Manual reporting is no longer just a paperwork hassle—it’s a revenue blocker. Rehab groups that submit late, incorrect, or incomplete Medicare reports risk delayed reimbursements, payment denials, audits, and even fines. CMS regulations are very severe. If you don’t follow them, you could be fined up to $1,000 a day across programs like Average Sales Price (ASP) reporting and Medicare Secondary Payer (MSP) data filing. Even little mistakes might lead to cash flow problems and slower operations for rehab organizations.
These reporting problems have a hidden cost behind the scenes. Nuance and Ignetica’s research showed that healthcare professionals spend an average of 13.5 hours a week on clinical documentation, which is more than a third of their working hours.
Submitting EDI for Medicare adds even more layers of difficulty. Your staff is caught battling on two fronts: clinicians are buried in paperwork, while admins are chasing after clean, compliant data to keep the revenue flowing.
This is where automation makes a big difference. We’ll go over a 6-step plan in this article that will help you make reporting easier, keep compliant with CMS, and set your rehab business up for growth that is efficient and scalable.
What Is Automated Reporting for Rehab?
Automated reporting for rehab lets rehab centers stay compliant and grow without being held back by manual bottlenecks. It makes working with complicated data easier, lowers the chance of making expensive mistakes, and makes it simpler for your teams to fulfill CMS and payer standards.
Core Components of an Automated Reporting System
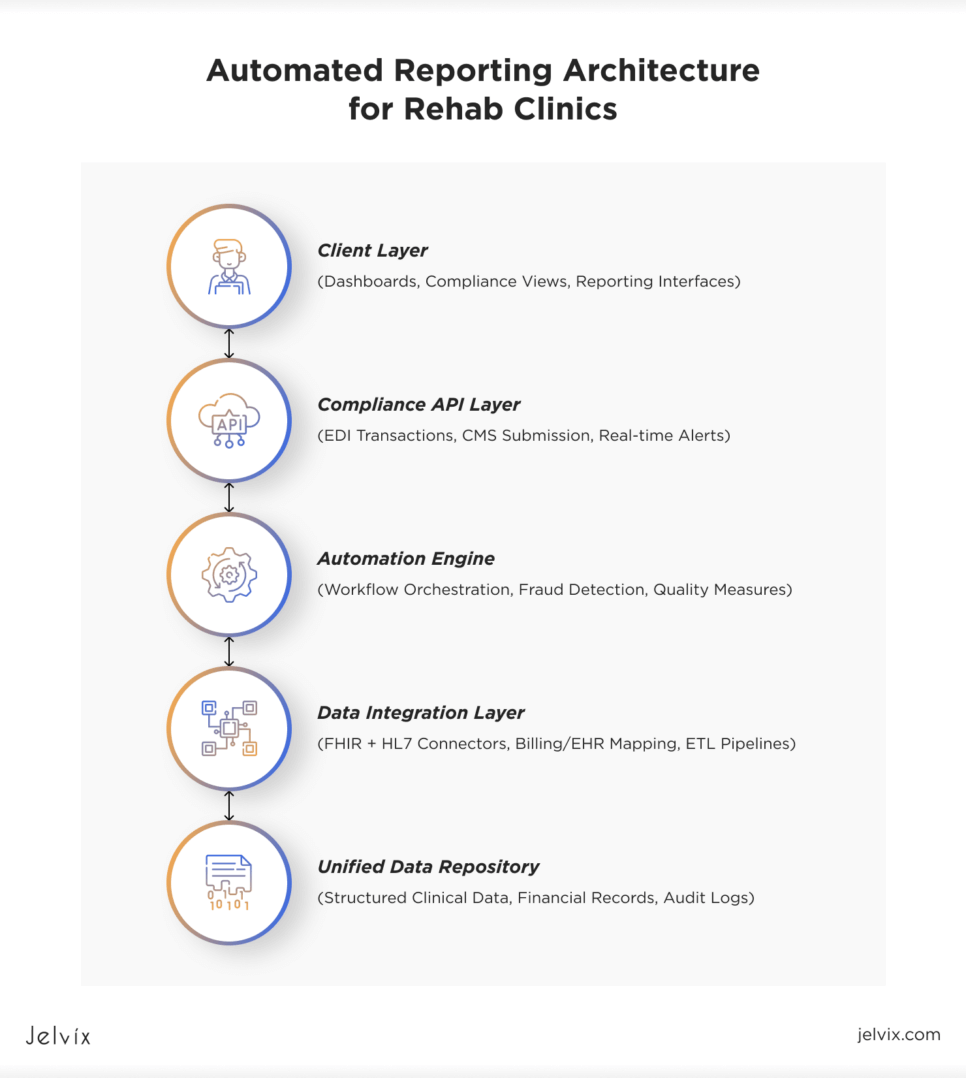
EHR Integration and Interoperability
Automated reporting depends on being deeply connected to the organization’s EHR mental health and rehab platforms at its core. Modern FHIR interoperability standards make it easier to do this by allowing safe, real-time data sharing across different systems.
