Recently, the Jelvix team has conducted a research study to learn about emerging trends in complementary technology and define the most popular use cases of RPA.
Artificial Intelligence has become an integral part of IT, HR, BPO, Manufacturing, Finance & Accounting, Insurance, and many other industries; the AI applications are getting increasingly sophisticated, thereby enabling the technology for sustainable development.
Meanwhile, current trends in robotic automation are improving and transforming industry organizations in numerous ways. In particular, the RPA technology enhances the speed and accuracy of manual processes and contributes to digital transformation on the global economic level.
In this guide, we will consider popular RPA use cases and learn how software bots use a combination of automation, computer vision, and machine learning to automate business processes.
On our blog, we talk about the use of new technologies in practice and share our insights to help our clients drive the digital transformation journey. You can learn more about our services here.
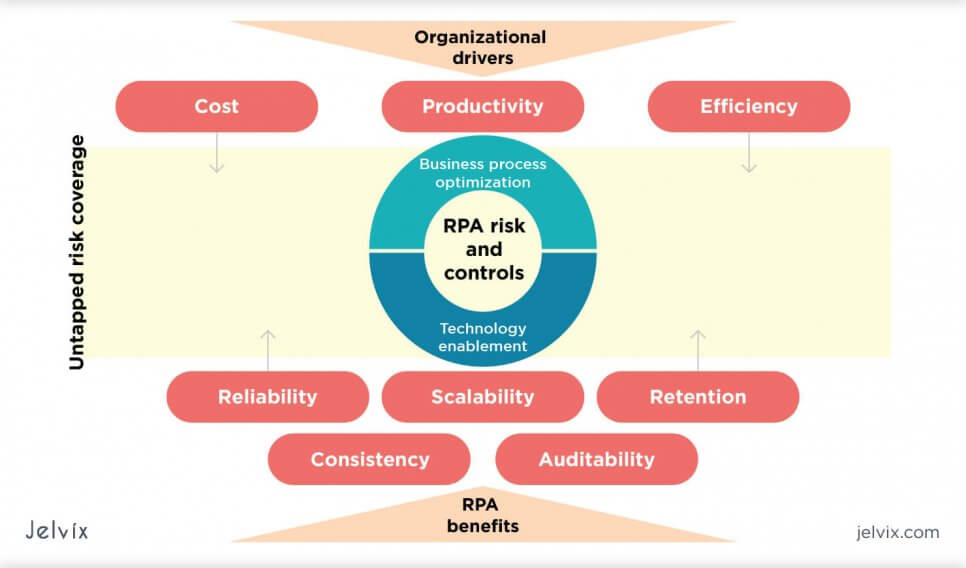
What is RPA?
First, let’s start by defining what RPA is. Robotic process automation, or simply RPA, is a form of business process automation technology that involves a software bot to automate enterprise operations, eliminating inefficiencies, reducing costs, and improving organizational performance. Through the use of RPA, companies can handle rule-based and structured business processes that are usually mundane and labor-intensive.
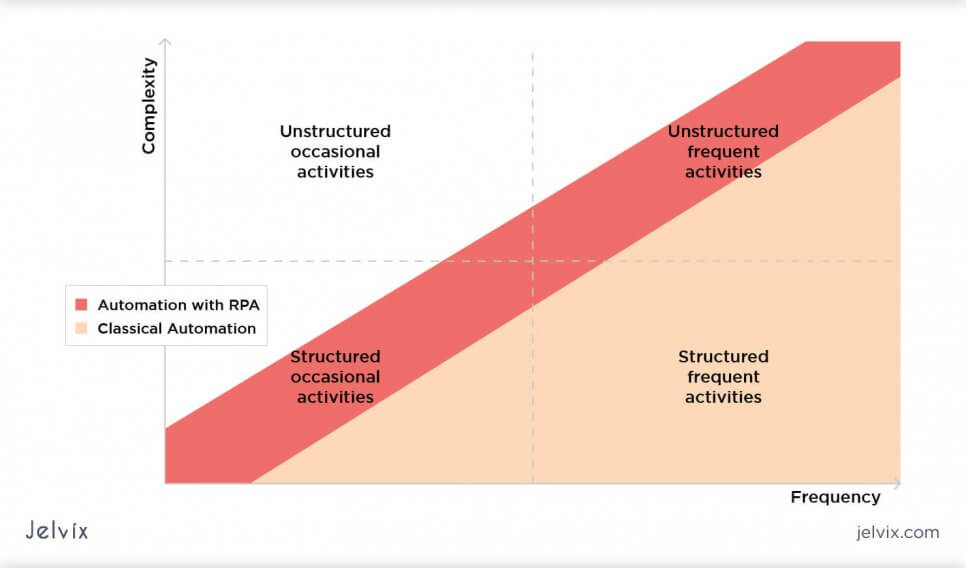
RPA bots can take on entire workflows of ERP data entries, from data gathering to logging, updating, processing, and validating. This may require data entry across systems without a common interface; some activities are simply too complex to automate through traditional means, and cannot be handled without RPA software.
