The journey of switching from paper-based healthcare routines to virtual platforms started long ago. By 2017, 94% of US hospitals had embraced EHR systems, and a subsequent 2019 survey revealed that 82% of office-based physicians were utilizing EHR as well.
As the healthcare landscape continues its digital evolution, achieving interoperability between health information technology systems becomes challenging. In this guide, the Jelvix team shares essential insights into the benefits and challenges of interoperability implementation, the standards required for its seamless operation, and strategies to ensure efficient interoperability across your HIT systems.
Why Is Interoperability Important in Healthcare?
Interoperability in healthcare refers to the ability of different health information technology systems to exchange and use health information. It is crucial for seamless data exchange, promoting patient-centric care. For HIT vendors, achieving interoperability taps into a growing market, offering innovative solutions for efficient and quality healthcare delivery.
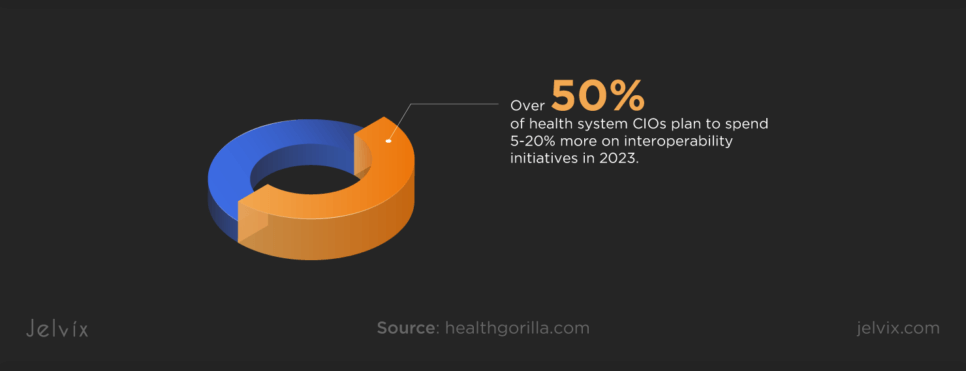
Prioritizing interoperability contributes to improved patient care and reduced errors. Notably, more than 50% of C-level executives planned to allocate up to 20% more on interoperability products and services in 2023, highlighting its pivotal role in shaping healthcare technology’s future. In essence, interoperability is essential for advancing technology, fostering innovation, and ensuring better outcomes for providers and patients.
Examples of Interoperability in Healthcare
Understanding the practical applications of interoperability in healthcare is crucial. The examples below illustrate how it contributes to a connected and efficient healthcare ecosystem.
Electronic Health Records
In the realm of healthcare interoperability, seamless integration of EHRs stands as a key example. Consider a patient visiting a primary care physician equipped with a comprehensive Electronic Health Record system. This system seamlessly connects with the patient’s existing health records, offering a holistic view of their medical history, medications, and past treatments. The interoperability of these EHR systems ensures that healthcare providers can access, update, and utilize patient information efficiently, promoting continuity of care.
Health Information Exchange Platforms
HIE platforms play a vital role in facilitating interoperability across different healthcare facilities. For instance, when a patient is referred to a specialist in a separate location, HIE platforms securely share relevant information — diagnosis, test results, and treatment plans — between the primary care provider and the specialist. This interoperability ensures that crucial patient data is accessible, fostering collaborative and informed decision-making.
Medical Devices
The integration of medical devices into healthcare systems illustrates how interoperability enhances patient care. Picture a patient using a wearable device to monitor health info at home. The data collected by the wearable seamlessly integrates with the patient’s EHR. This interoperability allows healthcare providers to access real-time health metrics remotely, enabling proactive interventions and informed decision-making based on up-to-date information.
Telehealth
Telehealth platforms integrating with EHR systems showcase how interoperability transforms virtual healthcare delivery. In a scenario where a patient has a virtual consultation with a healthcare provider, the interoperability between telehealth and EHR systems ensures seamless access to patient records. This enables healthcare professionals to conduct virtual visits, update treatment plans, and maintain accurate health information, providing efficient patient-centric care.
Pharmacy Information Systems
Interoperability extends to pharmacy information systems, streamlining the prescription process. Imagine a patient receiving a prescription from their primary care provider. The details are electronically transmitted from the provider’s EHR to the pharmacy’s information system. This interoperability ensures accurate medication dispensing, minimizes errors, and enhances patient safety by maintaining a connected healthcare ecosystem.
