Nowadays, digital transformation is more important than ever. We see its tangible effects on statistics and income lists. Fortune 500 companies spent 20 years before getting a billion-dollar worth. Startups get to their destination in less than four years, having enlarged the “unicorn” crowd to more than 1,200 companies in 2024.
Digital technology created revenue opportunities for what seemed to be thin air, and now online companies are on top of the business food chain. The major economic transformation has happened in less than a decade. The most exciting, but also intimidating thing is that this pace isn’t getting any slower. All businesses that haven’t crossed over to the online environment yet have to consider getting on board.
If you want your business to stay competitive by incorporating digital transformation, this article is for you. Read to find out how to implement a strategy for digital transformation for your industry efficiently and use it to increase the profitability of your enterprise.
Why Digital Transformation Is Essential for Business Growth and Profit Increase
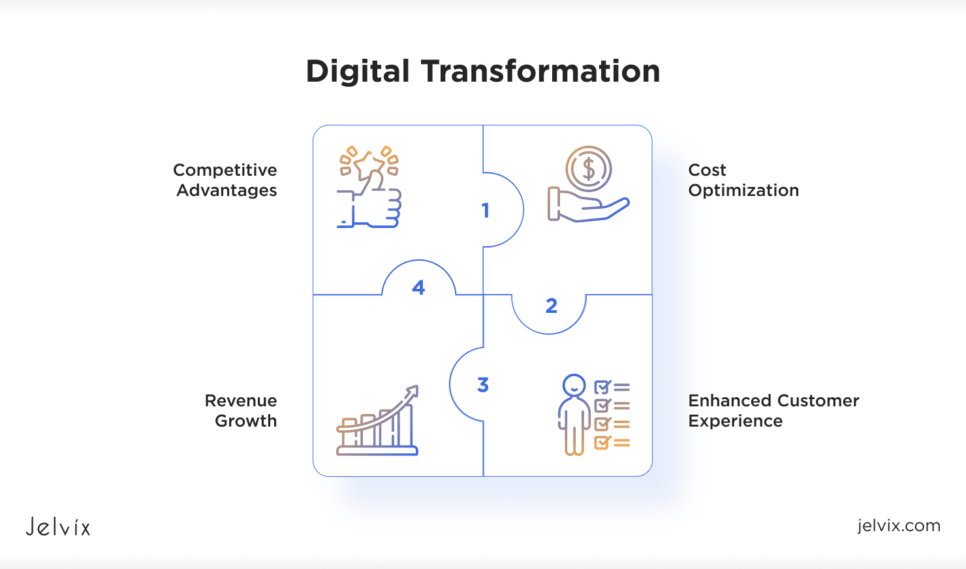
Digital transformation is an essential part of business growth. The integration of digital technologies can significantly impact return on investment, optimize operations, and drive revenue growth. Companies that implement digital tools, adopt automation, and go with AI development often see increased efficiency, reduced operational costs, and enhanced customer experiences. All these factors contribute to higher profitability.
Competitive Advantages
By modernizing your business processes through digital transformation, you can gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace. This can help you stay ahead of competitors, adapt to market changes, and attract a more tech-savvy customer base. With technologies like AI and machine learning, businesses can make smarter and faster decisions and personalize offerings to boost customer loyalty.
Cost Optimization
Through digital solutions, businesses can automate repetitive tasks, optimize workflows, and reduce the reliance on manual processes. This can lead to cost savings thanks to eliminating inefficiencies, which enhances overall profitability. In addition, cloud computing allows for a more flexible and cost-efficient infrastructure, reducing the need for expensive hardware investments.
Revenue Growth
Digital transformation creates new ways for businesses to generate revenue, like offering subscription services, digital products, or building new partnerships. By using digital marketing, personalized offers, and better customer service, businesses can engage more customers, increase sales, and expand their reach.
Enhanced Customer Experience
Digital tools like AI, mobile apps, and online platforms help businesses connect with customers in real time and offer personalized services that match their needs. This leads to a better customer experience, stronger loyalty, and more opportunities for long-lasting relations with clients.
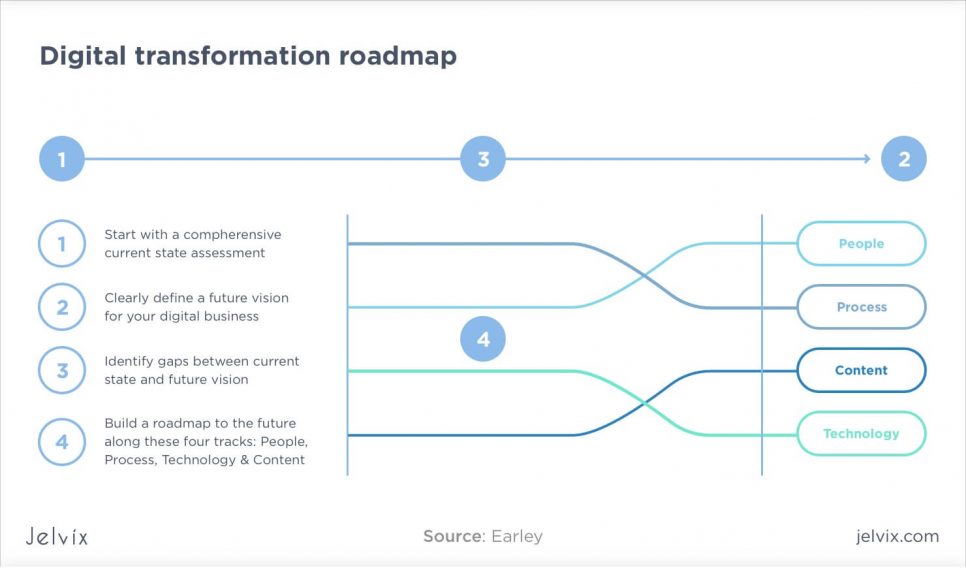
Understanding digital transformation meaning by building a roadmap
Companies can’t introduce technology transformations to their business models and markets overnight. It’s a gradual process, built on non-stop analysis and testing. This process is individual for each business – it depends on the state of the company, positioning, niche, relationships with clients, and the stages of growth.
Still, there is a unified framework that collects the key steps of digital transformation that are more or less the same for any company. These are building blocks that allow business owners to create unique approaches based on their customer data.
Digital transformation is based on three universal stages.
1. Business analysis
When a company starts the journey to digital transformation, its team still has to continue daily operations – client support, product delivery, order processing, logistics. It’s crucial, therefore, to make sure that digital transformation doesn’t disrupt the current customer experience.
How to prepare for seamless digital transformation?
- Research the matter – understand what digital transformation means and what resources it requires from your team.
- Define pain points – you need to outline the fields of your services that are in the most need of transformation. For instance, if you constantly receive complaints about delivery speed, this is where you should start your digital transformation planning. Solid clues usually come after conducting customer feedback evaluation and interviewing team members.
- Prioritize the satisfaction of your current customers. The fact that you are aiming at future progress shouldn’t distract you from matters at hand. A simple example: even if you are redesigning your company’s website, you should continue supporting the current version, providing it with content and technical support.
When you are done with these key actions, you can start laying ground to the methods of enterprise digital transformation – while still making sure that your company is well-functioning.
Find out how much enterprise software solutions development costs.
2. Prepare transformation at the team level
The common mistake of many companies on their road to digital transformation is the layoffs. The business owner decides to hire several trained specialists who have worked on building a tech-powered company and sees them as the key stakeholders. Other team members don’t have a clear idea of what is going on.
How to introduce your team to digital transformation?
- Back your claims up with statistics. Before you start convincing others about a particular strategy, you need to make sure you are going in the right direction. A good place to start is exploring market trends, competitor statistics, finding references – companies that have gone through the process, similar to the one that you envision, and collecting your data.
- Encourage colleagues to share their experiences. Team members can add their unique perspective on pain points, the ones that you might not consider at once.
- Assign a role in digital transformation to each team member. One person will be responsible for providing customer data, others will control logistics, while someone will keep track of changes in financial position through the transformation.
To keep track of your team’s opinion throughout the transformation, be sure to conduct regular meetings with the entire team, not just the experienced ”chosen ones.” Sure, keeping everyone in the loop takes time, but it’s a worthwhile long-term investment.
3. It’s time to come up with the system
Once you’ve identified the transformation area and introduced your team to plans, it’s time to start planning tangible changes. You need to come up with both a big system for the complete transformation and smaller subsystems dedicated to particular pain points.
How to standardize the transformation?
- Define your goals. They should be technological – what kind of online instruments you want to develop and implement (a website, mobile app, chatbot) – and financial – how much return you expect and how many deals transformation can help to close.
- Discuss metrics. We recommend using kanban managers for task tracking – you can define the weekly amount of work that you’d like to perform and check whether the team meets these requirements. With Google Analytics, you can check conversions and financial growth, which will be directly linked to your transformation activities.
