Healthcare is one of the most changing sectors, greatly influenced by modern technologies. The World Health Organization estimates there are about 2 million medical devices used worldwide, all of them categorized into 7000 generic groups.
Yet, the innovation doesn’t end there. An increasing number of companies are turning to software as a medical device (SaMD) solutions, which offer a more extensive range of functionalities compared to traditional medical devices and don’t depend on hardware.
If you aim to develop a custom SaMD solution but struggle to manage the whole process and keep up with complex industry regulations, this article is for you. You’ll find out the best practices and key steps to build a SaMD application that corresponds to the changing market demands and adheres to healthcare industry standards.
What is SaMD?
The International Medical Device Regulators Forum defines “software as a medical device” as a class of software solutions designed to carry out one or more medical functions without being part of a hardware medical device. SaMDs can diagnose, monitor, or offer treatment plans for various medical conditions. SaMD leverages data from diverse sources, including health records and personal monitoring devices, to assist physicians in providing medical recommendations to patients and support decision-making.
Software as a Medical Device Examples
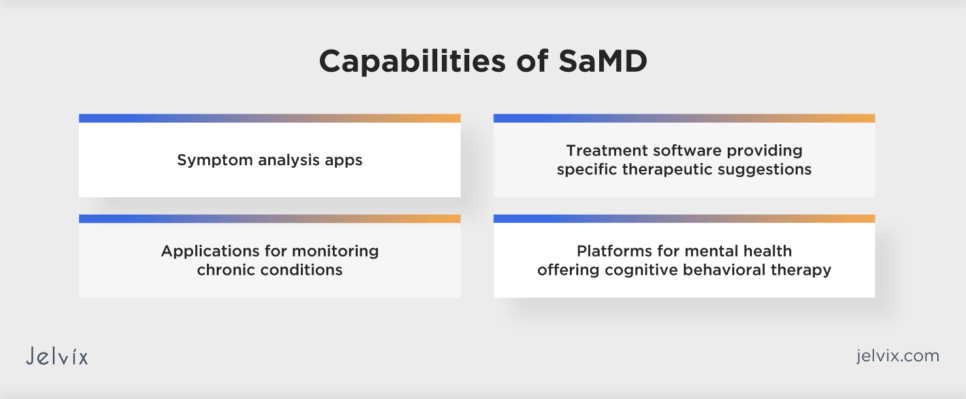
SaMD products can support various aspects of healthcare, from diagnosis to monitoring, enhancing patient care through technology:
- Diagnosis apps: mobile or web applications that analyze symptoms reported by the user or data collected from wearable devices to diagnose conditions like skin cancer or diabetic retinopathy;
- Treatment software: programs that provide specific therapeutic suggestions based on patient data, such as software that generates personalized rehabilitation exercises for patients recovering from surgery;
- Monitoring applications: apps that monitor chronic conditions, such as diabetes or hypertension, analyzing data from external devices (like glucose meters or blood pressure cuffs) to alert patients and doctors about potential health issues or adjustments needed in treatment;
- Mental health platforms: applications offering cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) for depression, anxiety, or PTSD, providing users with therapeutic exercises and tracking their progress over time.
Is Your Application SaMD?
To determine if your application is SaMD, consider the following criteria typically used by regulatory bodies like the Food and Drug Administration in the U.S:
- Medical purpose: your application must be intended for a medical goal, including diagnosing, monitoring, treating, or reducing the impact of a disease, injury, or disability;
- Operates independently: the software should function independently of any other hardware, though it may receive data from such devices. If it requires integration with a hardware device to operate, it might not be considered a standalone SaMD;
- Clinical benefit: the application must provide a clinical benefit or be intended to support or provide recommendations to healthcare professionals or patients regarding healthcare conditions.
If your application meets these criteria, it likely qualifies as a SaMD. This classification means it will be subject to specific regulatory requirements and standards to ensure its safety and effectiveness in healthcare settings.
