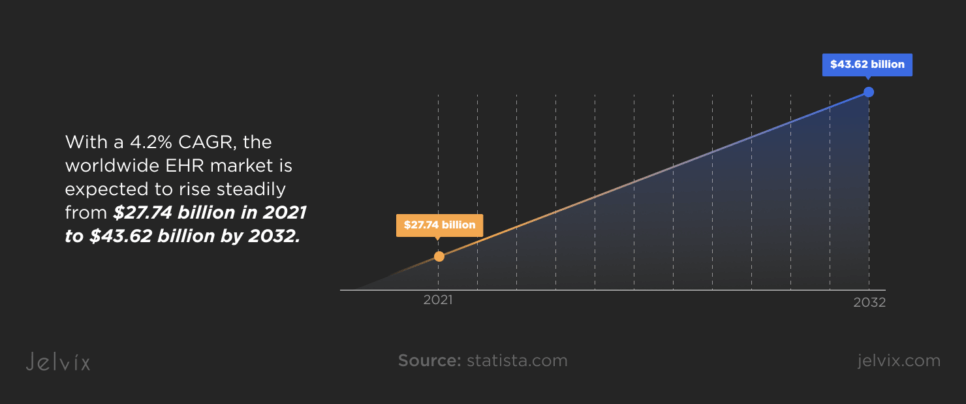
With a 4.2% CAGR, the worldwide EHR market is expected to rise steadily from $27.74 billion in 2021 to $43.62 billion by 2032. EHR systems have already been embraced by more than 90% of American hospitals; other markets are rapidly catching on while Europe, Australia, and South Korea are leading the way.
While adoption rates are skyrocketing, selecting the correct EHR system still presents difficulty. Every system offers unique features, pricing policies, and integration capabilities. Consequently, healthcare providers must carefully consider their options. A poorly selected EHR software might cause security concerns, slow processes, and add inefficiencies.
Comparing their features, costs, security, and general usability, this post will break down the top EHR programs of 2025. Whether you are a business executive seeking the best fit, a private practitioner, or a hospital administrator, this side-by-side analysis will guide your choice.
What Is an EHR System?
An Electronic Health Record (EHR) system is a digital version of a patient’s medical history that is safely kept and easily available to authorized healthcare practitioners. Unlike conventional paper records, EHR systems consolidate medical data, increase efficiency, reduce mistakes, strengthen security, and facilitate professional communication among individuals.
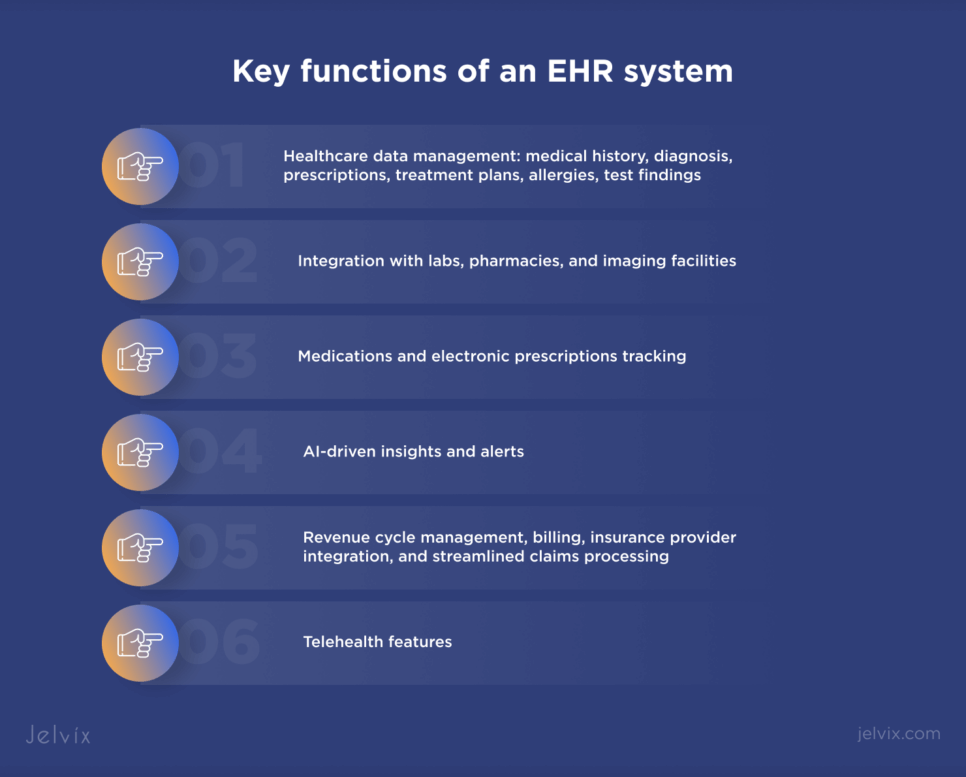
Key functions of an EHR system include:
- Healthcare data management: medical history, diagnosis, prescriptions, treatment plans, allergies, test findings, and so on;
- Integration with labs, pharmacies, and imaging facilities;
- Medications and electronic prescriptions tracking;
- AI-driven insights and alerts;
- Revenue cycle management, billing, insurance provider integration, and streamlined claims processing;
- Telehealth features.
Though occasionally used interchangeably, Electronic Health Records (EHR) and Electronic Medical Records (EMR) differ in several ways.
An EHR system is a comprehensible, interoperable record for distribution among multiple healthcare facilities. It guarantees continuity of treatment by letting specialists, clinics, and hospitals access and update patient data in real time. An EMR system, on the other hand, is mostly meant for use inside one practice or institution. It lacks the capacity to interact easily with other healthcare companies even as it digitizes patient records.
EHRs are better suited for hospitals, multi-specialty clinics, and organizations requiring broad data-sharing capabilities. They also support cloud electronic medical records, allowing for remote access, scalability, and enhanced security. EMRs, typically used in private practices, focus on internal record-keeping with EMR medical software tailored to a single provider’s needs.
