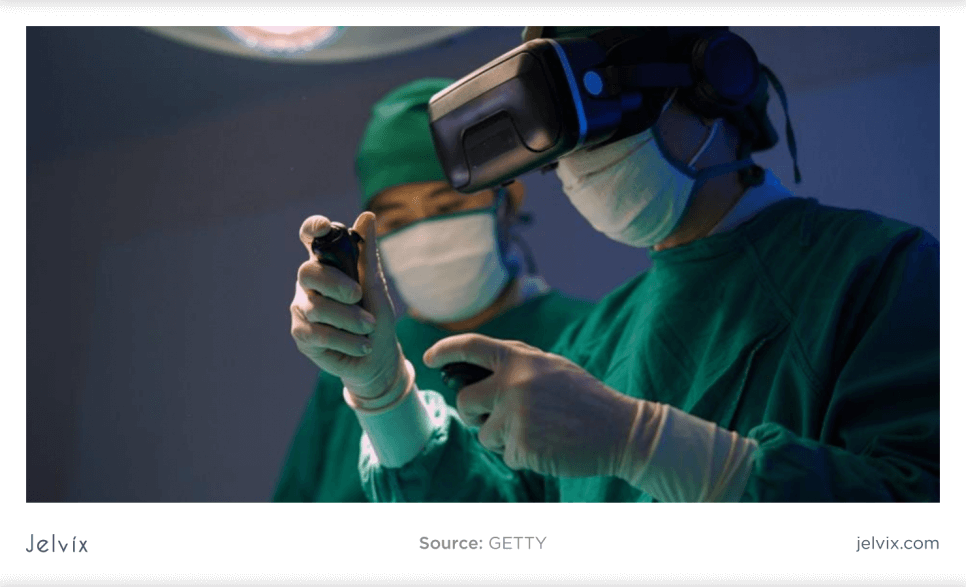
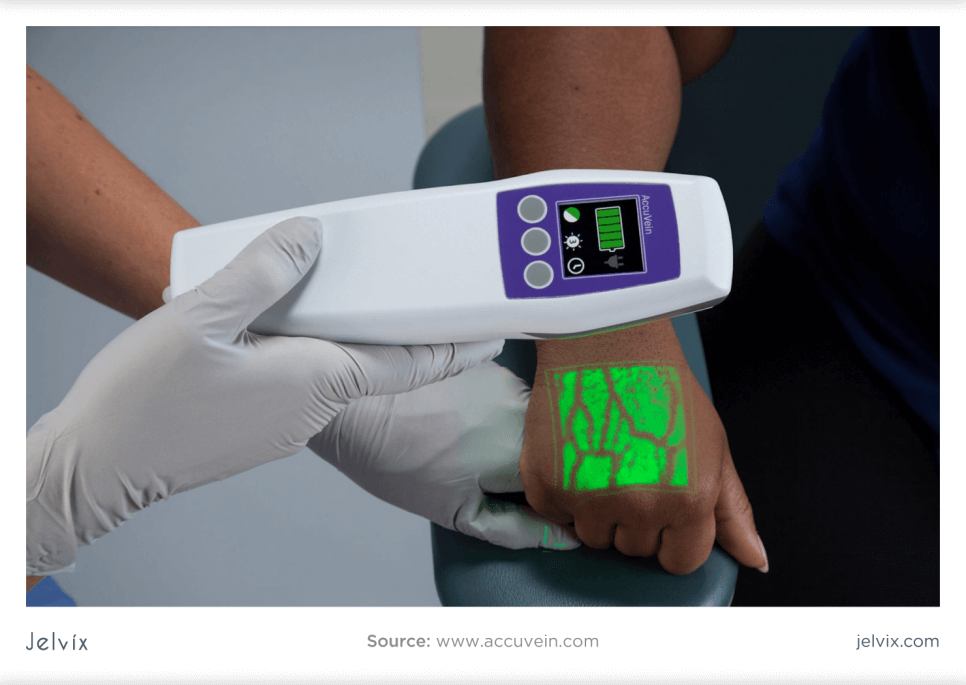
Market watchers say 2024 promises to be a challenging year for digital health executives and investors. Healthcare systems – a major segment of digital health buyers, are losing billions of dollars and are looking to cut costs.
