Our current generation of millennials craves instant gratification, evident in our fast-paced society and how we use the Internet today. It’s known that 55% of web users spend less than 15 seconds on a web page before losing focus. There’s more. 47% of users won’t wait more than two seconds for a website to load, and more than 60% will leave a site if they can’t find what they’re looking for within about five seconds. Slow-loading websites cost retailers around $2.6 billion in lost sales each year. This clearly explains why interactive and intuitive web designs have become more critical.
And with only 15 seconds to make a great impression and deliver value to web users, developers will certainly have their work cut out for them. However, the solution is to design better websites with great UI, excellent user experience, and responsive designs.
Bootstrap and Material Design have been helping developers achieve this goal for years now. And as they both are giants in the industry, there’s always the question of which is better than the other. We analyzed these two web development platforms, drawing out their similarities and appreciating their differences to understand the unique role in crafting high-quality websites and applications.
As a front-end developer, if you find yourself wondering which is a better design tool or struggling to decide which is better for your web design projects, sit tight and find the answers to your questions in our article on Material UI vs Bootstrap in a few short minutes.
What is Bootstrap material?
Bootstrap is a free, open-source CSS framework for building responsive websites and web applications. Who developed Bootstrap – it was Twitter. But now it is an independent platform. It provides powerful tools for building dynamic and adaptable websites and web applications. It is primarily built on CSS but also has some HTML-based templates and support from JavaScript components, mainly jQuery.
Since its launch in August 2011, Bootstrap has become one of the most popular web design systems. Bootstrap provides developers with an array of useful design elements and components for making websites and web apps that are highly optimized for mobile use, even without writing a single line of code.
Material: The Basics
Material Design by Google is an advanced design platform that furnishes developers with an exhaustive framework for creating websites and applications with highly interactive, mobile-first UIs and responsive designs. Material Design is based on the expanded card motif system Google Now uses.
It includes responsive grid-based layouts, animations, and transitions, aiming to deliver high-quality output and consistent UX across all platforms.
As a design language, Material has a set of guidelines and rules for approaching different design situations. But it’s more than just a design language.
Material brings a new meaning to design with fluid motions, tangible surfaces, and vivid colors. These elements mirror the real world with subtle visual cues, eliminating the need to engage the cognitive mind. It aims to eliminate ambiguity and create great UI/UX with the ultimate intuitive designs.
Material Design vs Bootstrap: How They Compare
Browser Compatibility
Every developer understands the importance of browser compatibility for websites and web applications. For a website to be compatible with different browsers, it needs to look perfect and remain functional in each one. This be a little tricky to achieve because web browsers interpret website code in different ways. Thankfully, both Bootstrap and Material took this into account and gave their design tools the ability to adapt to each browser and remain functional.
Browser compatibility doesn’t only determine how webpages appear on different browsers; it also improves web traffic and significantly boosts performance.
In this category, Bootstrap and Material are evenly matched. Bootstrap adjusts layouts and handles coding differences automatically, so it works on modern browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and even older browsers like Internet Explorer. Material Design focuses on smooth animations and adaptable layouts that work well on web and mobile browsers.
Responsive Grid System
We live in a fast-paced world where people work on-the-go, and virtually everyone spends incredible amounts of their time each day glued to their smartphones. Mobile phones have evolved to small computers, and accessing the Internet via these devices accounts for 51.53% of the worldwide web traffic, which only emphasizes the need for responsive web pages.
