The healthcare industry is overburdened with data–patient records, diagnostic findings, treatment plans, and insurance claims are just several examples that can be named. Information management has great value in bettering the patient’s health, increasing operational efficiency, and lowering costs. This is where healthcare data management comes into play–it is a system that supports gathering, storing, and organizing medical information while ensuring it’s secure and accessible.
The figures highlight the relevance of this market. According to the experts, the global healthcare data integration market was valued at around $1.05 billion in 2022 and is anticipated to witness a robust CAGR of 14.5% between 2023 and 2030. Similarly, the healthcare analytics market got stabilized at $43.1 billion in 2023 and will continue growing at a CAGR of 21.1% until 2030. Three factors push it: faster digitalization, more attention to patient-centered care development, and a high level of data processing in healthcare practice.
More importantly, there’s some truth lying behind the statistics: in healthcare data management, system or storage assurance is not the goal; it enables providers to make better decisions sooner. From real-time patient monitoring to predicting disease outbreaks, it is revolutionizing care delivery.
In this blog, we’ll explore healthcare data management processes. We’ll break down their components, benefits for medical facilities; challenges organizations must tackle, and evolving trends. By the end, you’ll understand why managing healthcare data isn’t just important—it’s essential for modern healthcare systems.
What is Healthcare Data Management (HDM)?
Healthcare Data Management (HDM), also called Health Information Management (HIM), organizes and maintains health data in digital formats. This encompasses data such as Electronic Medical Records (EMRs), Electronic Health Records (EHRs), and scanned handwritten medical notes. The information is then stored in secure digital systems, allowing easy access when required.
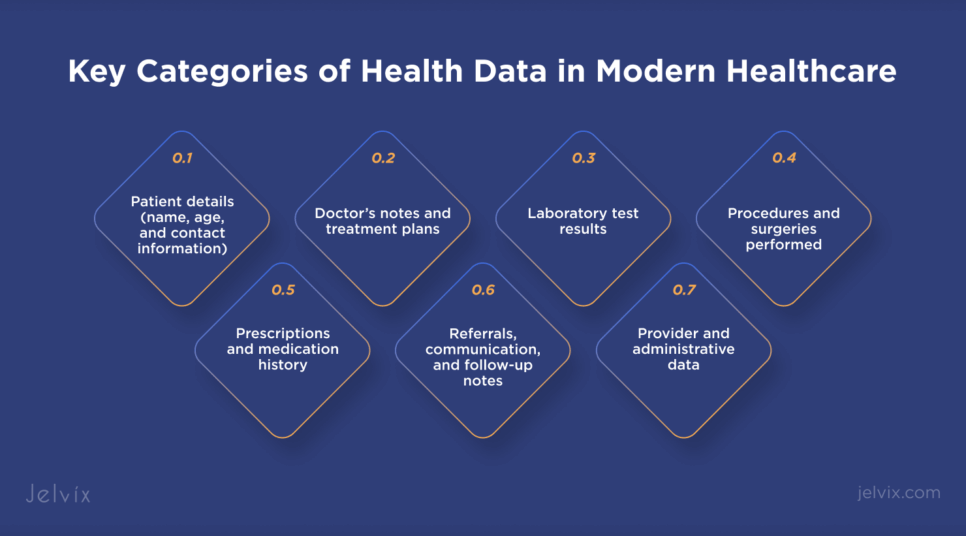
Health data covers a wide range of information, such as:
- Patient details (name, age, and contact information);
- Doctor’s notes and treatment plans;
- Laboratory test results;
- Procedures and surgeries performed;
- Prescriptions and medication history;
- Referrals, communication, and follow-up notes;
- Provider and administrative data.
Data management in healthcare offers more than just data storage; it also manages data across its lifespan. Data is generated, securely stored, organized, processed, and, at times, archived or destroyed. HDM ensures data privacy, allowing only authorized individuals to access sensitive information.
Why HDM Matters Now More than Ever?