Direct-to-consumer digital health companies face the dual challenge of inflation and a potential recession, which has led to a shift in strategy towards corporate clients. However, many healthcare organizations are still actively digitizing and even increasing spending on some technologies. One of them is augmented reality (AR).
Hardly considered no more than just a visually impressive format a few years ago, AR technology is now making a significant contribution to healthcare and its concern for life. So, many companies in the healthcare sector consider AR used as a priority tool in their work.
Augmented Reality Market Review
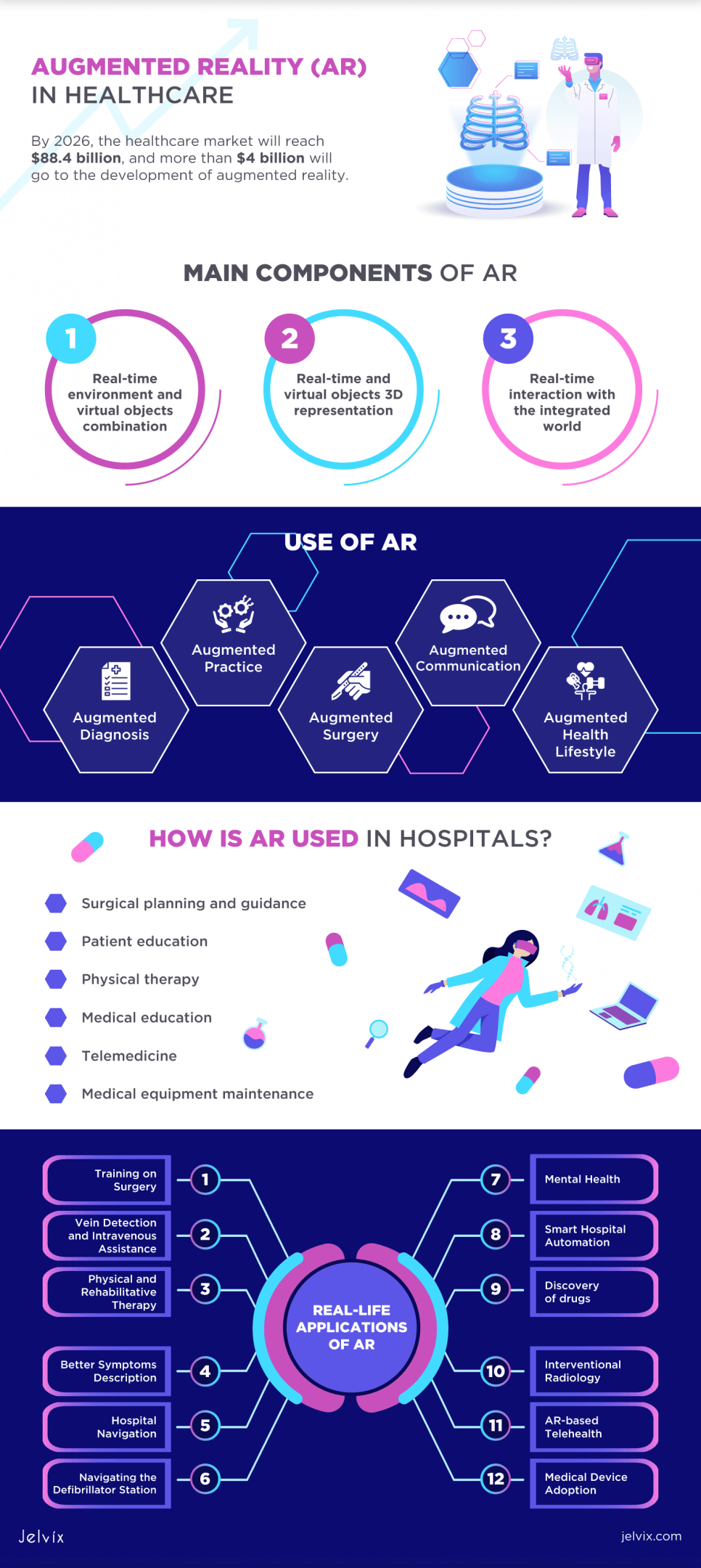
That technology is firmly established in medicine. By 2026, the healthcare market will reach $88.4 billion, and more than $4 billion will go to the development of augmented reality. There are many drivers of this phenomenon.
