Blockchain technology has gone far beyond its core concept and is now used in nearly every industry, including supply chain management, fundraising, insurance, global trade commerce, secure personal identity, and many others.
Not all organizations employ blockchain technology, but those who do, use its potential to beat the toughest challenges of procedural delays, human error, intermediation, etc. So, if you are a business owner, and you currently need to streamline your business process, incorporating blockchain would serve as a key solution to your problems.
Why a sudden hype for blockchain? In fact, blockchain isn’t overhyped, and it’s no longer a fringe novelty of crypto enthusiasts. The technology has gone far beyond the financial sector and continues to benefit various industries around the globe. In practice, there are many different types of blockchains being developed.
The Deloitte’s Global Research Survey suggests that this year, nearly 1,500 senior executives working in capital markets, industrial IOT, infrastructure security, global trade, and many more consider blockchain to be an ultimate tool to drive their organizational innovation.
Another research estimates that by the end of 2020, nearly 60% of CIOs will have blockchain integrated into their infrastructure. Accordingly, it follows that blockchain technologies can improve almost every business in every country.
In this guide, we are going to focus on the blockchain use cases and consider the main benefits of business digitalization.
So, What is Blockchain?
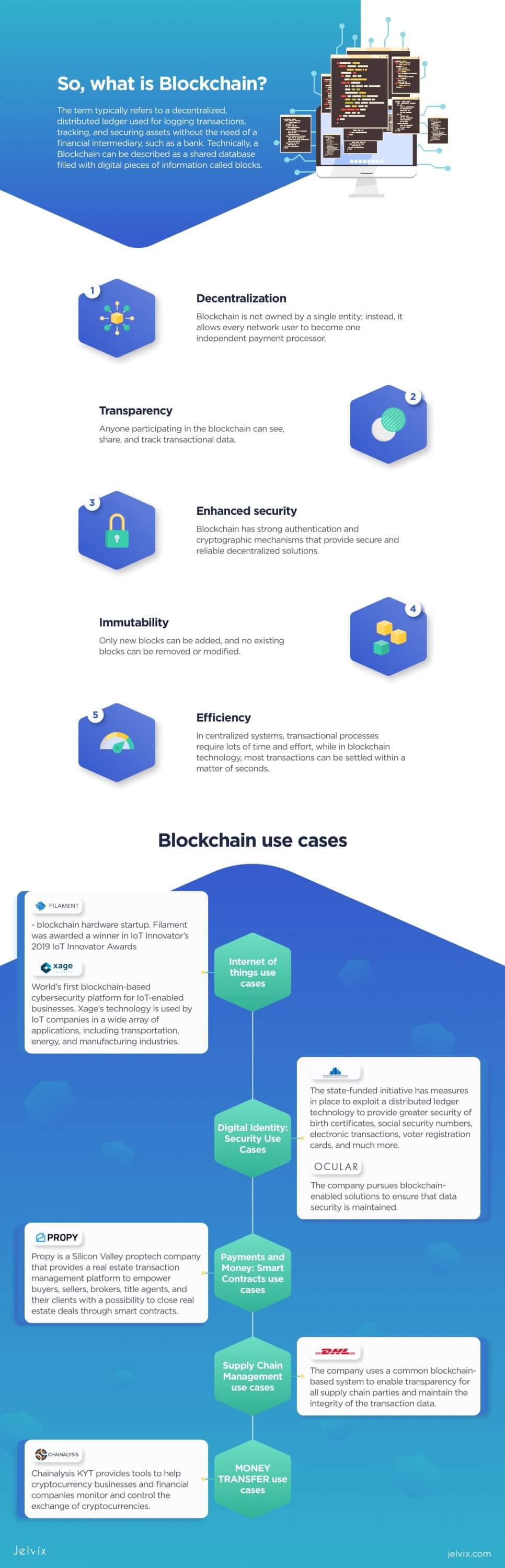
The term typically refers to a decentralized, distributed ledger used for logging transactions, tracking, and securing assets without the need of a financial intermediary, such as a bank. Technically, a blockchain can be described as a shared database filled with digital pieces of information called blocks.
