In May 2013, the renowned Google team launched the new project Polymer.js – an open-source, free JavaScript library intended for the creation of web applications based on the Web Components technology. As you may know, Polymer JS was one of the general sources of inspiration for Evan You to create Vue. Currently, the latest Version 3.0 of the library is supported by GitHub volunteers apart from the Google guys. We are going to make an objective Polymer JS review by listing the main Polymer JS features. Take a look at the pros and cons of this library, and figure out why use Polymer JS in your particular project.
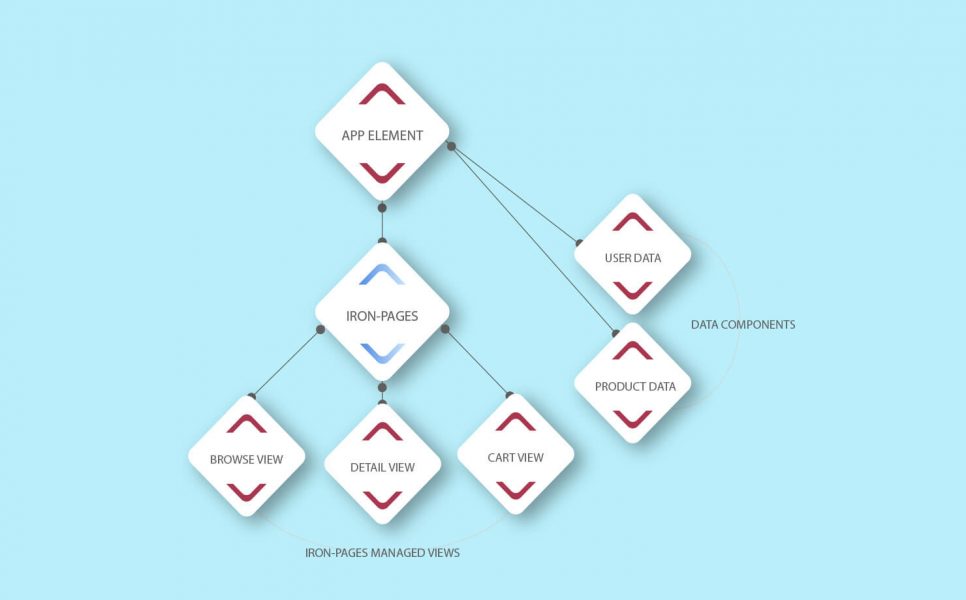
Understanding Polymer JS structure
Polymer.js structure consists of four interconnected levels:
-
- native: this initial level includes features currently available in all known browsers;
- foundation: this one includes the so-called polyfills – software code unavailable in certain browsers by default: the idea of Polymer.JS creators was to gradually eradicate such code fillers;
- core: this is an intermediary layer, which connects code from the previous levels with native Polymer project elements;
- elements: this layer contains functions characteristic to the Polymer library itself: those functions are, basically, building blocks for web apps that provide components for UI visualization, mockups, tools for connection of APIs, and others.
Such a structure allows creating ‘blocky’ solutions, the essential parts of which can be used repeatedly in other projects without the necessity to adapt them too much to the specifics of certain software code.
Polymer.js: main features
What can we say about the general Polymer JS features?
We’ll start by noticing that Polymer JS is popular due to the interoperable architecture of end products (finished apps). It, basically, allows building an app using separate modules, also called ‘lego blocks’ by the Polymer community. The unique, innovative approach rightly made this library one of the best solutions for writing the reusable, readable, and easily-maintained code.
There are also web components, the overall performance of Polymer.js is based on. Generally speaking, alongside with creating universal pieces of code Polymer web components also allow the maximum accessible level of code interaction with the help of built-in browser components.
Separate HTML elements can also be built with Polymer.js, which will become parts of the fully-functional web applications in the future. You can employ the elements for an unlimited number of times without trying to fully understand the specifics of code. All due to the declarative integration of those elements with an HTML page and no need to build anything from scratch.
Moreover, if developers use CLI Polymer, the compiler is built-in into the project by default. This allows reducing the total number of requests and decreasing the size of the whole project.
Last but not least, Google Polymer supports ES5, and ES2015 standards, which provides compatibility with all popular browsers.
You can find out more about the specifics of employing this library in practice, see the tutorial, and take a look at the Polymer JS example of code on the official website and Polymer Project Github page.
Polymer JS: a few words about cons
Our topic of discussion isn’t free of certain disadvantages, however. For instance, many Polymer users complain about the limit in the choice of tools for the realization of calculated attributes.
Apart from that, the library also uses certain pieces of code, which aren’t (yet) supported by some browsers by default. Alternatively, the maximum accessibility of web apps negatively affects their speed of performance.
Find out why we consider React JS faster than Angular.
Why do developers choose Polymer JS?
A bunch of reasons why experts often prefer to work with this efficient library includes the following:
- simplicity of creating software blocks with the help of web components;
- one- and two-way data binding support;
- universal code;
- high performance;
- scalability;
- compatibility with most existing browsers;
- various packages;
- prospects (Google experts constantly update the solution with new features and capabilities).
In this article, we told you what is polymer JS, and why this library should be used for the creation of scalable solutions. In order to realize the framework popularity, notice that it was used for building components for such renowned web services as YouTube, Google Earth, Google Play and Music. The library was also employed by Netflix, Coca-Cola, McDonald’s, and even IBM. Maybe it is a good idea to choose Polymer JS for your project… Ask for advice from the highly-qualified experts or, which is a very reasonable option, let them implement your new solution! Being top-notch specialists in our niche, we guarantee to deliver competitive, scalable software that meets all the required quality standards, and is built with a reasonable budget.
Need a certain developer?
Use our top talent pool to get your business to the next level.