- Keep reference collection. You need to analyze the strategies of successful competitors and take ideas on board.
Building a Digital Transformation Strategy and Approach
Creating a strong digital transformation strategy is essential to help your business achieve its goals. You need to combine technology, people, processes, and data to guide your digital efforts.
Aligning Digital Transformation with Business Objectives
A successful digital transformation strategy begins with understanding how digital tools can support your business goals. These can include improving customer satisfaction, increasing efficiency, or expanding your market share. Start by identifying key areas where digital adoption can make the most significant impact.
Stakeholder Involvement
Digital transformation needs everyone on board. This means getting leadership and teams from different departments involved. Having input from all areas, from operations to customer support, ensures the transformation aligns with your company’s needs. Leaders should set the direction, create a clear vision, and make sure teams have the resources and training to succeed.
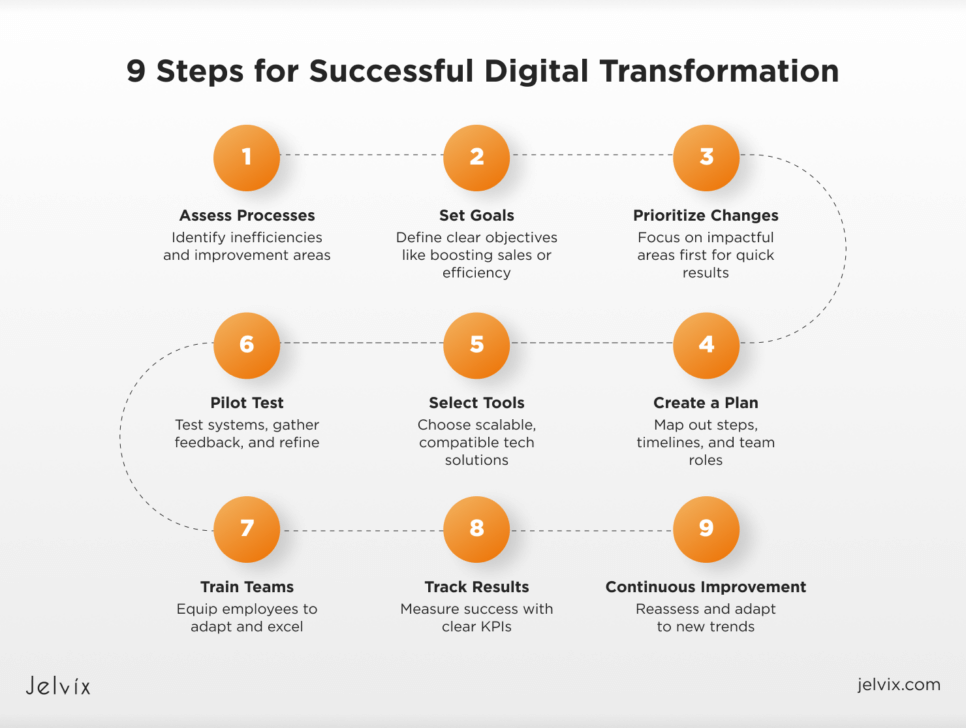
9 Steps for Successful Implementation
To successfully implement digital transformation in your business, it’s important to follow a clear, step-by-step approach. A few proven steps will help you reach the best results.
1. Evaluate Your Current Processes
Start by looking closely at how your business operates right now. Identify areas where processes aren’t as smooth as they could be or where technology could improve your business. Gather feedback and get a complete picture of where you can make improvements.
2. Set Clear Goals
Once you understand where changes are needed, set specific goals for your digital transformation. Whether you want to increase sales, improve customer service, or make your operations more efficient, make sure your goals are defined clearly.
3. Focus on Critical Changes First
Not every part of your business needs to change at once. Start by focusing on the areas that will have the biggest impact. For example, automating customer support or setting up a new system for managing customer data might be a good place to begin. By improving the most important areas first, you’ll see results more quickly.
4. Create a Plan
A detailed plan helps keep everything organized. Break down each step of your digital transformation, including timelines, resources, and the people involved. This roadmap will help keep your team on track and ensure you don’t miss anything important. Make sure everyone knows their role and how they can contribute.
5. Choose the Right Tools
The right technology is key to a successful digital transformation. Pick tools that can support your business goals and grow with your company. Look for software that will work well with your existing systems. Whether it’s AI, cloud computing, or automation tools, ensure the technology you choose helps your business run more efficiently.
6. Launch a Pilot Version
Before rolling out your digital transformation, start with a pilot version. Test the new technology in a controlled environment to identify potential issues. Gather feedback, make adjustments, and ensure everything runs smoothly before the full implementation.
7. Train Your Team
Your employees need to adapt to the new technology and processes. Provide training to help them understand how the changes make their work easier and more efficient. Make sure everyone has the support they need to learn and grow with the new system.
8. Track Progress with Clear Metrics
To know if your digital transformation works well, set up KPIs. These are simple measures like increased sales, faster response times, or higher customer satisfaction that show how well your changes are paying off. By tracking these numbers, you can adjust and improve whenever you need.
9. Keep Improving
Digital transformation doesn’t end after the first round of changes. Once you’ve made some improvements, keep assessing how things are going. Ask for feedback, look for new areas to improve, and stay open to adopting new technologies as they become available. A flexible approach will help your business continue to grow and adapt to new trends.
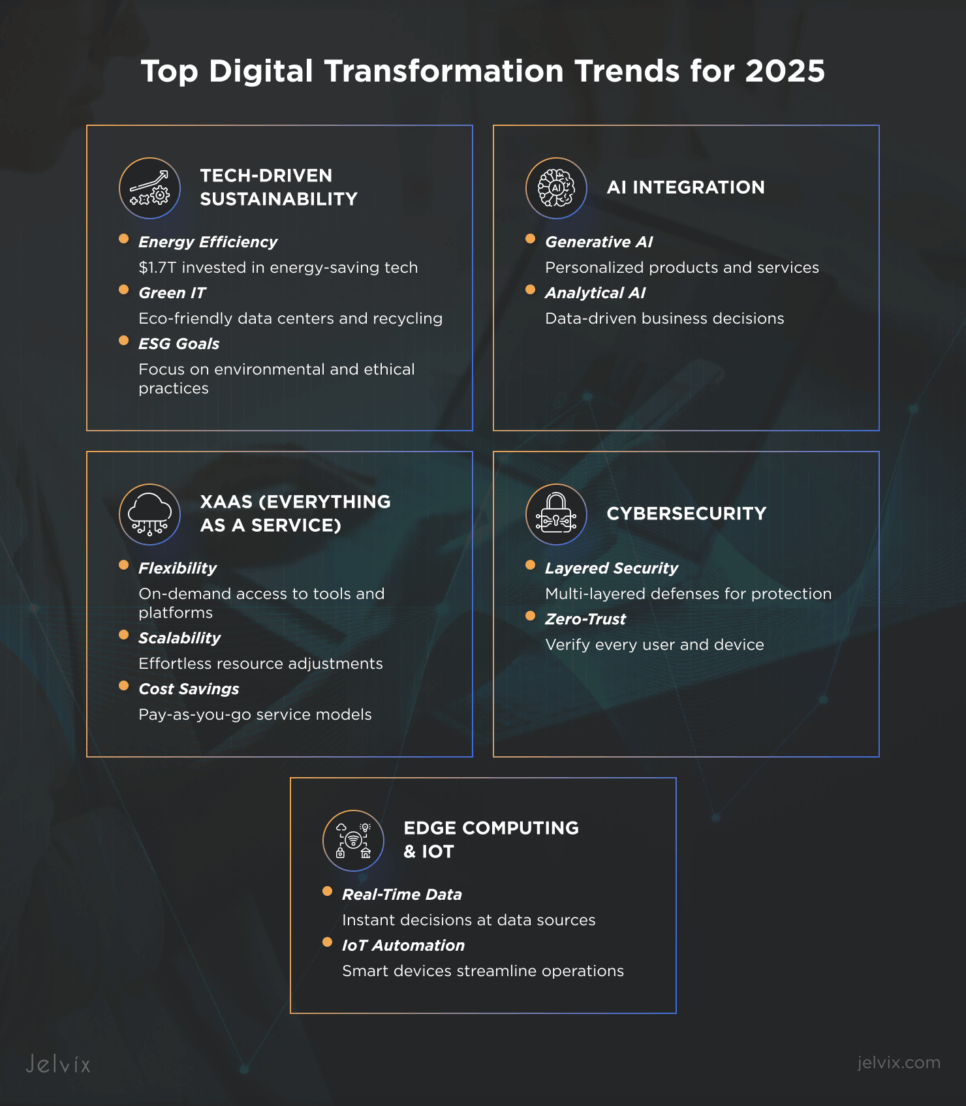
Digital transformation trends for 2025
Digital transformation is built on the successful combination of two development vectors: business and technology. You need to make sure that your company’s organizational processes don’t block the progress of the tech transformation.
