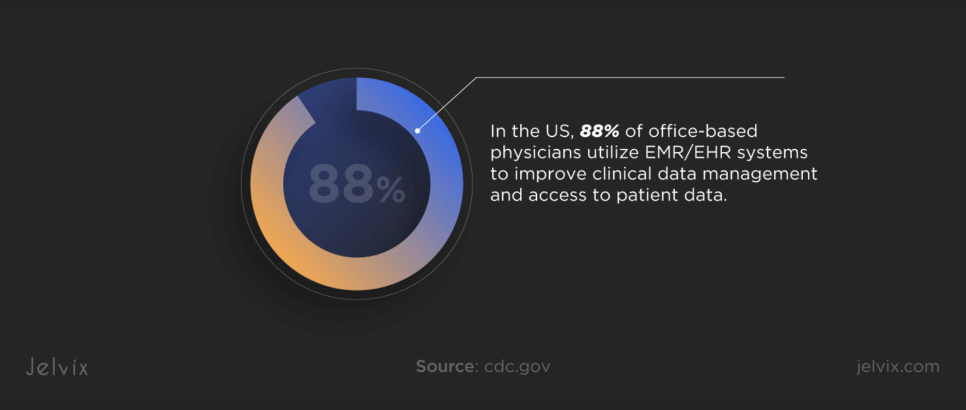
With more patients demanding online access to their health records, clinics widely adopt medical technologies. In the US, 88% of office-based physicians use EMR/EHR systems to enhance clinical data management and access to patient data.
However, clinics often struggle to optimize their EHR systems, missing the opportunity to enhance operational efficiency and reach financial goals.
If you want to know how to get the most out of your clinic’s EHR, keep reading. You’ll find out how to optimize electronic health records effectively and improve clinical workflows, reduce administrative burden, and maximize financial returns.
Understanding ROI Meaning in Healthcare and EHRs
Return on investment (ROI) is a metric used to evaluate the financial performance of investments compared to their costs. It’s a measure that helps businesses, including hospitals and clinics, assess the value generated from investing in technology, equipment, processes, or any other healthcare-related initiatives. In the context of EHR systems, ROI includes improvements in operational efficiency, patient care quality, and compliance with healthcare regulations.
Calculating ROI in healthcare can be complex, as it must account for both direct financial returns (like increased revenue or reduced operational costs) and indirect benefits (such as improved patient health outcomes or enhanced patient satisfaction). What’s more, healthcare ROI assessments often consider the long-term impact of investments on patient care quality and organizational efficiency.
Fundamentals of EHR Optimization
EHRs have already proven themselves as valuable tools for enhancing patient care. 75% of healthcare providers report that electronic health records allow them to deliver better patient care, while 88% indicate that EHRs produce clinical benefits for their practice.
However, EHR is not a one-time purchase that works as intended over the years. It requires constant optimization that involves refining and customizing the system to meet the unique needs of healthcare organizations and their patients.
Evaluating ROI for EHR optimization can help validate the investment in EHR technology, guide improvements, and ensure the system adapts to changing healthcare needs. Proper ROI assessment supports strategic planning and resource allocation, enhancing patient care and stakeholder engagement.
