We create, share, and store incredibly large amounts of data these days. Large enterprises and small companies process it to run their businesses and get helpful insights. Data is the bloodstream in the veins of the 21st century.
According to the research conducted by Finances Online, the estimated amount of data consumption is 74 Zettabytes in 2021. Moreover, this number will double by the end of 2024. One zettabyte of data comprises one billion terabytes. The estimated number of video games that a zettabyte hard drive can store is 60 billion.
However, what do most people know about data itself?
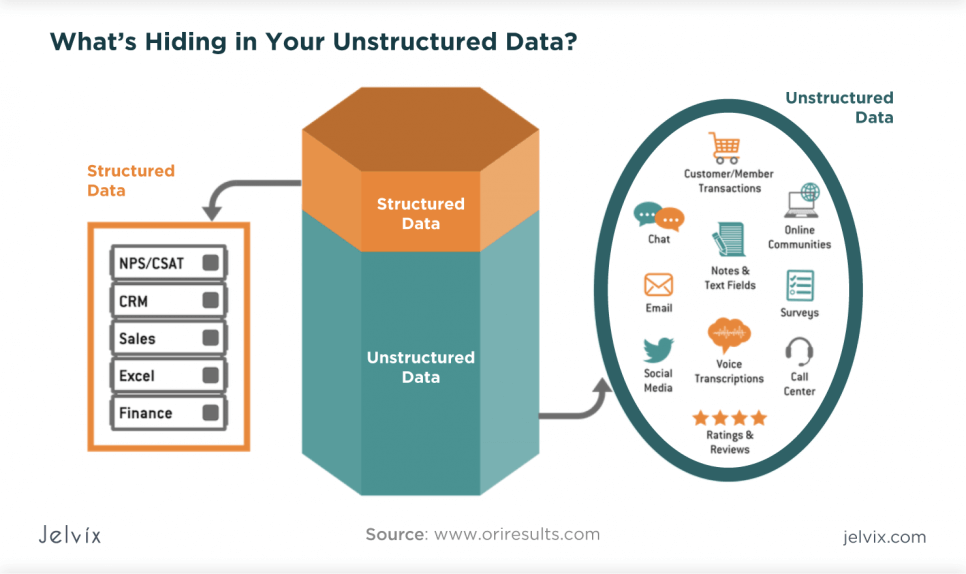
The information they cope with is numbers, names, or images. In most cases, all the information is divided into structured and unstructured. What is the difference between unstructured and structured data? Keep reading the post and discover everything you need to know about structured vs unstructured data.
Structured Data
The structured data definition is very simple. In a nutshell, it is a type of quantitative data that match particular criteria. It can be easily organized, sorted, and analyzed. The primary criteria of structured data are that all the records have the same format and consist of numbers or symbols. In most cases, structured information is stored in relational databases made of rows and columns.
According to the structured data definition from GeeksforGeeks, it is a type of data that a human or computer can easily access. Structured data is usually managed with the help of SQL (Structured Query Language). It allows managing data in databases with the help of requests that both users and machines can submit.
Usually, the information is stored in data warehouses because it can be easily analyzed. This type of data has a predefined data model that is not flexible as it always matches particular standards. The number of formats for structured data is very limited.
Source of Structured Data
The structured data definition says that both users and computers can generate this type of information, usually stored in relational databases. Nevertheless, computer systems are the primary source of structured data. Since computers are powered by particular logic and algorithms, they can easily generate, store, and analyze this type of data.
SQL databases are the primary source of structured data. These days machines collect a lot of data about users online. For example, according to recent research, Google gets 1.3 TB of data from Android and iOS devices. All the data comprises many records on how users utilize their devices, what apps they install, how much time they spend online, etc.
Another example of structured data will be SKU codes generated by inventory management systems. Considering that there must be a unique SKU number for each variation of the product’s different colors, shapes, and sizes, the number of SKU codes is growing dramatically every single day. Consequently, the amount of machine-generated structured data increases continually.
Nevertheless, there are also a lot of different sources of structured data that can be user-generated as well. For example, spreadsheets, OTPL (Online Transaction Processing) systems, online forms, and server logs can be a source of structured data. The most common file formats that store structured data are XML and CSV.