As the healthcare industry advances its digital transformation, the volume of generated data has grown exponentially. This data must be managed well and show a real-time picture of every patient’s health. High-quality data enables doctors to diagnose accurately, track treatment responses, and improve outcomes. But, with a huge amount of data, come a bunch of problems, too—data fragmentation, inconsistent records, and security risks. Inadequately managed, these issues can lead to misdiagnosis, treatment delays, and administrative inefficiency.
Advanced tools such as master data management (MDM) and healthcare master data management (hMDM) were developed to solve problems such as duplicate and mixed records. These systems integrate data from multiple sources into a unified and trustworthy patient profile.
Now, HDM is an important element of modern healthcare systems. It helps integrate data across diverse settings, including patient records, laboratory tests, and administrative processes. When integrated, this data helps healthcare providers improve decision-making, patient care, and operational efficiencies.
Medical Data Management Principles
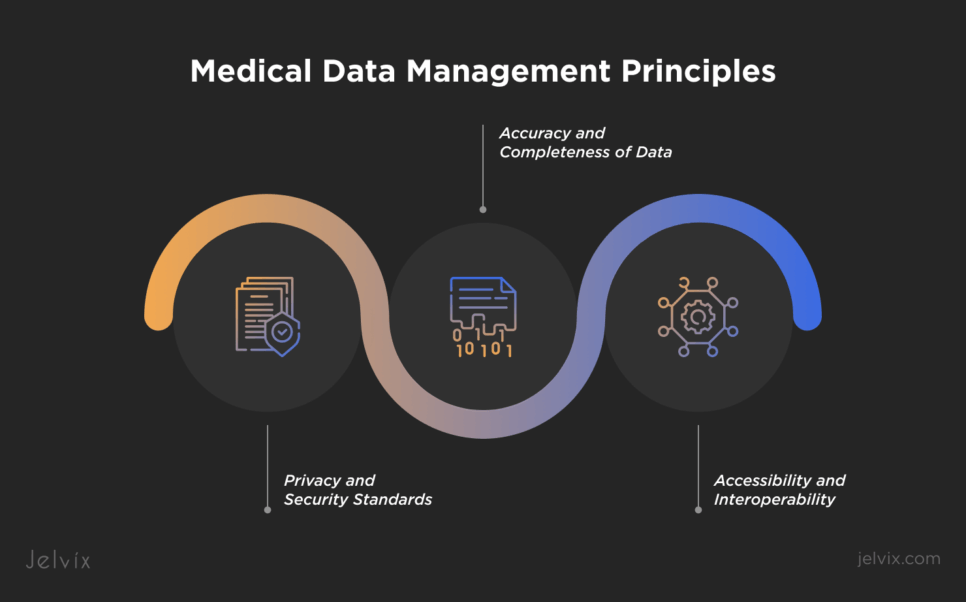
Health data management isn’t only about organizing files—it’s about saving lives. The right data, at the right time and in the right hands, can mean the difference between appropriate treatment and lost opportunities. Product data management in healthcare is based on three key pillars—accuracy, security, and accessibility.
Accuracy and Completeness of Data
Accurate and complete data is the backbone of healthcare. Every detail is important—a patient’s medical history, medication dosage, or lab results. Inaccurate or missing information may be a culprit for dire consequences, such as misdiagnoses and inefficient treatments.
For this purpose, healthcare organizations deploy automated systems to reduce data entry and validation mistakes. Data governance frameworks are also implemented to ensure consistency while eliminating redundancy and preserving data integrity throughout all systems. Accurate and complete information allows healthcare providers to make informed decisions that enhance patient outcomes.
Privacy and Security Standards
Healthcare data, from personal health histories to insurance information, is among the most sensitive types of information. For that reason, confidentiality and security in this area are not merely a priority; they are a duty.
Tight regulations such as HIPAA safeguard the confidentiality of patient information. However, the real issue lies in transcending compliance itself. From hospitals to clinics, healthcare facilities are more and more relying on advanced encryption solutions, multi-factor authentication, and even AI systems that can identify and prevent cyber threats before they occur. If patients feel their information is safe, they will be more likely to seek care.