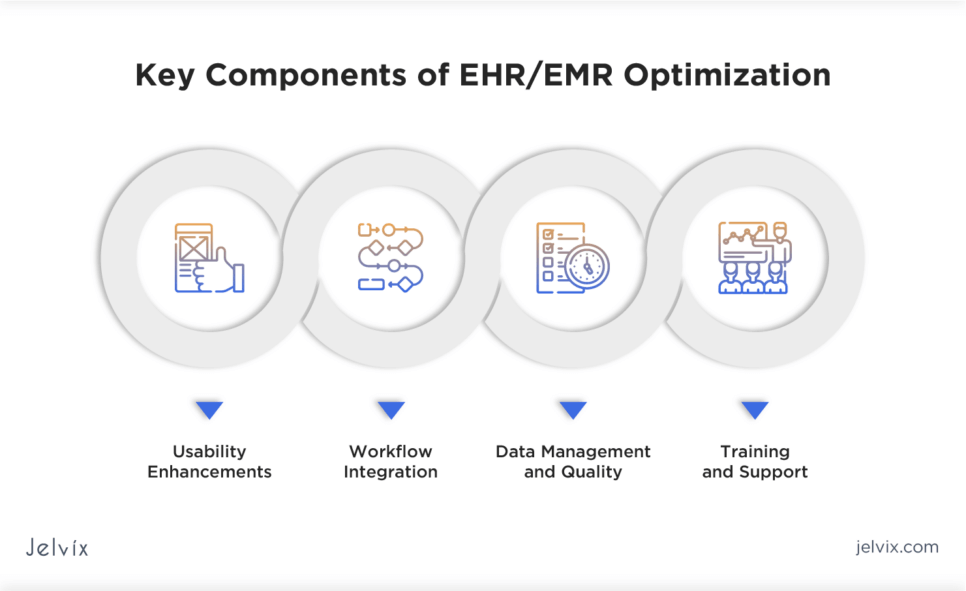
Key Components of EHR/EMR Optimization
EHR optimization is the process of continuously improving and tailoring the system to maximize its usability, efficiency, and clinical value where must-have aspects vary from user-friendly interface to performance monitoring.
Usability Enhancements
An intuitive user interface in an EHR can help physicians navigate the system faster, allowing them to spend more time on patient care. This increased efficiency can lead to higher revenue and lower operational costs.
Workflow Integration
Aligning the EHR with the clinic’s workflows helps to enhance existing processes. Automating routine tasks frees up doctors from administrative burden, improving care quality and potentially increasing the clinic’s revenue.
Data Management and Quality
Protocols for data accuracy and compliance can help improve data quality, reduce errors, and streamline billing processes. This optimization leads to operational efficiencies, cost savings, and better patient outcomes, directly enhancing the investment return.
Training and Support
Continuous education on new updates or changes will help ensure proficiency in EHR users. This can lead to more efficient clinical operations and reduced support costs, as less time is needed for troubleshooting.
How EHR Use Helps Improve Clinic Financial Performance
The adoption and effective use of EHR systems have a significant impact on the financial performance of clinics. By enhancing operational efficiency, improving revenue management, and contributing to patient care, EHRs offer a pathway to financial sustainability and growth for healthcare entities.
Reduction in Administrative Costs
Digitizing records cuts down on paperwork, administrative tasks, and storage costs, allowing staff to focus on patient care and other value-added activities.
Billing Accuracy
Automated coding and billing features in EHRs minimize errors, ensuring accurate reimbursement and reducing claim rejections.
Enhanced Patient Care
Immediate access to comprehensive patient data via EHRs supports better clinical decisions, improving care quality and patient satisfaction.
Data-Driven Decision-Making
EHR analytics enables clinics to use data for strategic planning, optimizing resources, and identifying opportunities for financial growth.
Value-Based Care
EHRs facilitate participation in value-based care models by tracking quality metrics and focusing on improving patient health outcomes.
Enhanced Compliance
Accurate and complete documentation in EHRs reduces liability risks and aids in compliance with healthcare regulations, avoiding fines.
