With the increasing shift of organizations toward cloud computing for addressing contemporary tech challenges, there needs to be more clarity regarding HIPAA compliance within the healthcare sector. A common misconception is that an organization has diligently safeguarded electronic health records and medical data by merely opting for a renowned public HIPAA-compliant cloud storage. This belief is somewhat hasty.
Yes, selecting a trusted public or private cloud is a commendable step to achieving HIPAA compliance. However, the burden of responsibility regarding data protection remains with the primary organization or its designated service provider. Let’s clear up these misunderstandings and discuss what steps organizations should take to be fully HIPAA-сompliant.
HIPAA and the Advantages of the Cloud
When discussing healthcare data, two essential concepts consistently rise to the forefront: HIPAA regulations and cloud storage. Both have their distinct importance in the modern healthcare landscape, each offering advantages and considerations.
Understanding HIPAA in Healthcare
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, commonly called HIPAA, was introduced in 1996 to safeguard and uphold the confidentiality of patient data. This law mandates certain protocols for organizations dealing with patient data to guard against unauthorized access or unintentional leaks.
A cornerstone of HIPAA is the Privacy Rule, which provides a framework for how Protected Health Information (PHI) can be utilized and disseminated. PHI (including electronic PHI or ePHI) pertains to any data linked to their Electronic Health Record comprising personal identifiers like names, addresses, social security numbers, birthdates, or medical documentation.
To stay aligned with technological progress, HIPAA has seen several updates. For instance, as of 2013, healthcare entities must partner with HIPAA-compliant cloud storage solutions for medical data storage. Non-compliance puts patient information at risk and can bring about significant repercussions for the provider.
What does it mean for cloud storage to be HIPAA-compliant?
HIPAA-compliant cloud storage, in essence, is a digital storage system that aligns with the stringent privacy and security standards set by the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
HIPAA doesn’t offer a formal certification to label a cloud service as fully compliant. Instead, many cloud providers strive to adhere to security protocols that align with HIPAA’s security directives. Key among these standards are frameworks like NIST 800-53 and FedRAMP. So, if you’re in the market for a HIPAA-compliant cloud storage solution, these are some benchmarks you’ll want to keep an eye on.
When we discuss cloud services adhering to HIPAA guidelines, we’re delving into ensuring the utmost protection of sensitive patient health information. It includes:
Technical Safeguards:
In the tech-driven world of healthcare, HIPAA compliance hinges on a fortified digital foundation. Drawing from leading practices, here’s what stands out in a HIPAA-ready digital setup:
- Secure Data Transfer: A compliant system guarantees the safe movement of patient details, ensuring responsible and transparent data sharing.
- Precision Access Control: Controlled data access is crucial for a health platform. Users must recognize their access rights, with oversight mechanisms to detect any breaches.
- Upholding Data Authenticity: Systems should deter unauthorized data modifications. There must be strict rules for adjusting or deleting records backed by robust tech tools.
In short, these safeguards guide tech professionals, helping them anticipate risks and craft realistic user scenarios in building healthcare solutions. With HIPAA, adopting a cautious stance rooted in thorough analysis and industry insights is wise.
Physical Safeguards:
While HIPAA-compliant cloud storage software security is paramount, the physical safeguarding of hardware is equally critical. Direct access to devices could open doors for cybercriminals, possibly exposing stored patient information. This risk persists even if you’re harnessing cloud storage for ePHI.
- Device Security: Each workstation within the facility should adhere to HIPAA guidelines and be supervised by IT security specialists. The areas housing servers and computers must have defined access controls. An immediate action plan should be in place for a breach.
- Restricted Facility Entry: Access to data centers should be strictly limited to personnel with authorized clearance, maintaining a high level of security for sensitive data storage areas.
- Data Sanitization: When decommissioning storage devices, it’s vital to ensure their data is irretrievably destroyed. Service providers like AWS ensure that the end-of-life data is securely erased in compliance with industry standards so that unauthorized parties cannot recover it. This process happens seamlessly, often unbeknownst to software developers and system maintainers, as part of the routine replacement of physical infrastructure.