One of the reasons for the increased demand for AR in healthcare was the pandemic. From 2019 to 2020, the medical field’s augmented and virtual reality market grew by 27%. After the recession of the pandemic, from 2020 to 2021, the demand for augmented and virtual reality (VR) has only increased.
According to GlobalData, there are 50+ established medical device companies, spanning technology vendors, and up-and-coming start-ups engaged in developing and applying AR/VR eyewear. Venture capital invested more than $250 million in virtual and augmented reality startups in 2022, according to Digital Health Business & Technology’s database. In March, virtual reality training platform OssoVR secured $66 million in funding, one of the year’s largest VR startup rounds.
What is Augmented Reality’s Role in Healthcare?
While AR and VR are changing the future of healthcare and medicine, the way AR is doing it is unique. Whereas virtual reality technology creates a three-dimensional world that completely separates the user from reality, transferring him through a virtual reality headset, in augmented reality, users keep in touch with reality, and information is perceived as quickly as possible. The three main components of AR include:
- Real-life environment and virtual objects combination
- Real-time and virtual objects 3D representation
- Real-time interaction with the integrated world
Read more about the role of the app development companies in medical diagnostics.
The interaction of the real world with the virtual becomes possible thanks to specialized:
- AR hardware. These can be sensors or tracking devices such as accelerometers, gyroscopes, GPS, digital cameras, or optical sensors. These are user-input devices such as microphones, touch screens, special clothing, or gesture devices.
- AR software. It includes applications and programs that receive data received from hardware. As a result of processing this data, applications allow you to create augmented reality.
AR applications run on various devices and combine situational and sensory perceptions to create a learning experience without additional equipment. AR is also considered less cumbersome than VR, which requires specialized hardware, headsets, and a learning curve.
How can Augmented Reality be Applied to the Healthcare Domain?
The use of AR in healthcare can be traced back to 1992 when the US Air Force started developing and using these systems in their laboratories to enhance human performance during medical operations and surgeries.
Gradually, the private sector jumped in and started developing innovative AR-based solutions that helped the medical world differently. By coming up with state-of-the-art AR systems, leading technology companies such as Siemens, Microsoft, Karl Storz, etc., helped simplify many complex medical procedures.
Augmented Diagnosis
When almost everything went digital, augmented reality in healthcare was the hardest to get online. For example, diagnostics and medical examinations could only previously be carried out with human participation. But now everything will change with Orcha Health – a highly efficient and convenient augmented reality solution that allows for patient assessment, diagnosis, and prescription.
Augmented Practice
Medical institutions are beginning to implement AR in their curriculum to provide students with valuable hands-on learning experiences through visualizing and practicing theories during training. Anatomy 4D offers a way to do that. This AR app shows the human body on real people or makes pictures in the book alive through the lens of technology and even makes questions to test and challenge their knowledge.
Augmented Surgery
AR technology allows surgeons to overlay digital information like CT scans and X-rays onto the patient’s body in real time. It gives them a complete understanding of the patient’s anatomy and helps them to make more precise incisions. For example, the MEVIS Surgery application allows for avoiding dangerous operations by assisting surgeons in identifying liver tumors without damaging important vessels inside the organ.
Augmented Communication
Medicine is challenging to learn and understand, especially if you are just a patient trying to get treatment records from your doctor. Google Lens is a great example of how AR improves communication between doctors and patients. For instance, with the Google Lens technology solution, new mothers can learn to breastfeed comfortably and on their own terms.
Augmented Health Lifestyle
There are augmented reality applications for healthcare that can have a long-term impact on people’s lives and allow them to lead healthy lifestyles without outside help. Take Dorothy, an app for people with memory problems that reminds them of daily tasks and needs, such as taking pills or going for a walk in the fresh air.
AR can motivate people; everything seems more fun when it’s become a game. The “Zombies, run!” app is ideal for those who find running boring. When you run from virtual zombies projected onto your device, you increase your speed and stamina, and time flies by.
How is Augmented Reality Used in Hospitals?
Augmented reality (AR) is used to improve patient care and treatment outcomes in several ways. Some of the most common applications in hospitals include:
- Surgical planning and guidance: AR is used in surgical planning and guidance to overlay patient-specific information, such as CT scans and X-rays, onto the patient’s body in real time. That allows surgeons to make more precise incisions and reduce the risk of complications.