As you can see above, some tasks are difficult to be automated with common technologies, simply because they involve high investments that rarely pay off. Moreover, the business climate is ever-changing: a company needs to continuously evolve its initial business activities to grow and stay relevant, so there is no better way than to keep them manual.
RPA Today
Modern RPA systems offer tools that partially or fully automate human activities. These kinds of tools cut a lot of time out of daily, weekly, or monthly tasks, freeing staff for more creative jobs and up-skilling. Often, back offices have hundreds of employees processing customer requests, transferring data from one system to another, printing, copying, etc.
For example, take accounting: 9 out of 10 office managers spend more than 15 hours a week on routine administrative tasks such as filling out forms or updating spreadsheets. Most big banks report that they are still managing customer-facing, front-end operations using manual tools, but would like to increase automation levels in their back offices.
While automation technologies are becoming more common within the financial sector, some banks are taking steps towards harnessing the considerable potential of this opportunity.
For example, one large universal bank determined that 50% of its operations, accounting for 45% of the current FTEs, could be fully automated. If an ideal level of automation was reached, these employees could be relieved of their back-office tasks.
Our research indicates that RPA offers solutions that can rescue these mundane procedures from needless expense and error. Moreover, by taking full advantage of RPA, companies, regardless of size and industry, can generate an improvement of more than 50% in productivity and customer service.
How Can RPA Benefit Industries Such as Banking, Insurance, and Retail?
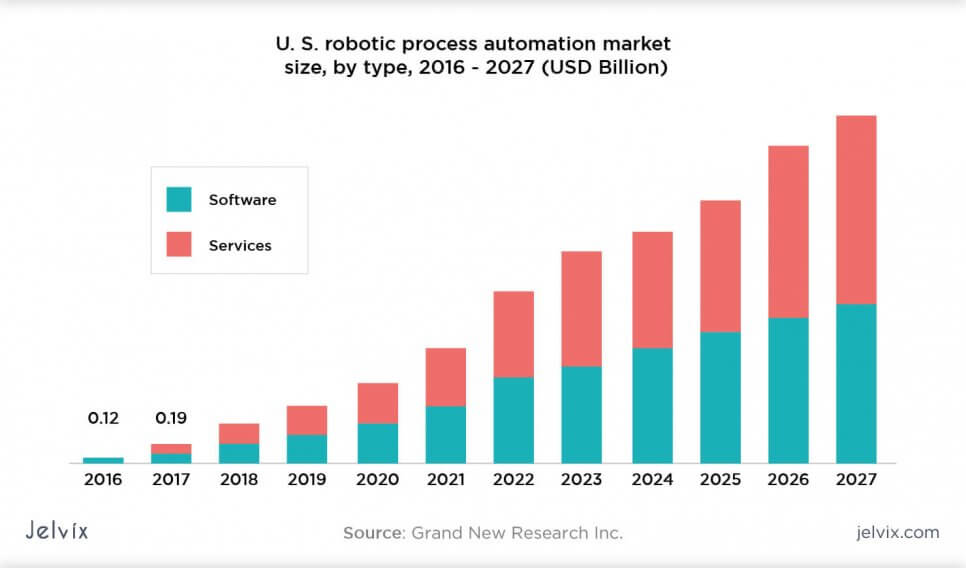
According to a new report by Grand New Research Inc., the robotic process automation market size is expected to reach $25,66 billion by 2027.