The combination of software and hardware protection layers solidifies the defenses against potential data breaches.
Administrative Safeguards:
Often, data management can be the Achilles’ heel in HIPAA compliance. Thus, when selecting HIPAA-compliant cloud-based storage, it’s imperative to scrutinize its administrative controls. Here’s a distilled list of essentials:
- Vendor Transparency: A HIPAA-compliant cloud provider should candidly discuss their compliance levels. They ought to collaborate on consultations and assist in framing administrative strategies.
- Staff Insight & Training: Opt for a vendor well-versed in HIPAA, ideally one with a track record serving healthcare entities. They should equip you with a robust knowledge base, preferably with the cloud functionalities elucidated in the HIPAA context.
- Data Access Protocols: Each institution should craft its data access blueprint. While vendors can offer guidance through official resources, the onus is on your team to tailor-make the process. Engage your tech and security teams to spotlight and address system vulnerabilities.
- Crisis Anticipation & Response: In tandem with the cloud provider, identify prevalent threats and chart out responses for each scenario.
To sum up, navigating administrative HIPAA safeguards is a shared endeavor. While the vendor illuminates the path with tailored resources, your team must adapt and implement these in alignment with your unique architecture and protocols.
Who Requires HIPAA-Compliant Cloud Solutions?
While HIPAA guidelines ensure the protection of PHI, it’s not just healthcare providers that need to adhere. HIPAA defines the subsequent as covered entities:
- Medical professionals who electronically share health-related information;
- Health insurance bodies, employer-sponsored health plans, and governmental healthcare payment programs (like Medicare or Medicaid);
- Entities like healthcare clearinghouses manage and process health data from various organizations.
Moreover, any organization supporting a covered entity in its healthcare-related tasks and functions must also abide by HIPAA. Since these supporting organizations might access, manage, or distribute sensitive health information, they’re obligated to uphold the same standards as covered entities.
Business associates falling under HIPAA’s purview include:
- Cloud solution providers (CSPs);
- Data storage agencies;
- Organizations managing insurance claims;
- Accounting firms;
- Medical documentation services.
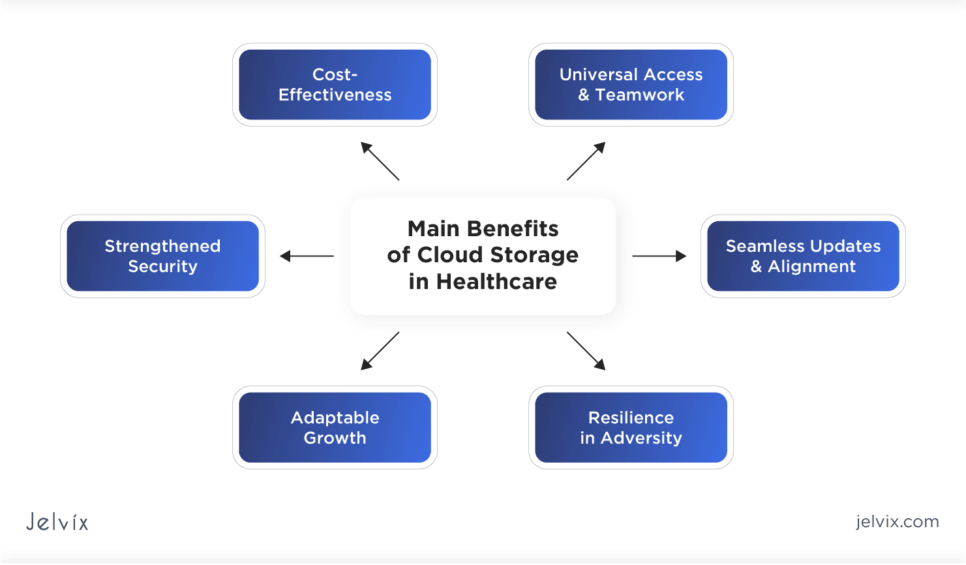
Benefits of Cloud Storage in Healthcare
In this discussion, we’ll delve into how cloud technology dovetails with HIPAA mandates and the benefits it presents to healthcare institutions.