- Patient education: AR is used to provide patients with a better understanding of their condition and treatment options. For example, doctors can use AR to show patients an interactive 3D model of their anatomy, which can help them explain medical conditions and procedures in a more accessible and understandable way.
- Physical therapy: AR assists patients with physical rehabilitation by providing visual cues and feedback to help them perform exercises correctly. That can improve the effectiveness of physical therapy and help patients recover faster.
- Medical education: Medical students and residents can use AR to learn about the human body in a more interactive and immersive way, allowing them to visualize and understand complex concepts that are difficult to grasp through traditional methods.
- Telemedicine: AR can be used in telemedicine to allow medics to diagnose and treat patients remotely. That can be particularly useful in remote or underserved areas with limited access to medical care.
- Medical equipment maintenance: Some hospitals use AR to maintain medical equipment. That allows the maintenance staff to access instructions and troubleshoot issues with equipment in real time, reducing downtime and increasing efficiency.
Overall, AR is being used in hospitals to improve patient care and treatment outcomes and to provide new ways for medical professionals to diagnose, treat, and educate patients.
Real-Life Applications of AR in Healthcare
Many companies have started capitalizing on this technology and its potential healthcare applications. Let’s explore some significant real-life use cases of AR apps improving patient medical experience.
Training on Surgery
Surgical augmented reality transforms how junior surgeons are trained in surgery rooms. One such app, Touch Surgery’ offers users to practice surgery anywhere and at any time. They use an interactive mobile surgical simulator that guides them step-by-step through every part of an operation and every decision made along the way.
Vein Detection and Intravenous Assistance
Healthcare augmented reality can help nurses and technicians become more effective by using AR as a handheld scanner that can be moved on the skin to see where the veins are in the patient’s body. The AccuVein application allows finding a vein on the first stick 3.5x more likely.
Physical and Rehabilitative Therapy
AR systems are actively used in кehabilitation, providing virtual objects or scenes from the real world. The system also offers automatic imaging, providing real-time biofeedback during rehabilitation. For example, patients can use augmented reality-enabled digital demonstrations from Meta to develop fine motor skills. The University of Tasmania study found that this approach produced positive results faster than face-to-face demonstrations.
Better Symptoms Description
Often, when explaining the prevalent conditions to the doctors, the patients either exaggerate or undermine their symptoms. That can lead to an error in some diagnoses and treatments. AR can help doctors have a better view of the condition, which surpasses the patient’s description without any scope of error; they can check and have a say in the patient’s real condition.
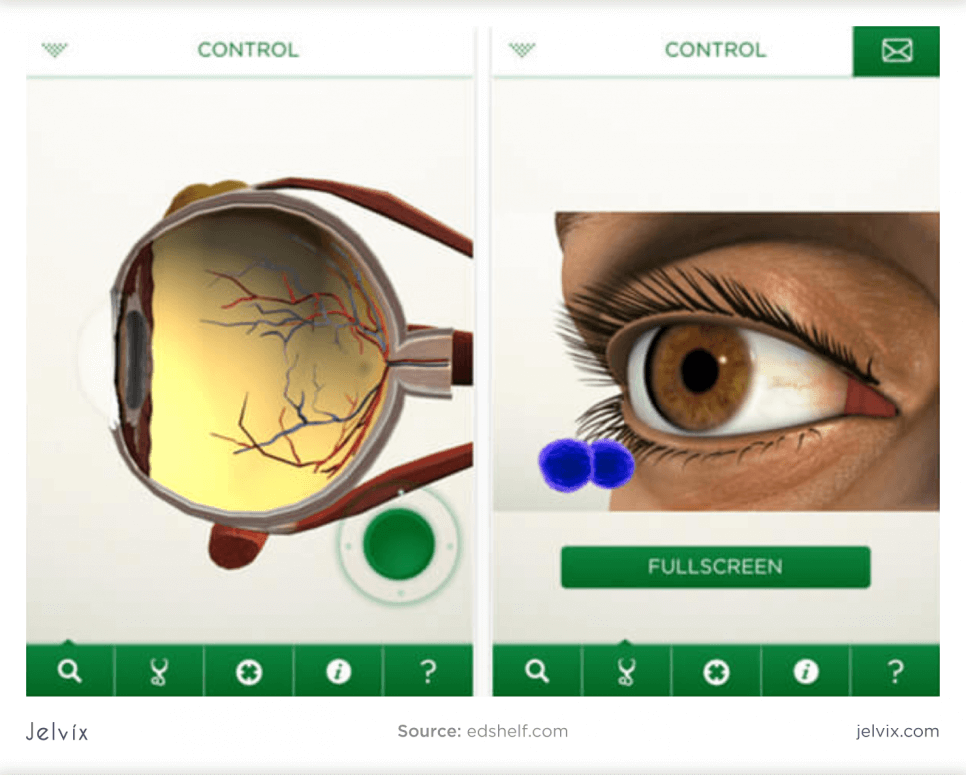
For example, the EyeDecide application allows you to see the eyeball from any angle by directly touching the image generated on the tablet and rotating it with your finger. It is also possible to reduce, expand, move, or make notes on the eye in almost any direction. All this assists in simulating various disorders and helps to diagnose more accurately.
