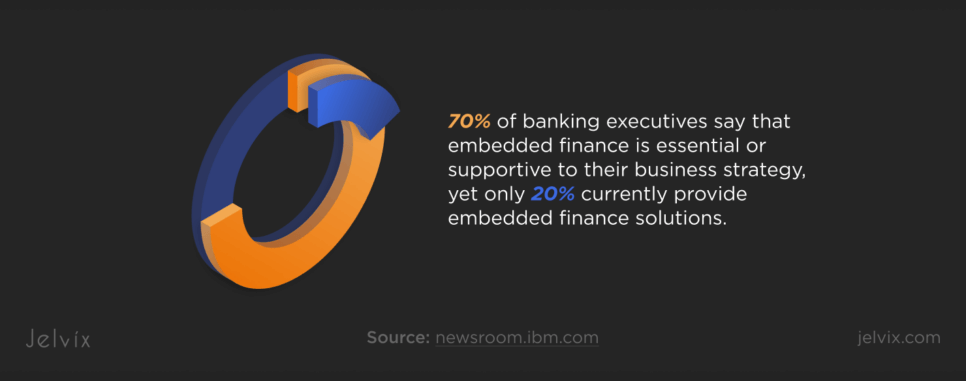
It may seem that the banking and finance sector is rapidly developing, following the latest tech advancements. About 70% of banking executives say their businesses are offering embedded finance solutions with modern capabilities. Yet, only 20% do this in reality.
One of the key reasons why financial companies fail to provide customers with advanced finance tech is their obsession with legacy systems. Although these are tested over time, their outdated frameworks slow down the innovation leaving banks outside the competitive edge.
If you aim to modernize your banking system to ensure speed and agility in core processes, this article is for you. You’ll find out why legacy banking systems aren’t a good fit for your business, what are the challenges of modernizing them, and what steps you can take to perform this process smoothly.
Banking Legacy Systems Explained
Old financial software that uses outdated frameworks and programming languages is known as legacy banking systems. Most legacy software has a monolithic architecture, which makes it hard to scale and integrate new features. However, these systems are still important for many banks because they can handle critical tasks, such as loan processing, credit services, account administration, and transaction processing.
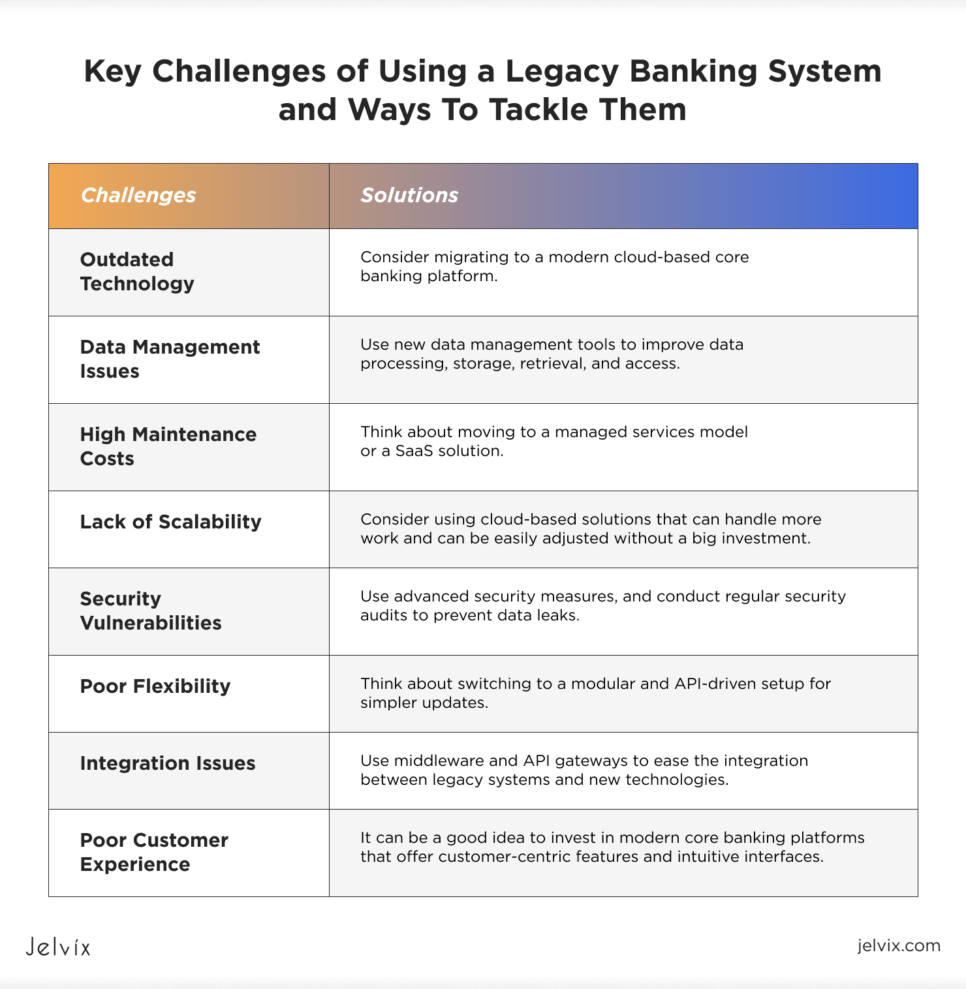
Key Challenges of Using a Legacy Banking System and Ways To Tackle Them
Dealing with old systems in the finance industry comes with a set of complexities that companies need to address. If not, they might not be able to offer clients the latest services and can end up losing them to competitors.
Outdated Technology
As you already know, legacy systems are built on old technologies that limit businesses from integrating new features and supporting growth. If you want to explore all the benefits of system integration with newer tech, consider migrating to a modern cloud-based core banking platform.
