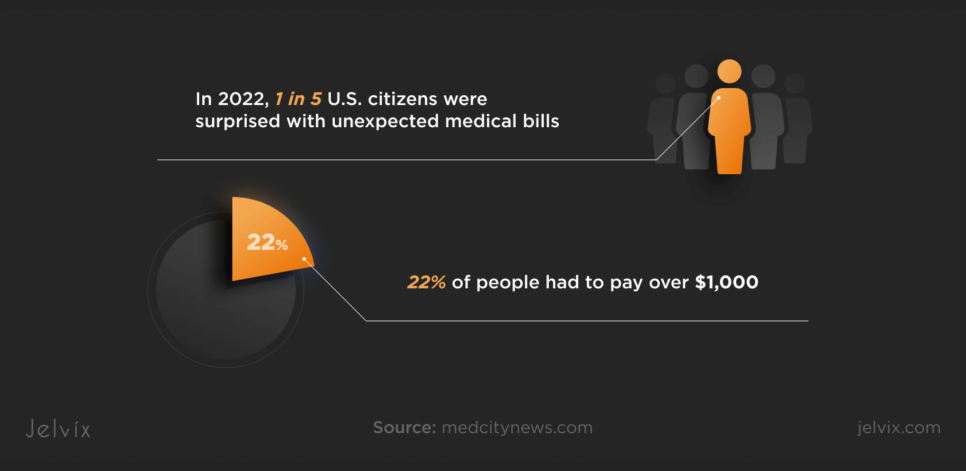
Errors in medical billing keep bothering healthcare providers and patients. In 2022, 1 in 5 U.S. citizens were surprised with unexpected medical bills, where 22% of people had to pay over $1,000.
This means that clinics still have no perfect solution for medical billing. As a result, patients are under threat of losing money, while clinics risk damaging their reputations.
If you want to optimize billing processes at your clinic with the help of digital tools, this article is for you. You’ll find out key differences between in-house and cloud-based billing, compare medical billing software, and learn to choose the best solutions for your clinical needs.
Short Overview of Patient Billing Systems
Patient billing systems are tailored software tools crafted to handle the financial operations within healthcare services. These platforms automate billing processes, ensuring that healthcare providers accurately invoice for services and efficiently manage the payment collection from patients and insurance companies.
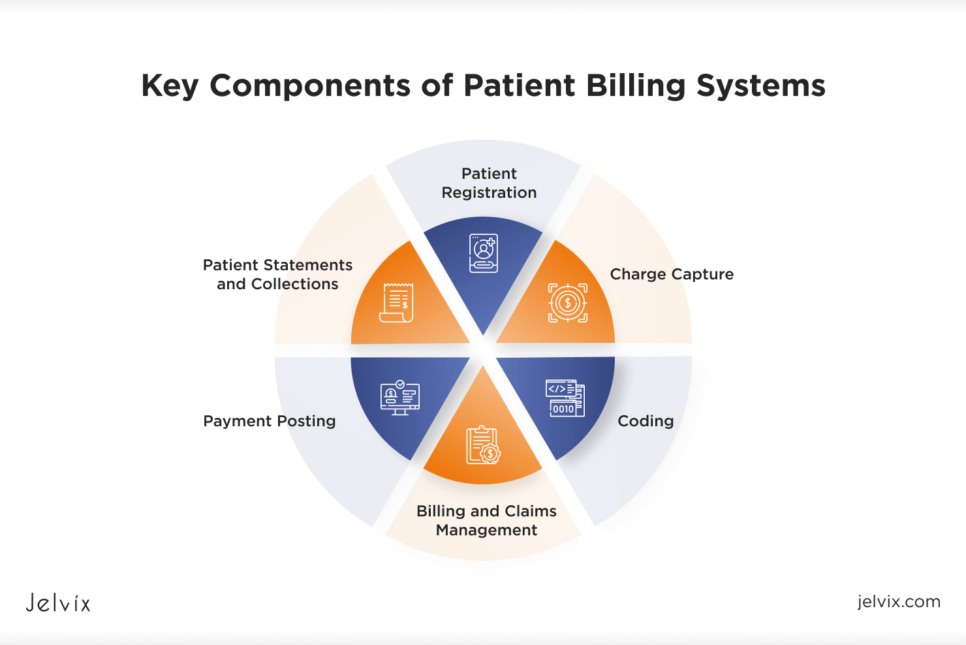
Key Components of Patient Billing Systems
Billing systems are pretty complex, as not only do they need to perform their intended functions well, but they also should support FHIR interoperability with other systems. They usually include several important components.
Patient Registration
This module collects and stores all relevant patient information, such as personal details, insurance coverage, and medical history.