Hospital Navigation
Modern hospitals are complex institutions that can be difficult for patients and new employees to navigate. One useful feature of AR is the development of navigation and navigation tools that help anyone navigate their environment. When these tools are available through a smartphone app, they are valuable for newbies and reduce the burden on help desk staff.
Resonai’s augmented reality healthcare solution does this with a virtual concierge, an app that can provide personalized building and indoor navigation directions. This tool gives tips to the requested departments at the patient level and allows patients to choose the ideal path. At the staff level, medical teams get a complete view of the facility to assist first responders in real time.
Navigating the Defibrillator Station
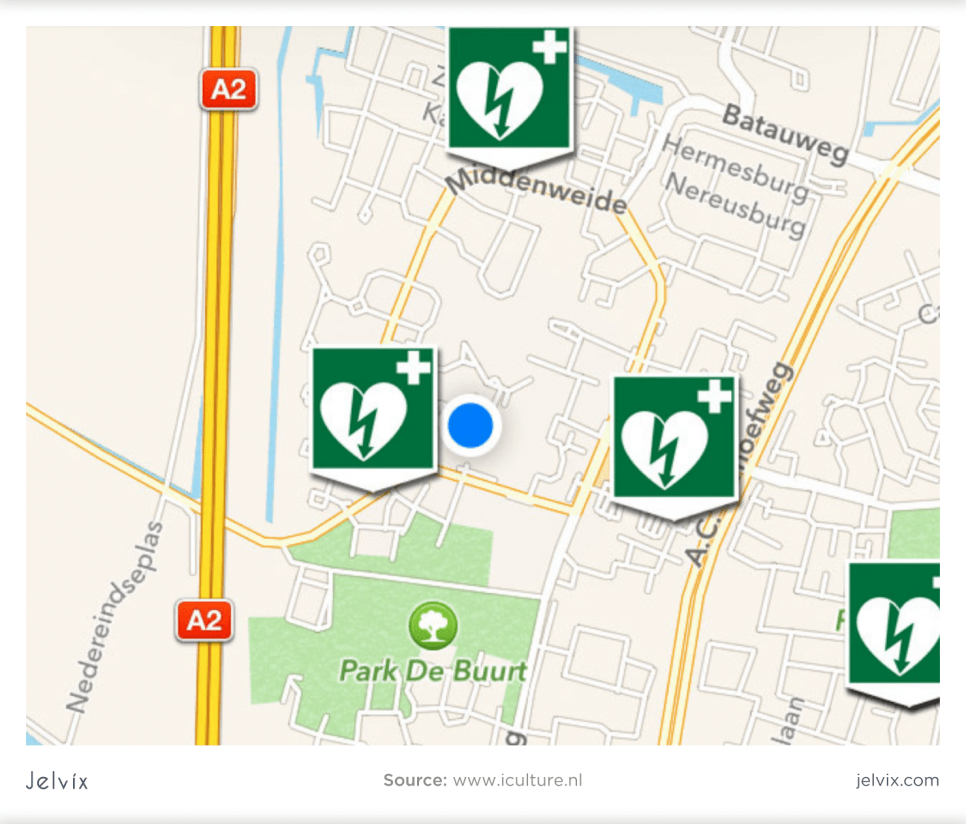
Many hospitals install defibrillators in emergency areas outside of traditional medical wards. With the right augmented reality tools, anyone with a smartphone can navigate to these defibrillators through the app’s interface.