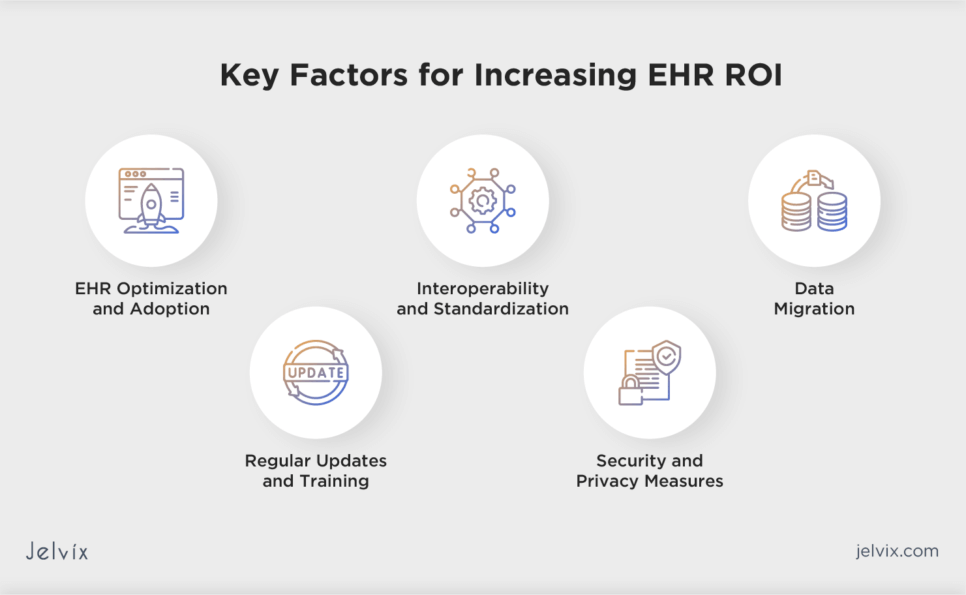
Strategic Planning for EHR Optimization
Integrating EHR systems into healthcare settings and their optimization is a strategic necessity for healthcare entities seeking to improve patient care and financial performance. A thoughtful approach to EHR optimization involves an assessment of current usage, identification of gaps, and the setting of achievable goals.
Assessing Current EHR Use and Identifying Gaps
The first step in EHR optimization is a thoughtful assessment of how the EHR system is used, where it falls short, and what users need the most. Identifying gaps in these areas allows healthcare organizations to implement targeted improvements, enhancing the overall efficiency of EHR systems in supporting patient care.
Setting Goals for EHR Optimization
With a clear understanding of the current state of EHR use, the next step is to set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for optimization. These goals may include:
- Improving clinical efficiency: streamlining clinical workflows to reduce the time spent on documentation, enhance the speed of information retrieval, and minimize administrative burdens on physicians;
- Enhancing data quality: implementing measures to improve the accuracy and completeness of patient data, and using analytics for better clinical and operational decision-making;
- Increasing system usability: customizing the user interface and functionalities to meet the specific needs of users, reducing the learning curve, and enhancing satisfaction with the system;
- Expanding interoperability: enhancing the ability of the EHR system to communicate with other healthcare systems, improving data sharing, and patient care coordination across different care settings;
- Meeting regulatory compliance: ensuring the EHR system meets all regulatory requirements and industry standards.
Setting these goals provides a roadmap for the optimization process, focusing efforts on areas that will deliver the most significant benefits to healthcare organizations and their staff.
Key Areas for EHR Optimization
Optimizing an EHR system is critical for healthcare entities looking to improve care delivery, enhance operational efficiencies, and ensure financial sustainability. Focusing on specific key areas can significantly impact the overall effectiveness and financial performance of EHR.
Enhancing Clinical Workflows for Efficiency
Optimizing EHR systems to enhance clinical workflows involves tailoring the system to fit the natural processes of care delivery. It means reducing unnecessary steps, automating routine tasks, and ensuring that critical patient information is easily accessible to physicians.
Strategies often include adapting the EHR interface to match the specific needs of different users, integrating evidence-based guidelines and alerts to assist physicians in making informed decisions, and automating task management, such as order entries, prescription refills, and patient notifications, to reduce the load on staff.
Improving Data Quality and Accessibility
The value of an EHR system lies in the quality and accessibility of the data it holds. Ensuring that data entered into the system is accurate, complete, and easily retrievable is a must.
Efforts to improve data quality and accessibility may involve developing and enforcing guidelines for data entry in healthcare to minimize errors, enhancing interoperability by using established data standards, such as FHIR, HL7, and CCDA, and using advanced analytics tools to generate insights that guide operational decisions.
Streamlining Documentation and Billing Processes
Documentation and billing are critical yet time-consuming aspects of healthcare that can benefit significantly from EHR optimization. Streamlining these processes not only improves operational efficiency but also enhances revenue cycle management.