Structured Data Use Cases
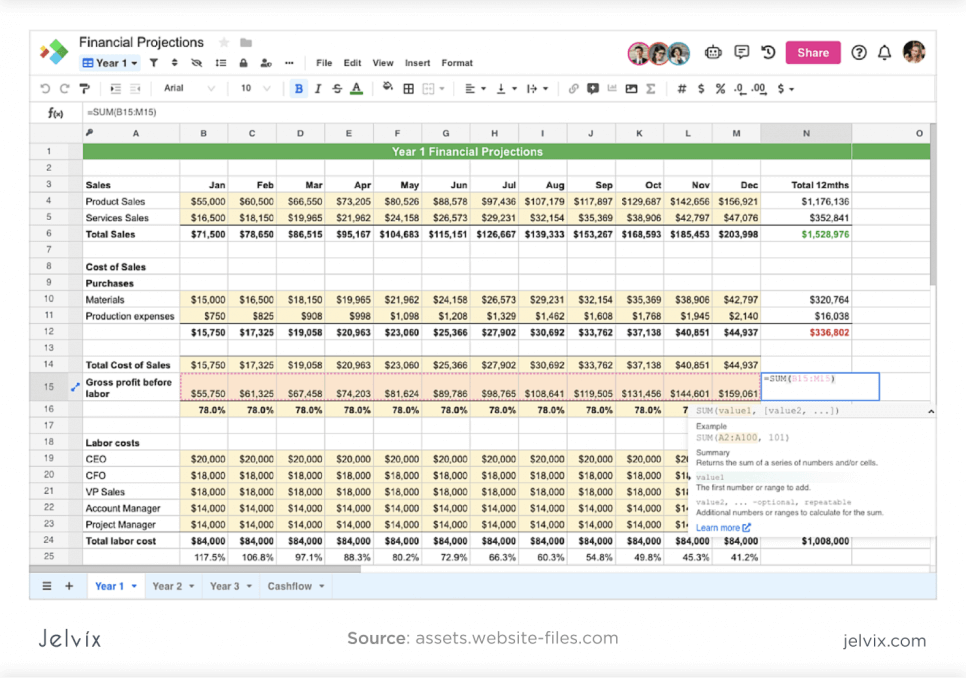
A spreadsheet that contains crucial client information is an example of structured data. It may consist of columns that imply the name, age, profession, citizenship, nationality, etc. Such data consist of numbers and letters. Every cell corresponds to particular information so that it can easily be addressed. Since the information meets particular standards, users can apply formulas. Also, they can edit data in bulk, sort it, or pick cells that match particular criteria in a few clicks.
Also, almost any customer management system operates structured data only. On average, it implies identified information about clients. The data is arranged according to particular needs, payment details, and other info. For instance, it may imply the date the first purchase was made, how much money is spent monthly, or the average response time. Since all the data is structured, it can be analyzed to get helpful insights.
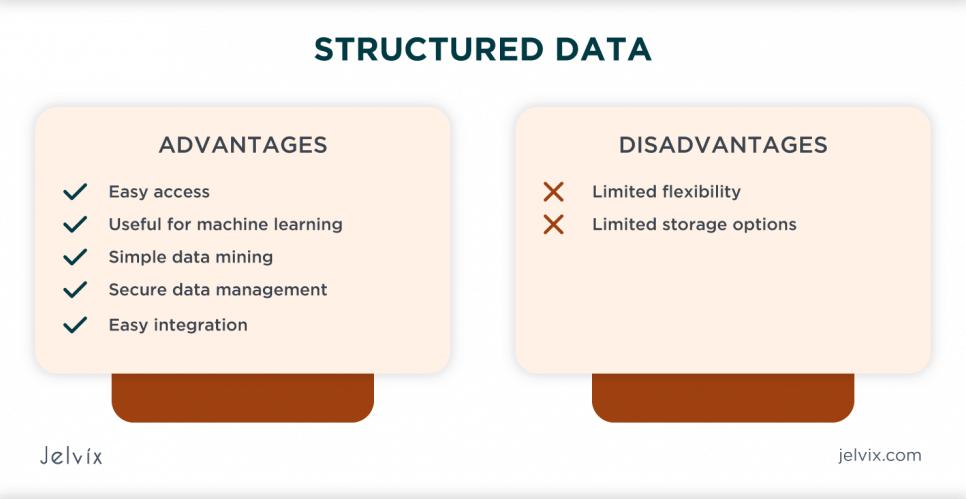
Advantages of Structured Data
- Easy access. Indeed, the primary benefit of structured data is that computers can easily manage it. Since all the information has a particular format, algorithms can quickly process it and deliver helpful insights. Moreover, users can also access and analyze structured data. It has predefined and solid patterns that relational databases use.