Discover the key to enhancing patient experience through EHR-CRM integration .
Current Standards for Interoperability in Healthcare Technology in the US and Europe
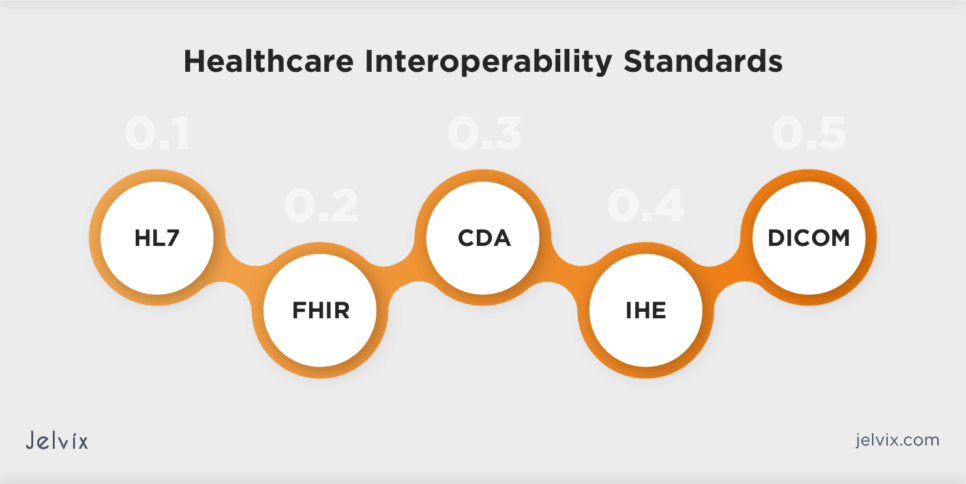
Interoperability in healthcare is facilitated by various standards that define how health information systems exchange and interpret data. These standards collectively contribute to creating a more connected and interoperable healthcare ecosystem, enabling seamless data exchange and improving patient care.
Interoperability Standards in the US
In the US, data interoperability standards for healthcare technology are governed by organizations such as Health Level Seven International and the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology. These standards aim to facilitate seamless data exchange and interoperability among healthcare systems and applications.
Health Level Seven Standards
HL7 has long been instrumental in shaping healthcare interoperability. HL7 standards, including HL7 Version 2 and HL7 Version 3, provide frameworks for seamless exchange, integration, and sharing of electronic health information.
Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources
FHIR stands out as a leading standard in U.S. healthcare interoperability. Developed by HL7, FHIR leverages modern web standards to facilitate the efficient exchange of healthcare information. Its emphasis on simplicity and flexibility has contributed to widespread adoption.
Clinical Document Architecture
CDA, an HL7 standard, defines the structure of clinical documents for exchange purposes. Widely used for summarizing patient information, CDA plays a pivotal role in fostering interoperable health information exchange.
Integrating the Healthcare Enterprise
IHE spearheads an industry-wide initiative to enhance the exchange of information among healthcare computer systems. The organization facilitates the improvement of healthcare interoperability by gathering case requirements, identifying standards, and developing technical guidelines for manufacturers to implement.
Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine
DICOM is an interoperability standard widely used in healthcare for the exchange and management of medical images and related information. It ensures that medical imaging devices and information systems from different manufacturers can communicate and share data seamlessly, promoting interoperability in the field of medical imaging.
Interoperability Standards in the EU and the UK
Interoperability standards in the European Union and the UK are governed by organizations like openEHR and NHS. They ensure consistency, compatibility, and collaboration among diverse healthcare systems and stakeholders.
Standards from NHS Digital
The UK’s National Health Service Digital has established interoperability standards to promote seamless data exchange within the NHS and across healthcare systems. These standards cover various aspects, including data formats, coding systems, and secure information-sharing protocols.
Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine – Clinical Terms
SNOMED CT is a comprehensive clinical terminology used internationally. In the UK, it plays a crucial role in standardizing clinical terms and enabling interoperability by providing a common language for healthcare professionals and systems.
OpenEHR
OpenEHR, used by the UK NHS Health and Social Care Information Centre, focuses on standardizing health information at the clinical level. It provides open specifications for the design and implementation of electronic health records, fostering interoperability by ensuring consistency in the representation of health data
Following interoperability standards in healthcare is crucial for seamless data exchange and collaboration. Standards like HL7, FHIR, and SNOMED CT ensure consistency, compatibility, and efficient communication among diverse healthcare systems.