- Strengthened Security: Leading cloud vendors prioritize and continually bolster their security frameworks, safeguarding data comprehensively. This commitment encompasses encryption during transit and storage, multi-factor authentication, and routine security evaluations. Such rigorous security measures not only align with HIPAA’s security standards but often surpass them, assisting healthcare providers in their compliance journey.
- Adaptable Growth: Another benefit of cloud services lies in their adaptability. Healthcare institutions can dynamically adjust their resources based on real-time demands, managing the influx of health-related data without steep preliminary infrastructure costs.
- Cost-Effectiveness: The overheads of in-house servers and data centers can be daunting. Transitioning to cloud solutions allows healthcare establishments to markedly trim down expenses linked to hardware upkeep and energy usage.
- Universal Access and Teamwork: The cloud allows medical professionals to retrieve patient records from almost any location, given the right credentials. That enhances teamwork and proves pivotal when swift, informed decisions are paramount.
- Resilience in Adversity: A notable feature of numerous cloud platforms is their inherent backup and disaster recovery functions. In the unfortunate event of data compromises or other setbacks, the cloud’s backup provision ensures prompt data restoration, curtailing potential operational halts and data losses.
- Seamless Updates and Alignment: Cloud service providers are consistently on their toes, refining their offerings in sync with technological progressions and legal stipulations. Such an anticipatory stance guarantees that healthcare entities remain in line with regulations, sidelining the need for recurrent internal IT refurbishments.
Cloud Providers
For those seeking HIPAA-compliant options for cloud services, several providers stand out for their commitment to maintaining the necessary standards. These providers include:
AWS Cloud
AWS Cloud stands out for its adherence to HIPAA and other vital healthcare security protocols. Its Quick Start feature allows users to set up a HIPAA-compliant environment rapidly. AWS maintains rigorous security benchmarks and matches its HIPAA risk strategies with FedRAMP, intended for federal agency providers, and NIST 800-53, a US federal security and privacy guide by the National Institute of Standards and Technology.
Microsoft Azure
Microsoft Azure is a cloud computing service created by Microsoft for building, testing, deploying, and managing applications and services through Microsoft-managed data centers. It provides software as a service (SaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and infrastructure as a service (IaaS). Azure is compliant with a broad set of international and industry-specific standards, including HIPAA, providing secure and compliant data residency and data protection.
Google Cloud
Google champions HIPAA compliance and is built on a robust infrastructure designed by a 700-strong security team. It undergoes third-party security audits and boasts tools optimized for electronic health record management. While businesses should adhere to security guidelines, Google Cloud guarantees healthcare organizations complete control over their records.
Oracle Cloud
Oracle Cloud offers a complete suite of cloud services, including IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, and ensures data security through advanced security technologies, operational practices, and compliance policies. It is also compliant with HIPAA, helping healthcare organizations manage PHI (Protected Health Information) securely.
Data Storage and Backup Solutions:
When it comes to storing data and creating backups, there are specialized services that also ensure HIPAA compliance. These include:
Microsoft OneDrive
Microsoft OneDrive is compatible with HIPAA guidelines, but businesses must actively ensure data security. While OneDrive’s foundational structure aligns with HIPAA, Microsoft offers extensive guidance, especially for Azure and Office 365 users. OneDrive stands out for businesses relying on Office integration. Microsoft emphasizes HIPAA adherence by restricting PHI access and through its range of compliance tools.
Dropbox Business
Dropbox Business is geared for HIPAA compliance. US clients can sign a business associate agreement for HIPAA-consistent collaboration. It offers defined sharing controls, permanent data removal, live account tracking, and secure external integrations. Security features include dual-factor authentication, TLS encryption, and 256-bit AES safeguards. It’s also been verified against ISO 27001 and SOC 2 standards.