- Useful for machine learning. These days, AI (Artificial Intelligence) and ML (Machine Learning) technologies are developing quickly. Structured data can help developers train machine learning algorithms. It makes information manipulation simple for algorithms. With the help of structured data, algorithms learn to manage unstructured data.
- Simple data mining. When a user needs to get a particular piece of information, structured data can help save many hours. It makes the search and extraction processes lightning-fast. Even if a spreadsheet implies thousands of rows, users can easily find the needed ones with no hassle.
- Secure data management. A lot of data used by companies needs to be stored wisely. It may imply sensitive information or credit card credentials. When all the data is structured, it can be easily encoded and decoded. Therefore, companies that use structured data can keep the information about their customers safe even in case of a data breach.
- Easy integration. Structured data can be easily integrated into other platforms and processed with various tools. For example, an inventory spreadsheet in the CSV format with the names of products, prices, images, quantity, and other characteristics can be easily integrated into an online store. Consequently, users can create thousands of product cards and run an online store in a few clicks.
Disadvantages of Structured Data
- Limited flexibility. According to the structured data definition, this type of information has a predefined structure. Consequently, in most cases, it is used for particular purposes only. It can hardly be updated or converted to be used for different purposes.
- Limited storage options. Structured data is stored in data warehouses, systems that have rigid schemas. Therefore, users need to update all the data if any requirements change. It may need to take a lot of computing power and time.
Structured Data Management Tools
Indeed, Microsoft Excel is a convenient tool for managing structured data. It foresees the ability to arrange all the data in a particular order, set data types for cells, and modify information in bulk. However, it isn’t the only tool used for managing structured data, though it’s very convenient. There are a lot of popular tools that are used for this purpose. The most popular ones are listed below.
- MySQL. It is the most popular relational database management system that can arrange structured data in rows and columns. Users can access data and modify it upon a need. Moreover, the tool makes it easy to search and update any piece of structured information.
- OLAP. The tool’s name stands for Online Analytical Processing. It helps users efficiently analyze structured data that is gathered in centralized storage. A lot of companies use it to conduct comprehensive analytical queries.
Unstructured Data
Another type of data used is unstructured. Qualitative data can hardly be processed by common tools used for information processing. What is unstructured data? In a nutshell, unstructured data defines all the information in any format. It can be images, videos, songs, speech recordings, etc. The diversity of formats is limitless.
Since there is no predefined model, it is stored in non-relational databases. All the unstructured information is not processed and is stored in its native format. It is not arranged, so users experience difficulty processing large amounts of unstructured data. Moreover, this type of information takes roughly 80% of all the stored data, making the task more challenging.
Source of Unstructured Data
Almost anything can be a source of unstructured data. These days, a lot of companies collect tons of data. But, since they cannot process the information, they store it in data lakes. It’s a perfect solution for storing raw data as-is. What is an example of unstructured data? It may be videos, emails, blog posts, heatmaps, etc.
Social media platforms and messages are the largest sources of unstructured data. Unlike computers, people don’t like keeping everything unified. They generate a ton of content every second and share it online. According to recent statistics, users generate 2.5 billion gigabytes of content every day. All the media is unstructured content that is stored on servers of different tech giants.
Unstructured Data Examples
Exploring the examples of unstructured data is the best way to understand this type of data. It can help distinguish unstructured data from structured information. In a few words, it’s any information that cannot be structured and analyzed because it doesn’t fit any predefined standards. Therefore, the publication you’re reading at the moment and all the media files are examples of unstructured data.