Why Does Choosing the Right EHR Matter?
Not every program for electronic health records is developed equally. While some EHRs serve tiny clinics needing a simple, easy-to-use interface, others are designed for big hospital networks managing thousands of daily patients. While some stress billing automation, telehealth, or compliance features, others focus on specialty care, like cardiology, behavioral health, or radiology, integrating diagnostics.
Given so many choices, it can be challenging to select an EHR and locate one that meets your requirements. While the correct system can improve patient care, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency, choosing the wrong one may result in long-term financial losses, security issues, and ineffective workflow.
Impact on Operational Efficiency
EHRs are revolutionary for hospitals. Due largely to their need for improved patient data management, financial tracking, and administrative coordination, hospitals account for 53.03% of the overall EHR market revenue. When the focus shifts from volume-based to value-based treatment, healthcare facilities prioritize systems that improve patient outcomes, helping to maximize resources. Providers are increasingly focused on solutions that enhance workflows rather than only digitizing records since EHR adoption in U.S. hospitals exploded from 9% in 2008 to 96% today.
Nevertheless, EHRs for specialty practices are defined by different priorities. For example, cardiology-oriented EHRs combine EKGs, echocardiograms, and cardiac catheterization data on a single platform. Electronic behavioral health records emphasize mental health processes and let practitioners monitor treatment outcomes over time. Ambulatory EHRs provide a lightweight, simple-to-use solution free of hospital-based system complications for smaller outpatient clinics.
Data Security and Regulatory Compliance
In addition to increasing efficiency, a well-chosen EHR guarantees compliance with government regulations, including HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), HITECH (Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act), and MACRA (Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act). Due mostly to government incentives like the Medicare Inpatient Prospective Payment System (IPPS), which rewards hospitals for using certified EHR systems that satisfy regulatory criteria, acute care hospitals accounted for 46.22% of the EHR market in 2023.
