By design, the data in any field of activity is a subject to systematization and structuring. The concept of “data analysis” contains the following stages:
- Dividing an array of data into subsets according to some features;
- Making conclusions of a certain nature from it;
- Transforming by a specific model.
This is relevant to any arrays of data, of any subjects and forms – analytical approach applies everywhere. Of course, there are different types of data analytics, since varying tasks need varying approaches.
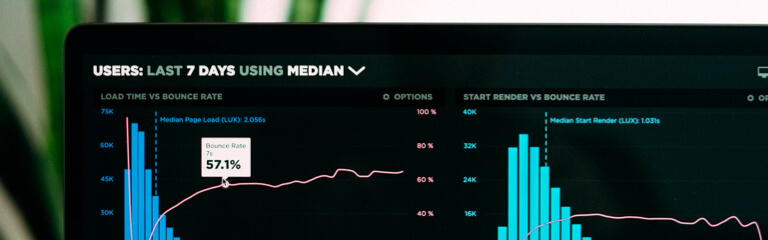
In the beginning, data analysis was mathematical. Now researchers attribute it to computer science and use in a wide variety of fields – from business to programming. Analytics allows getting answers to questions arising from specialists in various industries. For example – a company that had a stable profit that decreased or increased.
The data analyst can answer the questions:
- What has changed in the company’s activities or the external environment?
- Which areas generate the most profit?
- What actions should be taken to increase profitability?
- How to make the company more competitive?
Our experts have years of experience in this field and apply it to the businesses of our customers.
What types of data analytics exist?
There are several archetypal approaches to analytics that we consider universal.
Types of data analytics according to Jeffrey Leek
Most used currently is a classification by Jeffrey Tullis Lick. He identified 6 kinds of analysis.
Descriptive (common)
As a rule, this method of analysis is used for the primary information classification. Descriptive analysis is among the most used types of big data analytics. That is, analyzing large arrays of heterogeneous information.
The result of the descriptive analysis is the preliminary separation of data into subsets. It begins with a clarification of exactly what to deal with – the result is information about the quantity or volume of something. In business processes, the result of a descriptive analysis is usually not enough for making decisions. Besides, this allows systematizing the reports to investigate them further using other methods. This is the basic stage of analytics.
Exploratory
This method of analysis is aimed at identifying trends and patterns, unknown before. Its results also rarely are final. They are useful to generalize the information about previous actions and factors, and their impact on a process. As a rule, results of exploratory analysis look like structured tables.
Inferential
This approach allows getting statistical conclusions about the nature of objects and phenomena. Results of such analysis are required to build statistical models. Next, these patterns serve to conduct the actual work. For the inference, partial data is taken – certain excerpts from a total volume of information.
Predictive
This is a very popular method that allows making accurate hypotheses about further changes. As such, it requires the highest accuracy and multidimensionality of the input data. The smallest inaccuracies can lead to distortions in the system as a whole.
Causal
This type of analytics allows finding out how changing one parameter will cause changes in others. As a rule, causal analysis is carried out in randomized data arrays. There are approaches to infer causation in non-randomized datasets, but they are much more complex and hard to conduct.
Mechanistic
This method is the most challenging but necessary if you need to discover the parameters in the input data that differ in accuracy. Thus, the variables in certain object classes or individual objects are determined with the same accuracy.