Tech-Driven Sustainability in Business
Sustainability is becoming a key focus for businesses, and technology plays a big role in making it happen. Companies are turning to tech to help them reduce their environmental impact, save energy, and meet their sustainability goals.
Energy Efficiency
In 2023, businesses invested more than $1.7 trillion in energy transition technologies, and this tendency is only growing. This could mean switching to energy-saving equipment like LED lights, using smarter heating and cooling systems, or adopting tools that monitor and manage energy consumption to lower operational costs and reduce carbon footprint.
Green IT
Green IT means making sure that technology is as eco-friendly as possible. This includes using renewable energy to power data centers, designing energy-efficient systems, and recycling old equipment and electronics to reduce waste.
ESG Goals
Many companies are focusing on ESG — environmental, social, and governance — goals, which means doing business in a way that’s good for the planet, people, and society. By aiming to reduce their environmental impact, support social causes, and operate ethically, businesses can not only help the world but also build trust with customers and investors.
Integrated Generative and Analytical AI
AI continues to develop — its market is expected to surpass $1.8 trillion by 2030. It’s no surprise, as generative AI already assists in creating personalized content, products, and services, while analytical AI helps drive decision-making by providing insights from vast amounts of data.
XaaS: Everything as a Service
Everything as a Service, or XaaS, is a cloud-based model where businesses can access a wide range of services, such as software, infrastructure, and platforms, on demand. Instead of investing in expensive hardware and software, companies can now rent these services from providers.
Flexibility
XaaS allows businesses to pick and choose the services they need and exactly when they need them. This flexibility means they can scale their operations quickly without purchasing and maintaining physical infrastructure. Whether it’s adding new software tools or expanding storage space, companies can adjust services to meet their changing demands.
Scalability
As a business grows, so do its needs. XaaS offers the scalability to match this growth. With cloud services, businesses can increase or decrease their resources effortlessly. This allows them to stay efficient, even during periods of rapid growth or fluctuating demand.
Cost Management
One of the biggest advantages of XaaS is cost savings. Instead of making large upfront investments in hardware and long-term software licenses, businesses can pay for services on a subscription basis. This pay-as-you-go model means businesses only pay for what they actually use, which helps manage expenses and optimize budgets.
Key Trends in Cyber Security
The global cost of cybercrime is expected to reach $13.82 trillion by 2028, making security a top priority for businesses adopting digital transformation. To stay ahead, many companies adopt multi-layered cybersecurity, which means using multiple defenses to protect their data and systems.
On the other hand, the Zero-Trust architecture assumes that no one, whether inside or outside the company, should be trusted by default. Every user, device, and application must be verified before being allowed to access sensitive information.
Edge Computing and IoT Integration
Edge computing and the Internet of Things are changing how businesses use data, making operations faster and more efficient.
Real-Time Data Processing
Instead of sending data to a distant server, edge computing processes the data right where it’s created — on the device or machine itself. This means businesses can act on the information instantly, without delays. For example, in a factory, machines can detect a problem and fix it immediately, without waiting for instructions from a remote data center.
IoT Integration
IoT connects everyday objects like sensors and smart devices to the internet, allowing them to share data and even make decisions on their own. When combined with edge computing, IoT devices can process data locally, leading to faster decision-making. This helps businesses automate things like tracking inventory or scheduling maintenance, which saves time and cuts costs.
In enterprise, the responsibility of implementing innovation should be distributed between the team leader and digitalization experts. Keeping everyone involved in the process speeds up innovation and reduces the end cost.
Transform your business with Jelvix’s tailored strategies—modernize operations, drive innovation, and achieve sustainable growth.
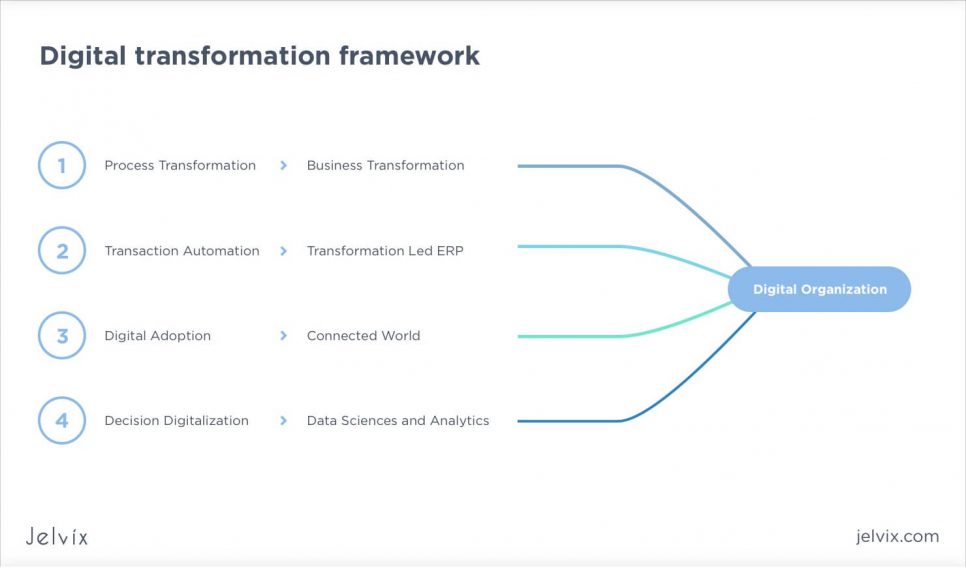
Digital Transformation Framework vs. Platform: Key Differences
It’s already clear that successful digital transformation relies equally on the theoretical understanding of the process as well as on the software solutions. One can’t substitute the other – you need to have both a framework and a platform in place.
What Is a Digital Transformation Framework?
A framework is your plan or roadmap for digital transformation that shows you the overall strategy: how to approach digital changes, what goals you want to reach, and what steps you need to take to get there. This framework helps you set the direction for the entire transformation.
When To Use Digital Transformation Framework
You need a framework at the start of your digital journey. It will help you decide what needs to be done and align everyone in your company around the same vision. It’s the first step to help you figure out what digital success looks like for your business.
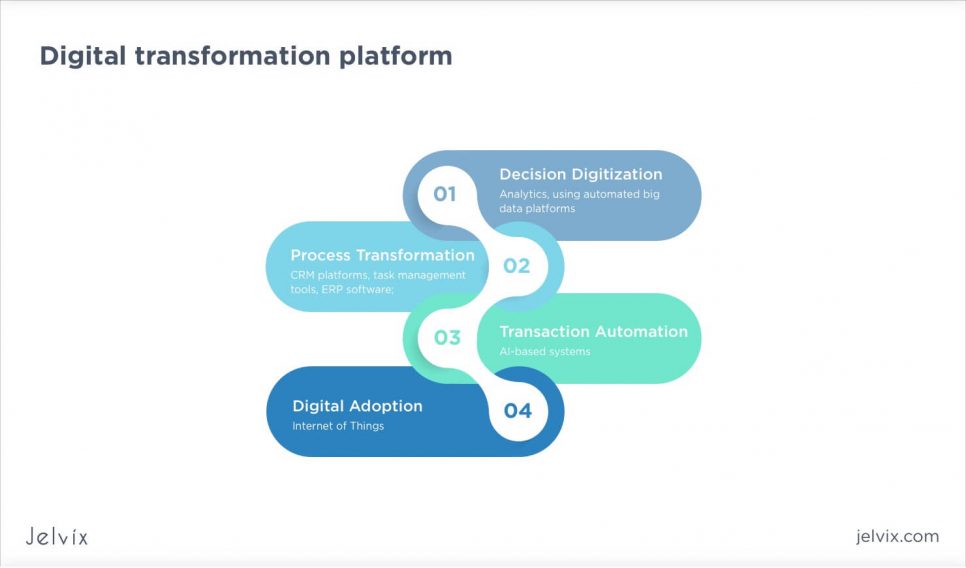
What Is a Digital Transformation Platform?
A platform refers to the actual tools and software you use to make the changes happen. These could be cloud systems, software for managing customer relationships, or platforms that handle data analysis.
When To Use Digital Transformation Platform
Platforms are needed once you have your roadmap in place. You need to pick the right platforms that align with your goals and help your business run more efficiently, reach customers better, or optimize internal processes.
How To Use Framework and Platform Together Efficiently?
To make digital transformation work, your framework and platform should work hand in hand.
Start with creating your strategy. Identify what you want to achieve and how technology can help solve your problems. This roadmap sets the course for your transformation. Once you’ve got your strategy, choose the right platforms to help you get there. Note that your framework should be flexible. As you start using your platforms, you may find new opportunities or challenges, so it’s important to adjust your plan as needed.