Still, one of the biggest issues is security. Cloud-based electronic medical records present new cybersecurity risks even while improving distant access and scalability. To prevent illegal access, providers must ensure their chosen system features encryption, role-based access, and regular compliance audits.
Long-Term Costs and Benefits
Although EHRs require a large upfront cost, if you choose the correct one, their long-term advantages exceed the expenses. While hospitals might pay anywhere from $1 million to $20 million, depending on system complexity and customizing, the average EHR implementation cost for a small practice runs from $15,000 to $70,000 per clinician.
Studies reveal that doctors who use EHRs save an average of 3.5 hours every week on administrative chores, improving efficiency and lowering operational costs. Faster claims processing, better billing accuracy, and fewer medical errors help hospitals also experience financial returns.
Cloud electronic health records (EHRs) provide specialty clinics with even greater savings by cutting paperwork, improving documentation accuracy, and integrating with diagnostic tools. For instance, cardiology EHRs free cardiologists from manual data transfers between imaging systems and patient records, allowing them to focus on treatment.
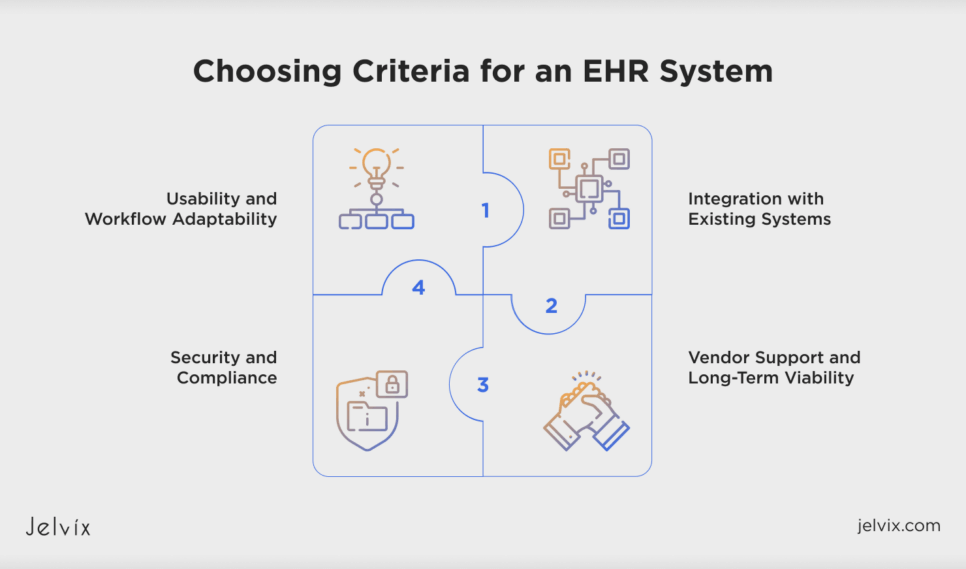
Choosing Criteria for an EHR System
Selecting the right EHR system among the various options on the market requires careful study. The best EHR system should match your workflow, compliance criteria, and financial situation. While well-known companies like Cerner and Epic lead the sector, EHR solutions for small organizations often prioritize cost-effectiveness and simplicity of use.
Usability and Workflow Adaptability
A good EHR system should simplify workflows. Usability impacts everything from patient record management to billing efficiency. When assessing EHR software vendors, look for:
- Intuitive Interface: Can staff navigate the system quickly, or does it require extensive training?
- Customization: Does the EHR allow you to modify templates, charting methods, and workflows to fit your practice?
- Specialty-Specific Features: Does the system provide tailored tools for cardiology, behavioral health, or pediatrics, such as electronic behavioral health records or diagnostic data integration?
EHR systems are even more critical for small clinics. Unlike hospitals with specialized IT staff, small clinics require plug-and-play solutions that reduce downtime and require less technical knowledge.