Other Classifications
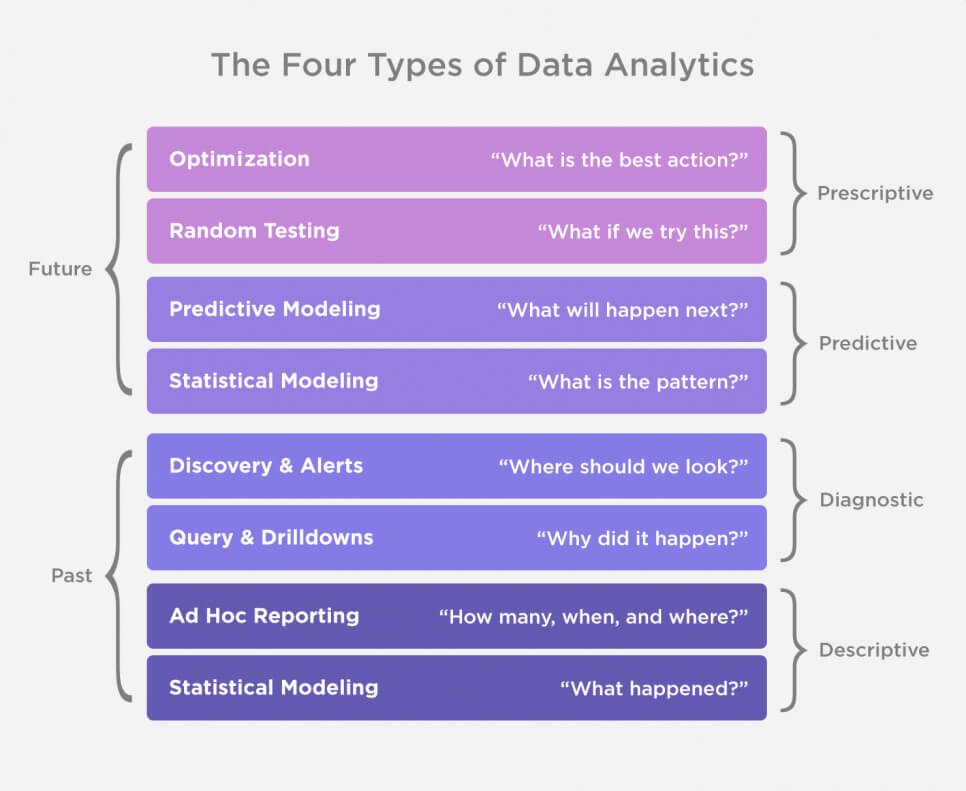
There are other data analysis classifications, which include 3 types of data analytics or 4 types of data analytics. Out of the 6 above mentioned, most often they name causal, descriptive, and predictive analytics. The combination of these three methods allows creating a holistic picture. Why did something happen, what is the current picture, and what upcoming changes can we predict on this basis?
One-dimensional and multidimensional analytical data processing techniques
There is another parameter by which scientists differentiate the information analysis methods. According to it, all analysis techniques, regardless of the mathematical method used, belong to two major classes:
- One-dimensional, also called descriptive. A descriptor is a single criterion by which data can be searched and sampled into a certain subset.
- Multidimensional. Such methods of analysis consider two or more descriptors. Researchers form and test hypotheses. How these variables relate? What causal relationships are formed between them? How many overlapping subsets do they share in an array of data?
In turn, multidimensional types of analytics are divided into cluster and factor analysis.
Cluster Analysis
In cluster analysis, an expert chooses a sample of objects that are within their subsets as close as possible to each other. Also, they have to be as different from other subsets as possible. This helps to identify the feature or series of features that divide these objects.
Factor Analysis
During the factor analysis, a scientist considers the largest possible number of parameters to analyze a certain object group. These parameters are combined into groups to get several instead of several dozen variables. For example, evaluating the company’s work, we can distinguish the parameters “level of service” and “product quality” instead of “efficiency of storage personnel”, “delivery accuracy”, “office comfort”, etc.
Read more about the value of customer reviews for the best software development company.
Data analysis automation software
Many advanced programs have been developed to automate data analysis. For example:
- Alteryx allows collecting massive arrays of data from a variety of sources, process them, and bring the results to a single standard. In turn, these can be further grouped, scouted for extra variables and relationships between them, etc.
- Tableau is a program with which you can visualize statistical information. It allows creating complex graphs demonstrating the results of analytical processing.
Need a certain developer?
Reach new business objectives with the dedicated team of professionals.