Rapid advancements in technology have spread to healthcare and can play a revolutionizing role in medical diagnostics. Particularly, software applications can contribute to clinical consultation and assessment, complement the physician-patient interaction, and make diagnostics more affordable and accessible, especially in remote locations and populations difficult to reach.
Today, many apps assist healthcare providers with patient screening, improve diagnostic accuracy, and pave the way for decentralizing care by pushing it from hospitals to patients’ homes. In addition to applications for medical professionals, there are self-diagnosis apps allowing patients to uncover the possible causes of their symptoms and seek advice and recommendations for treatment.
With many potential benefits for physicians and patients, healthcare providers and software developers are now investing in the development of applications that encourage self-care, enable easy communication between users and professionals, and allow physicians to manage patient care better.
Reasons to Develop a Medical Diagnosis App
Medical diagnosis apps have the potential to transform the way patients, clinicians, and hospitals approach healthcare. Some applications are designed for patients, while others assist physicians. Physician-oriented apps allow professionals to access comprehensive databases with symptoms, diseases, and drugs, provide treatment recommendations, and monitor vital signs such as heart rhythm, glucose levels, and blood pressure.
As they offer convenience, save time, and are easy to use, patients are also willing to use medical diagnosis applications. They enable users to check their symptoms, schedule an appointment and connect them to the most appropriate level of care.
Because of their user-friendliness, patients are not only increasingly using intelligent apps for diagnosis and triaging but have found them to be useful. A cross-sectional survey study published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research reveals that the overwhelming majority of people who use apps (90.1 percent) are satisfied with the information they received regarding their health problems.
More than half of the participants (51 percent) reported positive health outcomes, and 48.4 percent shared the findings with their primary care provider. Overall, most patients (90.1 percent) said they would use a self-diagnosis app again.
Physicians also show interest in mobile technologies that target different aspects of care, including follow-up treatment, assistance with diagnosis, self-care, and healthy lifestyles. A study published in Bioline International shows that 75 percent of practitioners find telemedicine applications useful and having good potential for diagnosis and case referral.
Patient and physician satisfaction prove that functional healthcare apps are set to gain wider acceptance.
Another reason to create such apps is to help overcome barriers in accessing healthcare in remote and rural areas. Distances, a lack of transportation options, longer commutes, and physician and nurse shortages impact healthcare access in rural areas.
Rural communities and hard-to-reach populations also have more elderly residents with chronic medical conditions requiring subspecialist care and frequent visits to outpatient facilities. At the same time, the number of hospitals serving rural populations has declined a lot over the last few years.
According to the WMD Health Equity Report, hospitals in the rural South lost more than 3,500 beds between 2005 and 2020. This happened mainly because of the low volume of patients and the fact that attracting physicians to work in rural areas has proven challenging. The more limited access to healthcare in such communities requires new care delivery models, and the use of medical diagnosis apps can be one of them.
Benefits of Mobile Apps in Disease Diagnostics
Mobile apps offer multiple benefits to healthcare providers and patients, including improved diagnostic accuracy, easy communication and triaging timely and affordable point-of-care, and better overall health.
Healthcare apps can help hospitals and emergency departments, in particular, to triage patients and prevent avoidable visits accurately. Some applications feature helpful tools such as a library of symptoms and associated medical conditions, pill identification tools, multi-drug interactions, and drug-allergy checkers.
In addition, physicians can locate medical records, lab results, and exam findings, diagnose patients and check new treatments against medical records. Users also benefit from push notifications with black box warnings, new healthcare research, and drug approvals.
Apps for patients fall into two categories – wearables for disease management and AI-powered symptom checkers, both of which have multiple functionalities. Wearable devices aid patients in monitoring chronic conditions such as asthma, heart disease, and diabetes by providing feedback based on user input. The data is then transmitted to a healthcare provider for further assessment.
