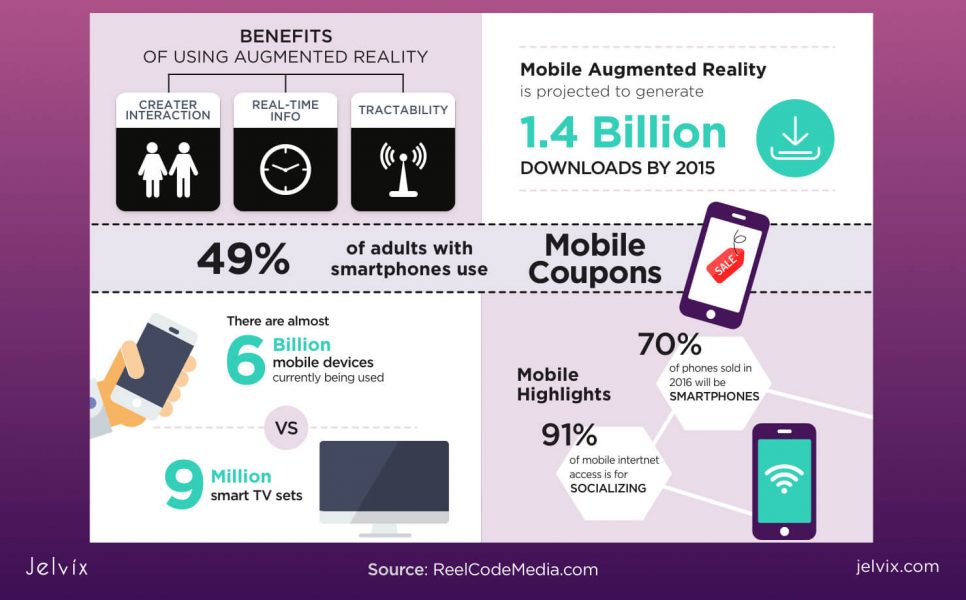
The augmented reality technology has come to stay and change the way we interact with the environment that surrounds us. Adding digitally generated objects to the real-life environment via smart devices can potentially transform every industry, from education and healthcare to entertainment and gaming.
If you are working on joining the hype, you should know your way around what you need to make it happen. That is why we have prepared an overview of the best tools for augmented reality development. Without further ado, enjoy!
Types of augmented reality applications
We can define several significant differences in the basic performance of most AR-based apps. Thus, some solutions focus on identifying graphic markers (like QR-codes or complex graphs), others process data received via GPS while the rest may combine both features. An emerging technology is a full-body motion tracking AR/VR solutions for those in the industries who require believable real world interactions inside their virtual world environments.
- Full-Body tracking solutions. The most progressive AR/VR full-body tracking solutions are represented by Manus VR. Manus launches Polygon full-body tracking for VR, and advanced Prime II gloves to enable whole body, tactile interactions in virtual reality. Natural body movements combined with realistic touch sensations heralds a new era for motion capture specialist Manus in hyper-realistic immersive VR team collaboration. Manus now provides users with a complete, robust and efficient VR system specifically designed for teams across the enterprise sector of automotive, manufacturing, engineering and life sciences, including creators of virtual experiences within media and entertainment.
- Marker-based apps. This is probably the most popular AR software principle. Markers can be various – from simple geometric figures (which are, usually, enclosed into QR-codes) to complex for digital perception physical objects like human faces. Such solutions are pretty resource-intensive in terms of man-hours that need to be devoted to them. Lots of time is required to process numerous different events;
- Apps that focus on GPS data. This type of solution, apart from the GPS connection, also requires a high-speed web connection. A typical example of such apps are various existing AR browsers;
- Gyroscope-based apps. Another common way to implement AR software – it may simply work with the data accumulated by the user smartphone’s gyroscope. With the help of this built-in feature, developers get to enliven virtual 3D objects on top of real objects in the physical environment;
- SLAM apps. Such solutions employ the concept of Simultaneous Localization and Mapping, which is based on collecting data from several sensors at once (for instance, from GPS, gyroscope, accelerometer, etc.). Similarly to the previous case of gyroscope-based apps, they draw up three-dimensional objects against the background of real objects; however, without using any markers.
