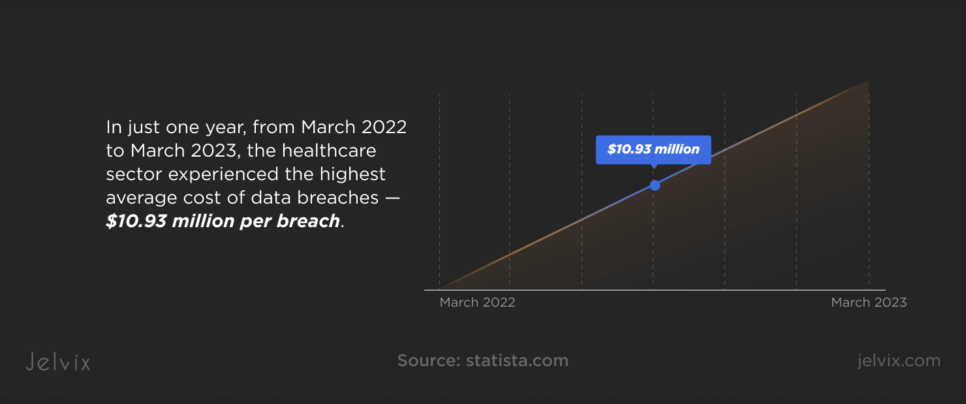
As the medical industry is getting more reliant on digitalization, it becomes vulnerable to cyberattacks. During just one year, between March 2022 and March 2023, healthcare experienced the highest average costs of data breaches — USD 10.93 million per breach.
The problem becomes more severe when clinics realize that security breaches lead to critical consequences, such as identity theft and compromised patient care, that affect the whole medical system.
If you seek ways to use modern tech without being exposed to data privacy violations, ransomware attacks, and other threats, read this article. You’ll learn more about the types of data you need to protect, key cybersecurity challenges to handle, and ways to prevent cyber threats at your clinics.
Securing Patient Data: Key Types To Know
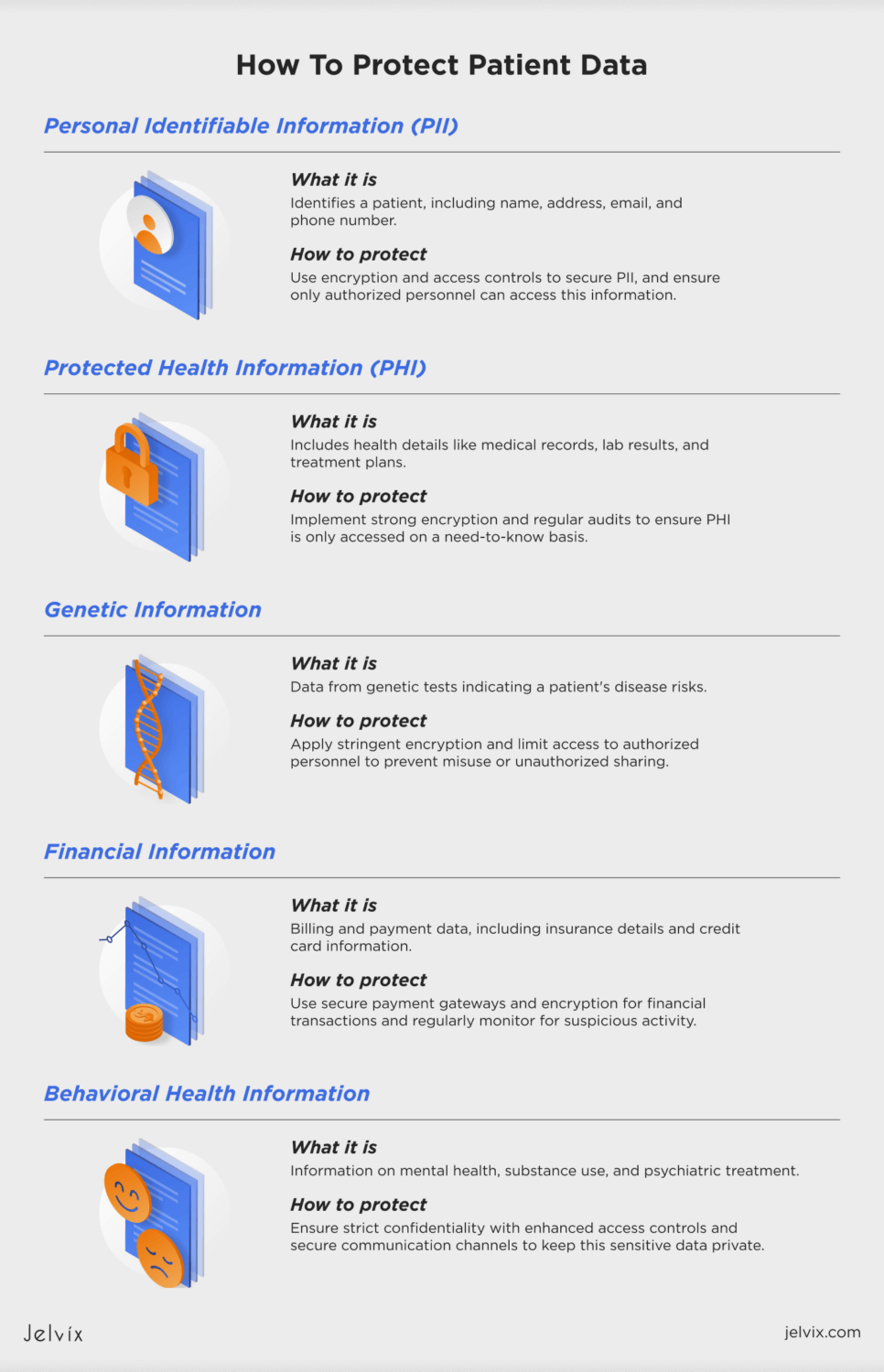
To protect patient data well, clinics need to understand different kinds of data. Whether it’s personal information, medical records, or financial details, each type needs specific measures to prevent breaches and unauthorized access.
Personal Identifiable Information