EDI for Medicare Submission
Automated systems make EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) easier for Medicare by handling the electronic transmission of eligibility checks, claims, remittance advice, and required CMS quality reports. This ensures that CMS deadlines are met, cuts down on mistakes made by people, and speeds up revenue cycles.
Real-Time Dashboards and Decision Support
Modern reporting for rehab also supports real-time dashboards, which give leaders clear views of how well the business is doing financially, how well patients are doing clinically, and how well they are following the rules. These dashboards are different from traditional static reports because they help businesses become more flexible and make better decisions as they grow.
Embedded Fraud-Prevention Triggers
An advanced fraud prevention system leverages AI fraud-detection flags to find strange trends in billing, documentation, and quality metrics. Organizations may fix problems early and lower the chances of audits, fines, or denials by finding issues before they submit.
Underlying Architecture: Data Warehouse or FHIR Integration Solution
Many leading organizations implement an enterprise data warehouse or deploy an advanced FHIR integration solution, which normalizes data from EHR, billing, labs, HR, and external partners.
This architecture enables:
- Automated generation of CMS quality-measure files (IQR, OQR, MSP, Price Transparency);
- Unified cross-site reporting;
- Longitudinal analytics for quality improvement and risk management.
Ultimately, automated reporting for rehab transforms compliance from a manual, reactive process into a proactive, strategic capability—crucial for organizations looking to scale efficiently under modern CMS reporting requirements.
Why Medicare Reporting Bottlenecks Keep Rehab Centers from Scaling
Rehab networks often have to deal with fragmented systems, like EHR mental health records for clinical data, billing platforms for finances, and registries for outcomes. Teams have to manually pull out, clean, and match this rehab information in order to send in a full report that meets CMS reporting requirements for employers and providers. This takes time and might lead to mistakes.
The lack of data interoperability makes system-wide visibility difficult. Leaders struggle to monitor outcomes, utilization, and income across locations. That’s why scaling without automation often means more errors, audits, and lost revenue.
The first step in solving this is to figure out how to improve interoperability in healthcare. This can be done by using automated pipelines and contemporary architecture to bring together EHR, financial, and operational data. That’s how treatment centers may create a solid base for both growth and compliance.
The Hidden Costs of Manual Reporting for Rehab
Manual reporting is rarely accounted for on balance sheets, but its costs compound across payroll, cash flow, compliance, and patient safety. For rehabilitation and mental health providers, these hidden costs quietly erode margins and operational capacity.
Learn how to maximize a healthcare ROI by optimizing your EHR system with better workflows, smarter integrations, and data-driven strategies.
Overtime Payroll and Compliance Risk
A study made by researchers from George Washington University (GWU) and Premier Inc. says that relying more on overtime, such as hiring agency nurses, makes patients less safe. In this setting, staff members are required to work more than their allotted hours due to manual reporting requirements, which increases payroll costs. Miscalculations of overtime in manually processed payroll can trigger compliance penalties, driving a surge of interest in automated employer-of-record (EOR) solutions.
Delayed Medicare and Medicaid Cash Flow
Rehabilitation centers rely heavily on Medicare and Medicaid reimbursements, but when claims reporting is still manual, even minor delays or errors can disrupt cash flow. Paper-based workflows are especially vulnerable to human error, leading to denied claims, protracted rework cycles, and unpredictable revenue streams.
These kinds of inefficiencies affect all parts of the business, from hiring people to making expenditures. Delayed payments directly limit the organization’s ability to pay for new initiatives or add more services.
Mounting Audit Penalties
It’s impossible to overlook the financial risk of manual reporting because of recent trends in enforcement.