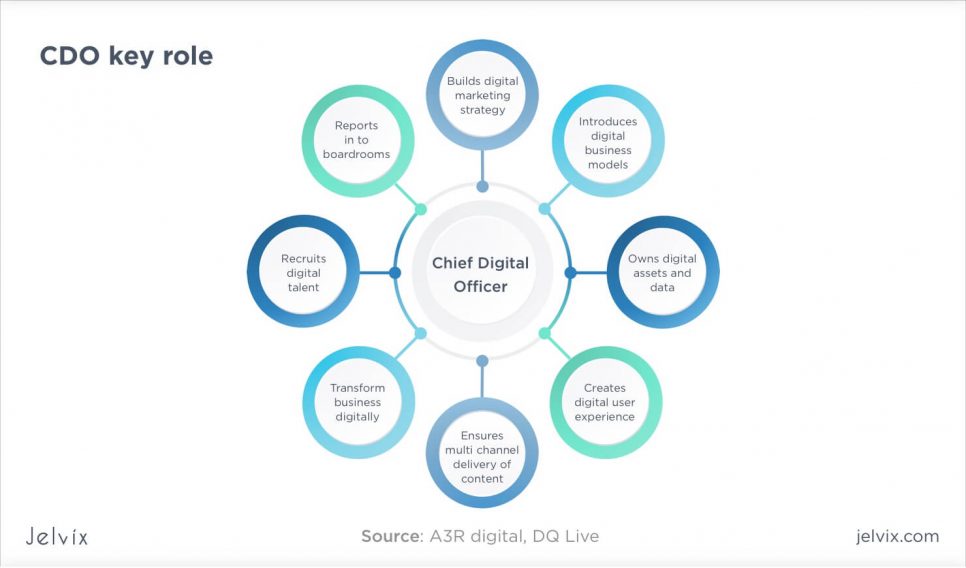
Chief Digital Officer as the leader of digital transformation journey
Chief Digital Officer is in charge of leading digital transformation. Some organizations prefer to hire a new member to fulfill the role of digital transformation manager, while others fill the position in-house. You can choose the strategy that fits you best.
CDO is the person who:
- cooperates with CEO, unit leaders, and financial offers, shaping the company’s strategy;
- makes sure that customer interests lie at the core of digital strategy, creates customer maps and describes a detailed customer’s point of view;
- decides which tech projects should be continued or abandoned, provides budgeting insights, and builds scaling plans;
- analyzes trends, scales the business landscape, keeps contacts with customers and partners, and revisits existing strategies;
- takes risks – Russen Reynolds Associates survey CEO showed that CDOs are much more likely to be disruptive and determined than other types of executives.
Most importantly, CDO is a person with a deep IT digital transformation experience. It’s someone who has a strong vision of where the company will be in 5 or 10 years and knows what steps to take now to get to that point. A good CDO is defined by strong analytical skills, software development expertise, and high-level communication abilities.
What can be transformed digitally?
The digital transformation process responds to the needs of emerging markets, clients, and competitors on many levels. Any aspect of business can be digitized – and there are affordable means around.
I. Customer experience
Superficial business transformations are a great place to start. They are directly visible to the end client and fast to implement. Also, there are multiple ways of approaching this matter – you can choose the way that fits your company and strategy the most.
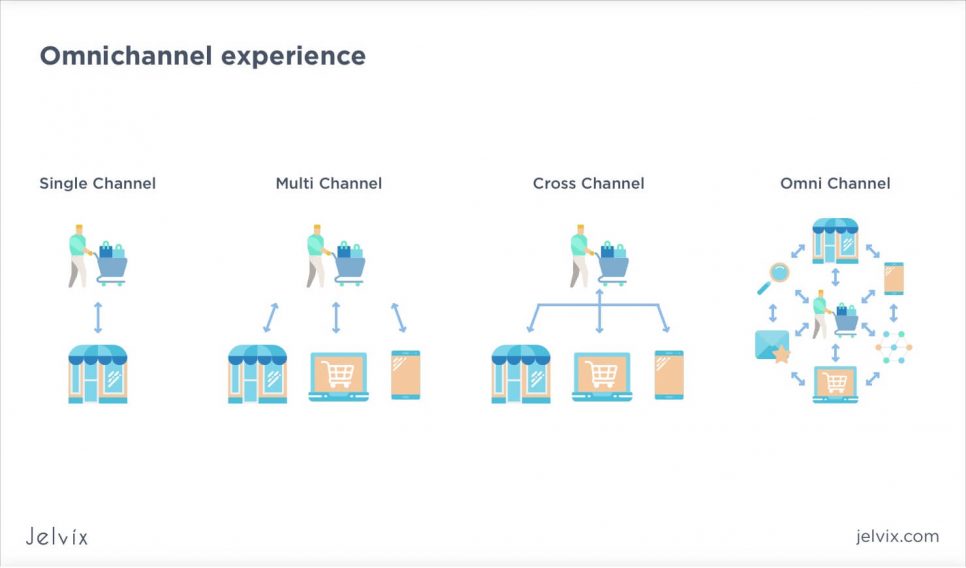
1. Omnichannel communication
Modern customers get information from multiple digital resources. Ten years ago, it was enough to communicate with a user on a single platform – e.g., a website. The next step was multi-channel communication – businesses were available on mobile devices and web applications – but each channel functioned separately. Cross channel experience united these different mediums – you could pick up where you left off on any channel.
Omnichannel communication uses an entirely different approach. The website is integrated with social media, email, search engines. All mediums where the company is presented should be united by one strategy.
2. Self-service and IoT
Online retail and offline shops are rapidly moving towards increasing self-service. The first steps towards exploring the innovations were made with Amazon’s checkout app and Sainsbury’s smart grocery shopping. It’s clear that the tendency is well received by the market, and will soon be widely picked up by big and small companies.
IoT is the massive drive of smart shopping experience. The technology integrates smart devices into a single network, connecting the customer directly to the shop’s database, providing a clear display of products right in their smartphones. They can browse the catalog, read and leave reviews, make purchases, and get follow-ups.
How can IoT self-service be implemented in retail?
- Self-service touchscreens, connected to the company’s computer devices – touchscreen sends the data to the company’s CRM, enabling automatic report generation;
- Connected applications and QR codes – by scanning the code, the visitor can connect to business’ digital platform and special offers;
- Mobile push notifications – soon, customers might automatically receive a push-notification as long as they enter the shop.
So far, the implementation of IoT self-service relies on tried and proven digital methods like web platforms or touchscreens, but the possibilities of the field are endless.
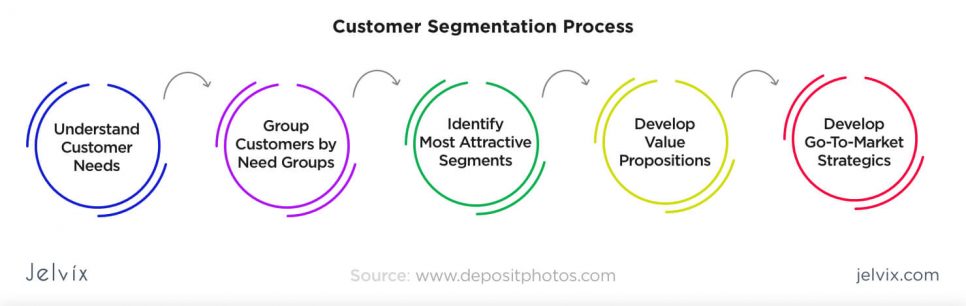
3. Better customer segmentation
When a company aspires to offer a wide selection of digital functionality, the importance of market awareness increases exponentially. You need to know how a user can benefit from a particular feature, and how to communicate your advantages in a personal way.
This is where customer segmentation steps in. The task is to divide the target audience into smaller, more manageable chunks. By specifying your target groups, you can highlight their needs more precisely, and pick a particular communication style for marketing activities.
Segmentation is done by a combination of several leading methods:
- Clustering – scientific segmentation based on mathematical algorithm analysis. You divide the target audience into small clusters, based on the smallest variations among customers – these characteristics lie at the core of archetypes.
- Complex segmentation – complex logic that allows you to prepare different user scenarios and work with thousands of variables- the segmentation software automatically sorts users by their affinity to a particular group;
- Behavioral segmentation: the company analyzes its customers’ buying patterns – aspects of brand choice (the crucial characteristics of a preferred product or company), sought benefits (what advantages matter the most), usage habits (how the product or service is used), buying preferences (online or offline shopping, for instance);
- Life-Cycle segmentation uses the customers’ age as the defining segmentation factor – the company sees the precise statistics on the demographic characteristics of their clients;
- Social demographic segmentation is slightly similar to Life-Cycle, only it targets a wider range of characteristics;
- Geographic segmentation – the audience is divided by their location;
- Customer needs – this system uses the need-based methodologies, like Pareto or ABC, to classify customers’ priorities and needs;
- RFM – this segmentation uses the client’s loyalty as a defining factor. Customers are divided into three groups – Recency (when the last purchase was complete), Frequency (how often a person makes such purchases), Monetary (customers should have enough resources to afford a purchase).