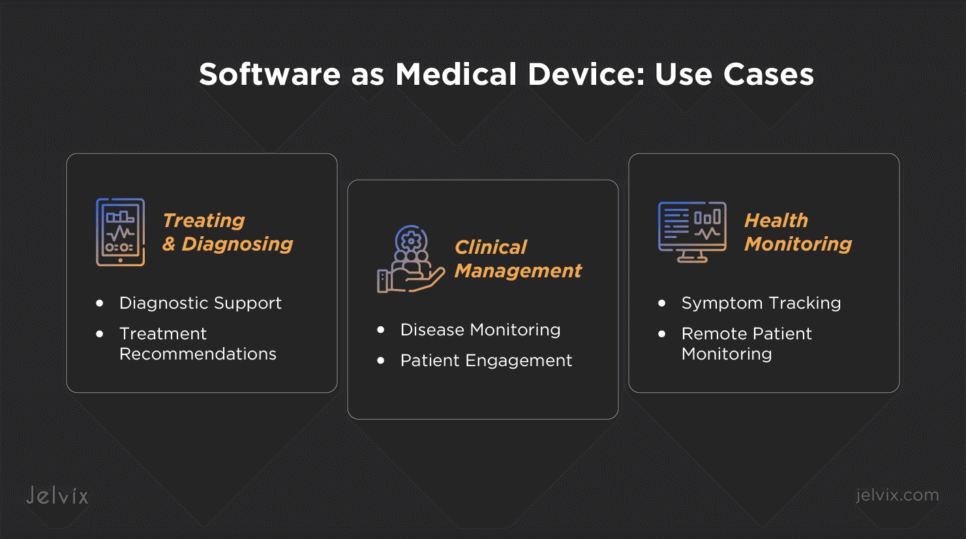
Software as Medical Device: Use Cases
SaMD products aid care delivery through a wide range of applications that allow healthcare entities to improve patient outcomes and streamline healthcare processes.
Treating and Diagnosing
SaMDs play a crucial role in the treatment and diagnosis of various conditions. By analyzing data from multiple sources, such as medical histories, diagnostic images, or direct patient inputs, these applications can identify health issues and suggest appropriate treatments.
Diagnostic Support
SaMDs can analyze medical images, such as X-rays and MRIs, to assist in identifying diseases like cancer or fractures, helping physicians make more accurate diagnoses.
Treatment Recommendations
These applications can offer personalized treatment options based on patient data, potentially adjusting medication dosages and aiding doctors in recommending specific therapeutic interventions.
Clinical Management
SaMDs leverage clinical management by offering tools to support healthcare professionals in monitoring and managing patient care effectively.
Disease Monitoring
Applications that track disease progression or monitor chronic conditions in real time alert healthcare professionals about changes in a patient’s condition that may require intervention.
Patient Engagement
SaMDs can engage patients in their care, providing features such as medication reminders or platforms for recording symptoms. This can improve patients’ adherence to treatment plans and facilitate communication between them and doctors.
Health Monitoring
SaMD applications focus on the continuous observation of patients to assess their health status or disease progression over time. Health monitoring SaMDs are beneficial for managing chronic conditions, post-operative recovery, and preventive care.
Remote Patient Monitoring
Remote patient monitoring apps allow healthcare pros to monitor patients’ vital signs, such as heart rate, blood glucose levels, or blood pressure remotely. This is especially useful for patients with chronic conditions like diabetes or hypertension, enabling timely adjustments to treatment plans without the need for frequent in-person visits.
Read about the remote patient monitoring and implementation steps.
Symptom Tracking
SaMDs enable patients to log symptoms or side effects in real time, providing valuable data for doctors to monitor treatment effectiveness and patient well-being. This direct input from patients enhances personalized care and can lead to more informed care decisions.
SaMD Market Stats
The SaMD market is on the rise. According to BCC Research, it is expected to expand to $8.2 billion by 2027, with a compound annual growth rate of 11.0% and North America leading the market. This growth is greatly driven by increasing patient demand for more convenient diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring.
Another factor that impacts growth in the SaMD market is the increasing adoption of IoT devices in healthcare. In 2021, 4 out of 5 patients favored remote monitoring in their care, resulting in a wider adoption of medical devices of various types. In turn, IoT and RPM adoption is mostly driven by the need to treat and monitor chronic diseases that have accounted for 74% of global deaths in 2023.
Industry Regulations To Consider When Developing Medical Software
The SaMD sector is under stringent regulatory control to ensure that these digital solutions are safe, effective, and reliable. Because of their direct impact on patient health and the potential risks involved, regulatory bodies worldwide established comprehensive compliance guidelines that help oversee the entire lifecycle of a SaMD, from development to deployment and ongoing support.