Accessibility and Interoperability
Data locked away is data wasted. Quick access to patient information can be life-saving for healthcare providers. Accessibility ensures that doctors, nurses, and specialists retrieve important records instantly, no matter the situation.
But accessibility alone is not enough. Interoperability ensures that these records function properly across various systems — a hospital, pharmacy, or telemedicine provider. Therefore, if a patient has had a blood test at one clinic, another doctor located hundreds of miles away should be able to see those results immediately. Interoperability can then support the care provided, eliminate superfluous costs, and enhance the overall experience for the patient.
When healthcare data is accurate, secure, and accessible, it becomes a powerful tool. It helps doctors diagnose faster, patients receive personalized treatments, and healthcare systems operate more efficiently.
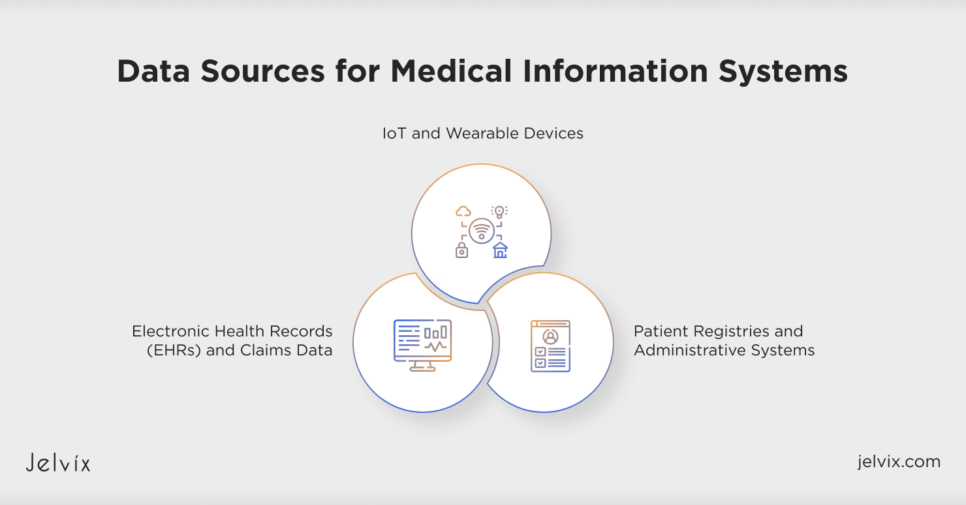
Data Sources for Medical Information Systems
Medical information systems depend on various data sources to deliver a complete perspective of patient health. These sources encompass Electronic Health Records (EHRs), claims information, Internet of Things (IoT) gadgets, wearable tech, patient registries, and administrative systems. Every contribution offers distinct perspectives, improving patient treatment and operational effectiveness.
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) and Claims Data
EHRs are the prevailing standard of patient data today. Unlike paper charts, EHRs offer an active and consolidated view of a patient’s medical history. This includes diagnoses and prescribed medications, lab test results, and radiology images. Such a complete digital record ensures that healthcare providers have immediate, secure access to critical information about any patient.
EHRs support advanced analytics in addition to direct patient interaction. Healthcare organizations can use EHR data to identify patterns, predict epidemics, and improve the efficiency of care delivery. Patterns in EHR data, for instance, may point to areas where preventive care is lacking, allowing organizations to remedy these gaps before they become more serious issues.
Claims data tells another side of the healthcare story. Generated every time a service is billed, claims data captures critical information, including patient demographics, diagnoses, procedures performed, and the costs involved. Whereas EHRs focus on clinical data, claims data reflects healthcare’s financial and administrative dimensions.
One of the most valuable aspects of claims data as a data type is its longitudinal aspect. It logs patient encounters with multiple providers over time, providing a long-term perspective on their healthcare journey. For example, if a patient has been treated for diabetes over a five-year span, claims data will show every visit, procedure, and prescription that was part of his treatment.
This information is much more potent in the aggregate. With claims data on millions of patients, policymakers can measure the effectiveness of their healthcare programs, identify opportunities to drive down costs and improve resource allocation. For example, with claims data, it can be identified where there are regional differences in access to care and then remediated with targeted interventions.