Data Management Issues
Old banking systems might struggle to handle lots of financial data well, which could mess up its accuracy and reliability. Use new data management tools to improve data processing, storage, retrieval, and access.
High Maintenance Costs
Legacy systems are typically expensive to maintain, as they require frequent updates and specialized staff. In fact, supporting this technology can cost banks over USD 57 bln in 2028. If you want to reduce maintenance costs, think about moving to a managed services model or a SaaS solution.
Lack of Scalability
Legacy systems can’t keep up when your customer base and workload grow. Consider using cloud-based solutions that can handle more work and can be easily adjusted without a big investment.
Security Vulnerabilities
Older systems are more at risk for cyberattacks and data breaches. To keep your data safe, use advanced security measures, such as encryption protocols, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access controls, and conduct regular security audits to prevent data leaks.
Poor Flexibility
Legacy banking systems are pretty inflexible and tough to change, making it hard to keep up with new rules, changing market demands, or growing customer needs. Think about switching to a modular and API-driven setup for simpler updates.
Integration Issues
Integrating legacy systems with new technologies can be complex, time-consuming, and costly. Use middleware and API gateways to ease the integration between legacy systems and new technologies.
Poor Custome
Legacy systems don’t possess the capabilities to provide a modern user experience, leading to customer dissatisfaction. It can be a good idea to invest in modern core banking platforms that offer customer-centric features and intuitive interfaces.