Integration with Existing Systems
The best EHR software should seamlessly integrate with:
- Lab and Imaging Systems: Can it connect with diagnostic tools and automatically upload test results?
- Billing and Insurance Platforms: Does it include built-in revenue cycle management or require third-party integrations?
- Telehealth and Patient Portals: Can patients access their medical history, schedule appointments, and communicate with providers online?
Two industry heavyweights known for their interoperability but different approaches—Cerner vs. Epic—are the most contentious topics among EHR software providers. Large hospitals use Epic because of its all-in-one, integrated system; Cerner is usually picked for its modular approach, which lets providers add capabilities as needed. Small businesses, however, may find either approach excessively costly or complicated, so cloud-based, lightweight alternatives could be more advantageous.
Security and Compliance
We already mentioned that many healthcare data breaches are linked to EHR vulnerabilities, so security should be a top priority. A HIPAA-compliant EHR must include:
- Data Encryption: Protects patient information from unauthorized access;
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Limits system access based on user roles (e.g., doctors vs. front-desk staff);
- Audit Trails: Tracks who accessed or modified records to prevent unauthorized changes;
- Regular Security Updates: Ensures the system is protected against emerging threats;
- For cloud-based EHR software, vendors must also comply with regulations like HITECH (Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act) and GDPR (for European providers).
Vendor Support and Long-Term Viability
Not all EHR software vendors offer the same level of support. Some questions to consider when evaluating EHR software companies:
- Availability of 24/7 support: If a system goes down, is assistance available immediately?
- Implementation and Training: Does the vendor provide onboarding help, or will you need to hire a consultant?
- Scalability: Can the system grow with your practice, or will you need to switch platforms in a few years?
- Vendor Stability: Is the company financially stable, or is there a risk they might discontinue support?
How To Evaluate EHR Vendors
When comparing EHR software companies, use this checklist:
- Request a Demo: See how the system handles daily workflows.
- Ask for References: Speak with existing clients to understand their experience.
- Review Pricing Models: Compare upfront costs, subscription fees, and hidden expenses.
- Check Compliance Certifications: Ensure the system meets HIPAA, HITECH, and other regional requirements.
- Assess Integration Capabilities: Verify compatibility with your lab, billing, and telehealth tools.
- Evaluate Support and Training Options: Determine how much assistance the vendor provides during implementation and beyond.
In the end, no EHR system fits everyone. The secret is to identify a solution that corresponds to the practice’s long-term financial goals, regulatory needs, and workflow. Next, we’ll compare the best EHR platforms of 2025, breaking down their features, pricing, and security measures.
Discover how we developed a personalized EHR system that optimized the clinic’s workflow while ensuring maximum privacy and security.
Top Electronic Health Record Systems and Software 2025
Epic Systems
Large healthcare companies typically choose Epic as their EHR, and its industry-leading interoperability defines it the most. Even if they use different EHR systems, its Care Everywhere solution lets hospitals, labs, and offices easily exchange patient data.
What makes Epic unique?
- Care Everywhere: Connects with other Epic and non-Epic systems, ensuring real-time data exchange between hospitals, specialists, and external providers;
- AI-Driven Predictive Analytics: Using machine learning, AI-driven predictive analytics seeks out high-risk patients and recommends preventative treatments;
- MyChart Patient Portal: One of the most user-friendly and widely adopted patient engagement tools.
Best For: Large hospitals and healthcare networks.
Limitation: Expensive and difficult to implement, requiring extensive staff training.
Cerner (Oracle Health)
Predictive analytics and AI-driven insights are well-known strengths of Cerner, today Oracle Health. It actively examines trends to enhance decision-making.
What makes Cerner unique?
- AI-Powered Clinical Decision Support: Alerts doctors of possible issues before they occur via real-time predictive modeling.
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure: Offers scalability and automated system updates, reducing IT overhead.