Carbonite
This cloud platform, designed with a focus on data backup and protection, emerges as a cost-effective choice for smaller healthcare entities. Carbonite’s capabilities in backup and disaster recovery are commendable. Files are encrypted once backed up, and the platform also aligns with stringent standards like the Massachusetts Data Security Compliance.
In conclusion, while these vendors offer tools and environments conducive to HIPAA compliance, healthcare institutions must actively ensure that their systems adhere to all requisite guidelines. Engaging with compliance experts during the cloud solution implementation phase is always wise.
HIPAA Compliance in Cloud Storage: A Guided Approach by Jelvix Experts
Though every company managing PHI must adhere to HIPAA regulations, no tech platform can claim to be inherently HIPAA compliant. True compliance hinges on the broader framework of how an organization integrates and oversees its technological resources. Even if a cloud storage system is meticulously designed to meet HIPAA standards, the organization must be responsible for deploying it correctly. Additionally, they must ensure that the system collaborates with its associated systems to maintain HIPAA compliance.
If healthcare IT or compliance isn’t your primary domain, navigating the steps above can seem overwhelming. As your presence in the cloud broadens, complexities inevitably arise. In such situations, partnering with an external provider well-versed in HIPAA nuances can be invaluable. They can steer you adeptly, ensuring that your operations in the public cloud remain compliant.
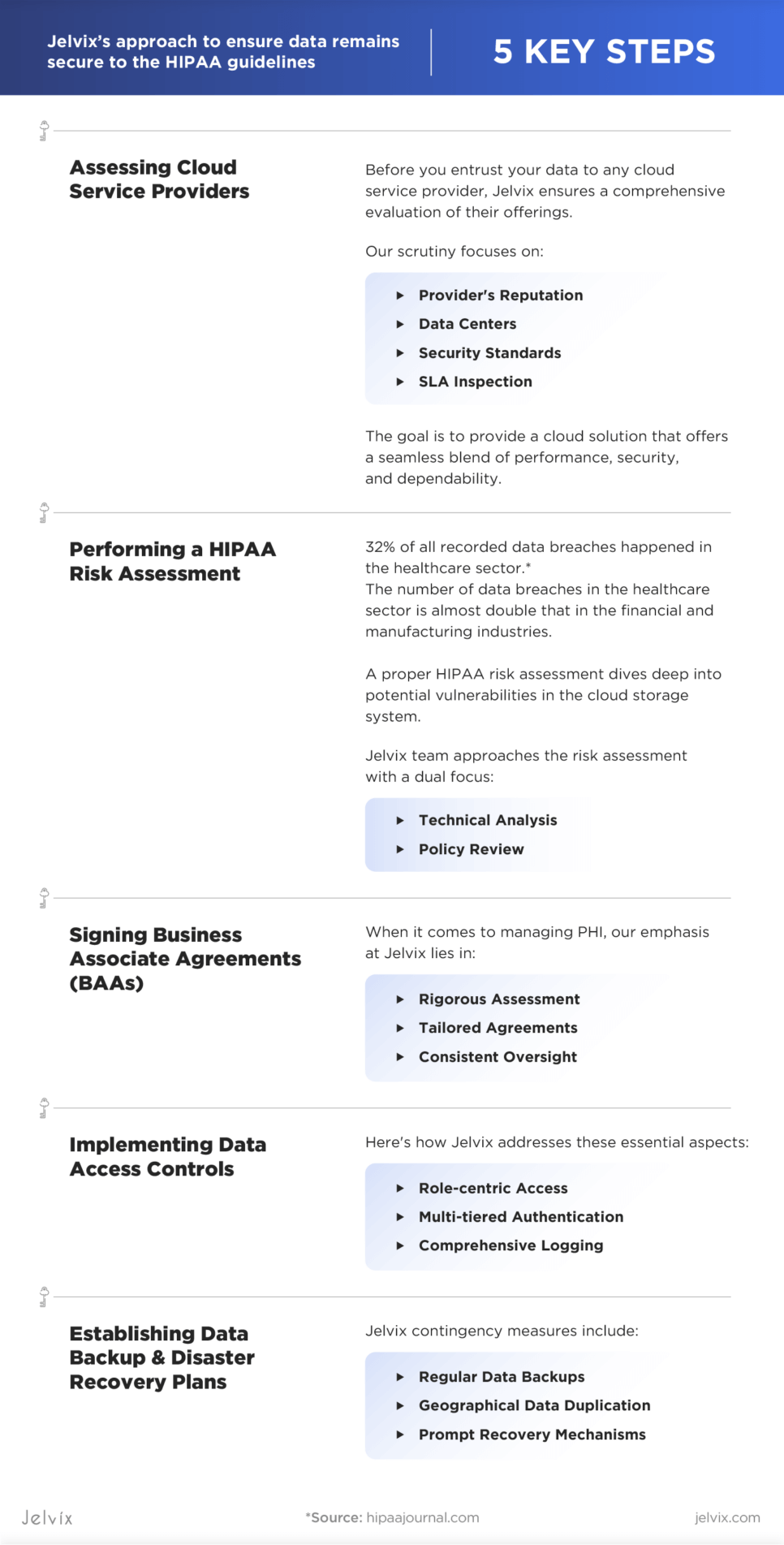
At Jelvix, we’ve honed a systematic approach to ensure your data remains secure, adhering strictly to the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) guidelines. Let’s delve into this process.
Assessing Cloud Service Providers
Before you entrust your data to any cloud service provider, Jelvix ensures a comprehensive evaluation of their offerings. We meticulously evaluate their infrastructure, security protocols, past performance, and overall reliability. Our scrutiny focuses on:
- Provider’s Reputation: We initiate our examination with a deep dive into the provider’s standing in the industry. That includes studying market trends, reading through customer testimonials, investigating awards, and any certifications that attest to their service quality and dependability. The goal is to establish a clear picture of the provider’s track record for reliability and excellence.