Waaark is an example of a Material-based website
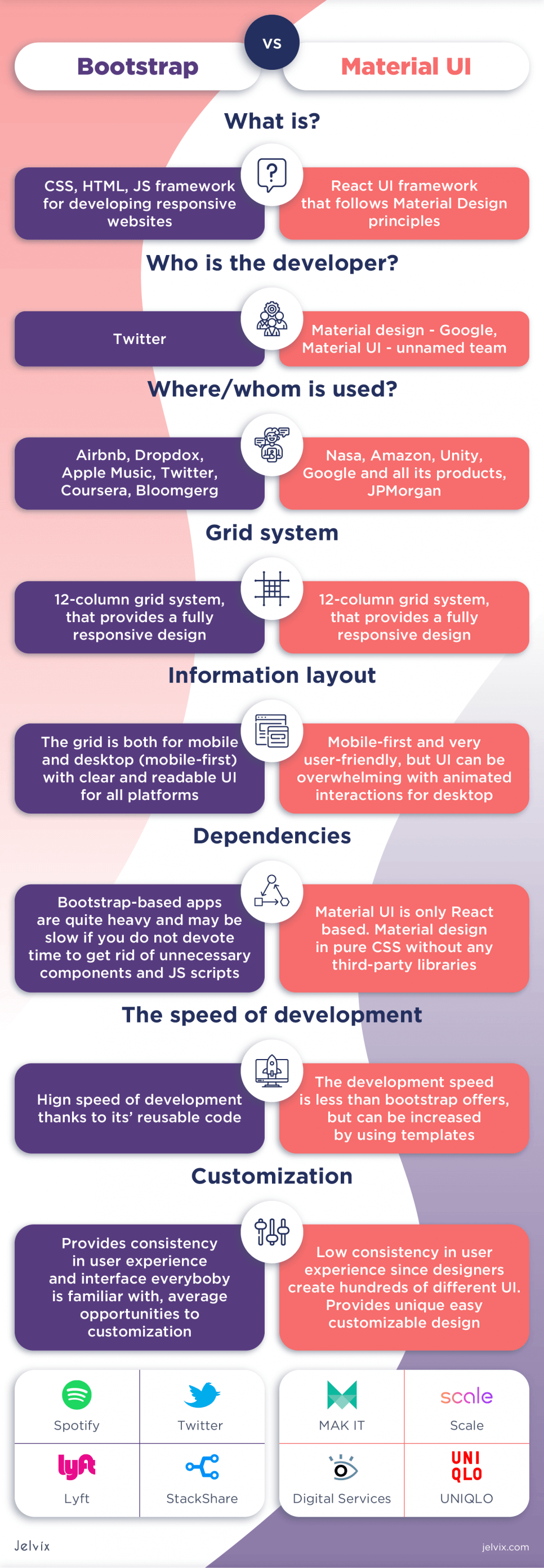
These two design tools utilize a grid system based on columns with similar structure and class names but not without distinct features. Created as a completely responsive framework for building mobile-friendly websites, Bootstrap anchors on a fluid 12-grid system to achieve the flexibility required for a high responsive mobile-first website.
The Bootstrap grid system uses containers, rows, and columns to ensure that apps and websites are adaptable to devices of varied screen sizes, especially mobile screens. This 12-grid system follows a series of defined rules; for instance, rows are only used to create columns; rows must be empty; rows and columns come together to create containers, etc.
Material Design also leverages a 12-grid system for creating its responsive UI. To ensure that developers give users an integrally responsive UI, Material’s 12-grid system uses columns, gutters, and margins to provide a very flexible layout, which achieves the ultimate goal of a completely responsive design.
And as the end-users switch from laptops to mobile devices, the website automatically resizes and rearranges its features to perfectly adapt to the new screen size. Responsive designs not only make working on different devices seamless but also improve speed and efficiency.
Customizable
Although both Bootstrap and Material are hinged on a 12-grid system with a set of rules and guidelines, they are both easily customizable. Any developer can create a unique website using either Material or Bootstrap, coupled with some imagination and a little creativity.
Bootstrap is built for easy web design, and with a few changes, you can make something of your own. However, Material Design offers more options for customizations and trumps Bootstrap in this section. Material offers more flexibility and gives developers more room to play around and come up with something truly unique, as it perfectly integrates rules and flexibility.
The developers using Bootstrap, who want to achieve the level of customization that Material offers, will have to first go through the Bootstrap framework to identify and discard design elements they do not need, and this can be tiresome.
Bootstrap vs Angular Material: Key Differences
Design Intent
There is no doubt that both Bootstrap and Material were created for web developments. However, at the very core, these two design platforms were created with completely different ideas.