- Sepsis Prediction Tool: Identify early warning indicators of sepsis up to 48 hours before symptoms start.
Best For: Hospitals and large healthcare organizations looking to leverage AI for proactive patient care.
Limitation: This can be complex to navigate, requiring significant onboarding for staff.
Athenahealth
Athenahealth is a cloud-based EHR that continuously learns and adapts based on user behavior. Unlike static systems, Athena adjusts workflows over time, making it easier to use the more you work with it.
What makes Athenahealth unique?
- Machine Learning Workflow Optimization: Learns from how providers interact with the system, offering real-time workflow suggestions.
- Embedded RCM & Billing Automation: Integrates billing straight into the EHR, therefore lowering errors and claim denials.
- Nationwide Data Network: Supports doctors in making evidence-based decisions using information from more than 160,000 sources.
Best For: Growing practices that want a scalable, continuously improving EHR.
Limitation: Limited third-party integrations requiring custom solutions for unique needs.
NextGen Healthcare
Unlike one-size-fits-all EHRs, NextGen is built for specialists. Whether you’re a cardiologist, dermatologist, or pediatrician, NextGen offers pre-built, specialty-focused workflows tailored to your field.
What makes NextGen unique?
- Pre-Configured Specialty Workflows: Designed specifically for 26+ medical specialties.
- Adaptive Charting System: Allows providers to customize templates on the fly without needing IT support.
- Integrated Telehealth for Niche Practices: Supports specialty-focused virtual visits, such as dermatology image sharing.
Best For: Specialty clinics and mid-sized practices that need tailored EHR solutions.
Limitation: Higher costs for smaller practices and customization can take time to set up.
eClinicalWorks
eClinicalWorks stands out with its original cloud storage technology, which divides patient data among nine worldwide data centers for the best security and dependability.
What makes eClinicalWorks unique?
- Grid Cloud Technology: Even during local server failures, it ensures zero data loss.
- AI-Powered Speech Recognition: With Eva, an AI assistant, physicians can document notes using voice commands.
- Robust Patient Engagement Tools: Includes a fully integrated patient app for mobile access to health records and telehealth.
Best For: Outpatient clinics and small practices that want affordable, cloud-based security.
Limitation: Customer support can be inconsistent, and system updates sometimes cause temporary issues.
Allscripts
Since Allscripts, now Veradigm, is well-known for its considerable degree of configurability, it is a perfect fit for healthcare organizations having to combine several tools into their workflow.
What makes Allscripts unique?
- Open API for Custom Integrations: Allows healthcare providers to build their integrations with labs, imaging systems, and external apps.
- Highly Modular System: Lets organizations purchase only needed features instead of an all-in-one package.
- Advanced Population Health Management: Supports large-scale patient data analysis for preventive care initiatives.
Best For: Large healthcare organizations that need maximum flexibility and integration options.
Limitation: Steep learning curve, requiring time-intensive customization.
Meditech
Meditech is designed for smaller hospitals that need enterprise-grade features without the complexity of Epic or Cerner.
What makes Meditech unique?
- Expanse EHR for Rural Hospitals: A streamlined version tailored for rural and community healthcare providers.
- Mobile-Friendly Interface: Physicians can access and update patient records from tablets and smartphones.
- Built-In AI Clinical Decision Support: Helps doctors make faster, data-driven medical decisions.
Best For: Mid-sized hospitals and rural healthcare facilities that need a robust yet simple EHR.
Limitation: Fewer third-party integrations compared to more prominent competitors.