IoT and Wearable Devices
Wearable devices, including fitness trackers, smartwatches, and even smart rings, can help monitor certain health metrics in real time. These consist of counting steps, tracking heart rates, checking blood oxygen levels, and following sleep patterns. For instance, a person wearing a smartwatch might get alerts when their heart rate is erratic, prompting them to seek medical advice before the matter gets out of hand.
IoT devices take this even further by allowing constant monitoring of the health condition of patients with chronic diseases. Connected blood glucose monitors, smart inhalers and remote cuffs that measure blood pressure let physicians check in on their patients from several miles away. This is particularly advantageous to elderly patients or those who remain in remote sites as it reduces the frequent in-person visits.
The magic of IoT combined with wearables is the huge amount of real-time data generated. Such data is analyzed to understand patterns and trends, which makes healthcare predictive. For example, an IoT device may report the early signs of condition worsening, thereby permitting timely, lifesaving intervention.
Patient Registries and Administrative Systems
Patient registries and administrative systems might sound less exciting like we saw with the wearables, but they are just as important in modern healthcare. A patient registry is, in simplistic terms, a database that tracks individuals with a particular disease, condition, or treatment. For example, the cancer registry collects information about diagnoses, treatments provided, and outcomes, which then helps researchers and clinicians improve care pathways.
Registries are not just about data; they tell a story. With the information gathered from thousands of patients, healthcare providers can determine trends, measure the effectiveness of treatments, and find areas where care is lacking. This results in better decisions and more tailored strategies in the healthcare approach.
Administrative systems, in contrast, emphasize the behind-the-scenes operations that ensure the healthcare facility operates smoothly. These systems manage scheduling, billing, resource allocation, and patient flow. Though they may appear purely logistical functions, the data generated is incredibly valuable.
Administrative data highlights, for instance, some inefficiencies in hospital processes, like waiting times or the unavailability of resources. Once these issues are resolved, healthcare institutions can achieve better efficiency, lower costs, and improve the experience of patients through healthcare services. Besides that, administrative databases normally contain demographic information about patients; thus, it is possible to correlate such data with clinical information to understand health trends among specific populations better.
Together, the EHRs, the IoT, wearable devices, patient registries, and administrative systems constitute a full continuum of healthcare information. That information not only captures the now but forecasts the future to prevent disease, enhance care delivery, and make healthcare smarter and more efficient.
Learn how we built an intuitive and secure EHR system for seamless clinic operations and ensured robust data management. Dive into the case study!
The Benefits of Better Healthcare Data Management
Efficient medical data management systems can reduce medical errors and lower operational costs. Hospitals that use healthcare data strategy also see greater clinical results and higher patient satisfaction ratings. These advantages are tangible, measurable, and revolutionary; they are not only hypothetical. Let’s see how better data management benefits three crucial domains: medical innovation, operational effectiveness, and patient care.
Enhanced Patient Care and Outcomes
Patients receive higher-quality care when health providers have access to accurate and complete data. A comprehensive view of a patient’s health allows doctors to make informed decisions quickly, lowering the chance of misdiagnoses or contradictory treatments.
Patient data management also enables proactive care. Predictive analytics, driven by structured data, can identify potential health threats before anyone shows symptoms. Consider, for example, algorithms examining patient data that can flag people at risk for developing heart disease and trigger early intervention.
They can also be life-saving; seamless access to data during an emergency is of utmost importance. Imagine that a patient comes to an ER unresponsive. When a system is well managed, providers can access crucial information such as allergies or current treatments on the spot, allowing them to treat patients more quickly and accurately.
Streamlined Operations and Cost Reductions
Healthcare data management not only improves patient care but can also transform organizations’ functions. Eliminating redundancies and optimizing workflows saves money and time.
Fragmented data systems frequently result in duplicate tests and unnecessary procedures, for example. Centralizing and providing access to records eliminates these costly inefficiencies. According to the Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS), hospitals that implemented comprehensive data management systems enjoyed as much as a 13% reduction in operating costs.