- Data Centers: The physical location and security of a provider’s data centers are pivotal. We investigate the geographic distribution of their facilities, considering political stability, regional data protection regulations, and the risk of natural disasters. We also scrutinize their operational practices, including disaster recovery plans and physical security measures, to ensure the data centers are fortified against both digital and physical breaches.
- Security Standards: We dissect the provider’s approach to encryption, looking at how they protect data as it moves across networks and when it’s stored on their servers. This examination includes an assessment of the encryption algorithms they employ, the robustness of their key management processes, and their strategies for maintaining data integrity and confidentiality.
- SLA Inspection: Service Level Agreements are dissected to uncover the precise terms of service. That involves examining the provider’s commitment to uptime, their protocols for handling outages, and their track record for maintenance and customer support responsiveness. The SLA provides the legal groundwork for the relationship, so we analyze it to ensure it aligns with our client’s needs for availability, support, and redressal mechanisms.
Through this meticulous evaluation process, Jelvix seeks to ensure that the chosen cloud service provider not only claims to offer secure and reliable services but also has the infrastructure, practices, and track record to back up those claims. The goal is to provide our clients with a cloud solution that offers a seamless blend of performance, security, and dependability.
Performing a HIPAA Risk Assessment
A proper HIPAA risk assessment dives deep into potential vulnerabilities in the cloud storage system. At Jelvix, our experts analyze the potential risks to the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of PHI stored in the cloud.
Using advanced tools and our accumulated expertise, we highlight areas of concern and provide a detailed roadmap to rectify any identified shortcomings, ensuring a secure environment for sensitive health information. Our team approaches the risk assessment with a dual focus:
- Technical Analysis: We utilize state-of-the-art tools for scanning for HIPAA-compliant cloud file storage vulnerabilities, ranging from potential data breaches to unauthorized access.