Charge Capture
It records all the services and procedures provided to the patient, from consultations to surgeries and lab tests.
Coding
This component assigns standardized codes (like ICD, CPT, and HCPCS) to the recorded services, ensuring compliance with medical and insurance regulations.
Billing and Claims Management
This module generates and submits insurance claims, tracks their status, and handles denials to ensure payment is received.
Payment Posting
It logs payments received from patients and insurance companies, updating patient accounts accordingly.
Patient Statements and Collections
It prepares and sends out bills and statements to patients and manages the collection of payments, including follow-up on overdue accounts.
In-House Medical Billing: Overview, Pros, and Cons
In-house medical billing involves handling the entire billing process within the healthcare facility. This means using the clinic’s staff and resources to manage tasks like coding, submitting insurance claims, and following up on unpaid bills.
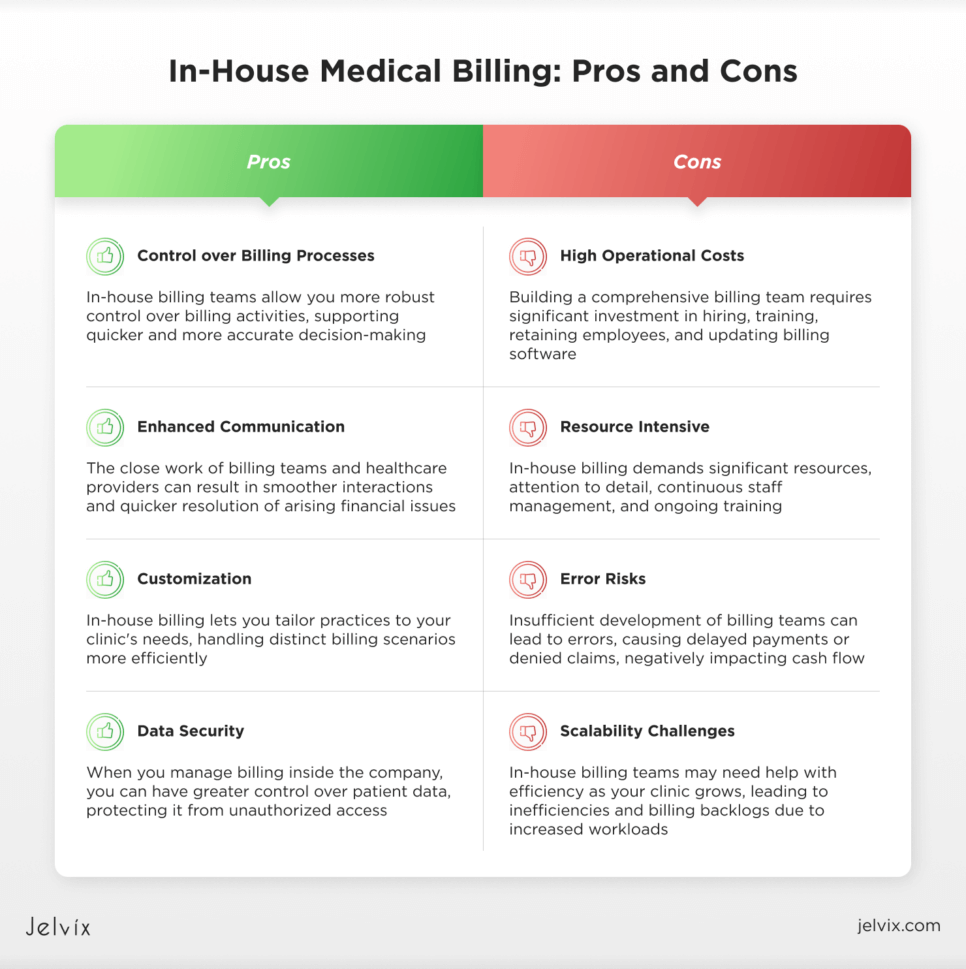
Pros of In-House Medical Billing
In-house medical billing can benefit larger healthcare practices that have the resources to manage their billing processes internally.
Control Over Billing Processes
In-house billing teams allow you to have stronger control over billing activities, supporting quicker and more accurate decision-making.
Enhanced Communication
The close work of billing teams and healthcare providers can result in smoother interactions and quicker resolution of arising financial issues.
Customization
In-house billing allows you to adjust billing practices to the unique needs of your clinic. This way you can handle distinct billing scenarios more efficiently.
Data Security
When you manage billing inside the company, you can have greater control over patient data, protecting it from unauthorized access.
Cons of In-House Medical Billing
Although in-house medical billing can be beneficial in some cases, it also brings disadvantages that hospitals need to consider.