Interoperability in Healthcare: Balancing between Benefits and Challenges
Interoperability presents both challenges and transformative benefits that healthcare specialists can’t ignore. Overcoming hurdles such as data security concerns, disparate standards, and resistance to change is pivotal for unlocking the full potential of interoperability. However, the rewards are substantial, encompassing improved care coordination, reduced medical errors, and enhanced patient outcomes.
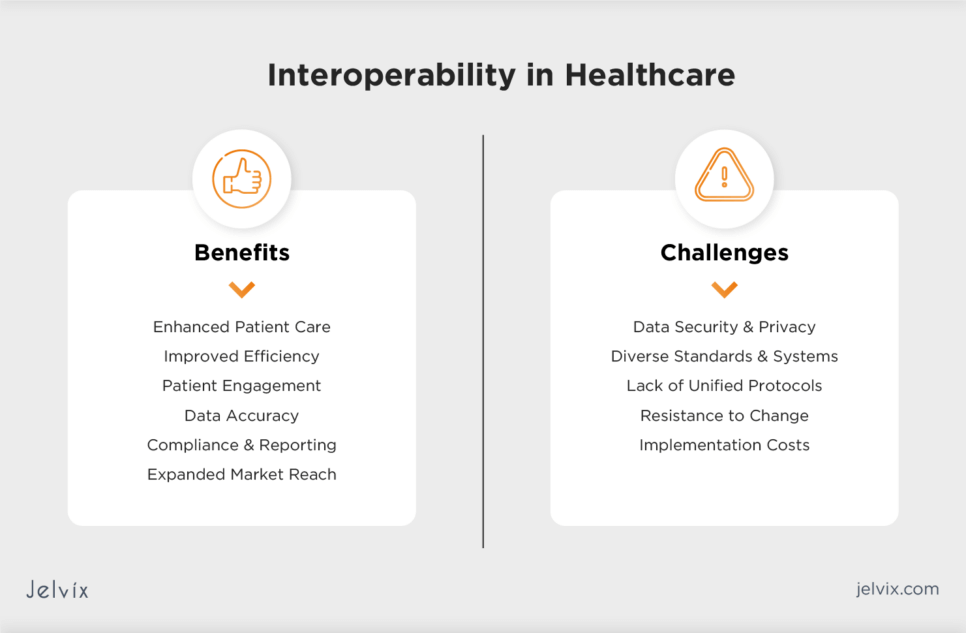
Benefits of Interoperability in Healthcare
Interoperability in healthcare information technology offers significant benefits to vendors, enhancing their solutions and overall market position.
Enhanced Patient Care
Clinical interoperability contributes to enhanced patient care by facilitating seamless access to comprehensive and up-to-date patient information. HIT vendors that prioritize interoperability empower healthcare providers to deliver personalized and well-informed care, resulting in improved patient outcomes. This focus further solidifies the vendor’s reputation and fosters trust among healthcare professionals.
Improved Efficiency
Interoperability streamlines workflows, automates repetitive tasks, and integrates seamlessly with existing healthcare technologies. This leads to increased operational efficiency and cost savings for healthcare providers.
Patient Engagement
Accessible and shareable health data empowers patients to engage actively in their healthcare journey, fostering collaboration between patients and healthcare providers. As a HIT vendor, you can create patient-centric platforms that leverage interoperability to provide individuals with easy access to their health data.
Data Accuracy
Interoperability enables efficient data exchange between different healthcare entities. Vendors offering solutions with robust data exchange capabilities are seen as valuable contributors to the evolving healthcare landscape, positioning them as leaders in the industry.
Compliance and Reporting
Interoperability ensures that HIT solutions align with regulatory standards, such as those outlined by HIPAA and other healthcare authorities. Compliant solutions not only avoid legal issues but also instill confidence in customers, making them more likely to choose the vendor’s products.
Expanded Market Reach
Interoperability allows vendors to create solutions that can seamlessly integrate with a variety of healthcare systems and platforms. This expanded compatibility enhances the market reach of their products, making them attractive to a broader range of healthcare providers.