Implementing templates, voice recognition software, and other tools within the EHR can make note-taking more efficient. Using EHR functionalities to automatically suggest appropriate billing codes based on clinical documentation can help reduce errors and denials. Finally, integrating billing and insurance verification systems offers the potential to streamline the revenue cycle process from patient check-in to final billing.
Leveraging EHR Features To Maximize ROI
To truly harness the financial benefits of EHRs, healthcare organizations should look beyond basic functionalities. By implementing advanced EHR features, they can achieve significant financial returns, ensuring a positive ROI on their EHR investments.
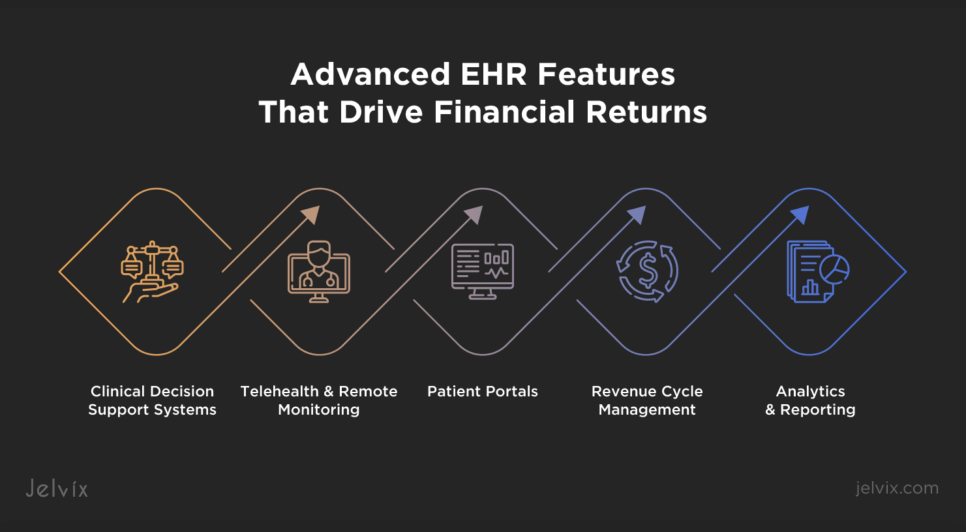
Advanced EHR Features That Drive Financial Returns
Advanced EHR features have the potential to drive financial returns by enhancing clinical efficiency, improving patient care, and streamlining administrative processes. Leveraging these features effectively can lead to significant cost savings and increased revenue.
Clinical Decision Support Systems
CDS systems offer real-time and evidence-based guidance to clinicians at the point of care. By aiding in diagnosis and treatment decisions, CDS systems can reduce medical errors, enhance patient outcomes, and decrease unnecessary testing and procedures, leading to substantial cost savings.
Telehealth and Remote Monitoring
Integrated telehealth functionalities expand service offerings beyond traditional clinical settings, allowing providers to reach a broader patient base and generate additional revenue streams. Remote monitoring capabilities enable proactive management of chronic conditions, reducing emergency visits and hospital readmissions, which are significant cost drivers in healthcare.
Experience the transformative benefits of RPM software developed by Jelvix. Optimize healthcare delivery and improve patient outcomes with innovative telehealth solutions.
Patient Portals
Patient portals improve engagement by allowing patients to access their health records, communicate with physicians, schedule appointments, and refill prescriptions online. Enhanced engagement leads to better compliance with treatment plans, which can positively impact the clinic’s reputation and patients’ trust.
Revenue Cycle Management
EHRs equipped with advanced revenue cycle management (RCM) tools can automate billing, coding, and claims management processes. These tools help ensure accurate billing, reduce claim denials, and accelerate reimbursement, directly impacting the organization’s financial health and ROI in medical billing.
Analytics and Reporting
Advanced analytics and reporting enable healthcare organizations to analyze vast amounts of data for insights into patient care trends and financial performance. These insights support strategic decision-making and identify opportunities for cost reduction.
