry:
- In 2014, Facebook acquired Oculus that created Oculus Rift, Oculus Go headset, and planned to release the Oculus Quest video game. Oculus was one of the first virtual reality companies that gained public support. The deal amounted to $2 billion.
- Samsung partnered with Oculus to release its Gear VR in 2015. It is a headset that uses a Samsung phone as the screen — thanks to it, it is more affordable than the competitors’ products. Users can download an app from the Oculus app store, mount the phone onto a headset and use it as a headphone or controller.
- In 2016, HTC collaborated with Valve, and the two companies released the HTC Vive VR headset along with the Vive Pro version. Both devices are relatively affordable compared to competing products ($499 and $799, respectively).
- In 2017, Apple released the ARKit — a development tool that allows the creation of AR apps for iOS devices. It is a built-in function of iOS 11. In 2020, Apple bought US-based startup NextVR, but they haven’t revealed their plans yet.
- In 2020, Facebook announced that they had acquired SANZARU — an American video game development company that created games for the Oculus VR platform. This cooperation will surely make a statement in the future of VR gaming.
Giant companies not only acquire the VR startups but also develop their own AR/VR projects:
- Microsoft has launched enterprise-oriented HoloLens mixed reality projects. It is an all-in-one headset that operates on Windows 10 and doesn’t need any computer connection. The device costs $5,000, but there is an option for businesses to rent it.
- Magic Leap makes wearable headsets creating realistic AR projections directly on the user’s eyes. The company conducted one of the most extensive fundraising campaigns among AR/VR startups and raised $2.4 billion with Google’s $542 million.
- Gaming was the primary focus of early VR products, and PlayStation couldn’t miss this opportunity. Their VR system already supports over 200 games compatible with PS4.
A 30-Year Timelapse of VR
In the nearest decades, the AR/VR technologies will be developing at a breath-taking pace. And although it is hard to predict the final destination point, we’ll give it a try.
2025 — AR/VR Merging
In the nearest future of virtual reality technology, the devices will create an incredibly realistic experience for humans. It will be almost impossible to tell the difference between the real and virtual worlds, between AR and VR.
By 2025, AR/VR will become standard in different industries and a common educational tool in classrooms like computers or smartphones.
Today, we collaborate remotely via Skype or Zoom connection. In five years, we will work together with our colleagues in a virtual environment. Full-dive virtual reality interaction will become as common as video calls. Of course, AR/VR devices will become more lightweight, easy-to-use, and affordable.
Now AR/VR are the technologies of the future. In five years, they will become our reality.
2030-2040 — Welcome to Mars!
Today the AR/VR market is divided into three sectors: enterprise, commercial, and consumer. The consumer sector is expected to get a major share by 2030. The AR/VR devices will become more affordable, and virtual reality gaming in the future will allow traveling to different realities or even to Mars.
By 2040, the space industry market value will reach $1 trillion. Today billionaires and enthusiasts, such as Elon Musk, Richard Branson, and Jeff Bezos, are determined to become the first to take humans to Mars.
Although it’s obvious that this project requires astronomical investments, and the majority of us will never leave our planet, it doesn’t mean that we will never see Mars landscapes with our own eyes! AR/VR headset is an excellent alternative for users to ‘visit’ Mars any time they want. This will also become the primary way to train the astronauts and prepare them for real Mars missions.
2050 – VR Shopping Assistants
Online shopping is a common thing, but there is a probability of buying an item that doesn’t fit you or doesn’t look good in your home. VR shopping allows trying the desired item on without leaving your room.
By 2050, each retail shop consumer will have their own virtual AI shopping assistant to advise the item according to their tastes and budgets. You will be able to try an item in a virtual changing room. VR headsets will create the atmosphere of a real department store. Consumers will also be able to buy groceries right from the farm or watch how the chocolate is made.
Conclusion
What is the future of VR? The experts agree that we will see the common adoption of VR in many industries in the nearest decades. The first companies to introduce AR/VR in their working routine will be the ones to get the most benefits.
Do you have a promising idea on how to use AR/VR in your business? Share your vision with our team, and we will build innovative software that will bring profit now, not in the next decade.
Need a qualified team?
Reach new business objectives with the dedicated team of professionals.