Price Transparency Penalties: The maximum penalty from the CMS is still $2 million, but the average penalty has gone up from $110,000 in 2021 to $511,000 in 2022. A Florida hospital was fined $979,000 in 2023, which shows how this trend is going. As of January 2024, CMS has indicated that good-faith efforts may no longer be sufficient to avoid sanctions if hospitals fail to fully meet transparency standards.
Medicare Secondary Payer (MSP) Penalties: Starting on October 11, 2024, not following the rules will cost you up to $1,000 a day for each late record, up to $365,000 a year for each instance. CMS will enforce penalties retroactively under a five-year statute of limitations.
IQR and OQR Penalties: Failure to meet Inpatient and Outpatient Quality Reporting standards triggers an Annual Payment Update (APU) reduction, cutting the 2024 3.1% Market Basket Update (MBU) by 25%. A hospital earning $20M annually could see an immediate loss of $168K, with compounding downstream effects.
CMS is cracking down on enforcement, which makes mistakes and missed deadlines too expensive.
Burnout, Fatigue, and Error Rates
Manual reporting adds cognitive load, leading to burnout—a known driver of clinical errors. A 2025 report found 68% of night staff and 53% of day staff struggle with focus due to fatigue, with 4% of night staff reporting medication errors. A 2024 meta-analysis showed burned-out doctors are 2.7x more likely to make mistakes.
Medical errors now cause over 250,000 deaths annually in the U.S., ranking as the third leading cause of death. For leaders focused on safety, reducing manual work is critical.
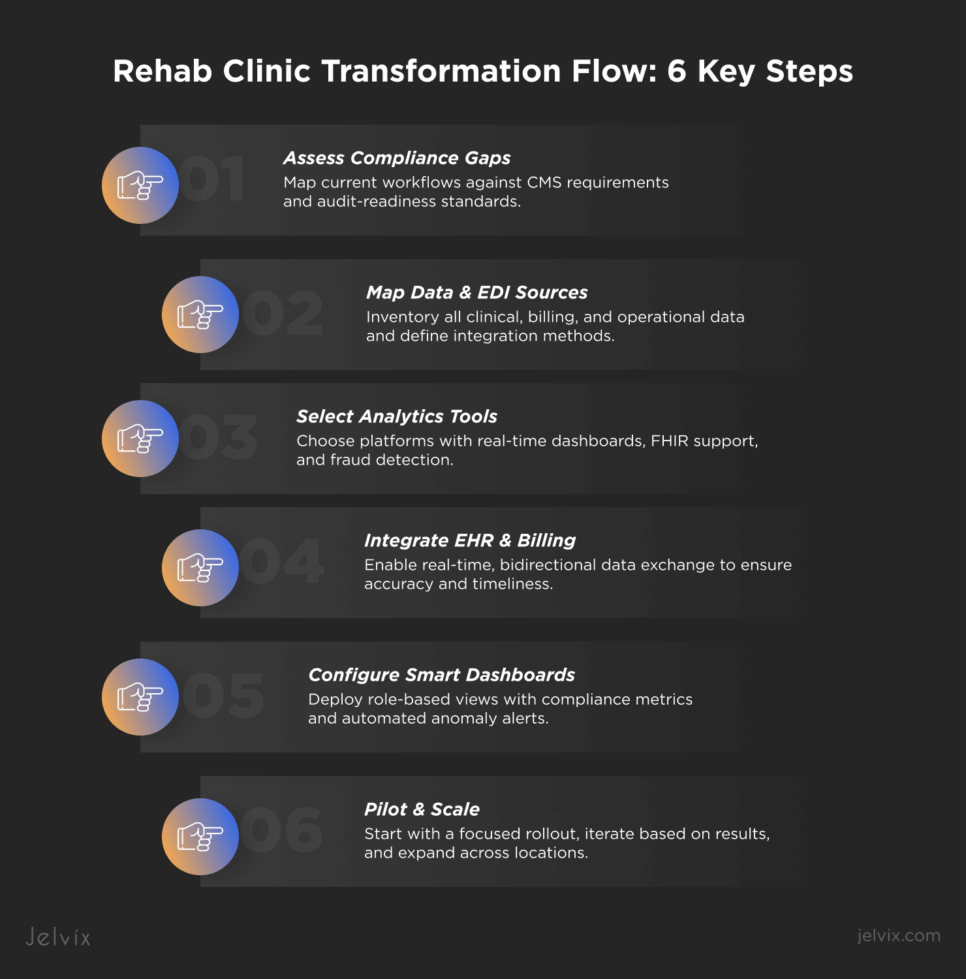
6-Step Playbook to Scale with Automated Reporting for Rehab
Step 1. Assess Gaps and CMS Regulations Requirements
The first step is to build an actionable baseline. Begin by mapping current workflows against the full set of CMS reporting requirements—not just for Medicare claims but across quality programs (IQR/OQR), MSP reporting, Price Transparency, and APU-linked measures.