High Operational Costs
To have a comprehensive billing team at your service, you need to invest a lot in hiring, training, and retaining dedicated employees. On top of that, you need to purchase and update billing software.
Resource Intensive
In-house billing requires substantial resources, attention to detail, and continuous staff management. You should also invest in training to keep the team up-to-date on current coding and billing regulations.
Error Risks
If you don’t put enough effort into developing your billing teams, they will make more errors. This will lead to delayed payments or denied claims, which can negatively impact your clinic’s cash flow.
Scalability Challenges
In-house billing teams may lose efficiency as your clinic expands. Increased workloads can become tough to handle, resulting in inefficiencies and billing backlogs.
Popular Examples of In-House Billing Systems
If you need software for in-house billing, consider looking through popular choices by seasoned healthcare SaaS companies.
Kareo Billing
Kareo is a go-to solution for small to medium-sized practices. This software offers features like claim tracking, patient statements, and financial reporting to optimize your billing processes. You can integrate it with your EHR system and create a unified platform for patient care and billing operations.
AdvancedMD
AdvancedMD offers a set of useful features, such as billing analytics, claims management, and denial management. This system integrates well with EHRs and practice management software, ensuring seamless data flow across different departments. AdvancedMD will suit most larger medical facilities.
NextGen Office
The NexGen Office system is tailored for various specialties, providing automated claims processing, real-time eligibility verification, and robust reporting tools. Its integration with practice management and EHR systems eases efficient data management and operations.
Cloud-Based Patient Billing: Pros and Cons of Medical Billing Outsourcing
A cloud-based patient billing system harnesses the power of internet-hosted software to oversee the financial side of healthcare. This system automates billing tasks, stores data securely in the cloud, and provides access from anywhere with internet connectivity.
Explore the key challenges and practical solutions for healthcare data migration to ensure a seamless transition while maintaining data integrity and compliance.
In other words, clinics can outsource medical billing services to cloud systems to optimize their operational efficiency and accuracy.
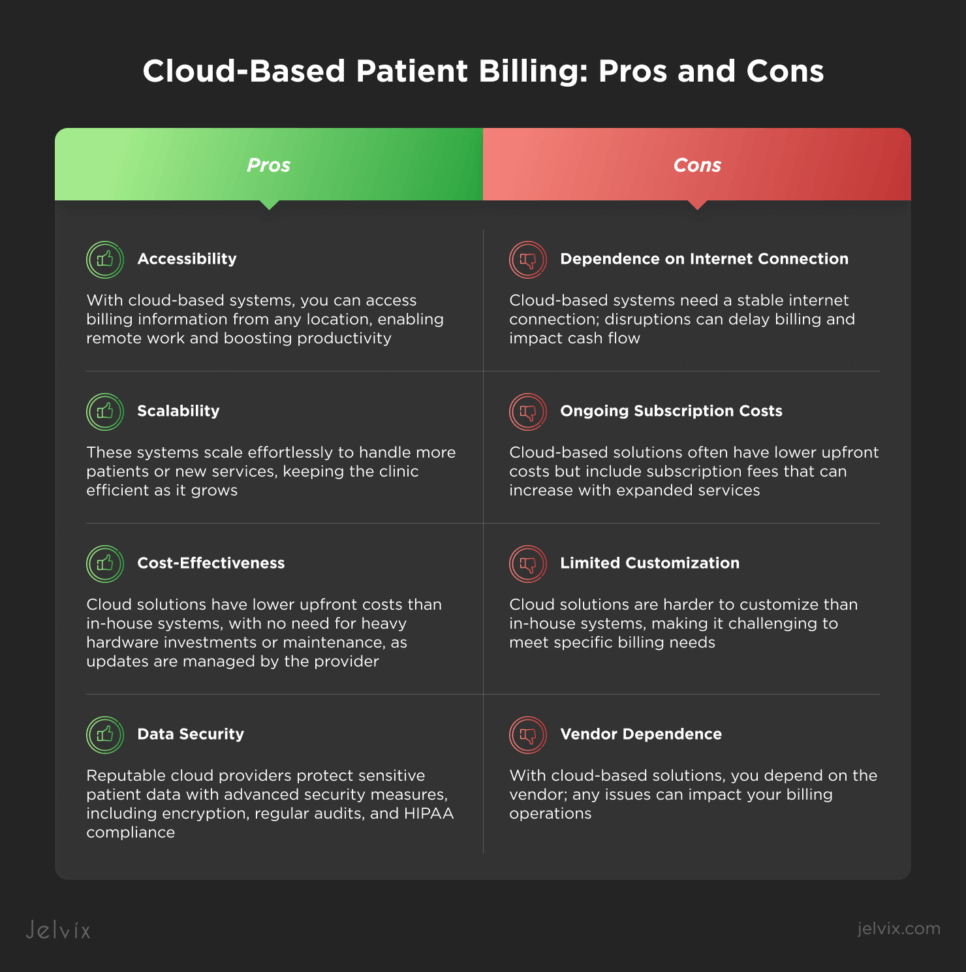
Pros of Cloud-Based Billing
Cloud-based billing systems are advantageous for smaller entities or those looking for scalability, as they offer flexibility, reduced upfront costs, and ease of access without the need for extensive IT infrastructure.