PII is any information that can identify a person. It is used to confirm a patient’s identity and includes info like full name, address, email, and phone number.
Protected Health Information
PHI covers a wide range of details about a patient’s health, medical history, and care they receive. It usually includes medical records, lab results, imaging reports, prescriptions, and treatment plans.
Genetic Information
Genetic info comes from genetic tests and can reveal a patient’s risk for certain diseases. This type of data is extremely sensitive and needs strong protection to prevent misuse.
Financial Information
Financial info involves data used for billing and payments. This includes insurance details, billing records, payment history, and credit card information.
Behavioral Health Information
This type of data includes info about a patient’s mental health, substance use, and psychiatric treatment. It is private and must be handled with extra care to keep it confidential.
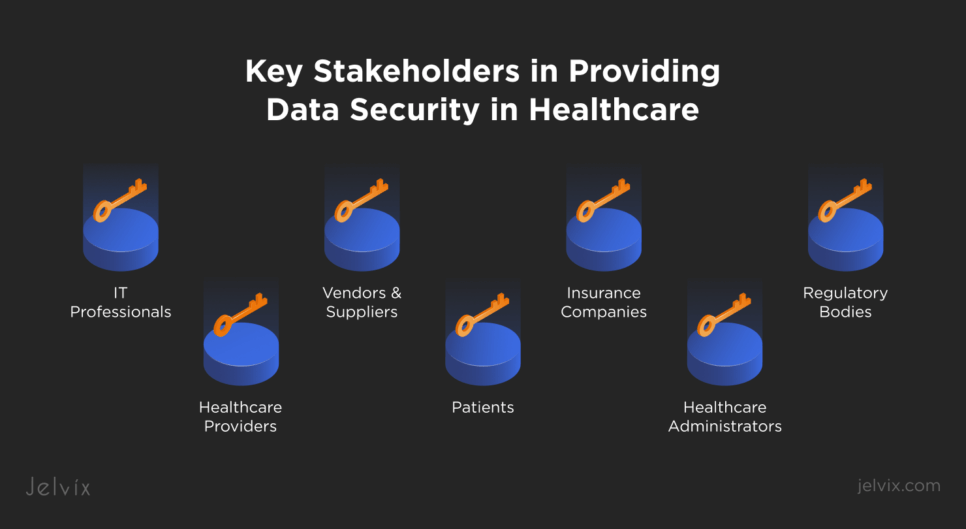
Key Stakeholders in Providing Data Security in Healthcare
Keeping patient data safe is a team effort that involves different participants. Everyone, from doctors to insurers, has a part to play in ensuring patient information stays private and secure.