Interoperability Challenges in Healthcare
While interoperability offers numerous advantages, it also presents challenges that demand careful consideration from HIT vendors. Recognizing and effectively addressing these challenges is crucial for delivering successful interoperable solutions.
Data Security and Privacy
Sharing sensitive health information raises concerns about data security and patient privacy. The Jelvix team recommends prioritizing robust security measures, such as encryption and access controls, to gain trust. Ensuring data integrity throughout interoperable processes is essential for building confidence among healthcare providers and patients.
Diverse Standards and Systems
Although interoperability standards, such as HLV, FHIR, open EHR, and NHS, are aimed at improving data exchange between diverse healthcare systems, their variability poses a challenge. Overcoming this obstacle requires alignment and standardization efforts. Vendors should invest in adaptable solutions capable of interpreting diverse standards, ensuring true interoperability across the healthcare landscape.
Lack of Unified Protocols
The absence of universally accepted protocols hinders smooth communication between disparate healthcare systems. Vendors face the challenge of developing solutions that can effectively translate and transmit data across different protocols to achieve interoperability. To address this challenge, vendors should unite in creating standardized protocols.
Resistance to Change
Healthcare systems often resist change due to established practices and concerns about disruption. The Jelvix team recommends navigating resistance by providing employees with clear benefits, user-friendly interfaces, and comprehensive training to encourage the adoption of interoperable solutions.
Implementation Costs
Adopting interoperable systems requires financial investment for technology integration, staff training, and system upgrades. To address this challenge, HIT vendors should consider phased adoption strategies. Instead of a full-scale overhaul, vendors can offer modular solutions that allow healthcare providers to integrate interoperable features gradually. This approach will minimize upfront costs and support a smoother transition for healthcare organizations.
Achieving Interoperability in Healthcare: Practical Guide for HIT Vendors
Achieving seamless interoperability of healthcare information systems is a pivotal element for the success of modern medical solutions. Vendors looking to implement effective strategies to reach interoperability are welcome to follow the practical guide developed by the Jelvix team.
Stay Informed on Industry Standards
Be aware of interoperability standards such as HL7, FHIR, and DICOM, described earlier in this article. Align your solutions with these standards to ensure compatibility and seamless integration with other healthcare systems. This will enhance your market competitiveness and broaden your loyal customer base.
Design for Flexibility and Integration
Embrace a modular and flexible design approach for your HIT systems. Utilize APIs and microservices architecture to enhance the interoperability of your solutions. This allows healthcare providers to integrate specific functionalities of your system into their existing infrastructure without disrupting the entire workflow.
Support Common Data Models
Ensure that your solutions support common data models like openEHR. This commitment to standardization enables consistent representation of healthcare data, fostering interoperability across diverse healthcare settings. In particular, adhering to openEHR standards facilitates the seamless sharing of patient records between different healthcare providers using openEHR-compliant systems.
Implement Standardized Communication Protocols
Choose communication protocols that have gained widespread acceptance in healthcare. Examples include HL7 and RESTful APIs that enable your system to communicate efficiently with other healthcare applications allowing for real-time data exchange.
Prioritize Security Measures
Integrate robust security features into your HIT solutions to safeguard patient data during interoperable exchanges. Encryption, secure authentication, and access controls are vital components. Compliance with healthcare privacy regulations, such as HIPAA, ensures data protection and fosters trust among stakeholders.
Offer Configurable Data Governance
Provide solutions with configurable data governance features. This empowers healthcare providers to adapt data governance policies according to their specific needs. A flexible governance framework promotes smoother interoperability while accommodating varying regulatory requirements.
Facilitate User Training
Design user interfaces that prioritize usability and provide comprehensive training resources for healthcare professionals. Well-trained users contribute to the effective utilization of HIT solutions, reducing the likelihood of errors and improving interoperability outcomes.
Engage in Interoperability Collaborations
Actively participate in interoperability initiatives and collaborate with other vendors. Collaboration fosters shared knowledge and accelerates the development of interoperable solutions. Engaging in interoperability communities will help shape industry best practices.
Regularly Update and Improve
Commit to regular updates and improvements in your solutions. Regular software updates that align with the latest FHIR standards will ensure that your system remains interoperable with other applications that adopt the latest FHIR specifications. Staying agile allows your products to remain compatible with the latest industry advancements, ensuring long-term effectiveness.