Resource allocation can also be improved through data-driven insights. Hospitals can analyze patient admission trends to improve staffing or predict equipment shortages for smoother operations. In addition, merging financial data with clinical records can highlight opportunities for cost-reduction programs, such as renegotiating supplier agreements or ensuring more accurate billing.
Improved Research and Innovation
Data is the cornerstone of medical research and innovation. With better healthcare data management, researchers gain access to diverse datasets that can uncover new insights into diseases and treatments.
For instance, examining large patient data sets has resulted in new insights into diabetes and cancer. When the pandemic broke out, sharing data across institutions sped up vaccine development by months and illustrated the power of collective information.
More efficient data management also facilitates personalized medicine. Researchers develop treatments designed for an individual patient by pairing genetic data with clinical records. This works well in oncology, where genetically targeted therapies based on profiles provide survival advantages.
Another critical benefit is the collaboration among organizations. Database sharing facilitates inter-institutional studies, uniting international expertise to address multifaceted health problems. Data management means research can be done more quickly, innovations can be delivered to patients sooner, and the healthcare system can progress.
Improved healthcare data management generates a chain reaction of beneficial results, from preserving lives to reducing expenses. It enables providers to offer tailored care, guarantees organizations operate effectively, and promotes innovative discoveries. In the current data-centric environment, efficient management is not merely an alternative—it’s essential for progress in healthcare.
Challenges in Healthcare Data Management and Ways To Overcome Them
You might ask: how can information management be a challenge? Healthcare data management is a two-edged sword. Although technology has the potential to revolutionize patient care, it also poses difficulties that call for calculated answers. These challenges include urgent concerns about data security and governance, as well as technical ones like system interoperability. Let’s examine the main issues and feasible solutions for them.
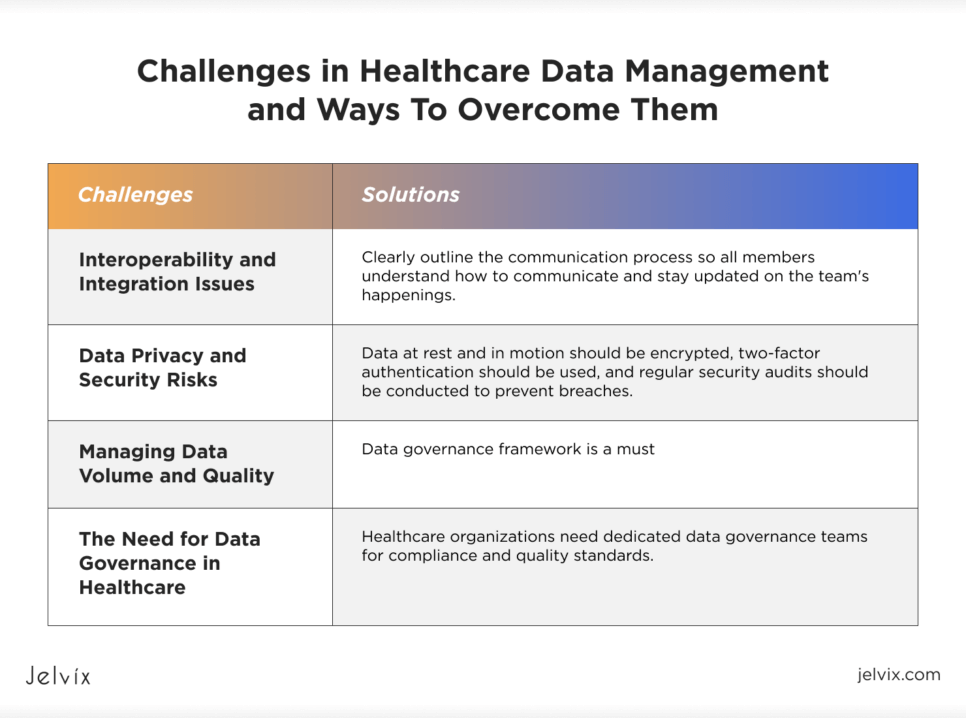
Interoperability and Integration Issues
Healthcare providers often use different systems to record and retain data. One hospital may employ a particular EHR platform, while the clinic next door might have another. This creates data silos, where important patient information is not being shared effectively across systems, leading to delays in care or lack of completeness of records.