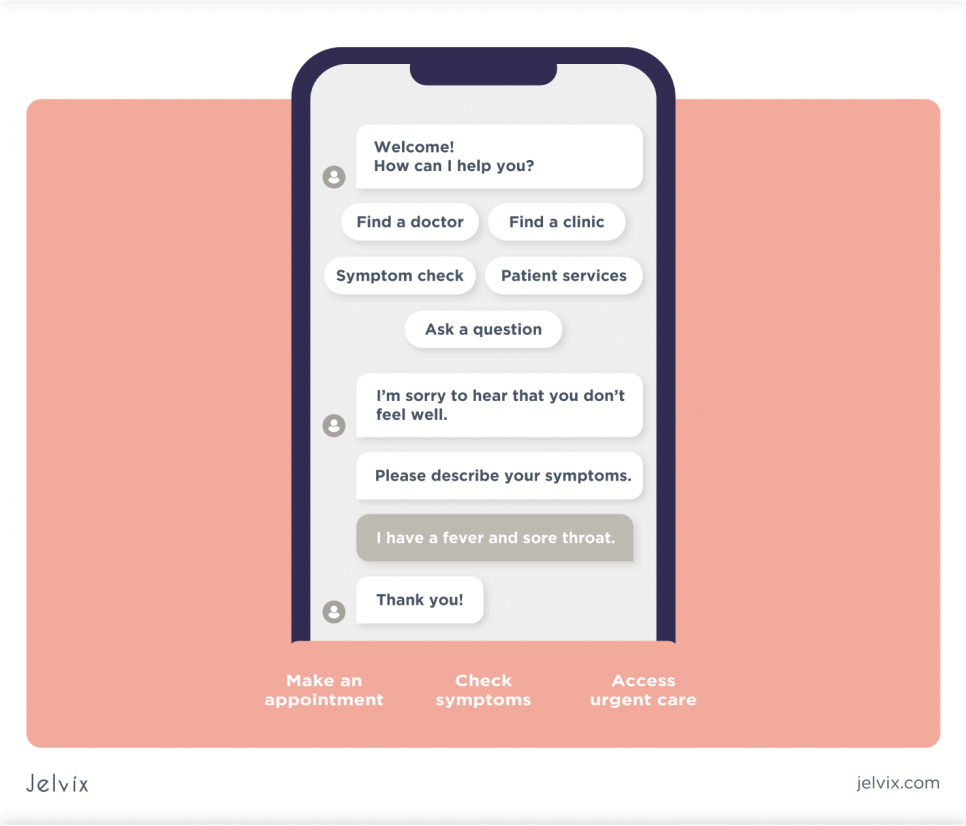
AI symptom checkers, the second category, process user input, offer a list of potential diagnoses rank-ordered by likelihood, and help patients with triage to smooth their journey into the healthcare system. They are useful in educating users on diagnoses that match their symptoms and informing them whether they should seek care and with what urgency degree.
Features for Medical Diagnosis Application Development
High-performance medical diagnosis apps are not only user-friendly but have helpful features such as geolocation, real-time chats, and patient and healthcare provider databases. For example, geolocation can be used to locate a patient in a serious or critical condition that requires immediate medical attention.
Patients can also locate nearby hospitals where they can seek care. Real-time chats allow users to connect with healthcare providers and get timely assistance. This is a useful feature to enable easy and quick access to care and build a trusting relationship with patients.
Patient information databases contain sensitive data such as diagnoses, reports, medical history, and prescriptions that healthcare providers and patients can access. Physician information databases store providers’ and doctors’ profiles and allow users to look up doctors and hospitals by location, availability, and specialty. Other useful functionalities include:
- Report management
- Lab appointment booking
- Voice and video calls
- File sharing
- Analytics
- Wearable integration
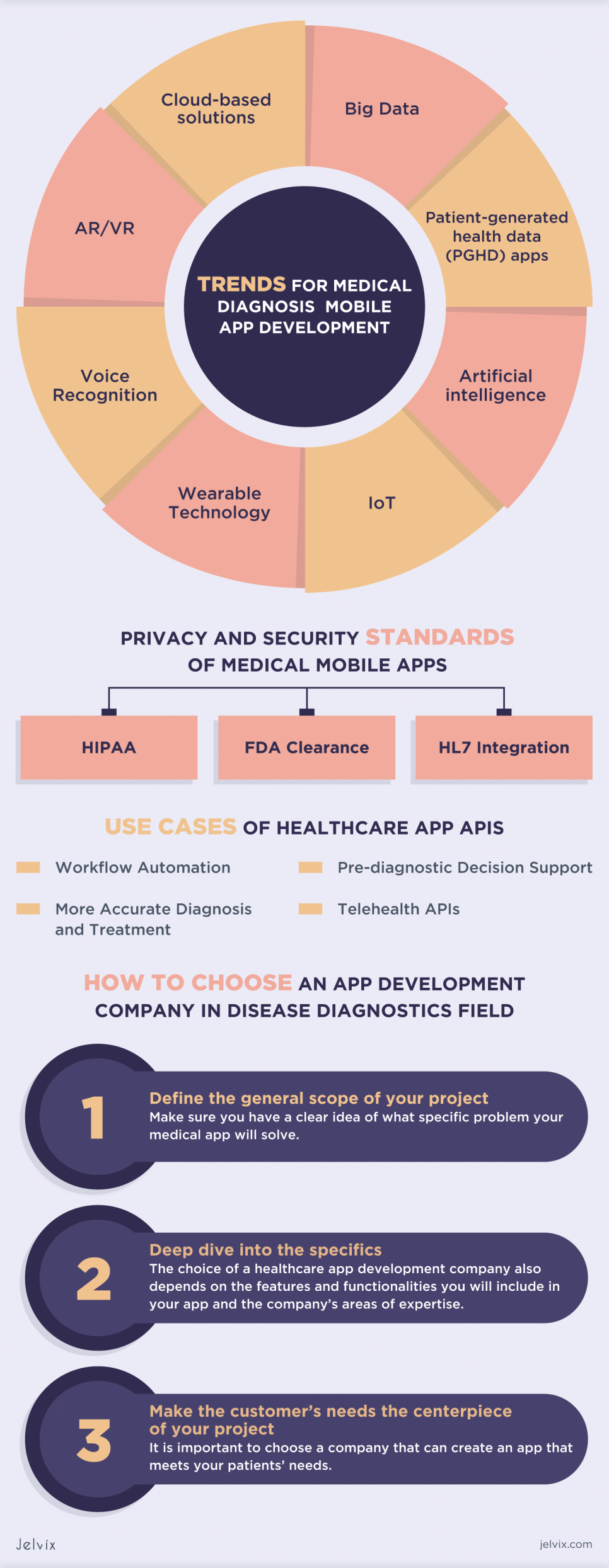
Trends for Medical Diagnosis Mobile App Development
The biggest drivers of change that have the potential to future-proof digital healthcare are cloud-based solutions, big data, patient-generated health data (PGHD) apps, artificial intelligence, IoT, voice recognition, AR/VR, and wearable integration.
Cloud-Based Solutions
Cloud-based solutions enable healthcare providers to store, access, analyze, and exchange high volumes of health information such as clinical notes, medical records, and patient experience. Using the cloud enables efficient and secure communication between hospitals, physicians, patients, and payers, and healthcare providers are already leveraging this technology.