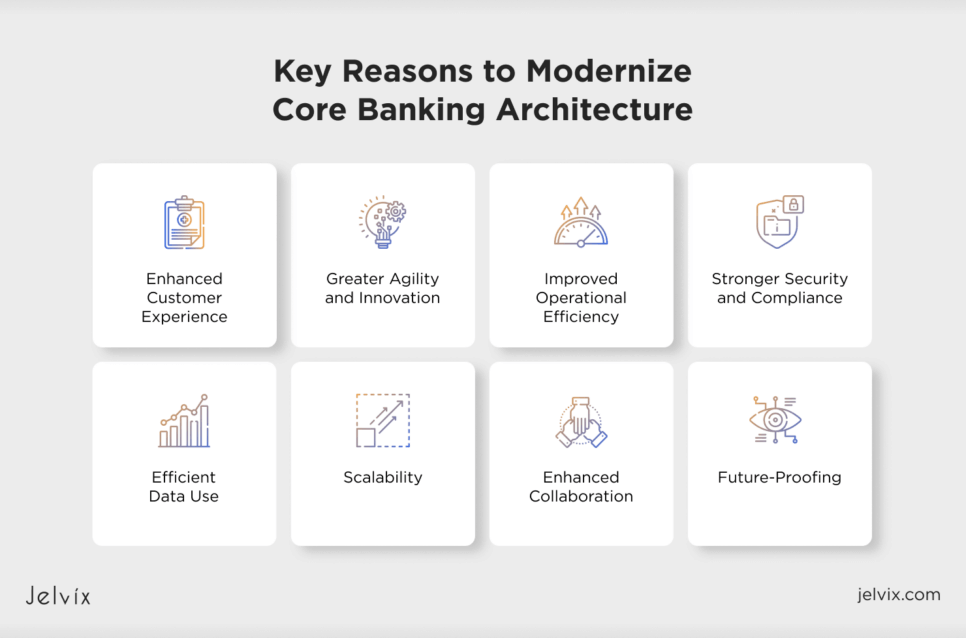
Why Modernize Core Banking Architecture: Key Reasons
Banks failing to personalize customer experiences face increased costs and reduced business agility. Modernizing legacy systems can enhance personalization efforts and provide various additional benefits.
Enhanced Customer Experience
Modern core banking systems offer advanced features that improve the customer experience. With seamless online and mobile banking services, personalized financial products, and faster transaction processing, banks can finally meet customer expectations, leading to higher satisfaction and loyalty.
Greater Agility and Innovation
Modern core banking platforms offer modular and flexible architecture, allowing financial companies to develop and deploy new products and services. This agility enables them to pursue new market opportunities, offer better services to clients, and stay ahead of competitors.
Improved Operational Efficiency
Banking application modernization reduces operational inefficiencies related to outdated tech. Modernization improves productivity by automating processes, optimizing workflows, and facilitating data management. As a result, banks can reallocate their resources more efficiently and enhance their competitiveness.
Stronger Security and Compliance
Modern banking systems are equipped with advanced security features that protect against cyber threats and data breaches. These systems also support new regulations helping banks build trust with customers.
Efficient Data Use
Modern systems offer better data integration and management, allowing financial entities to retrieve insightful analytics. This info helps understand customer behavior, offer tailored services to clients, and drive their engagement and retention.
Scalability
As more users seek financial services, banks extend their customer base, requiring a scalable patent system. Modern platforms can fulfill this need, accommodating growth without compromising performance.
Enhanced Collaboration
Modern banking platforms can ease collaboration between different departments and third-party service providers. This communication can lead to more innovative solutions, improved operations, and faster service delivery.
Future-Proofing
Updating core banking architecture ensures that banks are prepared for future technological advancements and market changes. This future-proofing helps maintain relevance and competitiveness in the financial market.
Check out how a leading fintech company's solution was modernized, including added support for new features and enhanced user experience and scalability.