On the technical side, this requires
- Data lineage mapping: Where does each required data element originate (EHR, billing, LIS, RPM)?
- Transformation logic: Which fields require normalization or translation before inclusion in CMS files?
- Submission pathways: What is the current pipeline for 837/835 transactions and other EDI or XML-based CMS files? Are they fully automated or semi-manual?
From a management perspective, leaders should assess
- Roles and ownership: Who is accountable for preparing, validating, and submitting each report?
- Audit readiness: Is documentation and data provenance sufficient to defend against a CMS audit?
- Scalability: Will current processes support additional locations or new service lines without adding a manual burden?
Step 2. Map Data Sources and EDI Pipelines
Start by conducting a comprehensive data source inventory—this goes beyond listing systems; it must also document data structures, ownership, quality, and the maturity of interoperability.
Key data domains to map:
- EHR mental health and physical rehab platforms — clinical outcomes, functional status, therapy minutes, orders, encounter details.
- Billing and Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) — patient demographics, charge capture, CPT/HCPCS codes, modifiers, payer info, payment posting, write-offs.
- Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) platforms — device data, transmission frequency, physician reviews, billing triggers.
- Laboratory Information Systems (LIS) — lab orders/results relevant to rehab information (infection control, medication management, chronic condition monitoring).
For each source, define:
- Data ownership: Who governs data quality and change management?
- Refresh intervals: Real-time, hourly, daily? What are acceptable data latency thresholds for CMS-compliant reporting?
- Interoperability method: HL7 v2.x, FHIR, flat-file, API?
- Transformation needs: Are mappings to CMS data formats already in place (e.g. NUBC codes for inpatient rehab)?
Next, analyze current EDI pipelines:
- Are 837 and 835 transactions fully automated, or do they require manual pre-processing?
- How are CMS quality reports (IQR, OQR, MSP, Price Transparency) currently generated—via internal BI, third-party clearinghouse, or manual file prep?
- Where are failure points (e.g., transmission errors, format mismatches, payer rejections)?
Finally, assess auditability:
- Does the pipeline provide traceability from the original source data to the submitted file?
- Can errors or exceptions be automatically flagged and remediated?
Leadership can build reliable Medicare compliance automation and make sure that reporting can grow without adding compliance risk by carefully mapping both data sources and EDI pipelines. Partnering with the right software development team at this stage can accelerate integration planning, reduce rework, and ensure audit readiness is built into the pipeline from day one.
Step 3. Select Rehab Data-Analytics Tools
Choosing the proper rehab data analytics tools is a strategic choice that affects how well an organization can grow safely and stay compliant. Many rehab networks today struggle with reporting inconsistent environments, with clinical analytics, financial performance dashboards, compliance tracking, and operational data dispersed across multiple platforms.
A good automated reporting architecture should bring all of these features together under a single data strategy. To that end, leadership teams should establish a formal evaluation matrix, incorporating input from compliance, finance, clinical operations, and IT to help them select the most suitable tools.
Your data tools need to function together seamlessly. Find a platform that has real-time dashboards and built-in templates for CMS reporting (such as IQR, OQR, and MSP) that can handle both structured billing data and more complicated inputs like EHR notes or device readings.
A major part of it is also automation. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) lets you automate operations like pulling custom fields from EHRs, matching remittances, and detecting problems.
Clinical interoperability matters, too. Your tools should connect easily to core systems—EHRs, billing platforms, LIS, and RPM—without relying on fragile one-off integrations. FHIR standards are essential, particularly as CMS and ONC requirements continue to evolve.
And when your business gets bigger, good governance becomes a must. You will require clear audit trails, trustworthy data lineage, and workflows that can be altered when rules or calculations change.
Step 4. Integrate Seamlessly with EHR and Billing
Automated reporting only works if the data from your EHR and billing systems is always the same and works together. Reports won’t match up with real care or revenue without it, which puts both compliance and cash flow at risk.