According to the West Monroe survey report, which included 300 company executives, 35 percent of care providers kept over 50 percent of their infrastructure or data on the cloud.
Big Data
Big data refers to huge volumes of unstructured and structured information collected, analyzed, modeled, and standardized. For example, in healthcare, statistics and population variables can be used to optimize ER admissions, improve patient predictions, prevent the onset of diseases and epidemic outbreaks, and research new treatments.
Patient-Generated Health Data (PGHD) Apps
PGHD apps are also gaining popularity. They collect information from patients and their families, including disease outcome and recovery, lifestyle, existing conditions, and medical history. This helps physicians to get a comprehensive picture of the patient’s health status outside traditional care settings.
The main types of apps here are health history, surveys and questionnaires, and patient and biometric activity. While still at an early stage, PGHD applications have the potential to fill information gaps, support personalized medicine, and improve patient outcomes.
Artificial Intelligence
AI plays a crucial role in transforming the healthcare sector. The technology includes intelligent solutions that can handle manual, repetitive tasks such as CT-Scans, X-Rays, scheduling tests, and check-ups.
According to a survey by Accenture, which includes organizations across 13 industries, healthcare providers are already leveraging smart technology solutions and rank first in terms of AI use.
Overall, 18 percent of healthcare organizations use AI-enabled technologies, compared to 10 percent of banking institutions and 8 percent of manufacturers. AI allows providers to discover new patterns, ensure that processes are self-optimizing and self-adapting, and better understand customers and markets.
IoT
The Internet of Things is made of devices connected to the Internet, all gathering, receiving, and sharing data. Hospitals already use IoT-enabled applications embedded with sensors for tracking the location of equipment such as oxygen pumps, nebulizers, defibrillators, and wheelchairs. Deployment of medical teams can also be tracked in real-time.