While Material Design focuses on how various design elements interact to create an aesthetically-pleasing website that is also mobile-friendly, Bootstrap is more concerned with making websites and web apps responsive and functional. This is the sole reason why Material Design offers more flexibility and gives room for creativity.
Dependencies
With tons of scripts, features, CSS classes, and jQuery dependency, Bootstrap has proven to be a somewhat complex framework. This gives rise to problems like a slow and bulky app with lots of useless features that lower performance and drain battery.
Optimizing your Bootstrap-based app and improving performance requires you to sort through the framework and remove any components you do not need. In contrast, Material Design has React-based components that are independent of each other, enabling developers to work with only what they need or want to use.
Apple Music is an example of a Bootstrap-based website
Design Process and Components
Both Material and Bootstrap come with an impressive number of components and guidelines that provide the foundation developers can build on. Here, you can find both similarities and differences within the design systems.
For instance, both Bootstrap and Material have menu components with very different implementations. The Bootstrap navbar component is equivalent to the toolbar in Material, but Material has a sidebar component, which Bootstrap doesn’t.
The design systems feature components for both a regular menu and a drop-down one, but incorporating the drop-down menu in your Material-based website will require a lot of twerks and plugins. At the same time, Bootstrap makes it as seamless and simple as other customizing options.
Bootstrap provides developers with a standard default system for creating easy websites and web applications, while Material offers a wide range of features for creating eye-catching websites with bold colors and engaging animations.
Consistency and Uniqueness
Bootstrap doesn’t just want to make building responsive and mobile-friendly websites easy for developers. It also aims to give both web users and developers some form of consistency across all platforms.
And there is a high level of consistency between Bootstrap-based websites and applications, making them very intuitive and user-friendly but at the same time not unique. When you think of creating a different and truly unique website, Material is definitely better than Bootstrap.
With very little UX consistency and highly customizable features, Material gives developers a plethora of options for creating tons of different UI with guidelines for colors, shapes, typography, animations, navigation, etc., and your only limit is your imagination.
Community Support
This is where Bootstrap shines. It has a large and active online developers’ community and an incredible amount of resources on its website to provide the developers using Bootstrap with the necessary support.
This ensures that web development is made as easy as possible and any problems encountered by developers are promptly fixed. Bootstrap also takes code documentation very seriously, which improves code readability, code maintenance, and usability by other developers.
The commitment of the Bootstrap team to fixing issues quickly and regularly improving the efficiency of their framework is really commendable. Material also offers community support for developers, but it doesn’t quite measure up to what Bootstrap already has in place.
Find out why we consider React JS faster than Angular.
What is Bootstrap Best for? Any Drawbacks?
Bootstrap is currently one of the most used UI libraries for developers. It offers an impressive collection of themes available and has all the requirements for tackling new web design projects in a relatively short time.
The Bootstrap framework is set up for both professionals and beginner developers who do not have any advanced design or coding skills. With Bootstrap, even beginner developers can find their way around and come up with beautifully designed websites in a short period of time. It requires minimal design skills, very little imagination, and almost no creativity.
The tons of integrated features make it possible for just about anyone with basic design skills to build a responsive website without having to write a single line of code themselves. All you have to do is select your desired theme, pay, download, and start making any changes you want.
While it seems like the perfect tool for building websites and web applications, Bootstrap does have a couple of drawbacks, which we discuss below.
Lyft is another Bootstrap-based website
It’s a Bit too Consistent
The Bootstrap framework was created to enable developers to build mobile-friendly and responsive websites, using a standard interface and investing very little time and effort. The end result is always a familiar interface that provides consistency in the user experience. However, there might be a problem with it – all Bootstrap-based websites have this uncanny resemblance to each other.
With bold headlines and similar typography, these websites are very alike and easily recognizable since none of them is unique. This is more so when different developers use the same theme for their websites despite the changes they may have made to the theme.
Since Bootstrap doesn’t give much room for customization, websites with similar themes even look more alike. And if you want something truly unique, Material UI and Foundation are some great alternatives to Bootstrap.