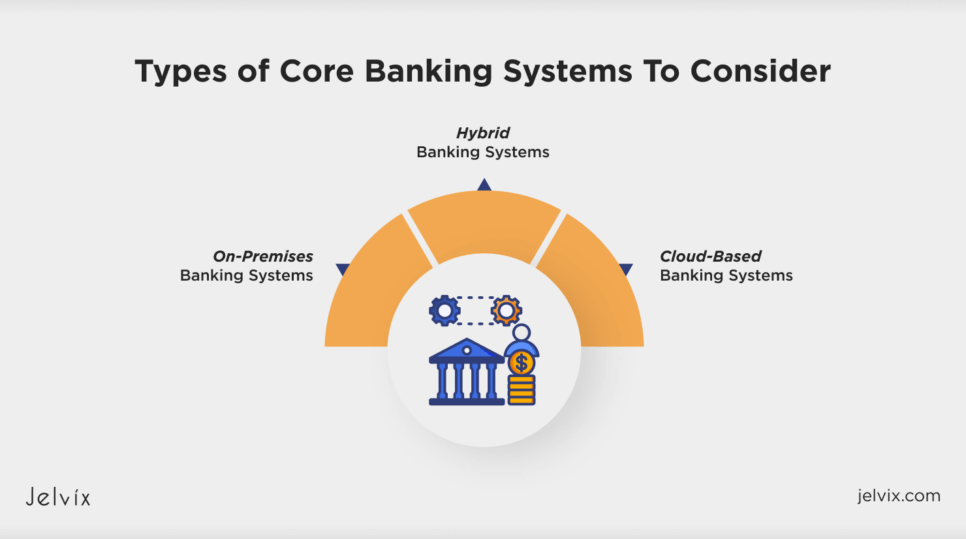
Types of Core Banking Systems To Consider
Modern banking systems come in various types, each designed to meet different needs. Understanding these types can help financial facilities choose the right system that aligns with their business goals and technical possibilities.
On-Premises Banking Systems
On-premises core banking systems operate on the bank’s own hardware. These systems provide full control over the software and data, allowing for high customization to meet specific needs. They are also secure but pretty expensive to support and maintain. What’s more, you can’t operate them without highly qualified staff which adds to the operational costs.
On-premises systems are best suited for large financial enterprises and established banks that possess substantial IT resources and the need for customization.
Cloud-Based Banking Systems
Cloud-based banking systems are hosted on the cloud service of a provider’s infrastructure and can be accessed via the Internet. These systems offer flexibility and scalability, making them a popular choice for modern banks. They involve lower upfront costs and don’t require in-house IT maintenance which makes them a cost-efficient solution.
Cloud-based banking systems are good for small to medium-sized banks and fintech startups looking for cost-effective and scalable solutions with minimal maintenance.
Hybrid Banking Systems
Hybrid core banking systems combine elements of both on-premises and cloud-based systems. They allow banks to maintain some systems on-site while using the cloud for others. They are flexible, offer better resource management, and allow gradual transitioning to the cloud.
However, hybrid systems can be complex to integrate and manage, accelerating the costs due to dual infrastructure. They are best suited for mid-sized banks that transition from legacy systems to modern architectures and want to maintain some in-house control.
Note that sometimes you can face a situation when none of the systems listed above suit your needs. In this case, you can request financial software development services from a tech partner to create a fully customized banking platform.
How Modular Banking Systems Support Customization
Modular systems consist of separate and interchangeable components or modules that can be customized and integrated as needed. This type of system provides flexibility and allows banks to update or add specific functionalities without overhauling the entire system.
Modular banking systems offer flexibility, customization, and scalability, making them ideal for fintech startups, small to mid-sized banks, and credit unions.
Open Banking Technology Overview: Main Features
Open banking is a financial technology that allows third-party service providers to access consumer banking, transactional, and other financial data through APIs. This technology promotes greater financial transparency, enhances customer experience, and drives innovation in the financial sector.