Data mining is one of the most interesting unstructured data examples to review. These days, many companies are not satisfied with the amount of structured data they have. Therefore, they analyze a large array of unstructured data with the help of data scraping specialists and AI. It helps them get additional structured data that will enhance the existing insights. Sometimes, unstructured data may be a source of crucial information for companies.
Besides, unstructured data helps create chatbots. In most cases, this type of data is used to help algorithms understand users’ requests. Consequently, chatbots can navigate users to appropriate sources of information. Also, they can share answers to the most widespread questions. It helps increase the customer care managers’ productivity.
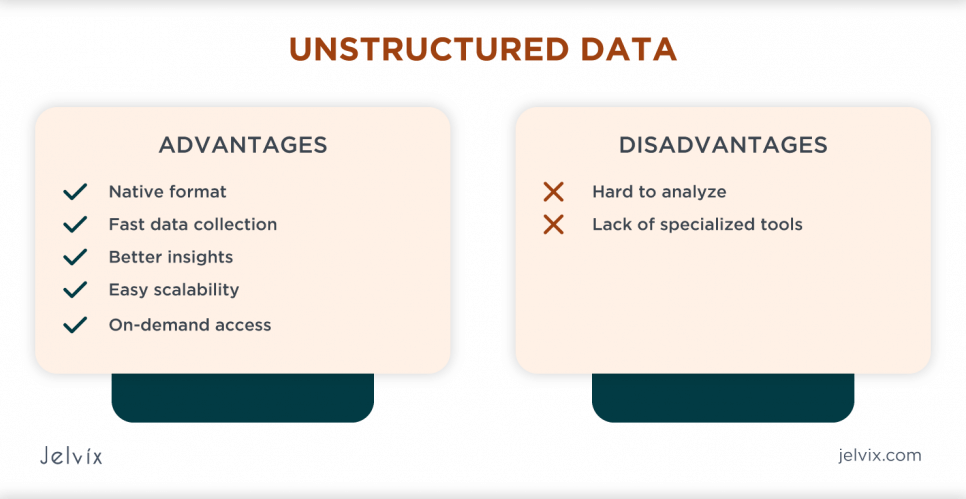
Advantages of Unstructured Data
- Native format. Unstructured data doesn’t need to fit particular requirements. Therefore, it doesn’t need to be converted. All the content generated by humans and robots is stored as-is.
- Fast data collection. It’s easy to collect unstructured data because it takes roughly 80% of all the information on the Internet. Moreover, since it doesn’t need to be predefined, there are no limitations that may sort out particular pieces of unstructured data.
- Better insights. Companies rarely use raw unstructured data because it is hard to analyze this type of information. However, it also can be a great source of useful insights that may help acquire data about customers or enterprises.
- Easy scalability. Unstructured information is stored in data lakes and doesn’t need to fit particular requirements. Therefore, there is no need to update a particular database structure if new information is added. Cloud storage or servers on-premises can be easily scaled to store unstructured data.
- On-demand access. In most cases, unstructured data is accessed upon demand. Therefore, it is cheaper to store it.
Disadvantages of Unstructured Data
- Hard to analyze. The primary drawback of unstructured data is that the number of formats is limitless. It makes it hard to analyze to get new insights. For example, unstructured data may imply text, videos, animations, or images. Data science specialties need to be hired to analyze them and get helpful information.
- Lack of specialized tools. Since there are no standards that unstructured information meets, a small number of tools can manage this type of data. In most cases, it’s required to use different tools to operate images, videos, texts, and other data types.
Unstructured Data Management Tools
Even though unstructured data implies a lot of different formats, it needs to be managed. To keep all the information in order and access, it is required to use particular tools. The selection of the best ones will help you find a tool that will fit your needs.
- MongoDB. It is a comprehensive platform that offers the ability to store many different data types. For example, users can store and use unstructured documents using different platforms with the help of this tool.
- Hadoop. It is a tool that offers the ability to manage and process large amounts of data in different networks. Moreover, the tool doesn’t have the required formats. So, it can manage any kind of unstructured data.
Structured Data vs Unstructured Data: Key Points
It’s hard to provide a complete answer to the question, “What are the structured data and unstructured data examples?” There are a lot of peculiarities that should be considered.
However, the comparison table below will help you grasp the main structured vs unstructured data differences.