It Ban Be too Bulky
As a framework that uses CSS and HTML templates with jQuery dependencies, this can add bulk to a site, making it unsuitable for simple websites. But there is a solution to this problem.
Creating a lightweight Bootstrap website will require you to discard every component you find useless first, but usually, this is not easy and takes a whole lot of time, which significantly reduces the speed of development.
What is Material Best for? Any Drawbacks?
While Bootstrap has the primary aim of helping developers make responsive websites fast, Material Design is focused on enabling developers to create the best UI/UX they can imagine.
Material Design is still very responsive and mobile-friendly. Still, it aims at creating profound interactions between design elements, transitions, and animations, ensuring they seamlessly come together to make a perfect replica of what is obtainable in real life.
It hinges on making interactions between users and surfaces more responsive and intuitive than ever and provides a comprehensive design platform with a set of guidelines for any form of complex design.
And following laid out guidelines, developers can better navigate the system and combine subtle animations with bold colors to come up with something interactive, intuitive, and authentic, not to mention visually appealing. Even as one of the best Bootstrap alternatives, Material Design still has a few drawbacks.
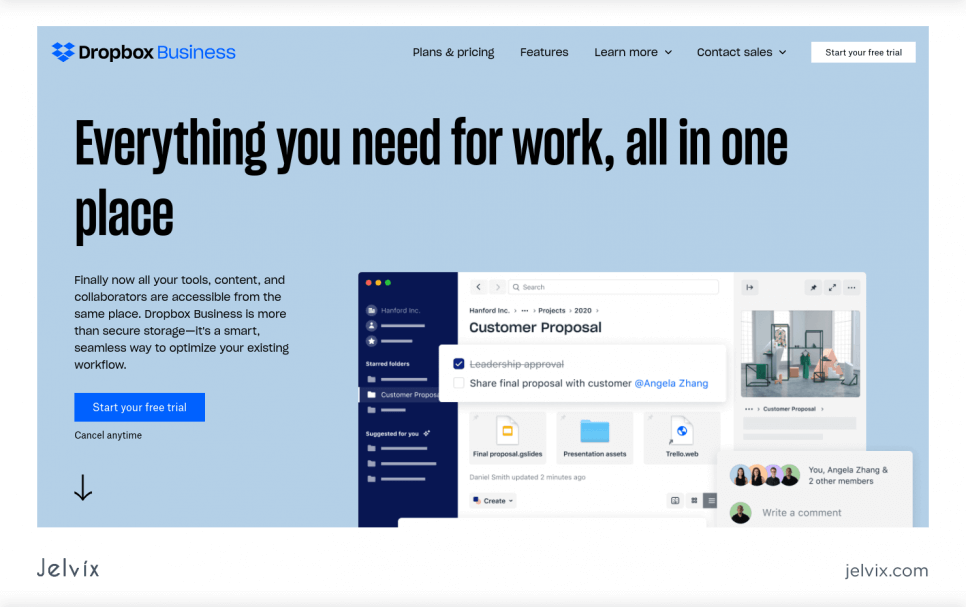
Dropbox Business is another Material-based website
It’s Somewhat too Comprehensive
Material Design has a comprehensive set of rules for tackling virtually all design problems. These guidelines provide developers with solutions to all potential design problems, which, on the one hand, is fantastic. However, it can prevent creatives from digging deep within themselves to provide inventive solutions to real issues, thereby impeding innovation.
The comprehensive nature of Material Design can also overwhelm beginner developers as they may feel lost in the vast and complex design specifications; exhaustive rules and considerations maybe a little too much for newbies.
Some Designs are Not Very Intuitive
We know the importance of intuitive designs. Users should never have to think or guess what actions different features and buttons represent on a webpage or a web app. Because when this happens, it significantly reduces the functionality and usability of the site, and a negative user experience defeats the whole aim of intuitive designs.
Creating intuitive designs means that every design element, including icons and buttons, should serve a clearly defined purpose. While Material Design has achieved this aim on many occasions, it still has icons that are not immediately recognizable, interfering with usability.