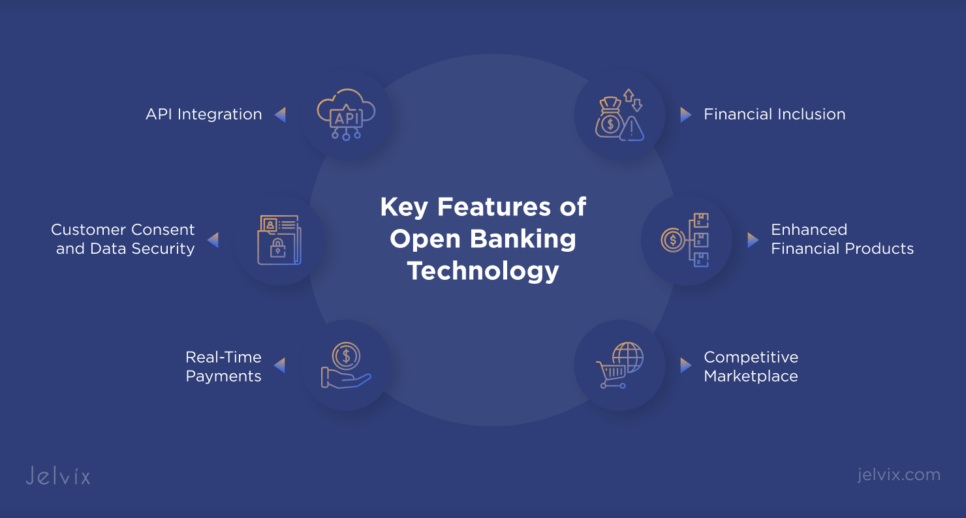
Key Features of Open Banking Technology
Open banking is a feature-rich solution that helps financial companies reach their operational and business goals.
API Integration
Open banking relies on APIs to allow different financial systems to securely share data. This feature facilitates integration between banks and third-party providers, enabling the development and integration of new services and applications.
Customer Consent and Data Security
Open banking frameworks prioritize customer consent and data security. Customers must explicitly grant permission for their data to be shared, ensuring transparency and control over personal information. Strong encryption and security protocols protect this data during transmission and storage.
Real-Time Payments
Open banking supports real-time payments, enabling instant money transfers between accounts. This improves cash flow management for consumers and businesses, enhancing the speed and efficiency of financial transactions.
Enhanced Financial Products
Through open banking, financial entities can offer personalized and innovative financial products. For example, they can tailor budgeting tools, loan calculators, and investment advice platforms to individual customer needs using aggregated financial data.
Financial Inclusion
Open banking makes it easier for underserved populations to access banking services. Through mobile banking apps and simplified account opening processes, more people can participate in the financial system.
Competitive Marketplace
Open banking supports a competitive marketplace where traditional banks and fintech companies can compete equally. This competition drives innovation, reduces costs, and enhances the quality of financial services offered to consumers.
Core Banking Modernization: 8 Steps To Move Your System to the Cloud
Updating a modern banking system in the cloud involves migrating your existing banking infrastructure to a cloud-based platform. This process can significantly improve scalability if performed correctly. The Jelvix team suggests that you follow a step-by-step approach for the best efficiency.
1. Assess Current Systems and Needs
Start by evaluating your existing systems to identify their strengths, weaknesses, and specific modernization needs. Determine which components will benefit most from cloud migration and ensure to meet all compliance requirements.
2. Choose the Right Cloud Provider
Pick a cloud service provider that offers robust security, financial stability, and experience with financial services. Ensure they meet your unique business needs for scalability, integration, and regulatory compliance.
3. Create a Migration Plan
Create a detailed migration plan that includes timelines and resources. Address potential downtime and data safety issues. Plan for a phased migration to minimize disruption and ensure data integrity.
4. Design Solution
Design a cloud solution tailored to your bank’s needs. This includes selecting the appropriate cloud architecture, defining data storage and access protocols, and ensuring that all necessary security measures are in place. Note that security should be the highest priority during this phase to protect sensitive financial data and comply with regulatory standards.
5. Implement Solution
Begin the migration according to the plan. Start with less critical systems to test the process and fix any issues. Gradually move to more critical components, ensuring continuous monitoring and troubleshooting to maintain data integrity and system functionality.
6. Test Carefully
Before going live, test the new cloud-based system to ensure it operates correctly and meets key performance and security standards. Include functional, performance, security, and user-acceptance testing.