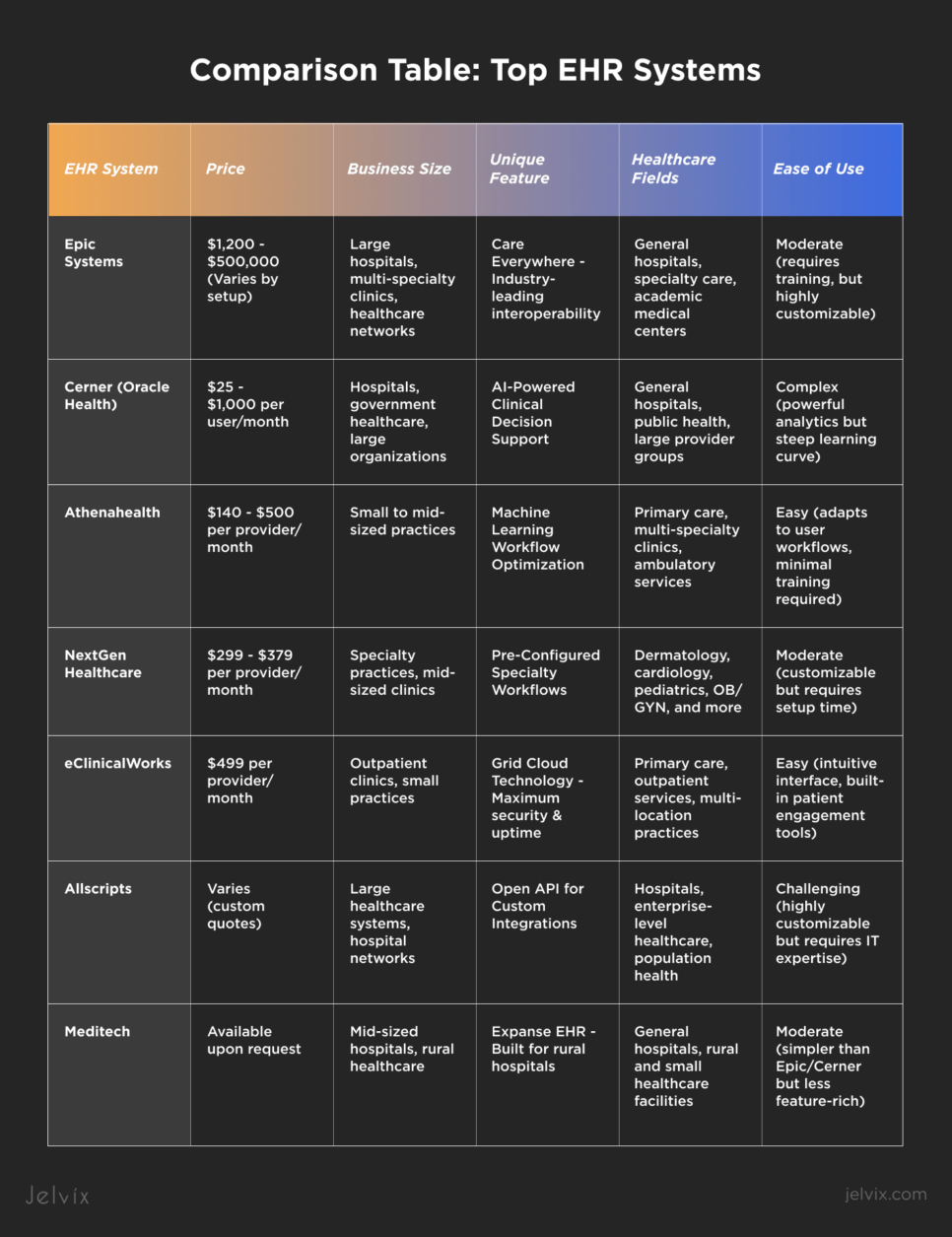
Comparison Table: Top EHR Systems
Specialty-Specific EHRs: What You Need To Know
Like a one-size-fits-all office suite, a broad EHR system covers the foundations but lacks the accuracy required in specialized fields. Imagine a cardiologist setting up a family practice EHR lacking ECG integration or a psychiatrist battling a system designed for surgical procedures. Specialty-specific EHRs fill in to close the gap in high-stakes situations where every second counts by providing customized solutions fit for particular requirements of every medical field.