For instance, the circular floating button you can see in many Android apps usually has space for only an icon with no descriptive text to specify what function it performs.
The floating action button is certainly beautiful and visually appealing, but if the icon is not immediately recognizable and users have to click on it to find out what purpose it serves, this constitutes a bad UX design. And in web design, aesthetics should never trump intuitive designs.
FAQs
Can We Use Bootstrap and Material Together?
Yes, it’s possible to work with Bootstrap and Material Design simultaneously. These two design systems have their differences, but they also have a lot in common, and you can use one to compliment the other.
For instance, if you’re working on a project with Bootstrap and decide you need a few components available in Material but not Bootstrap, you can incorporate whatever Material components you need to your Bootstrap project.
Alternatively, you can use Material Design for Bootstrap (mdbootstrap), which is a Bootstrap design tool for building Material Design apps with HTML, CSS, and JS.
Angular Material vs Bootstrap: Which Has a More Flexible Layout
From the discussions above, it’s apparent that Material Design has more flexibility and offers creatives more opportunities for customization while exploring their creativity. Bootstrap, on the other hand, maintains a more consistent UI/UX and has a less flexible framework.
Can I Convert Bootstrap to Material?
Despite the glaring differences between the two, the Bootstrap and Material frameworks have a lot in common; therefore, it’s absolutely possible to convert a Bootstrap website to Material. However, the simplicity of this endeavor will depend on the size and complexity of the website.
A simple Bootstrap-based website with only a few changes will be easier to convert to Material. However, if the site in question is large with a highly customized Bootstrap framework, it may be a little complex.
Do Professionals Use Bootstrap?
Bootstrap is undoubtedly an excellent design tool for developers, and professional front-end developers also find it useful. When working on a project, most professionals will use whatever tools that will permit them to accomplish their objective within a given time frame, and if it means using Bootstrap, then Bootstrap it is. It’s an excellent tool for building responsive and functional sites within a short time and with ease.
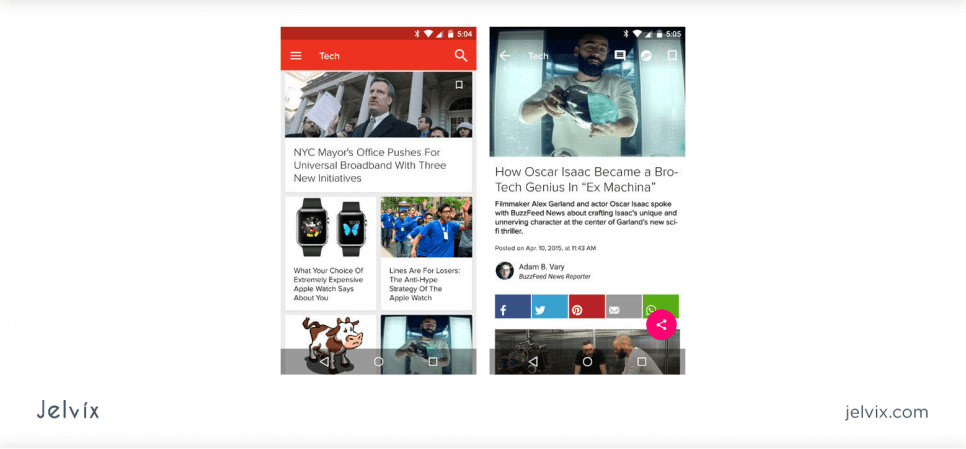
BuzzFeed is a Material-based mobile app
So here’s the big question!
Bootstrap or Material for Next Web or App Development Project?
As you may have guessed, the answer to this question depends solely on what project you’re working on and what objectives you’re striving to achieve. If you’re aiming at building simple but professional and highly responsive websites in the shortest possible time, then Bootstrap should be your go-to design tool.
But if you want a bit of sophistication, with vibrant colors, visual clues, and subtle animations that blend in with inventive and intuitive designs, think of Material Design. And if you want the best of both worlds, then it’s Material Design for Bootstrap (mdbootstrap).
Need a qualified team of developers?
Access the talent pool to scale your team capacity.