Customization and Integration with Other Systems
Customizing and integrating EHRs with other healthcare systems are essential for enhancing their effectiveness and financial benefits. Customization tailors EHRs to fit specific organizational workflows and patient needs, while integration enables seamless data sharing, minimizes duplication and errors, and optimizes billing processes. Together, these strategies boost EHR functionality, improve patient care, and streamline operations, leading to a more effective healthcare experience and cost reduction.
Training and Support for Staff To Increase ROI in Healthcare
Training and support ensure that healthcare staff can effectively use the full capabilities of the EHR system. By regularly engaging in training sessions and learning opportunities, staff can deepen their understanding of EHRs, improving their proficiency. This not only enhances the quality of patient data entered into the system but also empowers users to identify and suggest system customizations that better align with clinical workflows.
Implementing Support Systems for EHR Users
A robust support system is crucial for addressing the challenges users may face with EHRs. Providing readily accessible technical support and help desks ensures that users can quickly resolve issues, minimizing disruptions to patient care and operational workflows.
Establishing peer support networks within the organization can facilitate knowledge sharing and empower users to solve problems collaboratively. Also, offering online resources and documentation enables users to self-serve information on troubleshooting and system functionalities.
Discover the advantages and challenges of EHR real-time data entry and explore practical strategies to optimize your data management processes.
Measuring the Impact of EHR Optimization
То measure the impact of EHR implementation, healthcare organizations should use a comprehensive approach that involves identifying specific metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs), as well as conducting a financial analysis before and after the optimization efforts.
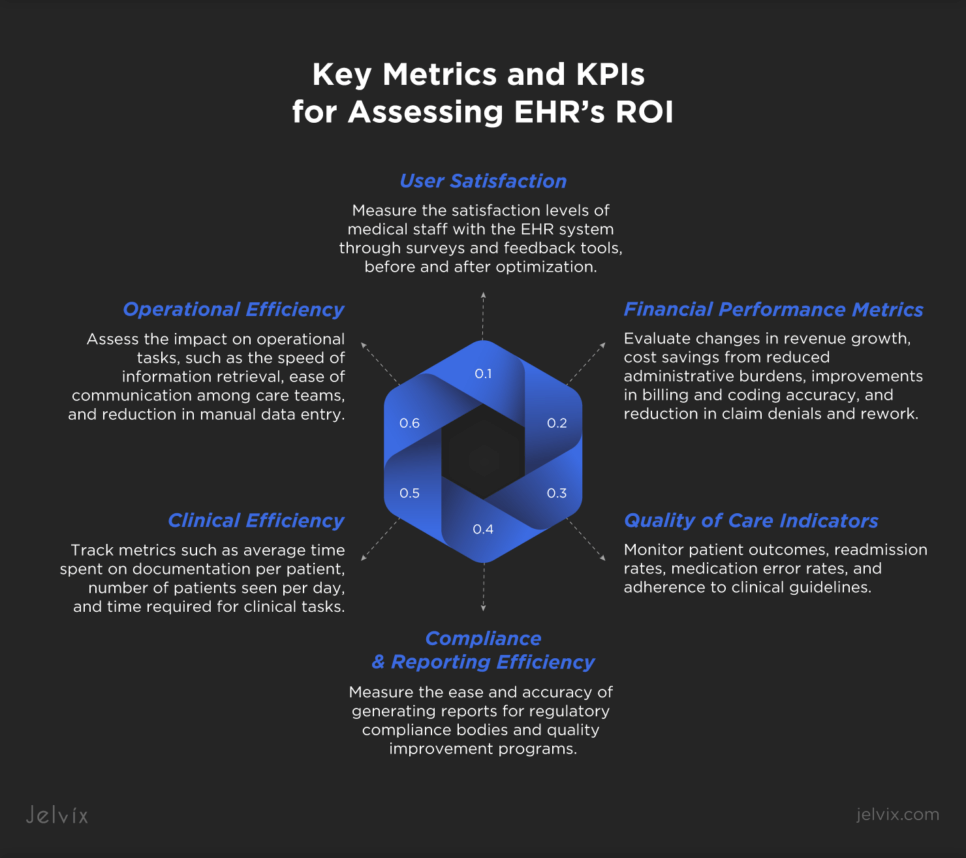
Key Metrics and KPIs for Assessing EHR’s ROI
The Jelvix team recommends that healthcare organizations focus on key metrics listed below to effectively evaluate the ROI of their EHR system.