Specialty-specific EHRs improve efficiency in many different disciplines as follows:
- Cardiology EHRs eliminate the need for manual data entry by directly entering electrocardiograms (EKGs), echocardiograms, cardiac catheterization results, and stress tests into patient records.
- Electronic behavioral health records (EBHRs) are designed for seamless patient care and provide mental health-specific tools, such as tailored progress notes, therapy session monitoring, and psychiatric medication management.
- Oncology EHRs help doctors create accurate treatment plans by offering cancer staging capabilities, chemotherapy scheduling, infusion tracking, and charting tailored to the field.
- Dermatology EHRs let doctors compare patient images over time by including lesion mapping, high-resolution imaging features, and AI-assisted skin disease identification.
- Built-in templated reports for fractures, musculoskeletal examinations, and pre/post-surgical tracking, orthopedic EHRs streamline paperwork.
- Ophthalmology EHRs combine retina imaging, optical coherence tomography (OCT), and visual field testing to guarantee smooth workflow for eye care professionals.
Specialized EHRs directly affect physician efficiency, patient care, and general practice effectiveness:
- Boosted Workflow Optimization & Efficiency: For experts, general EHRs can seem clunky and filled with useless functionality. Solutions tailored to a specialty cut the fat, hence lowering clicks, needless screens, and duplicate data entry.
- Better Clinical Decision Support: Specialty-oriented EHRs interact with cutting-edge diagnostics technologies not found in standard EHRs.
- Reimbursement Optimization & Regulatory Compliance: Many medical disciplines require specific reporting and billing codes. A cardiology EHR is preloaded with ICD-10 codes for cardiac diseases, and an oncology EHR has built-in facilities for tracking chemotherapy reimbursements.
Investing in the correct EHR system is about comfort for experts and providing the highest-quality treatment free from administrative distractions.
Cloud-Based vs. Server-Based EHR Systems: How Do They Compare?
Since cloud-based electronic health record systems run on remote servers, healthcare providers may access patient data from anywhere with an internet connection using any device. EHR software providers handle security, updates, and backups remotely rather than maintaining pricey in-house hardware.
Benefits of EHRs housed on the Cloud:
- Reduced Upfront Costs: Practices pay a subscription fee, making it an affordable option for EHR systems for small practices.
- Anywhere and Anytime: Cloud EHR systems are perfect for telemedicine and multi-location clinics, as doctors can securely access patient records from several sites.
- Automatic Updates & Maintenance: Cloud providers manage system changes, assuring compliance with new healthcare rules without downtime or manual intervention.
- Scalability: As the practice expands, cloud-based solutions scale naturally without requiring further hardware purchase.
Drawbacks of cloud electronic health records solutions:
- Dependency on the Internet: Real-time access to patient data may suffer from a slow or interrupted Internet connection.
- Ongoing Subscription Costs: While cloud EHRs have cheaper initial costs, monthly or annual fees build up over time and could result in long-term spending, perhaps higher than server-based systems.
- Data Security Issues: While cloud EHR providers extensively invest in compliance and encryption, remote patient data storage creates cybersecurity concerns, including third-party breaches.
Meanwhile, a server-based EHR (also called an on-premise EHR) is hosted on local servers managed directly by the healthcare provider. These systems offer greater control over data security but have higher upfront costs and IT maintenance requirements.
Advantages of server-based EHRs:
- Full Data Control: Patient records are stored locally, reducing concerns over third-party data access or external breaches.
- More Customization: Server-based EHRs allow deep integration with existing IT infrastructure.
- Works Without Internet: AN on-premise EHR continues to function even during an Internet outage, ensuring continuous access to records.
Disadvantages of server-based EHRs:
- High Initial Investment: Practices must purchase hardware, servers, and security infrastructure, making it a large upfront expense.
- Ongoing IT Maintenance: Dedicated IT staff is required for security updates, system backups, and troubleshooting, which increases operational costs.