Even though RPA implies that physical humanoid robots will be doing white-collar tasks, it means the automation of processes within the existing application landscape.
What are particular processes RPA can automate? Well, software robots can do various things, from simple copy-paste or typing activities to those as complex as fraud detection or accounts payable.
RPA bots work at the user-interface level and can manipulate and pass data to and from different applications, trigger responses, execute transactions, and perform other basic tasks that people do manually.
A company can use RPA tools to automate the existing workflow, infrastructure and back-office, thereby enhancing employees’ work, and overall company’s productivity.
Below is a breakdown of major RPA use cases across industries like Banking, Insurance, CPG & Retail.
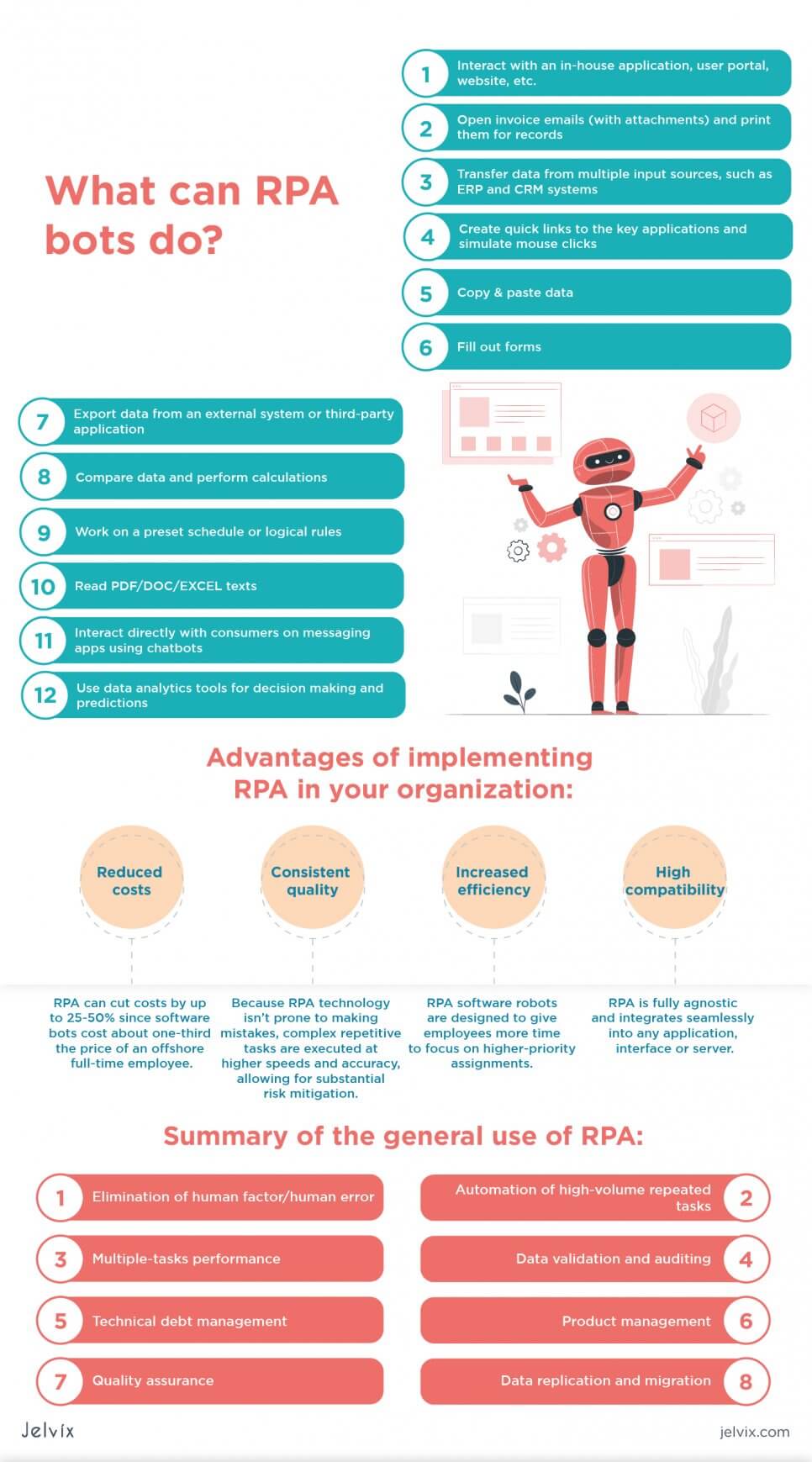
So, What Can RPA Bots Do?