Newer EHRs use FHIR-based APIs, while older ones use HL7. Middleware can bring various sources together, check important data like therapy codes in real-time, and stop expensive delays in submissions.
Point-to-point connections don’t scale. Instead, employ an integration that is flexible and service-oriented, supporting synchronization almost in real-time. This way, leaders can act on current data instead of relying on outdated dashboards.
Step 5. Configure Dashboards for Compliance and Fraud Prevention Systems
Start by defining role-based views. Different stakeholders need tailored insights. For example, clinical leadership monitors therapy intensity, functional improvement scores, discharge trends, and documentation gaps that may impact reimbursement.
Fraud prevention must be built into the dashboard layer through embedded anomaly detection. Effective systems apply machine learning or statistical scoring to identify deviations from historical norms.
Leaders need to keep an eye on compliance and revenue risk continuously, not only when they get reports at the end of the month. To support proactive action, dashboards should show current operational data from EHR, billing, and other systems. Working with an experienced partner can make this level of traceability and automation far easier to implement
Lastly, being able to audit should be a key design principle. Users should be able to go from high-level metrics to the transactions or source data that make them up, and they should be able to see how the values were derived.
Step 6. Train and Iterate for Continuous ROI
A big rollout all at once often fails because problems with data quality or workflow don’t show up until it’s too late. Starting with a quick-win pilot in a reporting area that has a clear effect, like IQR/OQR quality measure submission or Medicare Secondary Payer (MSP) reporting, is the preferred way to go.
In the pilot phase, the team can check the data pipelines, test the integration points, improve the dashboards, and make sure that the training materials match how things function in the real world. It also gives executives a model to employ to get buy-in from clinical, compliance, and finance divisions.
Once stability is proved, a rolling rollout should add new locations and service lines to the framework. Each phase should improve the mappings, training, and monitoring.
As the implementation goes on, executives should set up cycles of continuous improvement. These would be regular times to evaluate the dashboard’s performance, make sure the compliance metrics are correct, and update the fraud detection models. This feedback loop leads to greater, long-term ROI and sets the company up for growth that can be scaled and audited.
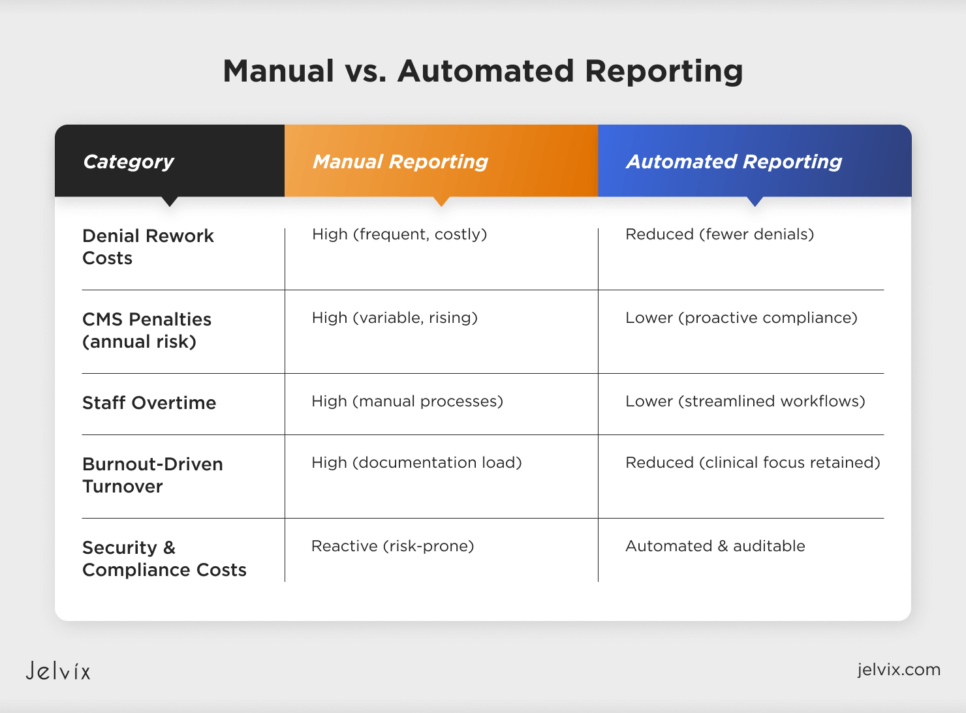
Cost-Avoidance Template: Savings from Medicare Compliance Automation
The benefits of automatic reporting go beyond just making things run more smoothly; they also include avoiding costs. Automation routinely makes things better in a few important cost areas:
Fewer denied claims and rework
According to public data from CMS, Medicare denial rates for institutional claims can be anywhere from 6% to 15%, and it costs between $25 and $118 to process each refused claim again. Automated reporting reduces the likelihood of human errors when coding, entering data, and ensuring timely submissions. This means fewer denials and less money lost.