Compliance Guidelines
In response to the challenges and opportunities presented by SaMD, the IMDRF introduced comprehensive compliance and quality management guidelines in 2013. These guidelines serve as a foundation for companies to safely introduce SaMD innovations into the healthcare market.
Explore the power of FHIR standards for healthcare interoperability and boost patient care efficiency.
SaMD Leadership and Expertise
A crucial initial step for companies entering the SaMD environment is to secure management support and cultivate expertise in SaMD product design and development.
Regulatory bodies emphasize the importance of having a skilled team with expertise in healthcare, software development, and regulatory fields. This team is responsible for ensuring that the SaMD complies with all relevant regulations and meets user needs.
Healthcare companies must also develop a clear regulatory strategy that outlines how their SaMD solutions meet specific regulatory requirements, considering the classification of the device, the intended use, and the target market.
SaMD Lifetime Support
Success in the SaMD market requires careful product management throughout the product life cycle, including product planning, risk management, documentation, and compliance.
Continuous monitoring of the SaMD after it has been deployed includes tracking the performance of the device, gathering user feedback, and reporting any adverse events to regulatory authorities.
Regulations also require that SaMD providers maintain and update their software to address any emerging risks, software bugs, or security vulnerabilities, ensuring the ongoing safety and effectiveness of the device. Companies should follow standard operating procedures (SOPs) for managing and complying with regulations effectively.
SaMD Product Implementation
SaMD compliance mandates follow specific systems and processes for product realization. SaMD providers should implement quality management systems (QMS) to cover all aspects of production, from software design and development to testing, deployment, and post-market activities.
Demonstrating clinical efficiency through robust clinical evaluations or studies is another regulatory requirement. This involves collecting and analyzing clinical data to confirm that the SaMD achieves its intended medical purpose without exposing users to any risks.
The IMDRF’s guidelines offer a structured approach to navigating the regulatory environment for SaMD apps, ensuring that companies can innovate effectively while upholding the highest standards of patient safety.
Medical Software Development: Key SaMD Functionality
SaMD applications offer a range of functionalities designed to improve patient outcomes, ensure data security, and streamline healthcare management processes. The Jelvix team recommends that your SaMD products include the features listed below.
Medical Functionality
Basic medical functionalities ensure that SaMDs can effectively support a wide range of healthcare activities, from preventive care and chronic disease management to acute care interventions.
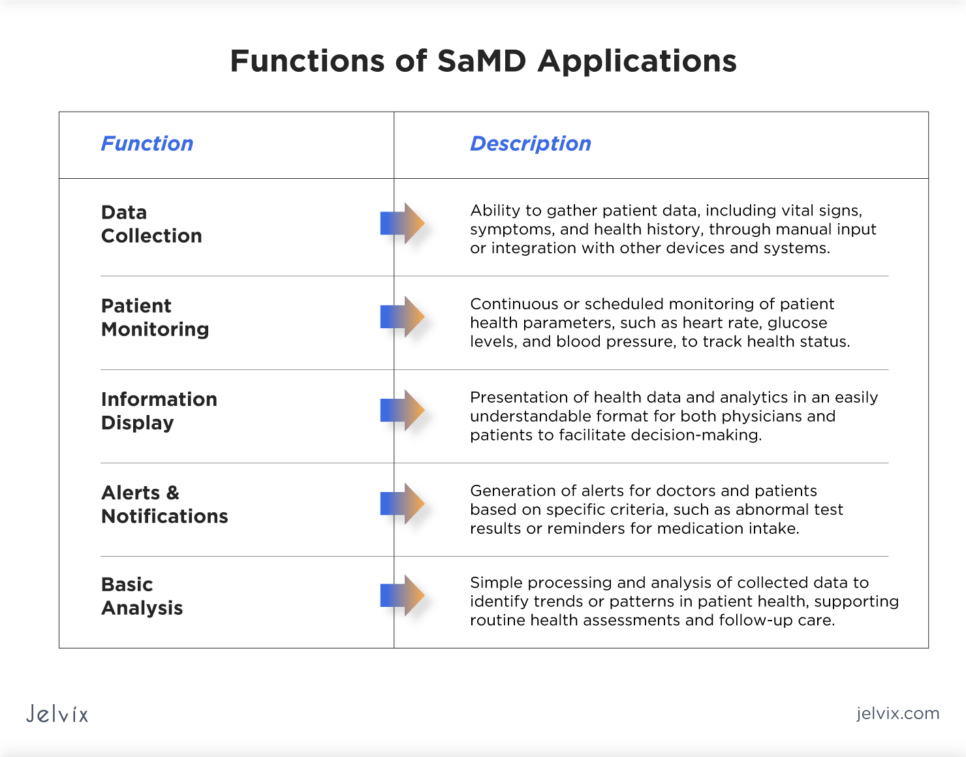
The basic functions of SaMD applications usually include:
- Data collection: the ability to gather patient data, including vital signs, symptoms, and health history, through manual input or integration with other devices and systems;
- Patient monitoring: continuous or scheduled monitoring of patient health parameters, such as heart rate, glucose levels, and blood pressure, to track health status and detect any significant changes that may require attention;
- Information display: presenting health data and analytics in an easily understandable format for both physicians and patients to facilitate decision-making;