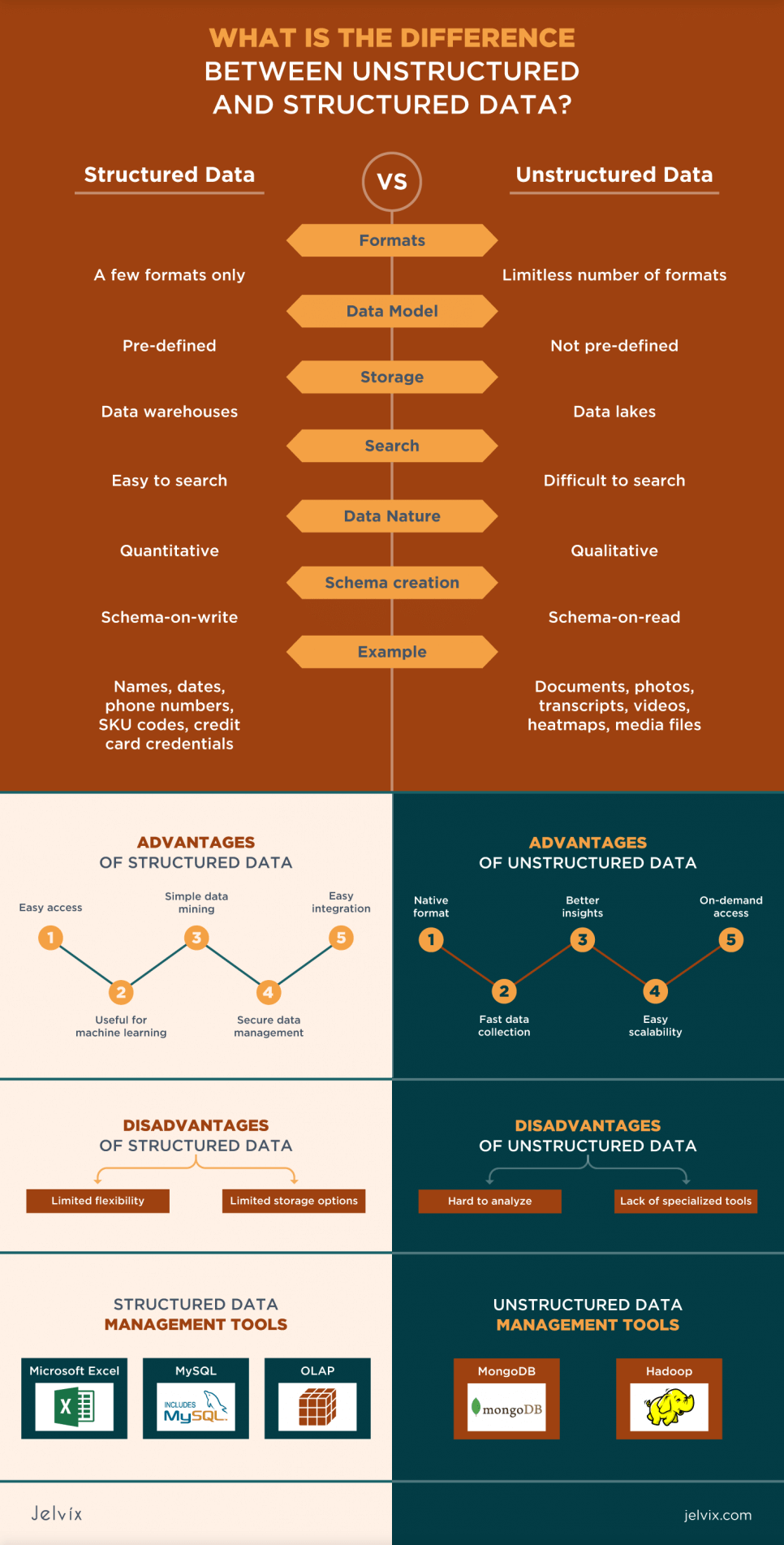
| Structured Data | Unstructured Data | |
| Formats | A few formats only | Limitless number of formats |
| Data Model | Pre-defined | Not pre-defined |
| Storage | Data warehouses | Data lakes |
| Search | Easy to search | Difficult to search |
| Data Nature | Quantitative | Qualitative |
| Schema creation | Schema-on-write | Schema-on-read |
| Example | Names, dates, phone numbers, SKU codes, credit card credentials | Documents, photos, transcripts, videos, heatmaps, media files |
Other Types of Data
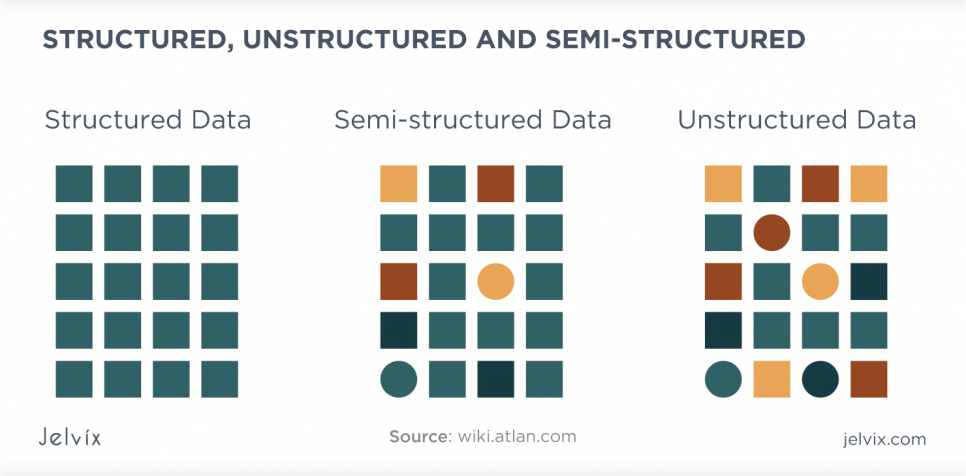
In the last decades, companies have had the need to tackle more and more challenges related to data storage and management. Consequently, dealing with such amounts of data as only structured data vs unstructured data options was very limiting for developers. So other types of data have been developed to simplify this process.
Semi-Structured Data
For a long time, lots of developers strove to build a bridge between structured and unstructured information. So, the semi-structured data format has appeared. It is a unique format that is not related to any of the mentioned above. Roughly, it takes 5% of the entire data and solves particular problems. It is crucial for businesses because semi-structured information is a blend of structured and unstructured information.
In a nutshell, it is similar to unstructured data. However, it uses metadata that brings the ability to use it efficiently. For example, users can arrange unstructured pieces of content like documents, images, videos with the help of this data type. It helps managers operate large amounts of unstructured information. Moreover, they can get more insights.
To imagine what semi-structured data is, you need to take a closer look at XML, a markup language. It helps both developers and machines understand how particular data should be arranged. It is a tag-driven language that helps developers update data structure.
Metadata