- Interact with an in-house application, user portal, website, etc.
- Open invoice emails (with attachments) and print them for records
- Transfer data from multiple input sources, such as ERP and CRM systems
- Create quick links to the key applications and simulate mouse clicks
- Copy & paste data
- Fill out forms
- Export data from an external system or third-party application
- Compare data and perform calculations
- Work on a preset schedule or logical rules
- Read PDF/DOC/EXCEL texts
- Interact directly with consumers on messaging apps using chatbots
- Use data analytics tools for decision making and predictions
That sounds good, but what does it mean in practice?
Loan automation application example
Before RPA was introduced, loan application processing in one of the major US banks required gathering and structuring data from multiple databases, which usually resulted in poor document filing and human error. Bank employees would monotonously copy and paste the data in Excel spreadsheets, and this repetitive, remedial task required at least 50 employees.
Furthermore, 6 other employees were checking the entered information for errors. The stats show that 20% of the first group of employees responsible for data entry made 1-2 mistakes daily, and at least one of 9 employees responsible for proofreading missed at least one of the mistakes.
After adopting RPA, 30 employees out of 50 were reassigned to perform other tasks, whereas the error rate of loan application processing has been reduced by 10-15 times.
Following this logic, medical organizations, for instance, can use automation to handle check-in processes, patient records, claims, billing, reporting, etc. In the HR and recruiting industry, RPA tools can be used to automate tasks such as updating employees’ information, onboarding new hires, sendings recruitment offers, compensation, and so on.
The Impact of RPA on Business
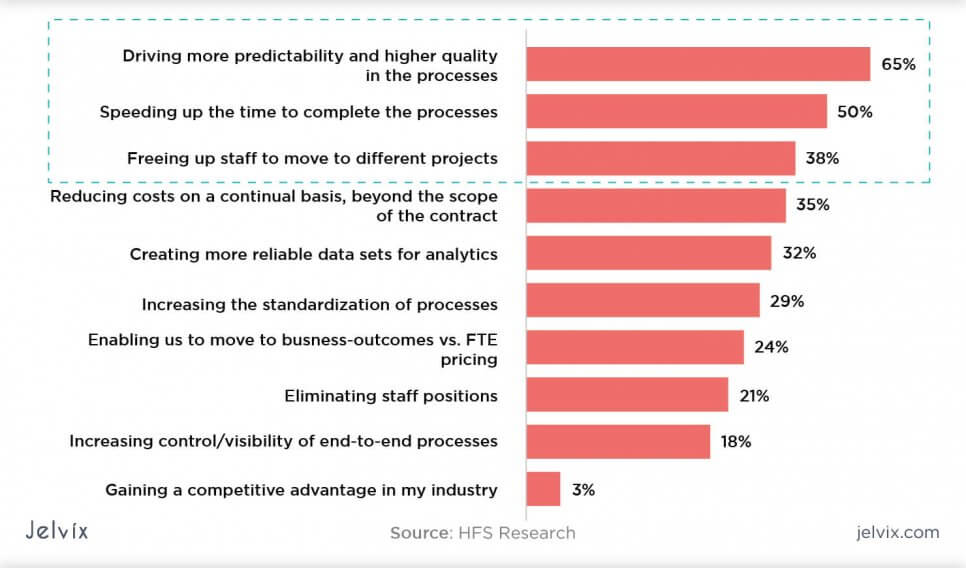
Now the time has come to assess the effectiveness of Robotic Process Automation in business. According to the survey conducted by HFS Research, many companies, that have integrated RPA into their digitalization solutions, have received tangible benefits and competitive advantage.
Listed below are some advantages of implementing RPA in your organization:
- Reduced costs. According to the Institute for Robotic Process Automation (IRPA), RPA can cut costs by up to 25-50% since software bots cost about one-third the price of a full-time offshore employee. Additionally, RPA software is a cheaper alternative to a full-scale BPM project.