- Policy Review: Beyond the technical aspect, we assess the provider’s policies, ensuring they’re up-to-date with HIPAA requirements and emphasizing PHI’s confidentiality and availability.
Signing Business Associate Agreements (BAAs)
At Jelvix, we don’t view a BAA as a mere formality. Instead, we see it as a binding commitment that mandates the meticulous handling of PHI. With our deep-rooted understanding of HIPAA guidelines, we work diligently to ensure your BAAs with cloud providers are comprehensive, capturing every vital detail. We act as your advocate, negotiating terms that clearly delineate compliance responsibilities ensuring all parties are on the same page.
When it comes to managing PHI, our emphasis at Jelvix lies in:
- Rigorous Assessment: Before formulating BAAs, we undertake a detailed assessment of third parties to affirm their adherence to HIPAA norms.
- Tailored Agreements: We believe in specificity. Hence, our BAAs are crafted to fit the unique dynamics of each partnership, with clear indications of roles, duties, and accountability, all in harmony with HIPAA mandates.
- Consistent Oversight: Once the agreement is in place, our vigilance continues. We actively monitor compliance to ensure every party involved upholds their end of the commitment.
Implementing Data Access Controls
But data safety isn’t just about storage. Controlling access is paramount. Here’s how we address these essential aspects:
- Role-centric Access: We’ve established rigorous protocols that grant data access strictly according to an individual’s role. This ensures that only designated personnel can access or modify Patient Health Information (PHI).
- Multi-tiered Authentication: Our security layers extend beyond simple password protection. That heightened security approach makes unauthorized access highly improbable, safeguarding your data even if login credentials fall into the wrong hands.
- Comprehensive Logging: By maintaining an exhaustive activity log, we promote accountability and transparency. This meticulous record-keeping ensures rapid detection and rectification of any unauthorized data interactions.
Establishing Data Backup and Disaster Recovery Plans
While our protocols are stringent, we’re also prepared for unexpected hurdles. Our contingency measures include:
- Regular Data Backups: Routine and automated data backups are a cornerstone of our approach, ensuring that no crucial information is ever lost.
- Geographical Data Duplication: We store your data across multiple centers, not just one. This multi-pronged storage strategy shields against localized challenges, including unforeseen natural disasters.
- Prompt Recovery Mechanisms: On the off chance of a data discrepancy or loss, our recovery strategies can quickly restore operations, limiting disruptions.
In essence, our thorough strategies not only protect your data but also ensure it’s readily accessible when required. When you choose our services, you’re entrusting your data to a dedicated team deeply familiar with HIPAA compliance.
Conclusion
Leveraging Cloud platforms for storing healthcare data presents numerous benefits. Primarily, it enables healthcare teams to delegate significant responsibility to the Cloud service provider. That means institutions only manage a handful of devices without the need for their own extensive server infrastructure. This delegation reduces the scope of responsibility and diminishes potential hazards and the likelihood of reputational fallout.
That said, the choice of a vendor is a strategic commitment that will shape your institution’s security posture. Regrettably, not all vendors are forthright about their alignment with HIPAA standards. And not every provider offers tailored onboarding processes for HIPAA data management. Even after investing in premium packages, you’ll often autonomously oversee data generation and governance.
Institutions might find big names like AWS or Google Cloud to fit their needs, but the financial obligation might be too steep for smaller entities. It’s crucial to evaluate your institution’s priorities and financial capacity and identify providers whose offerings match these criteria.
If you’ve shortlisted a cloud provider, our specialists can assist in crafting a business associate contract and establishing a HIPAA-aligned data framework. If you’re still on the fence, our cloud solutions team and cybersecurity professionals are ready to share insights to guide your decision-making process.
Estimate Costs for a HIPAA-Compliant Development Project
Jelvix’s healthcare IT experts will estimate the costs of HIPAA-compliant software development to help you allocate the necessary budget for your project.