User Satisfaction
Measure the satisfaction levels of medical staff with the EHR system through surveys and feedback tools, before and after optimization. High satisfaction levels often correlate with improved productivity and adoption rates.
Clinical Efficiency
Track metrics such as average time spent on documentation per patient, number of patients seen per day, and time required for clinical tasks. Improvements in these areas indicate that the EHR system is effectively streamlining clinical workflows.
Quality of Care Indicators
Monitor patient outcomes, readmission rates, medication error rates, and adherence to clinical guidelines. Positive changes in these indicators suggest that EHR optimization is enhancing the quality and safety of patient care.
Financial Performance Metrics
Evaluate changes in revenue growth, cost savings from reduced administrative burdens, improvements in billing and coding accuracy, and reduction in claim denials and rework. These financial metrics directly reflect the economic impact of EHR optimization.
Operational Efficiency
Assess the impact on operational tasks, such as the speed of information retrieval, ease of communication among care teams, and reduction in manual data entry. Operational improvements can lead to better resource utilization and cost savings.
Compliance and Reporting Efficiency
Measure the ease and accuracy of generating reports for regulatory compliance bodies and quality improvement programs. Efficient reporting can save time and ensure compliance with healthcare regulations, affecting financial incentives and penalties.
Conducting Financial Analysis
Conducting a financial analysis before and after EHR optimization helps understand the economic impact of investments in electronic health records. This process begins by establishing a baseline of financial performance before optimization, including direct costs, operational inefficiencies, and any revenue losses due to suboptimal billing practices.
After implementing EHR optimization strategies, a financial analysis is performed to assess changes in revenue, cost savings, and financial performance. This involves comparing pre- and post-optimization metrics such as operational costs, revenue growth, billing accuracy, and the efficiency of administrative processes.
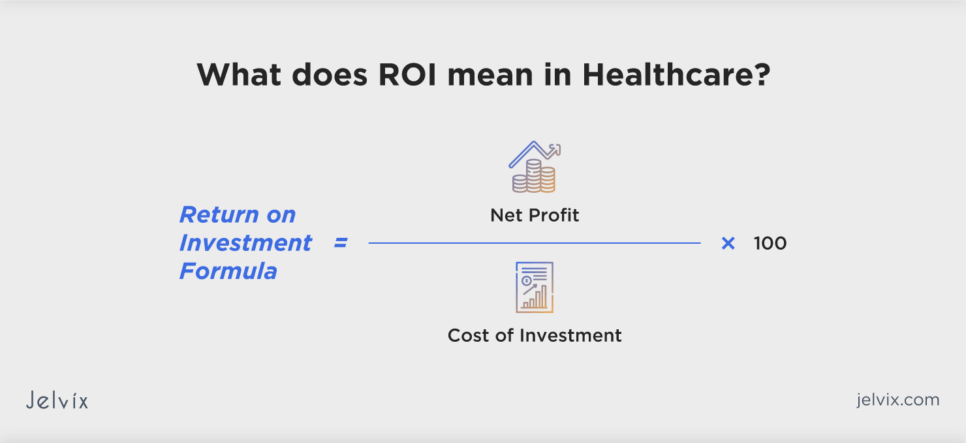
Calculating ROI and Payback Period
ROI is usually calculated by first deducting the investment’s initial cost from its final value, then dividing this result by the initial investment cost, and lastly, multiplying by 100:
ROI = (Net Profit / Cost of Investment) ×100.
You can also use another method:
ROI = (FVI − IVI) / Cost of Investment × 100, where FVI means “Final value of investment” and IVI means “Initial value of investment”.