Patients
Patients entrust healthcare facilities to keep their personal and medical information safe. They should stay informed about how their data is used and take steps to protect it. This includes using secure communication channels and checking their medical records for mistakes.
Healthcare Providers
Doctors, nurses, and other healthcare workers handle sensitive patient information daily. They need to follow strict rules to keep this data private and secure, from carefully managing EHRs to watching out for phishing scams and other cyber threats.
Healthcare Administrators
Administrators are responsible for creating and enforcing security policies in healthcare organizations. They make sure that staff is trained in data protection, manage who has access to patient information, and stay updated on the latest security laws and technologies.
IT Professionals
IT experts take care of the systems that store and process patient data, set up cybersecurity measures, such as role-based access controls and encryption, respond quickly to data issues, and ensure safe healthcare data migration when needed.
Regulatory Bodies
Organizations like HIPAA and GDPR set standards for data protection in healthcare. These regulatory bodies make sure that healthcare companies follow laws designed to protect patient information and hold them accountable if they don’t.
Vendors and Suppliers
Companies that provide healthcare technology, equipment, and services must ensure their products meet security standards. They need to protect the data they handle from unauthorized access on behalf of healthcare providers.
Insurance Companies
Health insurance companies manage large amounts of patient data, including medical records and billing information. They must have strong data protection measures in place and work closely with medical companies to ensure secure data exchange.
Learn how to create a secure and efficient e-prescription app for doctors with this comprehensive guide.
Real-World Healthcare Cybersecurity Cases
Healthcare data breaches can significantly impact patient trust and the reputation of your clinic. Analyzing known cyber breach cases can help you understand what dangers such intrusions can impose and how to deal with them.
Massive Data Breach
In 2020, Florida Healthy Kids Corporation experienced a major data breach that exposed the personal information of over 3.5 million people. This happened because their web hosting platform wasn’t properly secured. In response, the company took the compromised website offline, investigated the issue, notified the affected users, and provided tips on how to protect their identities.
Ransomware Attack