- Preference-based customization – the system analyzes customers’ goals and priorities and creates complex personal profiles.
Using even one of these systems is enough to provide you with a deeper view of your customers’ characteristics, priorities, and possibilities. With this data, you can create personalized, targeted advertising, humanize chatbots, and improve communication.
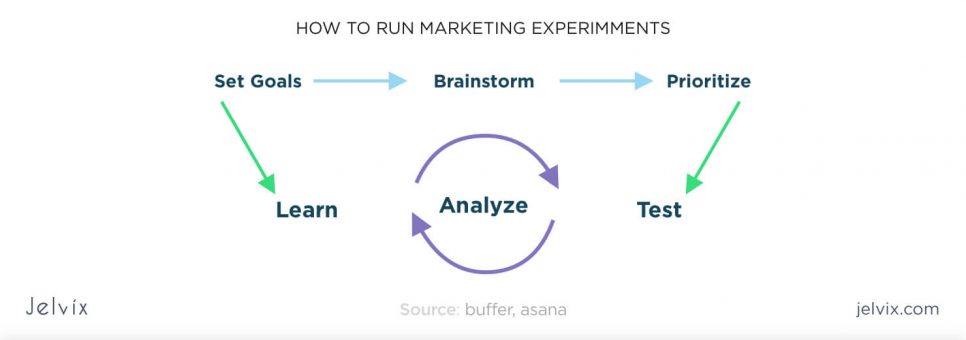
4. Marketing experiments (MNG: change management)
Once you get a precise idea of your target audience segmentation, you can start implementing solutions. However, you can’t expect the first version of an upgrade to be the best one. In most cases, you need to try out several options to find an optimal combination.
This is done with marketing experiments that are testing customers’ response to the innovation by checking the conversion.
Example: you want to implement a change on your website, and have two possible modifications. The best way to determine which one works best is by showing the option A to 50% of users, and option B – to the other half. By measuring KPIs via, for instance, Google Analytics, you’ll get a tangible idea on which option works best.
Successful digital companies implement an experiment-based management strategy. Whenever a new feature is designed, the team conducts a series of tests to get tangible customer feedback. This approach has an established name: MNG – Change-based management.
MNG is based on 6 key stages
- Identification – the first step to finding a solution is to recognize the problem after analyzing customer data.
- Preparation – this is the stage of ideation and planning; the challenge is broken into manageable chunks, and each of them is solved individually to be later combined into the bigger picture.
- Design – after a team has a clear vision of the solution, it’s time for implementation; this is also where the technical team steps in.
- Execution – this stage shouldn’t be confused with design, because you should have not just a ready feature, but a piece of functionality or interface that’s ready for the market release.
- Sustainability – maintenance is a long-term investment, which is why it’s so important to evaluate its costs and risks early on, as well as devise a strategy for its execution.
- Monitoring – a market is constantly fluctuating, and your customer needs change quickly as well. Be ready to update the solution any time – you can get a clearer idea by analyzing marketing KPIs and direct customer feedback.
The strategy of continuous integration is the key to building a sustainable digitalization strategy. Remember, you are not looking for a quick fix, but a long-term improvement. This means planning should lie at the core of all innovations.
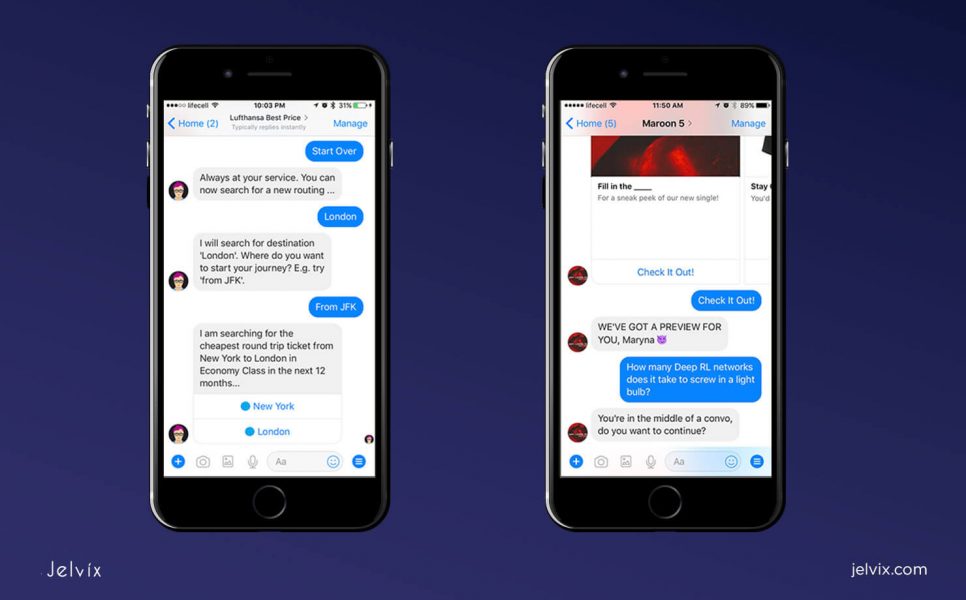
5. Chatbots (NLP chatbots, funnel chatbots)
Chatbots are the future means of consulting and customer interactions. Still, it’s worth to sum up why the technology has become so prominent in the modern tech market – let’s see what benefits it can offer.
- Fast reactivity: the use of chatbots reduces the response waiting time and shortens the amount of time, necessary to close the deal;
- Service quality standardization: chatbots don’t have the human error – they can’t be in a hurry or have a bad day. When there are people involved in consults, these things can break a deal.
- Fewer investments in hiring staff – chatbots reduce the amount of workload and make human “support” nearly obsolete;
- Mass service – a powerful chatbot can work with multiple customers all over the world simultaneously;
- A WOW-effect – so far, a customer doesn’t expect much from a chatbot, and using a personalized assistant speaks volumes about the company’s professionalism;
- New services – chatbots don’t have to be mere add-ons to your service’s functionality. In fact, they can lie at the core of entire business models.
Such versatility of chatbots is achieved by applying several architectures for different operations. Let’s take a look at the two most common chatbot types – funnel and NLP.
Funnel chatbots
These chatbots use clearly defined conversational patterns, based on sales funnels – the chatbots use shortcuts that would lead the customer to the positive outcome in the fastest way possible.
Advantages
- Easy to build – funnel chatbots use a simple dialog map with questions and answers;
- Messenger integration – such chatbots can be easily connected to Facebook Messenger, Viber, WhatsApp, Telegram, etc.;
- Payment processing – you can use custom modules that connect chatbots to banks’ APIs;
- Detailed analytics – funnel chatbot services provide their users with PDF-reports;
- Relatively low cost;
- This chatbot is an optimal solution for tech support – simply prepare answers to the most common questions.
Funnel chatbots work as a starting point of conversational marketing. They are cheap, fast to implement, and perfectly complete simple tasks.
Natural Language Processing Chatbots (NLP)
NLP chatbots provide more precise customization and rely more on the prepared template. Such assistants are prone to smart improvisation – a customer can come up with an unexpected question or an opening line, and the chatbot will puzzle out the meaning from individual words.
Advantages
- Adaptability – NLP chatbots work for all kinds of conversations, there are no strictly defined limits;
- Personalized offers – a chatbot can deliver a customized discount or digest based on a particular customer inquiry;
- Human-like communication – NLP chatbots don’t scare users away with the same answers, entirely unrelated to the question itself;
- WOW-effect – natural communication of a chatbot is still quite rated on the majority of websites and apps, so you have a chance to bring innovation to market;
- Long-term investment – since NLP hugely relies on AI and data science, it’s only natural that it will progress hand-by-hand with these innovations.
How to choose between the two?
Funnel chatbots are simpler and faster to implement, but their conversational ability is limited. Users sooner or later find themselves boxed into unoriginal answers – this surely doesn’t inspire loyalty. It’s a good first step towards conversational marketing, but it’s not the best long-term solution.
Natural language processing chatbots are much more universal – they rely on real-time phrase analysis and can come up with new answer options on the spot. They provide personalized and customized support and offers, which makes your marketing activities much more efficient. However, these chatbots are more expensive to design and customize, and it might be an excessive investment for simple purposes – e.g., technical support.