Another important thing to count is the payback period, a financial metric used to determine the time required for an investment to generate profits sufficient to cover the initial capital outlay.
The formula for determining this is the following:
Payback Period = Cost of Investment / Average Annual Cash Flow.
Investments that have a quicker payback period are generally perceived as being less risky.
Case Studies: Success Stories of EHR Optimization
Real-world case studies can become a source of valuable information about how healthcare companies develop, implement, and optimize EHRs to enhance patient care and benefit financially.
Increased Physician Productivity
The Southeast Permanente Medical Group (TSPMG), part of the Kaiser Permanente network in Atlanta, achieved notable success in lowering burnout rates among its healthcare staff by implementing an EHR system and optimizing it for the clinic’s needs. They reduced their burnout rate from 48% in 2022 to 43% in 2023, a significant improvement against the national average of 53%. As a result, physicians could spend more time on patient care, leading to enhanced patient satisfaction and trust.
Faster Access to Patient Data
The Regenstrief Institute implemented an FHIR-based EHR system to ease clinicians’ access to health information from the Indiana Network for Patient Care. This innovation cut search time from 3 minutes to 5 seconds, enhancing efficiency and decision-making in patient care by reducing the effort required to retrieve relevant patient information.
Improved Healthcare Delivery
The University Hospitals Birmingham NHS Foundation Trust in the UK successfully implemented the Cerner EHR system, leading to significant improvements in healthcare delivery. The system not only enhanced communication and collaboration among healthcare professionals but also improved patient experience by providing access to online services and simplifying the appointment scheduling process.
Challenges in Achieving ROI Through EHR Optimization
Achieving a positive ROI through EHR optimization represents several challenges for healthcare organizations that can impact the effectiveness of optimization efforts and the overall financial and clinical benefits. Overcoming these obstacles requires engaging users early in the optimization process, offering comprehensive training, and demonstrating the tangible benefits of the optimized EHR system to their daily tasks and patient care outcomes.
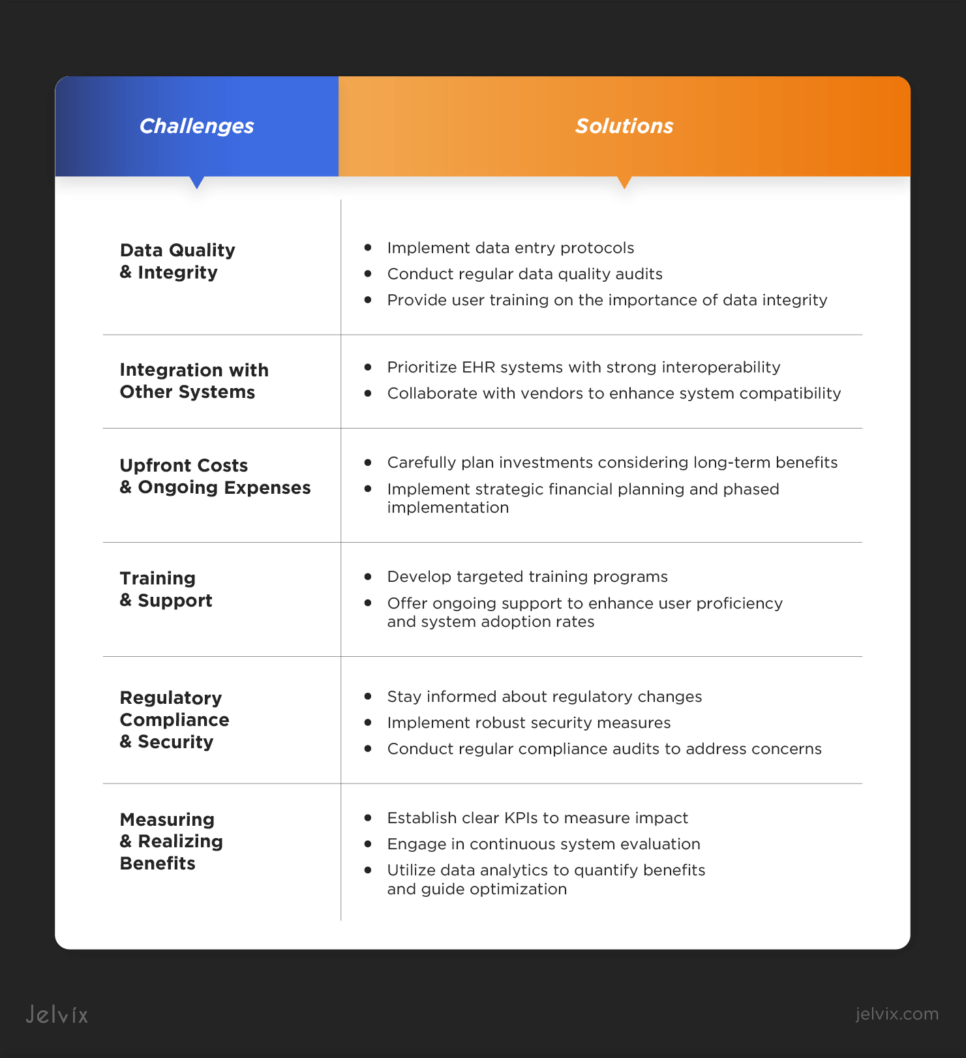
Data Quality and Integrity
Poor data quality can compromise clinical decisions and financial processes, so keeping it accurate and complete is essential for effective optimization. Addressing this challenge involves implementing data entry protocols, regular data quality audits, and user training on the importance of data integrity.
Integration with Other Systems