Scripps Health in San Diego faced a ransomware attack that disrupted their IT systems and impacted about 2.1 million people in 2021. The attackers encrypted sensitive files and demanded a ransom. Scripps Health responded by taking their systems offline, working with cybersecurity experts to investigate the issue, notifying affected patients, and offering free credit monitoring and identity protection services.
Phishing Attack
In 2021, UC San Diego Health was hit by a phishing scheme. Hackers accessed an employee’s email account and compromised sensitive patient data. In response, the hospital collaborated with cybersecurity experts to investigate the breach, informed the affected users, and provided credit monitoring and protection services related to identity theft.
Top Healthcare IT Security Challenges Clinics Need To Address
In 2023, more than 133 mln medical records were exposed as a result of data breaches. The key reason is that the industry faces numerous cybersecurity challenges as it becomes more digitized.
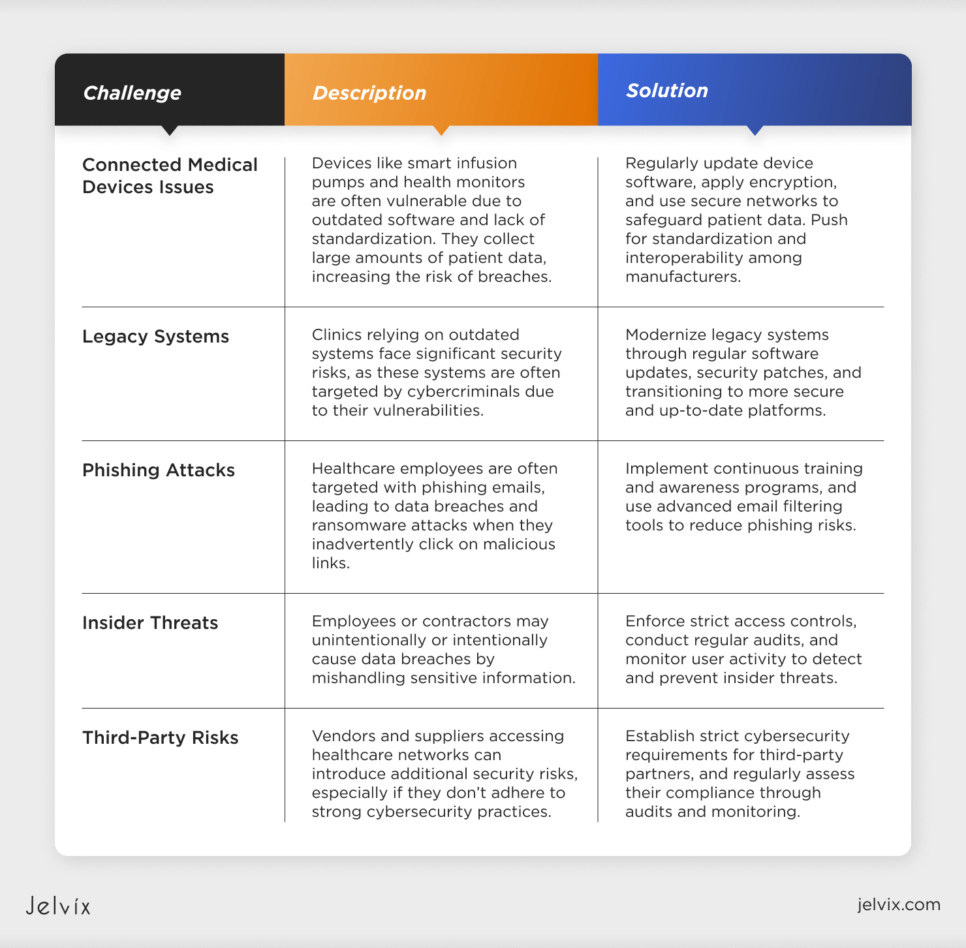
Connected Medical Devices Issues
Connected medical devices like smart infusion pumps and wearable health monitors offer significant benefits but also introduce security risks. These tools often run on outdated software, making them vulnerable to hacking. What’s more, they collect large amounts of patient data, which can be intercepted if not properly secured.
The lack of standardization across manufacturers and interoperability issues create additional security gaps, while the challenge of maintaining and updating these devices leaves them exposed to vulnerabilities.
Legacy Systems
Clinics that adopt healthcare software modernization often rely on legacy systems that seem comfortable and reliable. In reality, these systems are often riddled with security vulnerabilities, making them prime targets for cybercriminals.
Phishing Attacks
Phishing emails deceive healthcare employees into revealing sensitive information or clicking on malicious links, leading to data breaches and ransomware attacks. Clinics need to provide continuous training and awareness programs to combat this threat.
Insider Threats
Employees or contractors with access to sensitive data may intentionally or unintentionally cause data breaches. Implementing strict access controls and monitoring can help detect and prevent such threats.
Third-Party Risks
Vendors and suppliers with access to healthcare networks can introduce additional security risks. Ensuring third-party partners adhere to strong cybersecurity practices can help protect patient data.
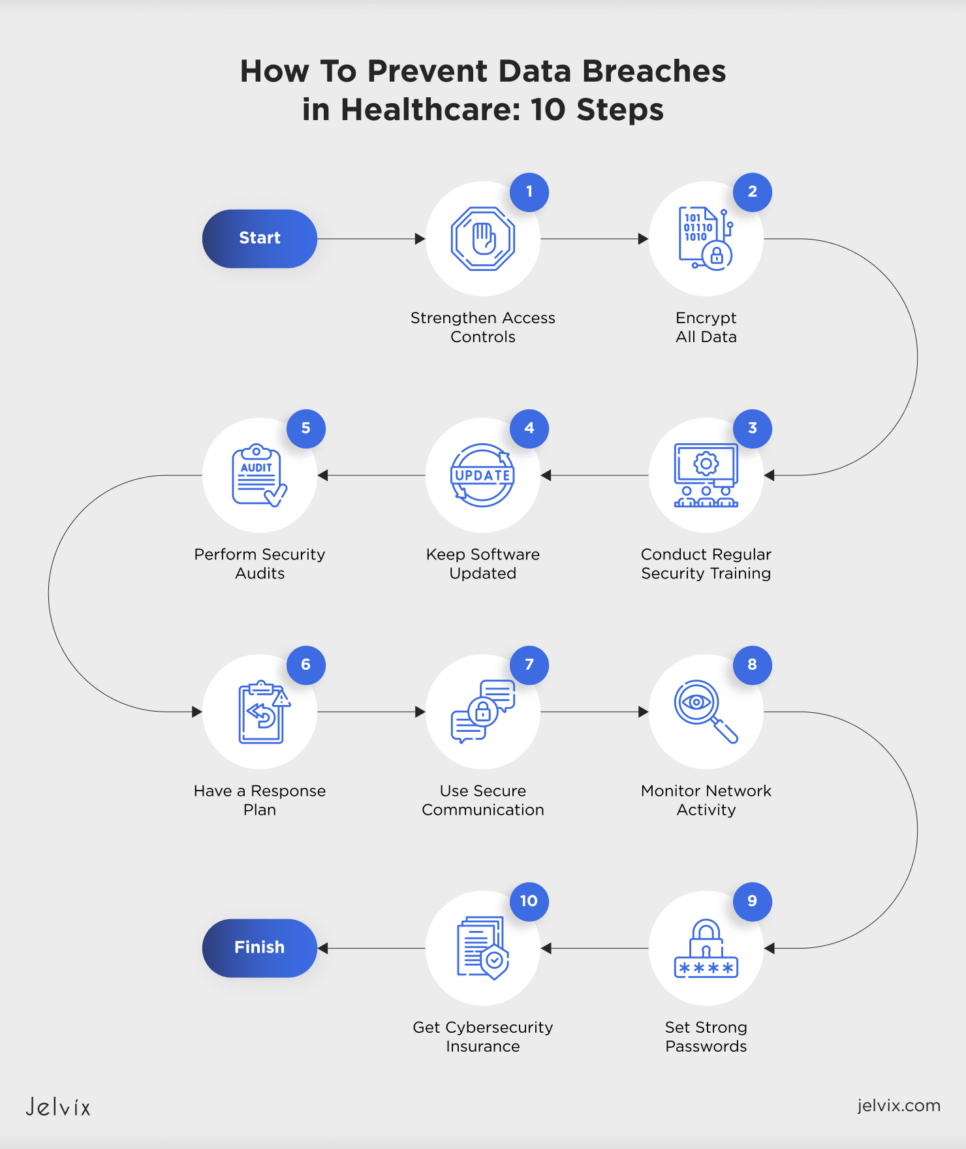
How To Prevent Data Breaches in Healthcare: 10 Steps