Blocks store the primary information about transactions, such as date, time, and purchase amount, and are bound together using strong cryptography techniques. To give you a clearer idea, imagine a strongly encrypted Google Document, in which each entry in the sheet depends on the previous, and only trusted network partners are allowed to create entries and access them.
The following are the main benefits of using blockchain in any industry:
- Decentralization. Blockchain is not owned by a single entity; instead, it allows every network user to become one independent payment processor.
- Transparency. Anyone participating in the blockchain can see, share, and track transactional data.
- Enhanced security. Blockchain has strong authentication and cryptographic mechanisms that provide secure and reliable decentralized solutions.
- Immutability. Only new blocks can be added, and no existing blocks can be removed or modified.
- Efficiency. In centralized systems, transactional processes require lots of time and effort, while in blockchain technology, most transactions can be settled within a matter of seconds.
Many business owners around the globe point out that blockchain technology helps them to reduce costs, improve operational efficiency, build trust, and secure finances.
Blockchain Use Cases
In this section, we will consider blockchain use cases and look at the real examples of companies that pursue finance digital transformation.
Internet of Things Use Cases
The popularity of machine learning is growing every day and has already transformed our understanding of edge computing. Today, many organizations of all types – businesses, governments, and nonprofits – are innovating through the Internet of Things (IoT). By utilizing cloud technology and big data, the IoT system manages to connect people, places, and products, and in doing so, it provides means for value creation and capture.
IoT systems generate large volumes of data that, besides network connectivity and power, require storage resources to transform this data into valuable actions and services. Today’s IoT systems rely on a centralized architecture model to authenticate, authorize, and connect nodes in the IoT network.
This central model presents a scalability challenge when trying to make the network’s size scalable. Applying the blockchain protocols to IoT can effectively address the problem of network scalability.
Particularly, a peer-to-peer blockchain architecture allows neighboring devices to interact with each other without using any centralized node between them; blockchain nodes build trust with each other to reduce processing overheads for verifying blocks while also providing end-to-end security.
IoT’s scarce resources for storage, energy, and computation created another obstacle for executing heavy cryptography algorithms. IoT devices collect a wealth of sensitive personal data, which needs to be protected and secured; however, accumulating such crucial data in centralized entities may create critical security and privacy risk.
Adopting blockchain distributed processing methods will ensure that the data remains immutable and untempered. Once the data is recorded in the blockchain, it cannot be modified or deleted without modification of all subsequent blocks.
So, IoT companies have to embrace blockchain technology to achieve resource efficiency and protect the security of the IoT transmit data.
How can blockchain solve IoT security and scalability challenges?
Since IoT applications are, by definition, distributed, it’s only logical that blockchain will help to address security, data privacy, and reliability of IoT devices. Here we focus on the main advantages of integrating blockchain in IoT.
- Data reliability. Using blockchain in IoT will ensure that data remains immutable and untampered. Blockchain uses consensus and mining algorithms, which slow down the creation of new blocks and make it hard to tamper with previous blocks.
- Resource efficiency. Decentralized blockchain architecture is designed to progressively reduce the processing overhead for verifying new blocks.
Below are several examples of US companies that have incorporated blockchains in their operations.
Filament
Industry: Blockchain services
Location: Reno, Nevada
Blockchain usage: The computing solutions that Filament provides include a combination of hardware and software, as well as professional and technical services. Originally a blockchain hardware startup, Filament is now working on machine learning technology enhancements to make it accessible to all organizations.
By combining distributed ledger technology and AI, Filament creates and trades financial products that securely interact with and transact value against the blockchain. In 2019, Filament was awarded a winner in IoT Innovator’s 2019 IoT Innovator Awards.