Seek Client Feedback and Input
Establish feedback channels to understand the specific needs and challenges faced by your clients. Incorporate client insights into your product development cycle, ensuring that your solutions address real-world interoperability challenges. Implementing features based on client feedback ensures that your solutions align with their unique requirements, enhancing overall user satisfaction.
Healthcare Interoperability Services Estimated Costs
Estimating the costs of interoperability in healthcare involves considering various factors essential for seamless data exchange and integration across healthcare systems. Here’s a breakdown of the most common elements influencing the estimated costs of healthcare interoperability services:
- System integration complexity: higher complexity may require more extensive coding, testing, and configuration efforts;
- Data standardization: implementing and adhering to established data standards might involve additional development efforts and resources;
- Security measures: costs are associated with encryption, secure authentication, access controls, and compliance with healthcare privacy regulations;
- Aligning with standards: comprehensive integration with industry standards such as HL7, FHIR, and DICOM may incur additional costs for development and compliance efforts;
- User training and support: investment in developing user-friendly interfaces, training modules, and ongoing support resources;
- Updates and improvements: budget considerations for ongoing software updates, aligning with the latest standards and technologies;
- Client feedback mechanisms: resources allocated for feedback collection mechanisms and iterative development based on client input.
Note that the actual expenses associated with interoperability across a healthcare system vary based on the specific needs, scale, and complexity of the implementation. If you would like to get accurate cost projections, we recommend that you get in touch with the Jelvix team for details.
How to Use APIs in Health IT Interoperability Implementation
Application Programming Interfaces play a pivotal role in facilitating healthcare interoperability. They act as bridges between different healthcare systems, enabling seamless data exchange and communication. By leveraging APIs, healthcare organizations can standardize data sharing, streamline workflows, and enhance interoperability between diverse systems.
Implementing APIs in health IT interoperability involves several key steps to ensure a seamless and efficient integration process:
Step 1. Assessment of System Compatibility
Before incorporating APIs, assess the compatibility of existing healthcare systems thoroughly. Identify the specific data elements that need to be shared and establish the necessary connections. Consider the infrastructure, data formats, and communication protocols to ensure seamless integration.
Step 2. Selection and Standardization
Choose suitable APIs that align with industry standards, such as HL7 FHIR. Standardization is crucial for ensuring uniform data exchange across different platforms. Select APIs that meet the specific needs of your healthcare systems while adhering to established interoperability standards.
Step 3. Security Measures
Implement robust security measures to safeguard sensitive health data during transmission. Utilize encryption, authentication, and authorization protocols to ensure data integrity and privacy. Prioritize security considerations to build trust and compliance with healthcare regulations.
Step 4. Data Mapping and Transformation
Map the data structure of different systems to ensure consistency in information exchange. Transformation processes may be required to convert data formats and standardize terminology to achieve true interoperability. Addressing semantic interoperability is vital for accurate communication between diverse healthcare systems.
Step 5. Integration with EHRs
Seamlessly integrate APIs with EHRs and other healthcare applications. This involves configuring the APIs to work harmoniously within the existing infrastructure. Ensure that the integration supports the functionalities required for efficient healthcare operations.
Step 6. Testing and Validation
Conduct thorough testing to validate the interoperability of systems. Identify and correct any issues related to data exchange, system connectivity, and overall functionality. Rigorous testing helps ensure a smooth and error-free interoperability implementation.
Step 7. Monitoring and Updating
Establish a robust monitoring system to track the performance of APIs and identify any potential issues. Regularly update APIs and associated systems to accommodate changes in healthcare standards or evolving technology. Continuous monitoring ensures the sustained effectiveness of interoperable solutions over time.
Jelvix Expertise: EHR Interoperability Solutions for Secure Medical Data Exchange
At Jelvix, we stand at the forefront of healthcare transformation, providing cutting-edge EHR interoperability solutions. Our expertise lies in crafting secure and seamless medical data exchange systems that align with the highest industry standards.
By integrating state-of-the-art technologies, we bridge the gap between disparate HIT systems, fostering a connected and interoperable healthcare environment. Our solutions not only enhance data accuracy but also elevate patient care through streamlined workflows and improved decision-making.
Whenever you require a piece of advice on developing an interoperable healthcare solution from scratch, need to improve an existing product, or seek a reliable tech partner, feel free to contact our managers. They are always ready to answer all your questions.
Unlock seamless healthcare data exchange with Jelvix—explore EHR interoperability for optimized medical systems.