- Consistent quality. Because RPA technology isn’t prone to making mistakes, complex repetitive tasks are executed at higher speeds and accuracy, allowing for substantial risk mitigation. Software bots operate on the rules they are coded with rather than human-based logic and therefore are immune to downtime or human error.
- Increased efficiency. RPA software robots are designed to give employees more time to focus on higher-priority assignments. Robots don’t take days off, weekends or holidays; add to this increased speed and decreased cycle time, and you’ll get high-quality end-to-end processes and supporting technology that will optimize your back office in a very short amount of time.
- High compatibility. RPA is fully agnostic and integrates seamlessly into any application, interface, or server.
Key Risks and Challenges Arising from RPA
- Costs. The RPA implementation process requires technical assistance and consultancy services. Also, with changes in the business process, RPA systems have to be readjusted as well. These processes entail add-ons.
- Process selection. Before implementing Robotic Process Automation into your business, you have to identify the processes which you want to automate.
- Reactive maintenance. For better (or for worse), robots cannot fully replace humans. The problem with RPA is that bots break, and if you put them in charge of business-critical tasks, they can break your business. So, to avoid this scenario, it’s important to have staff available to fix RPA bot breakage and provide them with troubleshooting documents.
- Monitoring. Monitoring bots is fundamental. For this, you should assign an RPA specialist to manage, control, and monitor your entire RPA program continuously.
- Cybersecurity and resilience. As robotics becomes mainstream, RPA bots pose a security risk as an attack surface. If the proper procedures are not incorporated, security vulnerabilities represent potential entry points for malicious hackers. To protect robots from cyber-attacks, make sure to grant management permission to trusted employees, and secure the RPA software environment with external controls.
- Luddism. Due to RPA’s potential to reduce the need for human power, employees usually rebel against automation. To prevent this from happening, business leaders create enthusiasm and support for RPA by engaging employees in developing the RPA strategy or/and repositioning them to more rewarding work.
RPA Use Cases
A report by Statista projects the worldwide RPA to register a CAGR of 27.7% from 2021 to 2030; the RPA market size is forecast to reach $23.9 billion by 2030.
Now, let’s take a look at some representative RPA use cases across various industries, including Manufacturing, Retail, Finance, IT, and HR.
1. Manufacturing
Robotic Process Automation enables manufacturing organizations to improve most of the processes within the Manufacturing domain. The existing practice of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Automation has already shown its effectiveness in monitoring cash, raw materials, production capacity, and business commitments: orders, purchase orders, and payroll.
Even more remarkably, RPA automation has increased the quality of other business functions, including logistics data, data monitoring, and product pricing comparisons.
Companies in the manufacturing industry were first to adopt automation technology, implementing processing lines and software bots to improve daily production activities (shipping and storage) and provide data accuracy (bill of materials, inventory reports, transportation management, etc.)
Statista reports that the factory automation segment is by far the biggest in the industry, and the bulk of investments in RPA technology is undertaken by discrete and process manufacturers. Accordingly, industrial software alone is expected to reach $59.5 billion by 2029.
The increasing investment by major manufacturing companies towards the implementation of RPA has opened up a huge potential for business growth.
Since the major focus has largely been on improving back-office processes, manufacturers can attain around 40% cost savings, improving productivity and reducing human intervention in redundant tasks; automating mundane tasks, as we mentioned above, will free employees up to more valuable and productive work.
2. Retail
Implementing Enterprise RPA is a great option for improving the company’s customer service standards, which is the primary concern in the Retail industry. Modern retailers implement new customer engagement CRM systems to provide excellent customer service and improve customer retention.
In case you can’t find a good solution for your CRM system, you could use RPA to automate processes ranging from filling, capturing data, updating and processing requests to extracting product data, inventory updating, importing websites, and email sales.
This just doesn’t stop there: the retail industry is expected to dive into extended futuristic automation and hence reach end-to-end robotic process automation. We encourage you to follow the latest RPA trends to deliver greater business productivity.
Below is a real-world example of a successful RPA implementation into organizational ERP.
Example: Many food supply & distribution companies are now considering automating delivery confirmation in ERP, following an Australian FMCG food company’s model.