XAGE SECURITY
Industry: Internet of Things, Cybersecurity
Location: Palo Alto, California
Blockchain usage: Xage is the world’s first blockchain-based cybersecurity platform for IoT-enabled businesses. They focus on autonomous data-driven, machine-to-machine IoT cooperations.
With the ability to self-diagnose and heal possible breaches, Xage leverages blockchain technology to manage billions of devices at once and protects industrial IoT operations against cyber threats and attacks. Xage’s technology is used by IoT companies in a wide array of applications, including transportation, energy, and manufacturing industries.
Digital Identity: Security Use Cases
For a long time, digital identity was considered an Internet equivalent to a real identity card or passport. However, that definition is only valid for a part of real-world identity attributes. Digital identity can be described as an online record containing “a set of attributes, traits, and preferences related to an external agent or entity,” where the agent or entity may be a person, organization, or device.
Thus, in the digital world, the link between physical identity and digital identity could become meaningful only if it is understood in terms of its present use as digital authentication.
For example, on sites like eBay, the key issues are one of both online reputation and ability to pay/buy. So, it is important to prove the seller’s digital identity to build trust in client relationships. In contrast, it is less important to know that the seller’s real-world national identity is the Bermuda Islands, where suing anybody for fraudulent or damaging activity is rather unlikely to end successfully.
Nonetheless, there are priority concerns associated with a digital identity that span more than one cluster area. Today, digital identity services experience a surge in fraudulent activity. The pandemic outbreak has triggered an unprecedented acceleration in the adoption of contactless payments in self-service.
Because businesses are now operating remotely, sudden spikes in contactless transactions consequently cause global digital fraud and identity theft.
According to recent statistics, the global digital identity solutions market is forecast to grow 17% to total $30.5 billion, up from $13.7 billion in 2019. Another research suggests that more than 16 million Americans complained of identity fraud and theft in 2017 alone, with identity being stolen every two seconds. This might suggest that digital identity has vulnerabilities inherent in digital identification systems.
In particular, the main problem lies in centralized identity systems. Having high-value data accumulated at one place exposes it to a higher risk of attack. So, it’s become clear that the future growth of online business requires trusted and highly-secure digital identity schemes that would give users greater control over their data while maintaining strong security and privacy.
Now, what can blockchain do to minimize the risk of digital identity data breaches?
In a blockchain, users have control over their data; instead of permitting third parties to access personal information, users can store their identity data in a secure encrypted digital hub. Individuals can control its sharing, manage the history of interactions, give and revoke permission, if necessary. A blockchain-based digital identity addresses several challenges that centralized models are currently facing.
Below you can see the main advantages of blockchain identity management:
- Decentralization. The user is the only person able to access all of their identity information and exploit data resources without interfering with another user’s data.
- Immutability. Hashing algorithms prevent identity data from being tampered.
- Transparency. Every node in the network can see the data that has been entered in the blockchain.
ILLINOIS BLOCKCHAIN INITIATIVE
Industry: Government, Technology
Location: Springfield, Illinois
Blockchain usage: Illinois has been outpacing other states by incorporating blockchain technology in digital identity systems. Last year, Illinois officials introduced the Illinois Blockchain Initiative, which seeks to support building out the blockchain ecosystem and promote government integration of the technology itself.
The state-funded initiative has measures in place to exploit a distributed ledger technology to provide greater security of birth certificates, social security numbers, electronic transactions, voter registration cards, and much more.