One example – AED4EU, was built for the Radboud University Medical Center in Nijmegen, Netherlands. This application allows users to bookmark external defibrillators and AEDs in a database. Combining the AED4EU with the Layar browser enables the AR to function to find and display the nearest AED.
Mental Health
Effective for many disorders, on-site coaching can now be done in the counseling room, with simulations and exposures controlled as needed. Fear of flying or horrific events that may underlie PTSD can be triggered with a single click using 360° video and Unity-based virtual worlds.
Smart Hospital Automation
Smart buildings use integrated technology systems to increase efficiency and help occupants with day-to-day operations. When devices are linked, facility managers can automate building functions, remotely manage control systems, optimize energy use, and significantly reduce operating costs. And this principle can be extended to medical equipment.
Smart buildings often use augmented reality for navigation, but AR also allows you to create digital twins – a 1:1 scale virtual model of the entire building. Digital twins make it easy to simulate emergency scenarios or visualize building changes. Building models can even be linked to real-time sensors, allowing facility managers and caregivers to locate assets anywhere in a facility more quickly.
Discovery of Drugs
AR technology is actively used for data visualization in drug development, which allows scientists and health experts to evaluate complex genetic data. The technology is being used to share information with other scientists working in remote locations. Since AR technology can provide a three-dimensional representation of images, we will observe the action of a drug in the human body in three dimensions.
Interventional Radiology
In short, this is a branch of medicine that uses medical images to perform several minimally invasive procedures. These include fluoroscopy, magnetic resonance imaging, etc., for diagnosing and treating diseases. Since AR can transform a CT image into a dense 3D structure map for medical imaging, it could be used to facilitate interventional radiology.
AR-based Telehealth
Telemedicine software allows practitioners to check vitals through a complete AR-based model, conduct necessary tests, and videoconference with experts through teleconsultation. Nomadeec, a medical device manufacturing company focused on telemedicine, uses Microsoft HoloLens to treat patients immediately. It is a new set of eyes and ears and can also help connect virtually with the patients to assist and consult them even though they are miles away.
Medical Device Adoption
Medical device manufacturers can use augmented reality to demonstrate how a device will perform in a specific location or customer premises. AR allows you to eliminate the physical transportation of products to the customer’s location, saving time and money and leading to an optimized sales process and increased customer satisfaction. Ultimately, this helps in the better adoption of medical devices by end users.
Does AR Have a Future in Healthcare?
Since all the tangible benefits of AR in medicine have already appeared, the future looks very optimistic. Augmented reality impacts all areas of the healthcare sector, from developing the skills of the next generation of medical practitioners to improving the detection, diagnosis, and treatment of conditions.
Moreover, with the spread of 5G technology, augmented reality will reach a new level. That will be critical to unlocking new ways of working, from improving reliability in the operating room to supporting remote patient monitoring. Ultimately, AR can help better patient care, a universal benefit for all of us.
Indeed, this technology has yet to be fully deciphered, including its security, privacy, and effectiveness concerning patient care. However, if done right and safely, it could change the next generation of healthcare.
What are the Pitfalls of AR in Healthcare?
While widespread digitalization and the adaptation of new technologies can bring many benefits to the health industry, it is also important to be aware of the risks. The key ones in the case of AR are the following:
Privacy and data protection
Devices using AR technology collect patient data, so their privacy and protection have become critical. Organizations interested in moving towards AR healthcare systems may need to commit to addressing privacy issues as an important foundational step.
Hacker attacks and security
Despite its many benefits, augmented reality technology is vulnerable to security threats and cyberattacks. The consequences of such actions can misdirect a vehicle using an AR-enabled navigation system and use it to cause accidents. Therefore, it is advisable to apply the principle of limited confidence and independently verify the data presented.
Conclusion
The adoption of AR technology will continue to grow as it demonstrates real value. The availability of AR applications will also expand as the technology matures. 96% of adult Americans own a cellphone, nearly three-quarters own a laptop, and half possess a tablet, which is clear proof that developers need to create AR applications and experiences that work on these and other devices.
But to work with such complex technologies, you need to find a reliable partner with expertise in augmented reality development. Jelvix is a company that has already created high-quality AR and VR solutions for various industries. Our knowledge in AR development, design, training, and support is the appropriate mix you will be looking for in a good AR vendor. Therefore, contact us if you have an idea for AR and VR applications!
Need a qualified team?
Access the talent pool to scale your team capacity.