Particularly, the Australian company provided software bots with the ability to extract and rename delivery docket pdf files, upload documents and match against sales orders in NetSuite cloud ERP, and report any unmatched deliveries.
As a result, the time required for processing the data was significantly reduced (by 95%), while process uptime and completion was 100%, achieving ROI by sidelining the process. The overall objective was to advance the delivery process (have real-time order and delivery visibility), ensure prompt resolution of non-delivery, and speed up a remittance of open invoices.
3. Financial Services
In the Financial Services sector, robotic automation is most commonly used to provide better compliance, mitigate risks, and improve overall customer experience. And this doesn’t stop here at all – the technology not only enables banks and finance companies to reduce manual efforts but also allows them to implement RPA into newer areas of the banking domain.
Due to easy implementation coupled with the ability to execute and maintain automation workflows (without coding), once set up, banking bots can take complete control of the systems.
This involves handling data validations, automatic report generation (e.g., filling in the SAR forms), customer onboarding, KYC and AML processes, mortgage lending, account opening, and financial claims processing.
So, in the extremely competitive banking sector, where everyone strives to attract clients with virtual solutions, workforce automation can play a crucial role in optimizing costs, increasing efficiency in processes, enabling scalability, and overall business growth.
4. IT
Automation is present in nearly every industry, and IT is no exception. There are many long-term, often tedious processes in engineering that involve human assistance.
Such processes include server patching, SQA queries (e.g., data query, data manipulation, data definition), file log monitoring, alert resolution, and many more. Even though these processes are of great importance, engineers hate them because there is no challenge in their routine nature.
Many IT departments spend more time than they might on password resetting, onboarding and offboarding users, while they could focus on more important, challenging tasks. Indeed, some systems don’t include the functionality to run back-end automation scripts, and in such cases, human intervention is indispensable.
For example, an IT department may already have a mostly automated system in place for account provisioning – the process which involves creating and updating user accounts, and changing accounts privileges.
Once the system administrator approves the request, the account is manually created. But to get the ball rolling, the administrator has to configure the new user’s security permissions manually.
Nevertheless, all the administrative processes mentioned in the first paragraph are suitable for RPA and can be executed by an RPA bot. As we have already mentioned, RPA bots are beautifully suited for automating thousands of functions across dozens of enterprise applications, from simple copy/paste processes to more holistic system analysis.
5. Human Resources
65% of HR specialists use Automation tools to process employment applications – RPA enables them to create a new digital business model for managing onboarding and offboarding processes, applicant sourcing, expense and reimbursement processes, etc.
In such cases, RPA can be used as a boost tool that not only enhances HR management but also brings efficiency and a faster return-on-investment.
For example, when hiring employees, their employment history, education, skills, and other important information is entered into different systems. In case these systems lack APIs, HR staff may need to transfer the data manually, instead of spending their valuable time on something more significant.
With the use of Robotic Process Automation, HR specialists can record themselves as they perform manual data transfers. A software bot can then use these recordings to automate the data transfer each time they receive a piece of new employee information, thereby making room in the recruiting team’s schedule so they can focus on important issues, such as improving the employee experience and the company’s workplace.
The following is the real-life use case example of HR automation.
Example: At UiPath, People Operations team employs an automated onboarding software to ensure that the employee admission process is comprehensive and carried out without further delay. Since the company specializes in automation technologies, no wonder they apply it to their own activities.
HR staff in UiPath used to manage vast amounts of employee data manually, spending much of the individual’s time on redundant, repetitive tasks. CHROs believe that an HR department has to offer an optimal digital experience as well as empower employees and retain top talent.
The new Digital Assistant demonstrates the high-level capability of completing the onboarding paperwork, allowing HRs to сonncentrate on more productive and practical duties such as CSR, enhancing a company’s reputation, and increasing employee retention.
Conclusion
We have come to the end of the article and hope you have enjoyed reading. Now that you have learned a little bit more about Robotic Process Automation, you can consider integrating the technology into your business.
Remember that your new RPA system must be aligned with your business strategy and goals. Define the desired ROI and ensure Policy and Corporate compliance. If you are not sure what processes to automate first, start with large, repetitive ones.
If you’d like to find out about our AI and machine learning services, get in touch today.
Need a certain developer?
Ramp up your development resources to reach new business objectives.