Accessibility
With cloud-based systems, you can access billing information from any location, enabling remote work and boosting productivity.
Scalability
These systems are designed to scale effortlessly, accommodating increases in patient numbers or the addition of new services, ensuring the system remains efficient as the clinic grows.
Cost-Effectiveness
Cloud solutions generally have lower upfront costs compared to in-house systems. There’s no need for hefty hardware investments or maintenance as updates are handled by the service provider.
Data Security
Reputable cloud providers employ advanced security measures to safeguard sensitive patient data. These include encryption, regular security audits, and adherence to healthcare regulations like HIPAA.
Cons of Cloud-Based Billing
Note, however, that cloud-based medical billing isn’t perfect and imposes a few drawbacks.
Dependence on Internet Connection
Cloud-based systems require a stable internet connection to work well. Any disruptions can limit access to the billing system, delaying billing processes and impacting cash flow.
Ongoing Subscription Costs
Although cloud-based solutions usually impose lower upfront costs, they also involve subscription fees that vary depending on the services you need. These costs can grow, especially if your facility expands its services over time.
Limited Customization
Unlike in-house systems, cloud solutions are more difficult to customize. If you have specific billing needs, it can be challenging to adjust the system to meet your requirements.
Vendor Dependence
When you purchase a cloud-based solution, you immediately become dependent on its vendor. If any issues arise, they can negatively impact your billing operations.
Cloud-Based vs In-House Billing: Medical Billing Software Comparison
If you struggle to choose between cloud-based and in-house billing systems, start by evaluating aspects like cost, scalability, and security. Understanding how these factors are different for both systems can help make the correct choice.
Cost Analysis
Cloud-based billing systems can offer lower initial costs, generally thanks to no need for hardware purchases. The ongoing expenses usually include subscription fees, and the total cost of ownership is often cheaper as there’s no maintenance or upgrade needed.
In-house billing systems usually involve high initial costs due to hardware purchases. The ongoing expenses include maintenance, upgrades, and potential IT staffing. The total cost of ownership can be higher due to continuous upgrades and support needs.
Implementation and Setup
Cloud-based systems offer quicker setup times because the vendor manages the infrastructure. These systems are designed for ease of use, with vendors usually providing training and support resources.
On the flip side, in-house systems demand more time and expertise for setup, involving complex hardware and software installations. This complexity requires a dedicated team for implementation and ongoing management, making the setup process time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud-based systems offer scalability, easily adapting to fluctuations in patient numbers or service demands. They offer the flexibility to access the system from various locations and devices.
In contrast, in-house systems are limited by their physical infrastructure, making scalability a tougher challenge. Their flexibility is also restricted, as they generally require access within the facility’s network, limiting remote accessibility.
Security and Compliance
Cloud-based systems are built with high-security standards, including data encryption and regular updates. They usually comply with strict regulations like HIPAA and GDPR, ensuring data protection and privacy. However, security and compliance depend heavily on the provider’s reliability.
In-house systems, on the other hand, offer direct control over security measures, which can be customized to specific needs. This requires dedicated staff to manage and maintain security protocols, ensuring compliance with relevant regulations.
Maintenance and Support
Cloud-based systems come with the benefit of vendor-provided maintenance and support, including regular updates, patches, and technical assistance. This reduces the burden on internal staff and keeps the system up-to-date.
Conversely, in-house systems place the responsibility of maintenance and support on the organization. This requires a seasoned team to handle updates, troubleshoot issues, and ensure smooth system operation, increasing the costs associated with maintaining the system.