Metadata is a key element that makes semi-structured data searchable and categorizable. It is a particular type of data that defines unstructured information with the help of tags and semantic markers. They identify specific information types and simplify the unstructured data management processes.
The best example of metadata is alt text that images may have. It helps define what is displayed in a particular picture. Unfortunately, Google algorithms cannot recognize all images to search for correct ones. Alt tags help robots identify images for further search. Metadata can include information about the date, location, and technical specification of hardware used to make a snap.
Concluding Words – the Future of Data
Thanks to the information provided in the post, you can find the answers to the questions, “What are the three types of data?” and “What is the main difference between structured and unstructured data?” However, the questions “What will happen to data in the future?”, and “Which type is the best?” remain.
Unfortunately, it’s impossible to choose the best type of data. Any type of information has its perks, advantages, and drawbacks. Therefore, if you consider what type of data to use, you should first analyze your needs. This will help pick the right data format. In case you struggle analyzing your demands and picking the right solution, Jelvix’s expertise in big data will help you get rid of any problems.
Note, the future will be data-rich. Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence are being developed at an extremely high pace. Therefore, companies will analyze raw unstructured data to get helpful insights. If you want to overcome your competitors and get a lot of helpful data about customers, feel free to reach our specialists. We will help you build a comprehensive data management system that will satisfy all your demands and needs.
Need a qualified team?
Extend your development capacity with the dedicated team of professionals.