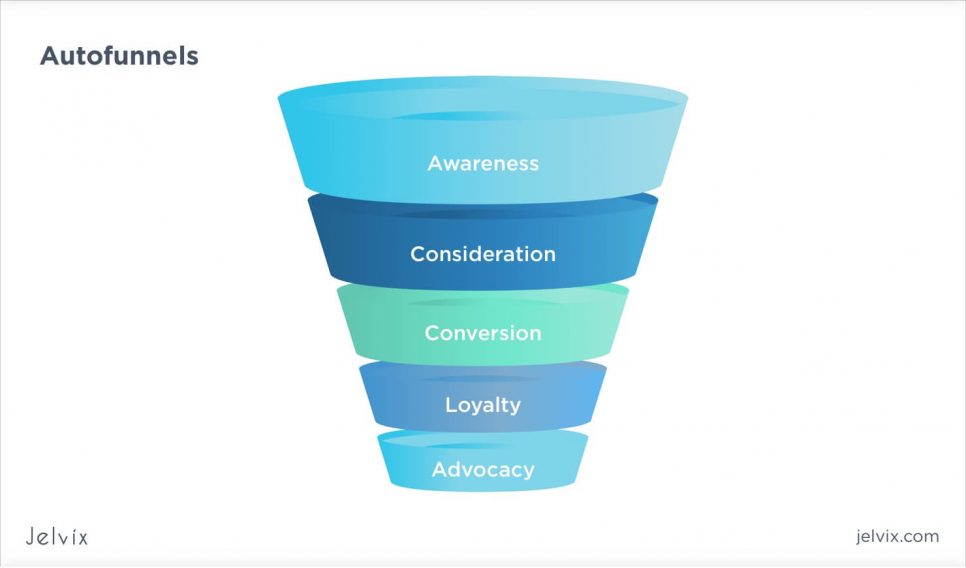
6. Autofunnels
Digital transformation is based on finding a new approach to attract and retain clients. This process gets exponentially easier if you have an auto-funnel – the path that a potential lead has to undergo to convert into the company’s customer.
The sales funnel has three key stages:
- Awareness. From a client that hasn’t heard about your company, the potential customer has to recognize your brand’s name.
- Consideration. When a customer evaluates a purchase, your company will be included in the list of potential options. This is where the rational component of purchase choice comes in – a client consciously compares the benefits of all brands and picks the ones that correspond to the most urgent needs.
- Conversion. The final stage where a lead is converted into a customer. The first step is making a decision – here, a person contacts you or leaves an order. The last stage is the deal finalization, up till the payment is complete.
For each stage, the company should adopt an appropriate communication channel. Ideally, the customer should have contact with you via different means.
The most common contact points include the following means:
- Targeted advertising for the awareness stage. Facebook, Google, Youtube ads familiarize potential clients with your brand and create particular associations about your brand. The quality of this first impression determines the success of the next communication methods.
- Prolonged contact. After a person has seen the mentions of your brand, your next task is to prolong the interaction by making sure a lead visits your website, social media page, etc. Be sure to include Calls To Action in all your communication.
- Follow-ups. Motivate your client to sign up or a newsletter or subscribe to social media. Make sure all this information is publically available on your website.
- Personalized contact. Here, the social media pages and blog comes in. Make sure that you pick a relatable tone of communication – the client should be open to contact you in case any questions arise.
- Starting a conversation. By this point, a lead should leave an inquiry on the website, contact you via social media, or write the comment at your blog page. At this point, your goal is to promptly respond and talk through the client’s concerns.
- Closing the deal. Here, you make a clear commercial offer. It can be personalized – your message via an email, typically in B2B, or automatically generated an offer with discounts – works in online B2C storage.
We encourage you to develop different automated funnels for various segments of the audience and use automated solutions like chatbots or CRMs to keep track of follow-ups and personal communication.
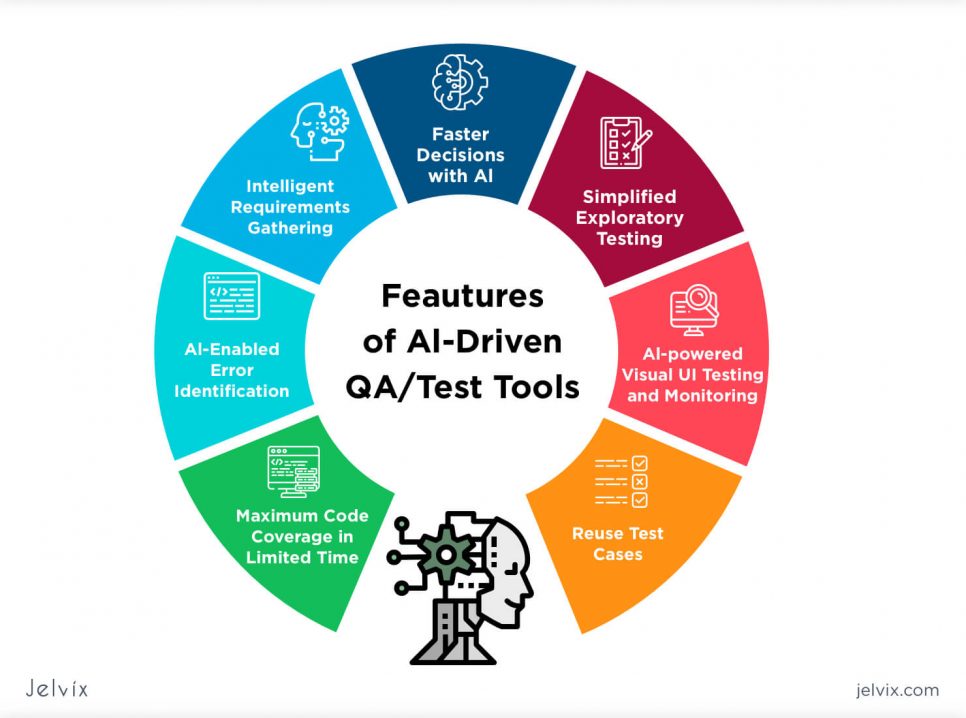
7. AI quality assurance
We already discussed the importance of implementing a test-based strategy for every planned innovation. The best part is, you don’t have to run these check-ups manually. Artificial Intelligence Quality Assurance, with the series of automated tests, helps you to outsource dull and repetitive work, leaving you in charge of devising strategies and overviewing results.
The benefits of automated testing
- Automated structure of the application – AI checks written code and unites it into a single architecture;
- Issue identification – automated testing looks for technical issues and reports them in interactive files;
- Critical user paths – Artificial Intelligence determines which parts of the functionality are the most essential to the ends’ users and further app maintenance;
- Data-based automated tests – AI uses all the information for designing scripts for the test implementation.
A similar approach can be implemented for team quality checks.
- AI records and analyzes video and audio data, recorded from employees’ screens, and determines the quality of customer support.
- AI creates a united database with quality reports that a manager can look up anytime.
- AI defines possible problems and checks all received data on these “pain points.”
Automated quality assurance provides a manger with tangible data, doing the planning, and investing more transparent.
8. Personalization: CRM, scripts, flex price
To keep track of multiple communication methods and audience segments, you need to store and manage this data in a dedicated file manager. The simplest solution is using a Customer Relationship Management software.
Possibilities of CRM
- Create an interactive database for all client contacts and leads – this is a place where you’ll be monitoring all contact points and personal info;
- Make personalized offers – the CRM can distribute discounts based on customer activity, and personal information – birthdays, holidays, etc.;
- Personalized follow-ups – the CRM automatically generates follow-up letters and sends them by a defined schedule;
- Measure conversion – you can integrate CRM into your analytics and see what communication interacts led to the purchase;
- Record and predict sales – CRM keeps track of successful deals and collected profits, providing you with regular reports and data-based forecasts.
Best CRMs: Zoho, Salesforce, Insightly, Pipedrive, Freshsales.
The majority of CRMs also support additional plugins, which means you can tweak the built-in functionality according to your business industry at the first stage of development. You can download add-ons for financial healthcare, retail, agriculture, technology, and other industries.
II. Personnel
Transforming your interactions with a customer is a big step forward, but it’s not the only solid foundation for digital transformation. The next step is transforming team dynamics, and management approaches.
1. New digital corporate culture
A new digital strategy should be powered by a fresh outlook on work efficiency. You need to introduce technology to your inner operations, in the way you distribute tasks, measure productivity, communicate, and exchange information.
Build a result-driven team
To be efficient, you have to refocus from basic 9 to 5 mentality, and put the emphasis on the result itself. Task control should be focused on quality evaluation and the measurement for the number of resources spent.
Agile management methodologies – Agile, SCRUM, Lean Production, Lean Startup – are based on constant work evaluation and priority reevaluating. The workday starts with regular standup meetings where team members report on their progress and outline tasks for the day.
2. New project management approach
The efficiency of the work is defined by the result – each employee knows how the work contributes to conversion, internal operation, and customer satisfaction. By adding CRMs to the mix, you can check directly how your employees’ actions contributed to new sales.
Agile software
This software provides you with quantifiable data on how much your employees work and what they manage to achieve.