Staying away from audit penalties
As CMS gets tougher on enforcement, fines for Price Transparency, MSP reporting, and quality measure programs can now be in the hundreds of thousands or millions of dollars. Automation makes reports more accurate and timely, which reduces the number of audit flags and the likelihood of civil monetary penalties.
Costs of overtime and burnout are lower.
Reporting by hand leads to extra hours worked and staff burnout, which raises attrition and replacement expenses. Automated solutions make it easier for administrators, keep labor expenses stable, and keep employees longer.
Automating security and compliance
Companies also reduce the risk of HIPAA violations, data breaches, and associated fines by incorporating security compliance automation into their reporting pipelines. Automated data handling ensures that access is regulated, there are audit trails, and data integrity problems can be fixed more quickly.
Manual vs. Automated Cost Lines
In short, the cost of not automating continues to rise, driven by both regulatory complexity and operational inefficiency. Organizations that deploy modern automated reporting frameworks position themselves to scale safely, maintain margins, and avoid avoidable financial losses.
Compliance & Fraud Prevention: Staying Ahead of CMS Audits
One big benefit is the automated audit trail. Every change to the data, every submission, and every interaction with a user is recorded in a way that can’t be changed. This makes it easy to see how the data moves from the source systems to the final CMS files. This ensures that, in the event of an audit, leadership can demonstrate exactly how the stated numbers were derived, with full access to the underlying clinical and financial data.
Immutable logs also support security compliance automation. Automated solutions assist in defending against unauthorized changes and support HIPAA, HITECH, and other regulatory frameworks by implementing role-based access rules and keeping track of all data handling actions. This lowers the risk of legal problems and makes internal governance stronger.
Dashboards are very important for managing risks before they happen. Automated reporting systems bring up high-risk claims and data errors before they are sent in, which lets compliance teams act quickly.
By finding these trends before they are submitted, businesses may fix any compliance problems before they lead to CMS denials or audit inquiries. This protects both their reputation and their revenue.
How to Choose the Right Tech Partner for Scalable, Compliant Reporting
Choosing the right tech partner can make the difference between a system that scales and one that creates new risks. When evaluating medical software development vendors, look for:
- EHR-ready APIs that enable seamless data flow across platforms;
- HIPAA and FHIR compliance baked into the architecture;
- Deep Medicare EDI expertise to support accurate submissions;
- A real-time analytics stack with dashboards and proactive alerts;
- Well-defined vendor support SLAs to ensure uptime and responsiveness;
- A zero-trust security model to safeguard sensitive patient and financial data.
The right partner helps you build a resilient, CMS-compliant foundation for growth.
Learn how to choose the right health tech partner to accelerate innovation, ensure compliance, and build scalable digital solutions in healthcare.
Conclusion
Automated reporting delivers measurable gains across cost reduction, compliance assurance, and operational scalability. By eliminating manual bottlenecks, rehab organizations can reduce overtime, avoid audit penalties, and accelerate reimbursement cycles. A well-designed reporting framework also gives leaders the confidence to expand services and locations without increasing risk or costs.
It’s no longer optional to be able to stay compliant with CMS, keep an eye on fraud risk, and see performance in real time. As rules get stricter and competition grows, companies that update their reporting will be in the greatest position for long-term growth.
Jelvix can help if your team is exploring ways to automate healthcare workflows.
With extensive experience in medical software development, we specialize in the seamless integration of healthcare systems. Our team partners with rehabilitation and mental health providers to build scalable, secure, and audit-ready solutions.
Book a free consultation — let’s discuss how we can support your goals.
Need a reliable tech partner?
Get a dedicated development team aligned with your goals, processes, and tech stack — fully committed to your product success.