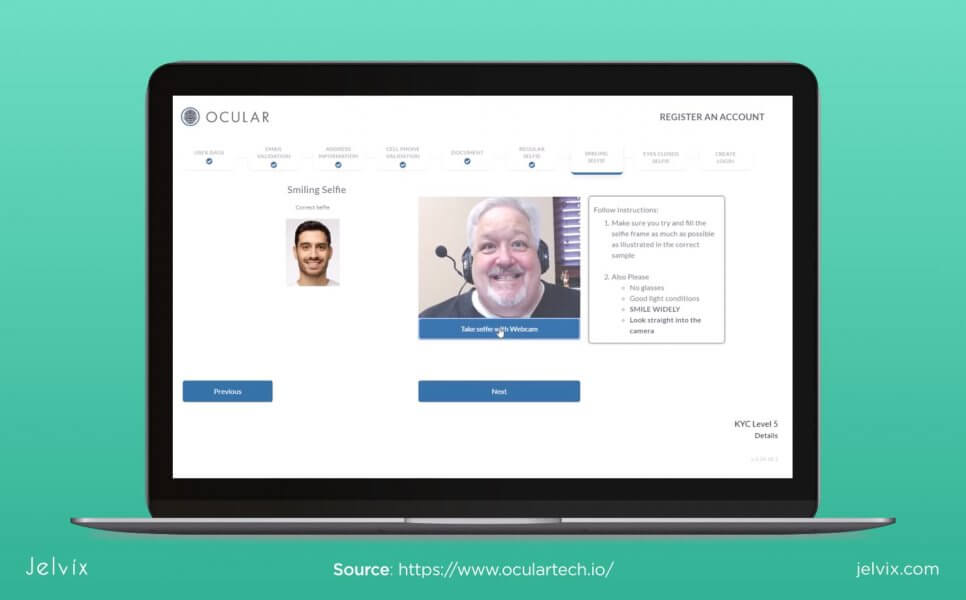
OCULAR
Industry: Cybersecurity, Fintech
Location: Los Angeles, California
Blockchain usage: Ocular is an Anti-Money Laundering (AML) compliance platform that provides instant verification of the identity of the client (KYC). The company pursues blockchain-enabled solutions to ensure that data security is maintained.
In particular, the technology’s biometric security systems include facial recognition tools that scan faces of individuals applying for government-issued IDs. By storing identity information on blockchains, governments get a chance to prevent forgery of documents (fake passports, foreign visas, refugee IDs, etc.)
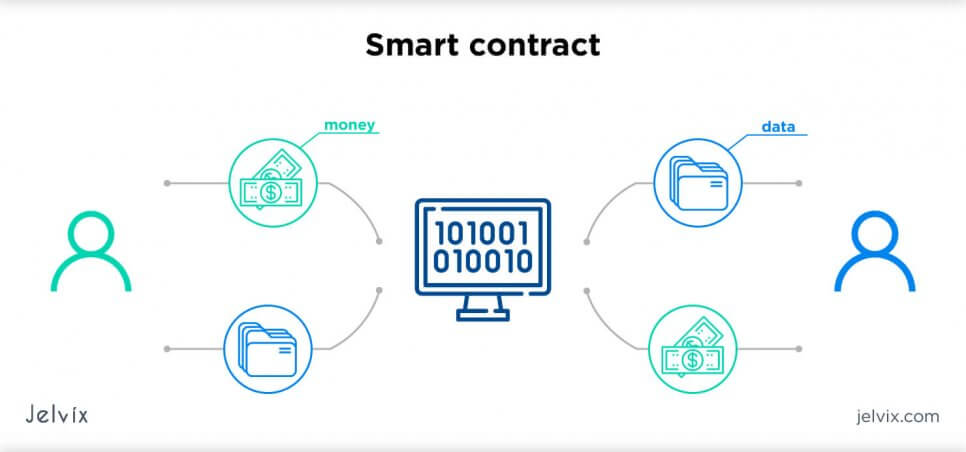
Payments and Money: Smart Contracts
A smart contract can be defined as a self-executing contract which is intended to digitally control and enforce the negotiation of a contract. Smart contracts are almost indistinguishable from regular contracts, except that the agreement of a contract is automatically enforced in real-time on a blockchain.
This greatly facilitates the efficient conduct of an agreement, since it excludes the presence of intermediaries and provides more accountability.
Why are blockchain-based contracts considered as beneficial?