Wearable Technology
The increasing adoption of IoT-enabled healthcare apps paired up with wearable technology is also a promising trend that can prevent the occurrence of serious health conditions. Used for remote patient monitoring, healthcare apps keep track of and send data to physicians, including physical activities, heart rate, sleeping patterns, and glucose readings.
This data allows physicians to monitor the patient’s condition over time, identify patterns and potential issues, and offer advice and recommendations.
Voice Recognition
Based on natural language processing, voice recognition apps are mainly used in doctors’ offices and practices. They enable practitioners to update electronic medical records and dictate patient diagnosis notes conveniently. By shortening the average appointment longevity, voice recognition software allows physicians to see more patients.
AR/VR
Augmented reality and virtual reality have multiple applications in healthcare, from reducing anxiety in pediatric patients undergoing painful procedures and enhancing posttraumatic stress disorder treatment to helping pharmacy students to understand the effects of different medications.
AR is also increasingly used as a patient engagement tool, especially in orthodontia and aesthetic medicine, where medical immersion enables users to better understand the intended result of a procedure.
Check out software development methodologies useful tips for the long life of your mobile application.
Privacy and Security Standards of Medical Mobile Apps
Medical apps are designed to collect, measure, and send sensitive health information that must be kept secure. With the increasing adoption of mobile applications by healthcare providers, the volume of data transmitted among patients, hospitals, doctors, nurses, and pharmacies is also increasing. This raises the question of data security and compromised patient privacy.
In the U.S., regulations such as the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) offer some general guidance regarding privacy and security issues.
HIPAA
For medical software to be compliant, it must meet the physical and safety safeguards under the HIPAA Security Rule. Covered entities must implement technical, physical, and administrative safeguards to protect personally identifiable health information held or shared in electronic form. Examples of covered entities are health maintenance organizations, healthcare providers, and health plans. If an app is designed to share personal data with a covered entity, it needs to be HIPAA compliant.
FDA Clearance
FDA is tasked with ensuring the security, effectiveness, and safety of medical devices. Healthcare applications that require FDA approval include software and devices that process patient data or are used for diagnosis, treatment, or assessment. No approval is needed for software that provides access to educational or reference materials and apps for electronic file sharing.
HL7 Integration
Health Level 7 (HL7) governs how electronic health data is shared between software used by different healthcare providers. The goal is to ensure that information is processed and transferred consistently. The HL7 standards are not binding and simply provide guidelines for sharing clinical data. HL7 protocols also enable patients to access their medical records, improve transaction workflows, and automate exchange.
In addition to regulations that focus on mobile medical apps and sensitive data, it is important that all stakeholders, including hospitals, authorities, and policy-makers, collaborate and develop safety, privacy, transparency, and usability standards.
Check out software development methodologies useful tips for the long life of your mobile application.
APIs in Medical App Development
Using APIs or application programming interfaces for healthcare app development offers multiple advantages, including improved analytics for better treatment outcomes, reliable data storage, fast and secure data management, and improved cooperation capabilities to foster innovation.
APIs that feature advanced threat prevention capabilities allow for reliable storage and data management. They enable instant access to health-related information such as research and medical records. This allows professionals to access practical information based on clinical data, discharge and census statistics, expert knowledge, patient records, and other existing references.
Additionally, as APIs offer immediate access to data, they encourage cooperation and foster innovation in the field of medical research. With their help, scientists can process and analyze the results of multiple studies to identify patterns and study the development and risk factors for infectious and genetic diseases.
Finally, application programming interfaces integrate information from multiple systems to create comprehensive data sets. The use of such data sets helps improve analytics and treatment outcomes.
Use Cases of Healthcare App APIs
Workflow Automation
One use case of APIs in healthcare settings is to automate workflow and reduce administrative burden. They can be used to streamline data management and data movement between insurance companies and healthcare providers. Using open APIs can also improve interoperability between incompatible applications and devices.
More Accurate Diagnosis and Treatment
APIs enable patients to share their health records with hospitals and practices. They connect wearable devices such as asthma monitors, biosensors, and ECG monitors with an ЕHR system. This enables physicians to access and monitor data shared by the devices, thus assisting them with clinical decisions.
Pre-diagnostic Decision Support
Symptom checker APIs are designed to help patients identify the possible causes of their symptoms. They include two components – a knowledge database and a diagnostic engine. The knowledge database contains information about treatments, diseases, and symptoms and is continuously updated by healthcare professionals. The diagnostic engine processes and analyzes user input, including laboratory tests, symptoms, and demographic data.