The Fix: Establishing common standards, such as FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) and HL7. They can serve to connect these disparate systems. For example, FHIR allows different EHRs to “speak the same language,” allowing data sharing. Furthermore, middleware solutions can make interoperability easier without needing to change the existing infrastructure by integrating systems across disparate technologies.
Data Privacy and Security Risks
Data breaches continue to be expensive for organizations around the world in 2024. The Cost of a Data Breach Report 2024 by IBM indicates that the average cost linked to a data breach increased by 12% compared to the previous year, making it an average of $4.62 million per breach. The healthcare industry remains the most impacted sector, averaging breach-related costs of $10.93 million per incident due to the nature of the data involved. Why is healthcare such a prime target for ransomware attacks? The sensitive nature of data.
The Fix: Strong cybersecurity is not up for debate. Data at rest and in motion should be encrypted, two-factor authentication should be used, and regular security audits should be conducted to prevent breaches. In addition to technology, employees must be trained on privacy protocols; human error contributes to many data breaches. Beyond legal protection, remaining compliant with laws such as HIPAA (for the U.S.) and GDPR (in the EU) fosters trust from patients.
Managing Data Volume and Quality
Healthcare produces vast data—estimates indicate that by 2025, the industry will account for 36% of global data generation. The hard part is ensuring healthcare data quality: it should be accurate, relevant, and available. Duplicate records, incomplete entries, and old data can all result in compromised care quality and inflated costs.
The Fix: Data governance framework is a must. This involves implementing clear data entry standards, regular validation to identify errors, and leveraging AI-powered tools for automated quality checks. AI algorithms can, for example, flag duplicate records or highlight discrepancies in patient histories to ensure reliable data becomes available across systems.
The Need for Data Governance in Healthcare
Without robust governance, data is a liability instead of an asset. Therefore, laws and regulations like HIPAA and GDPR exist to guarantee that data management stays responsible and to safeguard patients, providers, stakeholders, and all parties involved. For example, HIPAA outlines explicit regulations regarding the handling of patient information, while GDPR enables individuals to oversee the utilization of their personal data.
The Fix: Healthcare organizations need dedicated data governance teams for compliance and quality standards. Reading the evolving regulations can become a mammoth task; hence, regular audits, policy updates, and training programs are mandated to keep the teams aligned with the growing demands. Access controls, real-time monitoring, and similar tools help mitigate the risk: only authorized personnel can handle sensitive information.
Addressing these challenges isn’t just about staying compliant or avoiding fines. It’s about delivering better healthcare. Interoperability guarantees that doctors know everything about a patient’s health. Robust security protects patient trust. Good data quality in healthcare information systems allows for better diagnoses and, ultimately, better outcomes. And good governance creates conditions for innovation while holding systems accountable.
Best Practices for Effective Healthcare Data Management
Organizations may maximize their data usage while preserving accuracy, security, and compliance by implementing best practices. Here’s how to accomplish it successfully:
- Establishing a Centralized Data Strategy. Combining patient data from multiple sources into a single, cohesive system is known as a centralized data strategy. It improves care coordination, decreases medical errors, and increases patient outcomes. For example, better patient outcomes and fewer adverse events can arise from healthcare providers having centralized access to medical data and using it to inform their decisions.
- Leveraging Advanced Analytics and AI Tools. Healthcare organizations may derive actionable insights from massive amounts of data by utilizing artificial intelligence (AI) tools and advanced analytics. These technologies can forecast health trajectories, find at-risk individuals, and customize treatment solutions. For example, predictive analytics can help forecast patient admissions, improve resource allocation, and reduce wait times.
- Ensuring Staff Training and Awareness. Human error accounts for nearly 70% of data breaches in healthcare. Data management relies on properly trained staff. Training healthcare professionals on best practices in data management should be mandatory to ensure accuracy, integrity, and regulatory compliance. Regular orientation programs can minimize human errors, improve data quality, and maintain patients’ confidence. For example, training staff on data privacy protocols of how to avoid breaches and obey laws such as HIPAA and GDPR.