Cybersecurity threats can cause serious problems for your hospital, compromising patient information and disrupting essential services. The Jelvix team suggests that you follow proven steps to set strong security for the patient data you work with.
1. Strengthen Access Controls
Implement role-based access controls to limit who can access sensitive data based on their job roles. Use multi-factor authentication to add an extra layer of security and prevent unauthorized access.
2. Encrypt All Data
Make sure all patient data is encrypted with protocols like AES and RSA when it’s being sent and stored. Encryption helps keep patient info safe from undesired users.
3. Conduct Regular Security Training
Educate your staff regularly about cybersecurity best practices. Teach them how to recognize phishing emails and handle sensitive information safely.
4. Keep Software Updated
Always update your software, including antivirus and anti-malware programs, to protect against known security threats and vulnerabilities.
5. Perform Security Audits
Conduct regular security checks to find and fix potential weaknesses in your systems and processes. Address the arising safety issues as soon as possible.
6. Have a Response Plan
Create a detailed plan for how to respond to cyberattacks. This plan should include steps for communicating the issue, containing the attack, and recovering from it.
7. Use Secure Communication
Ensure all communications involving patient data use secure channels. This means using encrypted emails and messaging services to keep data safe.
8. Monitor Network Activity
Keep a close eye on network activity to spot unusual behavior that might indicate a cyber threat. Use advanced tools like intrusion detection systems and intrusion prevention systems to spot the issues as they arise.
9. Set Strong Passwords
Implement policies that require strong and complex passwords for employee accounts. Encourage the use of password managers to help staff create secure passcodes.
10. Get Cybersecurity Insurance
Consider investing in cybersecurity insurance to help cover the costs of a data breach, including legal fees, notification costs, and recovery efforts.
Discover key strategies to successfully scale your healthcare SaaS business while navigating industry challenges in this guide.
3 Cybersecurity Regulations in Healthcare You Need To Know
To set up proper cybersecurity measures, medical facilities need to understand key regulations, what they mean, and what they require.
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
HIPAA sets the standard for protecting patient health information. It requires healthcare providers, insurers, and their partners to put strong security measures in place to protect EHRs and other sensitive data sources.
Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act
The HITECH Act encourages the use of health information technology and strengthens HIPAA rules. It increases penalties for not following HIPAA and expands breach notification requirements.
General Data Protection Regulation
GDPR is a major data protection law in the EU that affects any organization handling the personal data of EU citizens, including healthcare providers. It requires getting explicit consent from patients before collecting and processing their data and allowing them to access and delete it.
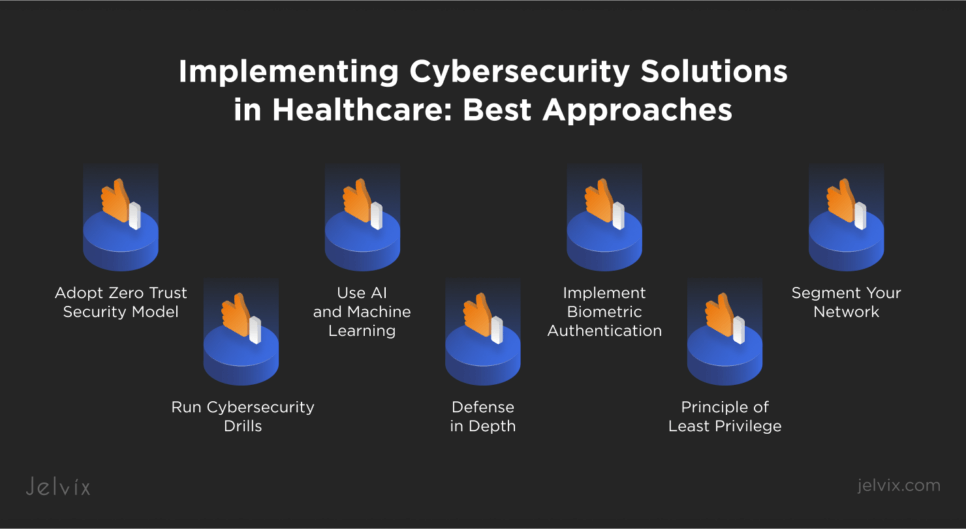
Implementing Cybersecurity Solutions in Healthcare: Best Approaches
No matter what type and quality of data your clinics work with, you need to adopt cybersecurity solutions that ensure the highest security level. You can follow the proven approaches listed below to enhance cybersecurity across your healthcare settings.
Adopt Zero Trust Security Model
Zero trust network access is an approach that goes “never trust, always verify”, no matter if users are located inside or outside your network. Verify every user and device trying to access your clinic’s network, constantly monitor for threats, and grant access to sensitive data only if users truly need it.
Use AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence and machine learning can help detect threats faster and more accurately. These technologies can analyze large amounts of data to find unusual patterns that might indicate a cyber threat, allowing you to act quickly. Common software choices include Amazon Macie and Amazon GuardDuty.
Segment Your Network
Divide your network into smaller sections. If one part gets hacked, the attacker can’t easily access the entire network. For instance, you can use subnets in AWS virtual private cloud to create segments within your environment.
Implement Biometric Authentication
Use biometric authentication like fingerprint scans and facial recognition for extra security. This method is more secure than traditional passwords and makes it harder for unauthorized users to access your systems.
Run Cybersecurity Drills
Regularly practice cybersecurity drills to prepare your team for potential cyberattacks. These exercises help identify weak spots in your response plan and ensure everyone knows what to do if an attack happens.
Defense in Depth
Build multiple layers of security controls throughout your IT infrastructure. Use a combination of firewalls, intrusion detection systems, encryption, and other measures to create a strong defense, making it difficult for attackers to penetrate your network.
Principle of Least Privilege
Ensure that users and devices have only the minimum level of access necessary to perform their functions. Limit access rights to reduce the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive information. Regularly review and adjust permissions to keep up with this principle.
How Jelvix Helps Create Solutions To Enhance Data Security in Healthcare
Protecting patient data is getting more difficult. However, clinics can opt for digital solutions with built-in security measures to keep sensitive info safe.
At Jelvix, we can develop a custom healthcare solution for your clinic based on your unique demands. We focus on developing and seamlessly integrating such solutions into EHRs to set a safe and interoperable medical environment.
If you want your digital tools to enhance clinical workflows rather than become targets of cyber threats, contact our experts. They will offer a consultation based on your cybersecurity needs.
Need an expert development partner for your project?
Collaborate with a dedicated team focused entirely on bringing your vision to life.