- Alerts and notifications: generating alerts for doctors and patients based on specific criteria, such as abnormal test results or reminders for medication intake, to ensure timely actions are taken;
- Basic analysis: simple processing and analysis of collected data to identify trends or patterns in patient health, supporting routine health assessments and follow-up care.
Advanced Medical Functionality
Advanced medical features relate to technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning to perform complex medical tasks. These might involve analyzing diagnostic images for signs of diseases such as cancer or heart conditions, monitoring vital signs to predict potential health issues before they become critical, and aiding physicians in providing personalized treatment plans based on a patient’s health data.
Telemedicine is another advanced feature, which enables remote consultations between patients and doctors. It’s especially valuable for those in remote or underserved areas, improving access to medical advice and services. With a telehealth solution, SaMD can support real-time communication and secure medical data exchange, narrowing the distance between patients and healthcare teams.
Data Storage and Compliance Features
A critical aspect of SaMD functionality is its approach to data storage and compliance. These features are vital for managing sensitive patient information and ensuring that SaMDs meet the standards set by healthcare regulations. Implementing data storage and compliance features ensures that SaMDs can be trusted by both doctors and patients, maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of health information while supporting the delivery of high-quality care.
Cloud Data Storage
Cloud data storage is a scalable and efficient solution for managing the vast amounts of data generated and used by SaMD applications. This includes patient health records, diagnostic images, treatment plans, and other health-related data. Cloud storage allows for real-time access to data by authorized users from anywhere, facilitating telehealth services and remote patient monitoring. What’s more, cloud infrastructure supports healthcare interoperability, ensuring that critical health information is securely exchanged among various devices and systems.
Security Compliance
As SaMDs monitor and manage sensitive health data, they should adhere to strict security requirements to prevent unauthorized access, breaches, and other cyber threats. Security compliance in SaMD applications encompasses a range of measures, including:
- Encryption: encryption both at rest and in transit ensures that data is converted into a secure format that is unreadable to unauthorized users;
- Access controls: implementing role-based access controls limits data access to authorized individuals who require it for legitimate medical or administrative reasons, reducing the risk of unauthorized data exposure;
- Audit trails: maintaining comprehensive audit trails provides a transparent and reviewable data access log essential for security audits and compliance checks;
- Regulatory adherence: SaMDs should adhere to strict regulations such as HIPAA in the U.S., GDPR in the EU, and other relevant local laws. Compliance with these standards ensures that SaMDs meet the highest levels of privacy, security, and data management;
- Multifactor authentication: adding MFA requires users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access to the SaMD, significantly enhancing security. This layered approach to authentication makes unauthorized access much more difficult, providing an additional layer of security against potential breaches.
Management Features
Efficient management features are vital for the marketing success and user adoption of SaMD products. These features help ensure that the software is used as intended and reaches its target audience.