Achieving seamless integration between EHRs and other healthcare systems can be resource-intensive and complex. Lack of interoperability can limit efficiency gains from EHR optimization. Possible healthcare solutions include prioritizing EHR systems with strong interoperability and collaborating with vendors to enhance system compatibility.
Upfront Costs and Ongoing Expenses
Balancing the significant upfront and ongoing expenses of EHR optimization against anticipated financial returns is challenging. Organizations should carefully plan their investments, considering long-term benefits and potential cost savings. Strategic financial planning and phased implementation can help manage costs while pursuing optimization goals.
Training and Support
Providing adequate training and support to all EHR users is crucial but challenging due to diverse user tech-savviness, time constraints, and resource limitations. Developing targeted training programs and offering ongoing support can enhance user proficiency and system adoption rates.
Regulatory Compliance and Security
Navigating healthcare regulations and ensuring EHR compliance are ongoing challenges. Staying informed about regulatory changes, implementing robust security measures, and conducting regular compliance audits to address regulatory concerns.
Measuring and Realizing Benefits
Identifying metrics to measure the impact of EHR optimization and realizing anticipated benefits can be difficult. Benefits like improved patient outcomes are hard to quantify. Establishing clear KPIs, engaging in continuous system evaluation, and leveraging data analytics can help quantify benefits and guide further optimization efforts.
The Future of EHR Systems and Clinic ROI
Artificial intelligence promises to transform EHR systems, with 90% of US physicians planning to use AI for tasks like data entry. Meanwhile, 82% of hospitals with basic EHRs offer telehealth to improve access to care. As a result, we’ll see wider use of patient portals and online appointment scheduling tools.
Additionally, the use of telemedicine and remote patient monitoring is on the rise. By 2025, it’s expected that over 70 million patients in the U.S. will use RPM tools, showing a clear trend toward integrating these technologies with EHR systems.
How To Achieve ROI with Custom EHR Solutions
Integrating and optimizing EHRs can significantly impact organizational workflows, the quality of patient care, and financial outcomes. A properly developed and optimized EHR system can elevate the standard of care, while the use of a legacy system can lead to challenges.
At Jelvix, we offer expertise in customer EHR development, implementation, and optimization tailored to meet the unique requirements of healthcare entities. If you require professional guidance or assistance in transforming your EHR system, contact us to enhance your healthcare technology infrastructure and improve patient care.