New digital business models
If you want to create a new service or start a company, it’s cheaper, in the long run, to consider implementing digitally-based business models at the very beginning. Tech-based products attract new clients and investors, and you save yourself the hassle of implementing the innovation later on.
Technology changed the way we think about business and customer benefits. Now, your clients seek for different advantages, and they want to see fresh ways of receiving those.
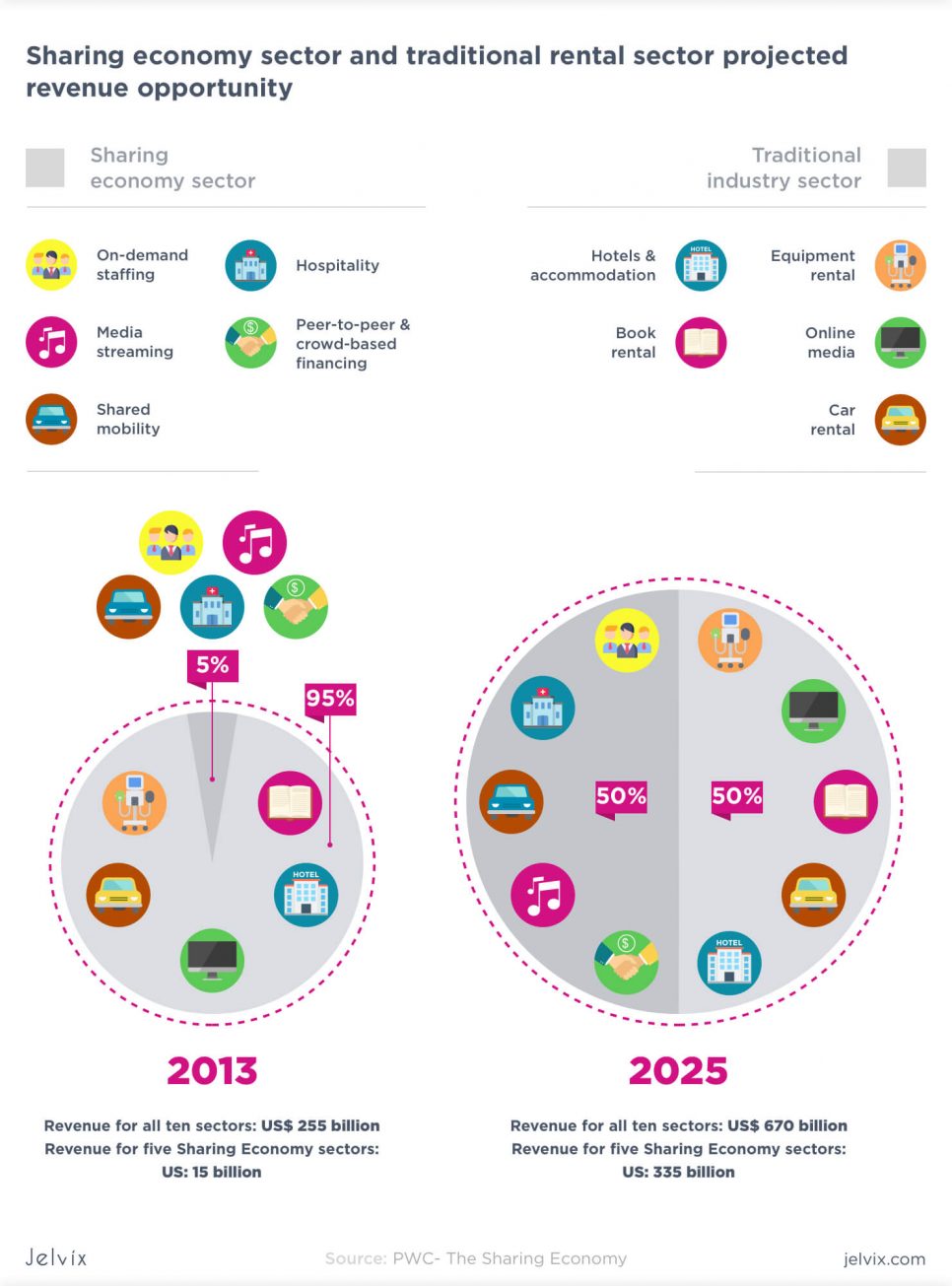
Sharing economy
The basic idea is, you don’t have to own a product in order to serve it to clients. Examples of Uber and Lyft – transportation companies don’t own any cars – serves as an example to all business owners out there.
Examples of successfully shared models
- BookMooch – a startup that allows people to loan and rent books;
- Olio and Foodsharing – companies that encourage sharing of leftover food for nutrition, animal feed, and composting;
- Kiva – lending to people in developing countries and a way of doing charity;
- Fon is a startup that encourages opening WiFi networks, rewarding users with unlimited access to millions of networks all over the world;
- BlaBlaCar – joined carpools to save money for transportation and optimize car expenses.
The sharing economy can be successfully adapted in almost any field, but especially retail, accommodation, delivery, and online media.
Outsource, Pay-Per-Use, SaaS
You can implement a new way of providing services and getting paid for them. The digital transformation gave rise to three main approaches to distributing services.
- Outsourcing – companies can use remote services instead of hiring a remote team for software development, customer support, testing, design. You can fall on either end of the spectrum – outsource time-consuming work, or be the provider of such services.
- Pay-Per-Use – the service provides the user with the free access to browsing features – a customer can explore the demo-version of the product. However, to actually use the product or service, a user has to pay for a single purchase.
- Subscription as a Service – instead of receiving a single payment per customer, you can charge the user on a monthly or weekly basis. Examples of SaaS approach are Adobe with its creative cloud, Netflix, Audible, Youtube Premium, and other subscription-based services.
Each of these business models has a quickly developing market, but you need to move fast if you want to outgrow the competition. These business models have been on the market for more than 10 years, and you have to deal with already established competition.
Innovations for digital transformation
Business models can base on a particular modern technology, using it as a competitive advantage to attract customers and investments. We’ve seen the rise of AI-based financial startup, blockchain platforms, and IoT smart wear, implemented by companies that started their development with a clear innovation in mind.
1. Blockchain
The textbook definition of technology is that it’s a decentralized digital ledger, used for multi-device transactions. Each participant creates their own database on their server – the information isn’t saved to single third-party storage.
Blockchain is successfully used in multiple industries
- Fintech: blockchain has plenty of untapped potential for conducting commission-free international transfers, building crypto coins, storing financial records, etc.;
- Education: Sony Global Education recently launched a blockchain platform for verification procedures in schools and universities;
- Real estate – blockchain renting marketplace with verified data on each object, secured from hacker attacks;
- Healthcare: the industry, more than any other, depends on safe data storage and exchange – blockchain can power a united medical database and allows doctors in different hospitals safely exchange records, and patines will be able to access their profiles anytime.
Blockchain offers a safer data exchange method because hackers don’t have a single potentially vulnerable point to target – to compromise the network, they need to get access to the majority of connected devices.
2. Drones
In 2025, the drone market is predicted to reach $63.6 billion, with multiple industries adopting the innovations. Let’s take a look at what fields can benefit the most from investing in the unmanned aerial vehicle market.
- Agriculture – drones can easily fly hundred-hectare files, forming accurate imagery of the territory. With smart software, drowns can automatically send these images to the company’s storage.
- Insurance – drones provide a reliable way of evaluating occurred damage and provide the stakeholders with detailed updates on the incident;
- Construction and architecture- the management and keep track of their multiple objects simultaneously. Also, investors and clients can stay updated on the progress of their construction.
- Logistics – drones respond to the challenges of warehouse management by promptly delivering stocks and providing last-mile delivery.
The application of drones is not limited to these vectors only – they can be successfully adapted to any kind of industry, where monitoring is a priority.
3. Voice assistants
Siri and Alexa already provided a glimpse of how a smart voice assistant can deliver a new experience of receiving information and ordering products and services. Let’s take a look at how you can integrate existing voice assistants into your business model.
- Traveling and Tourism: Expedia, a booking service, released an Alexa extension that provides users with hotel reservation updates, flight data, rental services;
- Ecommerce – companies can develop their customer care plugins for Alexa – these plugins are typically able to check order status, contact the user to the website, provide data on returns, and so on;
- Hospitality: a brand new service “Alexa for Hospitality” allows guests to manage their booking information, checkout time, request additional services, and connect to the staff.
These are just basic examples of how voice assistants can bring you closer to the client, integrating your business in the customer’s daily life. In reality, the application of Alexa and Siri is not limited to these industries – you can easily find a pre-made solution for your industry, or create a custom extension.
4. Internet of Things
Smart connected devices allow businesses to connect different devices to the same application or web page. You can send requests directly between devices, without having to perform manual work. This seamless integration allows connecting physical things to devices, as well you can create smart clothes, cosmetics, shoes, and others.