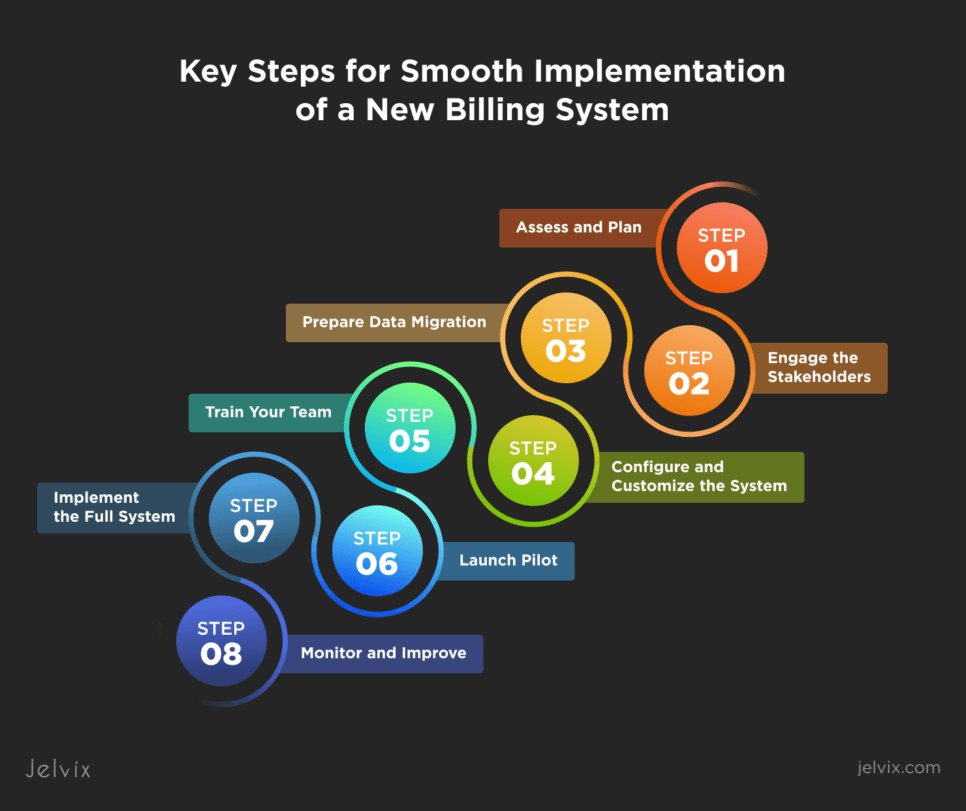
Transitioning to a New Billing System: Key Steps for Smooth Implementation
Transitioning to a new billing system in healthcare involves several critical steps, each aimed at ensuring a smooth and successful changeover.
1. Assess and Plan
Begin by carefully assessing your current billing processes, identifying pain points, and defining the goals for the new system. Develop a detailed project plan outlining timelines, resources, and key milestones.
2. Engage Stakeholders
Engage all relevant stakeholders, including billing staff, IT personnel, and healthcare workers, from the outset. Their input is invaluable in selecting the right system and ensuring it meets all operational requirements.
3. Prepare Data Migration
Prepare for healthcare data migration by conducting a comprehensive audit of existing billing data. Clean and organize the data to eliminate any inaccuracies or redundancies. This way, you’ll ensure that the transition does not disrupt ongoing billing operations and that all historical data is preserved accurately.
4. Configure and Customize the System
Once the new billing system is selected, configure it to align with your practice’s specific workflows and requirements. Customize features and settings to optimize the system for your operations. This phase may involve integrating the billing system with existing systems, such as EHR and practice management software.
5. Train Your Team
Provide comprehensive training for all users of the new billing system. This training should cover all aspects of the system, from basic functionalities to advanced features. Ensure that staff members are comfortable with the new system before it goes live to minimize disruptions and errors.
6. Launch Pilot
Conduct a pilot test of the new billing system with a small segment of your operations. This will allow you to identify and address any issues before full implementation. Gather feedback from users during this phase to make necessary adjustments and improvements.
7. Implement the Full System
Roll out the new billing system across the entire entity once the pilot test is successful. Ensure that the system is fully operational and that all users are effectively using its features.
8. Monitor and Improve
Continuously monitor your new system’s performance and gather feedback from users. Regularly update and maintain it to address any emerging issues. Also, conduct regular reviews to identify areas for further optimization and enhancement.
Learn how predictive analytics and RPM are transforming healthcare, enhancing patient care through advanced technology.
How Jelvix Helps Develop Cloud Management Software for Medical Billing Needs
Providing accurate patient billing is critical for modern clinics, especially now that more systems are involved in healthcare processes. At Jelvix, we specialize in developing tailored cloud management software to meet the specific needs of medical billing.
Our experts can help you evaluate your current billing needs and choose the software that suits your needs best. They can also help develop custom medical billing software that will easily integrate with your existing systems. Contact us if you need guidance. The Jelvix team is always happy to help.
Looking for a skilled team?
Expand your development capabilities with our dedicated professionals.