With smart contracts, you can virtually exchange everything (money, shares, real estate, etc.) and verify shipments and payments in real-time, while saving businesses time and money.
So, with the popularity of blockchain-based contracts rising across all levels of government, healthcare, and the real estate industries, enabling technology for other sectors is only a matter of time. A concise example of blockchain technology use in smart contracts is given below.
PROPY
Industry: Real Estate
Location: Palo Alto, California
Blockchain usage: Propy is a Silicon Valley proptech company that provides a real estate transaction management platform to empower buyers, sellers, brokers, title agents, and their clients with a possibility to close real estate deals through smart contracts.
With a decentralized title registry system, the platform provides means required for an instant title issuance and offers solutions for consumer interface, offer, and transaction management.
You may be curious about the most promising blockchain trends for 2021. Our blockchain technology experts have gathered some insights to share with you in this article.
Supply Chain Management
Supply chain management is another great example where blockchain technology has brought an opportunity for businesses to develop and grow. As is well known, the SCM industry’s objectives are well-defined product development, efficient sourcing of materials, and production of quality and logistics.
As supply chain mapping involves various independent parties (freight forwarders, logistic service providers, transport operators, etc.), it brings to the fore an issue of accurate communication and transparency. For most product-making companies, these are key performance indices that support the profitability of the business. When KPIs are not met, the business is bound to fail.
So, how does the distributed ledger technology address the challenges of poor tracking and inefficiency of supply chains?
Blockchains allow two or more parties to securely share access to the same data and act as a single source of truth. All recorded transactions from multiple sources are immutable and maintain a time-stamped audit trail of all packaging and supply chain labeling events.
Furthermore, blockchain technology removes the need for intermediaries and thus enhances transparency, that in turn, helps stop counterfeits and thefts.
From a consumer’s point of view, blockchains help end consumers to verify the product’s purity and origin, as well as track product delivery, time, and location.
Below is an example of effective blockchain use in supply chain management.
DHL
Industry: Logistics, Supply Chain
Location: Plantation, Florida (US headquarters)
How it’s using blockchain: DHL is one of the largest global market leaders to integrate blockchain technology into the supply chain. The company uses a common blockchain-based system to enable transparency for all supply chain parties and maintain the integrity of the transaction data. The technology helped DHL to gain a major presence in the US and reach a higher level of consumer satisfaction.
Money Transfer
Last but not least is an example of blockchain use in money transfers. As we mentioned at the very beginning of this guide, before blockchains gained critical mass, their primary focus was cross-border payments and trade finance.
Accordingly, the distributed ledger technology gained its popularity due to its immutability and decentralization features. In terms of financial management, these factors helped to upgrade financial processes and offer companies a secure, digital alternative to control international money transfers.
According to a recent ComputerWorld article, the distributed ledger eliminates bureaucratic, paper-heavy procedures, and reduces third-party fees; it can save the largest banks $8-$12 billion a year. Now let’s see an example of blockchain use in finance.
CHAINANALYSIS
Industry: Fintech, Cryptocurrency, Cybersecurity
Location: New York City, New York
Blockchain usage: Chainalysis KYT provides tools to help cryptocurrency businesses and financial companies monitor and control the exchange of cryptocurrencies. The company’s due diligence software provides the necessary means to develop public-private partnerships and detects any type of criminal activity, including frauds, money laundering, and compliance violations.
CHAIN
Industry: Fintech, Cloud
Location: San Francisco, California
Blockchain usage: Chain offers financial services a trusted cloud infrastructure. With the use of cryptographic ledgers, the company provides ultimate implications for safe and efficient cryptocurrency transfers.
Summary
We hope that this comprehensive guide will be useful when choosing your blockchain technology for building consensus and trust for your business. We want to play our part and help you integrate blockchain in your project. Please see our Expertise page to learn more about our blockchain development solutions or contact our experts directly.
Need a qualified team?
Boost your business capacity with the dedicated development team.