Effective healthcare data management involves technology, strategy, insights, and people. A centralized system guarantees availability, advanced analytics reveal data insights, and trained employees ensure system security and compliance. Implementing these best practices can improve outcomes, cost savings, and sustainable long-term success for healthcare organizations.
A Future Outlook of Healthcare Data Management
The future of healthcare data management is bright. Emerging technologies, new global practices, and a growing focus on data-driven healthcare are set to reshape the industry. These advancements will improve patient care, simplify operations, and drive innovation.
First, we’ll talk about emerging technologies:
- Artificial Intelligence: AI can analyze vast datasets rapidly to detect trends, predict results, and help diagnose diseases. For instance, AI systems are used to detect breast cancer with a 95% accuracy rate, assisting doctors in the early detection of the disease.
- Blockchain ensures secure and transparent data management. It also prevents unauthorized changes to records and secures data sharing. This is vital for highly private and accurate electronic health records (EHRs).
- Predictive Analytics: Predictive analytics examines historical data to predict future health patterns. It aids in forecasting patient risks, devising treatments, and sidestepping complications.
Around the world, healthcare organizations are adopting smarter ways to manage data. As we’ve mentioned before, standardized data is one of them. It allows different systems to share information easily, improving coordination between hospitals, clinics, and pharmacies.
Healthcare providers continue to invest in security; stronger cybersecurity measures protect patient records. With rising cyberattacks, healthcare providers have become more interested in encryption and regular system audits.
What’s also becoming fresh is patient data ownership. Patients are gaining more control over their own health information. Giving patients access to their records builds trust and encourages them to participate in their care.
This was about now. What about the future? The future of healthcare is data-driven. Here’s what it looks like:
- Personalized Care: Doctors will use data to create treatment plans tailored to each patient. This means better results and fewer side effects.
- Proactive Healthcare: Predictive tools will help identify health issues before they become serious. Early interventions save lives and reduce costs.
- Efficient Operations: Data insights will streamline hospital workflows, reduce waiting times, and cut costs. Patients will get faster with better care.
No longer a back-office function, healthcare data management is now better described as the backbone of modern healthcare. Whether it’s improving patient outcomes, enhancing operational efficiency, or driving cutting-edge breakthrough research, effective data management is a common thread that runs through all aspects of the industry. It ensures the right information gets to the people who need it at the moment they need it to make more informed decisions and, ultimately, better care.
Conclusion
The future of healthcare data management aims to develop a more intelligent, secure, and patient-centered system rather than merely focusing on technology. By utilizing AI, blockchain, and predictive analytics, healthcare providers may provide better care and create a healthier society.
Transforming healthcare data management is what we do at Jelvix. From enhancing interoperability and securing sensitive records to facilitating predictive analytics, we offer the subject matter expertise your organization needs.
With our advanced technologies and experienced team, you’ll gain the tools and expertise to stay ahead in an evolving industry. Let Jelvix guide your data management transformation and drive the future of healthcare.
Get in touch today to create the perfect solution tailored to your needs!
FAQ
Why is healthcare data management critical in modern medical practice?
Healthcare data management ensures accurate, safe, and easily available data, which is essential for providing high-quality care, cutting expenses, and promoting medical advancements.
What types of data are most vulnerable to breaches in healthcare systems?
Cyberattacks target personal health information (PHI), payment details, and sensitive clinical records the most. Effective security measures, including encryption and access controls, can mitigate these risks.
What’s the difference between data governance and data management in healthcare?
Data governance focuses on policies, standards, and compliance, while data management involves the technical processes of collecting, storing, and utilizing healthcare data.
How can outdated legacy systems affect healthcare data management?
Legacy systems could pose security problems, impede interoperability, and slow down data retrieval. These issues can be fixed by incorporating middleware or upgrading to modern systems.
How can patients benefit directly from better healthcare data management?
Patients benefit from quicker diagnosis, more individualized care, easier billing procedures, and more record-keeping openness.
Need high-quality professionals?
Scale your development capacity with top-level expertise and resources.