Here is the list of industries that are already massively disrupted by the Internet of Things.
- Transportation – smart cars can communicate with each other, preventing accidents and sending requests concerning road safety;
- Manufacturing – an IoT unit can be attached to the manufactured item to keep track of its location, stage of development, and logistics;
- Agriculture – smart equipment can check air, soil, and water, control pumps and monitor employees efficiency; all picking tech can be connected as well;
- Healthcare – it’s possible to connect MRI machines, cardiac monitors, and ventilators to online databases and seamlessly update patients’ status.
IoT can be used to enhance any online solution and connect it to a physical offline device. This makes the application possibilities practically limitless in any industry.
5. 3D printing
This is the manufacturing method of the future, and it’s no wonder that companies of various industries decide to jump on board.
- Education – teachers can offer their students realistic 3D models, applicable in physics, engineering, biology, chemistry, and other scientific fields;
- Healthcare – there are already companies that explore possibilities of printing out realistic organs, bringing education and demonstrative benefits to physicians and their patients;
- Military – 3D printed models allow armies to successfully train in prototypes vehicles, buildings, and objects, and it also has groundbreaking defensive applications that could be used to protect civilians;
- Fashion – it might not be long till we see printed clothes on mass markets; it’s a cost-efficient way of production that minimizes expenses on human resources.
3D printing can be applied anywhere – from groundbreaking innovation to everyday needs. The best thing is, its potential is still hugely untapped, which means you can become a leading innovator in your market.
6. AR / VR
Augmented and virtual reality is already getting at its peak point – it’s not some far-reaching innovation; in fact, it’s already widely explored in entertainment and manufacturing. That’s not to say, however, that the market couldn’t use more innovation – there are still multiple unexplored areas. To understand what are the possible application of the innovation, let’s take a look at existing concepts applied in key industries.
- Automobile: BMW and Jaguar Land Rover use virtual reality to test our the visual design of their new car models and perform basic functionality tests;
- Healthcare: although there is an ongoing debate in the medical community about the benefits of AR and VR to the human brain, some hospitals are already implementing VR for pain relief during painful patient recoveries;
- Retail: eBay has recently launched the VR department store where customers can try on clothes and test our goods. And it’s not just fashion getting a makeover. Last year, eBay launched “the world’s first virtual reality department store” in partnership with Australian retailer Myer. Is this the future of shopping?
- Tourism: tourists can try out holiday destinations, accommodations, and attractions before buying a ticket.
VR allows end-users to try out the service or product before making a final decision. On top of that it can be used as a service on its own for entertainment or educational purposes.
7. Ecosystem approach to technology
To build a long-term digital business, companies need to think beyond one product and regard long-term implementations instead. Let’s take Slack as an example.
The app was launched in 2013, but the team didn’t stop being the fastest growing tool of the year. Instead, they launched an entire platform where developers and project managers can create and manage products. They analyzed their target audience, and after seeing that the majority of their users work in IT, created a dedicated platform that would fill those needs.
To create long-term solutions, business owners should consider the following aspects:
- Integrating add-ons and plug-ins – you need to enable users to adapt the functionality to their needs;
- Creating cross-platform solutions – you want to be able to connect your tool to other services ;
- Creating additional tools – you can make extensions yourself and selling them as an additional product to your main offer.
8. Narrow niches
Creating a one-and-for-all solution hasn’t been an efficient approach for a while. In the future, with extensive personalization trends, it doesn’t look like things will change much. If anything, niches will become more narrow, and companies need to define their target segments more precisely than ever.
You can determine your niche by completing the following steps
- Overview your segmentation – devise what kind of separate products and specialized offers you can offer to each small segment;
- Come up with a personalized set of benefits;
- Make sure that the end design reflects the differences of your target audience;
- Break your support team into smaller subunits that will handle particular requests for a specific niche.
Don’t aim to create multiple niche products simultaneously – instead choose and implement narrow solutions one by one.
Data analytics
Data analytics allow companies to prevent mistakes and avoid financial damage. It’s the core of your plans and strategies.
The main functions of data analytics
- Data foundation – the information is implemented into tech solutions and is actively used for inner operations – logistics, warehouse management, marketing etc.;
- Reporting – data-driven insights are compiled into reports and used for communication and strategizing;
- Performance management – companies collect data on the team’s efficiency and compare initial KPIs with delivered results;
- Predictive – analytics identifies problematic errors;
- Prescriptive – after a potential problem is detected, the system comes up with data-based solutions; usually, such systems also include ML algorithms that provide a smart insight into the collected information.
Accounting and financial management system
Automated accounting and finance management tools provide businesses with prompt updates of their budget, income, expenses, and profits. The core functionality of the software relies on budget execution, reporting, monetary client profiles, and tax documentation.
It’s a must-do investment for any scaling company. When the number of revenue streams grows along with regular investments, you need to keep track of the sustainability of all implemented solutions. Also, you need to see the monetary results of the transformation.
Systems: ERP, DocFlow, Digital
ERP is a centralized platform that integrates all major company operations, from HR to logistics or procurement. It combines the features of CRM, financial manager, and analytical tool. It’s an all-in-one platform where you get access to multiple built-in tools. However, the downside of using an EPR is that such a system is too complicated – it takes time for staff to get used to the extensive functionality – and expensive.
For documentation management, it’s best to use dedicated software – it will provide richer customization options and cost less than a complex solution. The leading methodology for document management is a Doc Flow – a system of digital activities that automate document creation, editing, management, and storage.
Extract Transform Load
The software can’t substitute the united data management framework – remember, digital transformation relies both on frameworks and technological implementations. For successful innovations, you need both.
The most common framework of data management is known as Exact-Transform-Load or ETL. The framework works in three stages.
- Extract – the data is taken out from the database. It’s collected from different channels and prepared for processing.
- Transform – extracted data is processed; usually, this means changes in files’ size or formats. This step makes data compatible with other databases or algorithms.
- Load – extracted and transformed data is loaded into the end database.
Reasons to use ETL
- The system allows reading data from different types of databases and transferring thousands of objects simultaneously;
- You can connect various libraries and their metadata storages;
- The maintenance is much cheaper since you can always freely send data from one storage to another, depending on the operation.
- ETL works best for complex data manipulation – if you have multiple datasets, you need to bring them to the single denominator – and ETL is great for such purposes.
Business Intelligence and descriptive analytics
Descriptive analytics strives to provide detailed reports with multiple contexts for a single number. For instance, if you want to generate a sales report, descriptive analytics software will not simply calculate the portion, but also analyze these numbers in relation to last month, quarter, and year. You will also see how much time and money was spent to achieve such results.
You can use ready-to-go solutions, like Sisence or Alteryx, or build a custom descriptive API. In fact, the second option usually works better, even though it’s more expensive. In the long- run, you want to have a well-tailored analytics software created with your business specs in line. Analytics is a very specific field – the methodologies and algorithms vary from company to company – the differences between different fields are even more drastic.
Artificial Intelligence for analytics
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning algorithms are a perfect fit for personalized analytics. Business owners and managers can rely on these smart insights if they are not sure about the company’s vector of development, or use these insights to define next moves. Let’s take a look at some examples of AI applications in business intelligence.
- HubSpot uses AI for content management to identify the interests of potential clients and defines potentially interesting topics based on their blog’s analytics;
- Pinterest applies machine learning in their content delivery, advertising settings, spam moderation, and content analysis;
- TrademarkVision uses AI analytics to get insights on logos that are similar to registered trademarks.
How to use AI for analytics?
- AI behavioral analysis – Artificial Intelligence can track users’ actions on the website and provide insights;
- Performance management – AI does a great job at determining the productivity of team members; it can also offer personalized advice about improving an employee’s results;
- Recommendation systems – business managers can’t possibly be experts in all fields of their company management; you can’t know software development, logistics, manufacturing details, ad retail specifics on the equally high level. AI can shorten this gap and provide business owners with advice on their “weak” points.
However, it’s worth taking into account that even if AI-based analytics are impartial, people who implement them, might not be. Hence, you need to be aware of your own decisions and make sure they don’t contradict with data-based insights. It takes time and training to find a fine line between relying on technology and pursuing your own initiative – although modern systems indeed make planning much easier.
Conclusion
Digital transformation is a continuous journey based on constant ideation and testing. A company can’t stop after implementing one innovation. New technology projects should be in progress all the time. Otherwise, it will be difficult for the business to achieve a long-term effect.
There are multiple routes that a company can take to transform digitally. The best way to decide the starting point of your strategy is by analyzing your market and customers. Seek solutions to urgent issues and optimize your workflow with technology – that should be your priority. Jelvix is a digital transformation company that navigates you through the complexities inherent in digital transformation initiatives.
Need a qualified team?
Access the talent pool, start digital transformation now.