7. Train Your Staff
Provide comprehensive training for all staff members to help them become proficient with the new system. Training should cover new functionalities, security protocols, and any changes in workflow resulting from the modernization.
8. Go Live and Monitor
Launch the new cloud-based banking system and continuously monitor its performance. Be prepared to promptly address any issues and optimize the system as needed to meet operational needs and user expectations.
Following these steps will help you move your core banking system to the cloud smoothly, making your operations more efficient and secure.
Pros and Cons of Modernizing Legacy Banking Systems
Modernizing legacy banking systems involves transitioning from traditional, often outdated, software to a newer one. Yet, the process isn’t perfectly smooth and imposes both advantages and drawbacks.
Pros of Modernizing Legacy Banking Systems
The benefits of modernizing legacy systems can provide substantial benefits in terms of efficiency, customer service, and competitive advantage.
Enhanced Efficiency
Modern systems can process transactions faster and more efficiently, reducing operational costs and improving customer satisfaction.
Improved Customer Experience
New technology can provide more personalized and seamless customer interactions, enhancing mobile banking features, and offering more self-service options.
Increased Security
Modern systems often incorporate better security protocols and technologies, reducing the risk of data breaches and fraud.
Regulatory Compliance
Updated systems are better equipped to adapt to changing regulatory requirements, helping banks avoid penalties and legal issues.
Scalability and Flexibility
Newer systems are more adaptable to changes in the market and technology, allowing banks to more easily scale operations or integrate new services.
Cons of Modernizing Legacy Banking Systems
Just like any complex process, modernization involves drawbacks. Addressing them requires careful planning, significant investment, and effective change management to mitigate the associated risks.
High Initial Costs
Upgrading legacy systems can be expensive, involving significant upfront investment in new software, hardware, and integration.
Integration Challenges
Integrating new technology with existing systems can be complex and disruptive, sometimes leading to downtime or data migration issues.
Training and Adaptation
Employees must be trained to use new systems, which can be resource-intensive. What’s more, staff accustomed to old ways of working can be resistant to new tech.
Dependency on Technology Vendors
Modern systems might increase your bank’s dependency on third-party vendors for continuous updates and support.
Security Risks During Transition
The transition period can expose new vulnerabilities, especially if data migration and system integration are not handled securely.
How Core Banking Modernization Impacts ROI
Upgrading old banking systems to modern platforms is a big decision for banks. This move can bring significant benefits, making it a worthwhile investment for financial companies.
Cost Reduction
Modernizing legacy banking systems often leads to reductions in operational costs. By transitioning to cloud-based platforms, banks can decrease their infrastructure-related expenses. The pay-as-you-go model of cloud services aligns costs with usage, preventing overinvestment in unused capacity.
Increased Revenue
Modern systems offer enhanced capabilities, such as improved data analytics and integration with new digital services, and can open up additional revenue streams. For example, banks can offer financial products tailored to individual customer needs, which can attract more customers and increase cross-selling opportunities.
Measuring ROI
To measure the ROI of modernization, banks should consider both tangible benefits (like cost savings and revenue growth) and intangible benefits (like customer satisfaction and operational resilience). However, don’t expect to see results very soon, as ROI becomes apparent over time as the bank uses new capabilities brought about by the modernized systems.
Jelvix’s Approach to Core Banking Modernization
At Jelvix, we recognize the need for financial companies to modernize their banking systems and can provide support for their efforts. Our approach to modernizing core banking systems focuses on using advanced technology to transform traditional systems into efficient, scalable, and secure financial platforms.
We start with a careful assessment to tailor a modernization strategy to your goals. We also enhance scalability, reduce maintenance costs, and provide flexibility by using up-to-date cloud-based solutions.
If you need help upgrading your legacy banking systems, our team can help. Reach out to our experts for a tailored consultation on your business needs.
Need a reliable tech partner?
Our expert healthcare software development team is here to help you achieve your business goals.