- Limited Remote Access: A server-based solution typically requires a VPN or remote desktop setup to access records outside the facility.
The decision between cloud-based and server-based electronic health record software ultimately depends on budget, security priorities, and practice size.
- Need flexibility and low upfront costs? Go cloud.
- Need full control and can handle IT maintenance? Server-based might be better.
- Running a small clinic or multi-location practice? Cloud is likely the best fit.
- Operating a large hospital with strict data policies? Server-based EHR may be worth the investment.
Both solutions have their place in modern healthcare development, but as more providers embrace telehealth, AI-driven analytics, and remote care, cloud-based EHRs are quickly becoming the industry standard.
The Power of Custom EHR Development
Off-the-shelf EHR software is the fastest and most practical choice available for most healthcare practitioners. Leaders in the sector–Meditech, Cerner, and Epic–provide fully built, regulatory-compliant systems that fit very well with diagnostic tools, patient portals, and medical billing. These solutions are meant to fit a broad spectrum of healthcare environments, so they are a dependable alternative for companies looking for a tested system with less required setup time.
Convenience does, however, come at a price—financial and in terms of flexibility. Although ready-made EHR software providers constantly change their systems to match industry standards, they might not have the customization needed for specific processes.
Conversely, custom-built EHR systems provide unparalleled adaptability and specifically targeted capabilities. A custom EHR is built around the company’s particular demands, ensuring a flawless user experience and integration with current systems instead of adjusting processes to match the software. Custom EHRs allow large healthcare providers and research labs to combine special capabilities such as AI-driven analytics, precision medicine technologies, or sophisticated telehealth capabilities.
Said otherwise, creating an EHR from scratch is no easy chore. The expenses are much more than buying a pre-built system; they call for a large outlay in compliance testing, cybersecurity, and software development tools. Another consideration is the chronology; unique solutions can take months or even years to evolve, depending on the complexity. Furthermore, the company’s responsibility is continuous maintenance, security patches, and regulatory upgrades, so a committed IT team is needed to guarantee long-term compliance and functionality.
In many cases, the best answer is somewhere in the middle: selecting a highly configurable, ready-made EHR that lets you create custom modules or ensures third-party integrations. Many leading EHR systems today allow API access so that providers may improve their systems with more capabilities without creating a whole new platform. This hybrid method allows healthcare companies to strike a compromise between cost-effectiveness and customization, resulting in a system that meets their demands without overstretching their resources.
The decision between custom and ready-made EHRs ultimately depends on the company’s budget, scalability needs, and degree of desire to handle continuous IT demands. A commercial EHR is an obvious choice for individuals who require a system swiftly and reasonably affordably. However, for healthcare providers with unique requirements, investing in a custom-built EHR could be the only option.
The Smart Way to Choose – Download Your Guide to Selecting the Right Healthcare Tech Partner!

Conclusion
EHR systems are developing beyond simple record-keeping. As technology evolves, healthcare professionals are searching for solutions that increase efficiency, boost patient involvement, and easily fit with current processes. AI is quickly becoming a major player in helping to identify medical dangers, automate administrative chores, and simplify decision-making. Cloud-based platforms are also becoming popular, offering flexibility, cost savings, and real-time upgrades free of on-site maintenance.
Interoperability is still the first concern. More technologies are being developed to link public health networks, private practices, and hospitals, so simplifying data interchange and closing gaps in patient care are essential. Simultaneously, providers are looking for greater customization. One-size-fits-all solutions can fall short, particularly for specialty clinics and multi-location healthcare companies that require adapted features.
A custom EHR can be the best fit for those seeking off-the-shelf solutions. A system developed around specific processes guarantees improved integration, regulatory compliance, and long-term adaptation. Jelvix can assist in designing and developing a custom EHR solution that matches your requirements. Contact us to find out how a customized system might maximize your practice and raise patient care standards.
Need high-quality professionals?
Unlock new business opportunities with the first-rate dedicated development team.