In-App Guidelines
In-app guidelines provide users (both healthcare pros and patients) with clear instructions on how to effectively use the SaMD. These guidelines empower users to use the SaMD more efficiently, leading to better health outcomes and positive user experience. In-app guidelines usually include:
- Tutorials: interactive tips that guide users through the features and functionalities of the app, ensuring they can leverage its full potential;
- Best practice tips: recommendations on best practices for using the app in clinical settings or daily monitoring, enhancing the quality of care and user experience;
- Notifications: patients receive alerts on taking medicine or doing exercises, while doctors are notified about patient checks or medical manipulations;
- Compliance information: info on regulatory compliance and data protection practices, reassuring users about the safety and privacy of their data.
Marketing
Effective marketing strategies are essential for the successful launch and sustained adoption of SaMD products. Key marketing efforts include:
- Educational content: creating and distributing content that educates the target audience about the benefits of the SaMD, establishing the product as a valuable tool in healthcare;
- User testimonials: sharing success stories and testimonials from early users can provide real-world evidence of the SaMD benefits, encouraging adoption;
- Digital marketing campaigns: using social media, email marketing, and online advertising to reach potential users, raise awareness, and drive adoption;
- User feedback: surveys to collect feedback from users, enabling SaMD developers to understand user satisfaction, identify areas for improvement, and tailor the product to better meet user needs.
Through targeted marketing efforts, SaMD providers can effectively communicate the value of their products, differentiate them in a competitive market, and encourage widespread adoption among physicians and patients.
8 Steps To Develop Medical Device Software
Developing SaMD applications involves a structured and careful process to ensure the final product meets the strict standards of safety, functionality, and regulatory compliance required in healthcare. The Jelvix team recommends that you adopt a step-by-step development approach to make the whole process logical and comprehensive.
1. Gathering Requirements
The first step involves understanding the specific needs the software intends to address, including medical objectives, user needs, and regulatory requirements. This involves consultations with healthcare professionals, end users, and regulatory bodies to ensure a comprehensive understanding of what the software needs to achieve.
2. Creating a Roadmap
Based on the gathered requirements, create a detailed project roadmap, outlining the development lifecycle, key milestones, and timelines. This strategic plan will serve as a guide for the project, ensuring all stakeholders are aligned on the goals and timeframe.
3. Writing Specifications
With a clear roadmap in place, the next step is to write a detailed specification document. This paper outlines the software’s functionality, architecture, data flow, security measures, and compliance considerations, serving as a blueprint for the development team.
4. UX/UI Design
The design phase focuses on creating an intuitive and user-friendly interface. For medical device software, the UX/UI design must consider the diverse range of users, from patients to healthcare professionals, ensuring ease of use, accessibility, and clarity in presenting medical information.
5. Product Development
Product development involves coding the software according to the specifications. This stage employs agile development methodologies, allowing for flexibility, ongoing testing, and iteration based on feedback. Developers must adhere to the best practices in coding, security, and data protection, especially when handling sensitive health information.
6. Quality Assurance
QA is a critical component of the development process, involving rigorous testing to ensure the software functions correctly, meets all specifications, and complies with industry regulations. Testing includes unit tests, integration tests, usability tests, and security tests, among others.
7. Deployment
Once the software has passed QA testing, it is ready for deployment. Deployment strategies may vary, including rolling out the software in stages or a full launch, depending on the complexity and scope of the product. Proper planning is essential to ensure a smooth delivery to users.
8. Support and Maintenance
Make sure to conduct ongoing support and maintenance after deployment to address any issues, make necessary updates, and ensure the software remains compliant with any changing healthcare regulations. This stage involves continuous monitoring, user support services, and regular updates to improve functionality and security.
Jelvix Expertise in Medical Software Engineering
While the advantages of SaMD products for clinics are undeniable, not every healthcare facility can leverage them due to the complexities involved in their development. Building SaMD requires expertise in both technical and legal domains, making it challenging for many clinics to pursue independently.
If you’re aiming to improve healthcare outcomes through a SaMD application, collaborating with a proficient software development partner is essential. At Jelvix, we specialize in streamlining the process of building SaMDs by employing proven development methodologies, leveraging the latest technologies, and adhering to stringent security standards.
For tailored consultation on achieving your healthcare objectives through SaMD applications, our experts are ready to assist you. Contact us today to explore how we can help you navigate the complexities and realize the full potential of your healthcare innovations.
Streamline Your SaMD Development with Jelvix
Get in touch for personalized consultation on developing technology solutions for the healthcare industry.