Then the engine links information from the knowledge database with patient input, offers care recommendations, and navigates users to the right endpoints of care. This is known as triage. The three triage categories are non-urgent, urgent, and emergency when patients need immediate care.
Based on the patient’s symptoms, how long they last, and their age and gender, the symptom checker will offer care recommendations such as telemedicine, a walk-in clinic, urgent care, family physician, or emergency services.
Telehealth APIs
Telemedicine APIs have multiple applications such as lab test ordering, appointment scheduling, remote visits, and patient data exchange. Other functionalities that users benefit from include e-prescriptions and prescription refills, remote monitoring, and electronic billing. These services can be delivered in a variety of ways, such as reminders, push notifications, patient web portals, and health apps.
On the other hand, API providers include MedTech companies, knowledge bases, EHR systems, and web services. They offer access to a range of patient services through software integration.
Additionally, drug data APIs that connect apps and health systems to pharmaceutical databases, descriptions of supplements and drugs, FDA data, standard terminology, and a lot more.
How to Choose an App Development Company in Disease Diagnostics Field
Choosing an experienced healthcare app development company can facilitate long-term accomplishment by streamlining operations, easing the burden on healthcare staff, and thus improving the quality of patient care.
Define the General Scope of Your Project
There is a wide choice of applications depending on your goals, including patient and medical personnel communication, medical dosage, e-prescription, appointment, telehealth, diagnosis, and urgent care apps. Make sure you have a clear idea of what specific problem your medical app will solve.
Deep Dive Into the Specifics
The choice of a healthcare app development company also depends on the features and functionalities you will include in your app and the company’s areas of expertise. Some of the common features of healthcare applications include live chat, tracking, geolocation, scheduling, doctor profiles, and push notifications. But if you are after a custom feature.
In that case, you should first consider if the development company of your choice has the necessary level of expertise, years of experience, and skillset to appease your demands.
Make the Customer’s Needs the Centerpiece of your Project
It is important to choose a company that can create an app that meets your patients’ needs. According to the Accenture Digital Study Survey, patients are more likely to choose a healthcare provider who offers digital functionalities such as videoconferencing (49 percent), telemonitoring (53 percent), and electronic prescription refills (77 percent).
Other capabilities that patients would like to see are text or email reminders regarding follow-up or preventive care (70 percent), secure email communication (69 percent), and booking, canceling, and changing appointments online (68 percent).
Conclusion
Medical apps assist clinicians with diagnosis, optimize communication, expand reach, and allow decisions to be made in a timely manner. Mobile apps for patients also come in handy, especially where access to care is more limited. They help users determine whether their symptoms are unsupported or could imply a serious condition requiring urgent medical attention.
In the foreseeable future, AI-powered technologies will continue to aid healthcare professionals across all possible domains of medicine, including research, training, education, and health and medical care. They will have a more active role in the examination, history taking, interpretation, and investigation to establish a clinical diagnosis.
Prescription writing is another area in which medical apps can be particularly useful by offering information about different drugs, interactions, dosages, locally available brand names and generic drugs, FDA clearances, poisonings, and side effects. Most importantly, mobile medical apps offer disease-specific information useful to patients, paramedics, physicians, and healthcare providers and can significantly improve health outcomes.
Apps also help improve connectivity, availability, and quality of care and will thus become well-integrated into the healthcare system in the near future. Whether used by patients to manage and better understand their health or by hospitals to enhance patient care and data access or streamline processes, medical science is set to be transformed by the increasing adoption and development of more sophisticated apps.
Terry Tateossian is the Founding Partner of Socialfix Media, award-winning digital marketing agency focused on emerging technology and media working with companies in launching innovative products and gaining market share. She is also the founder of Amplified3, a complete marketing agency management suite for smart digital asset management, asset distribution, and team training.
As we delve into the transformative impact of app development companies on medical diagnostics, it’s clear that technology is paving the way for more accurate, accessible, and affordable healthcare solutions. To explore how these innovations are specifically advancing the healthcare industry, visit Jelvix’s Healthcare Industry Solutions, where the fusion of technology and healthcare is creating new possibilities for patient care.
Need a certain developer?
Access top talent pool to reach new business objectives.