10 best augmented reality tools to consider
If you have already been searching for the appropriate tool for your project, you may feel lost in the sea of various SDKs out there. The choice isn’t that easy, indeed, but we are here to help you make a wise decision.
1. Vuforia
Of course, we are going to start with perhaps one of the most popular AR frameworks. This SDK for AR app development framework was introduced by renowned Qualcomm – a company that used to initially specialize in the research and development of the wireless means of communication as well as SoC electronic microchips.
In the core of the platform lies a QCAR library written in C++, which contains targets (image cube, cuboid, cylinder, word targets, and frame markers) and image rendering features. Targets in Vuforia are, basically, real objects, recognizing which, your application can array virtual objects in the needed locations and corresponding proportions.
Vuforia also features Extended Tracking (when the object remains captured even after it leaves the frame, which provides capabilities for implementing apps with augmented reality that factually surrounds the user) and Smart Terrain.
Solutions created with Vuforia are supported by:
- Android,
- iOS,
- Universal Windows Platform, and
- Unity Editor.
Even though you can use it for free, this option is good only for hobbyists, because it comes with limited functionality and watermarks. The main features that Vuforia offers developers include:
- Vuforia Object Scanner: recognizing 2D and 3D objects;
- Text recognition with in-built 100,000-word English vocabulary and the option to create your custom one;
- VuMarks: barcodes that can contain data or act as markers;
- Video playback when a certain condition is met (for instance, when the target surface or image is detected);
- Virtual buttons that can turn any surface into a touchscreen;
- Smart glasses support;
- Storing data on the device or in the Cloud.
Pricing: free + paid subscription plans (Classic – $499 per time, Cloud – $99 per month, Pro for commercial use, the pricing is individual)
2. Wikitude
The list of the top augmented reality SDKs wouldn’t be objective without Wikitude. Thus, Wikitude is another extensively popular framework for creating AR-based apps, which was first launched back in 2008 by an Australian software development company.
This SDK is constantly improved upon and updated – the latest Wikitude SDK 9.12.0 was released in July 2022. Up-to-date Wikitude features an array of built-in capabilities (including various rendering features) and is quite accessible as a whole.
The platform is quite flexible so that developers can create customized solutions and render objects via third-party tools while still working on it. For that, however, one has to write a piece of JS code with the help of Wikitude JS SDK or Wikitude Native SDK.
As a matter of fact, with Wikitude, you get a full-blown online studio for arraying static augmented reality objects. All that you need to employ rendering is upload an image to the studio, add AR objects, generate JS code, and paste it into the project.
Wikitude is supported by all major platforms:
- Android,
- iOS,
- Windows for tablets.
If you use Wikitude to develop your application, you can:
- import and render 3D objects with SLAM technology;
- build apps for smart glasses;
- store data in the cloud or on the device;
- employ location-based services;
- use JavaScript API, Native API, Xamarin, Unity3D, Cordova, Titanium for development;
- employ object, scene, and image recognition features;
- use Wikitude Studio to add, manage, and manipulate virtual objects without any coding necessary.
Pricing: a free trial with watermarks + paid subscription plans (starting from €1,990 per one app)
3. ARKit
ARKit is a package of profiled tools first introduced during the WWDC 2017 event. It offers a principally new approach to augmented reality technology. In particular, the solution is capable of identifying dimensions of the surrounding and consider lighting conditions to integrate virtual objects with real life as seamlessly as possible.
Moreover, it supports Arkit Unity and has a unique feature: there is no need to connect any additional directional markers like iBeacon for orientation and routing in this SDK.
As you may know, this toolkit for augmented reality development was created and launched specifically for creating mobile software for the iOS platform by Apple. This means you can create apps only for iPhones and iPads with this SDK, so it may be your best augmented reality SDK if you aim to make an AR exclusively for these devices.
ARKit is compatible only with Apple platforms:
- iOS 11 or newer.
Let’s take a look at its main features:
- 2D image detection and tracking;
- space and 3D objects recognition;
- sharing the AR experience with other users which allows creating multiplayer AR games;
- horizontal planes detection;
- lighting estimation for making virtual objects look more realistic;
- facial tracking.
Pricing: free
4. ARCore
ARCore is, basically, Google’s response to Apple’s ARKit. Unlike Apple, Google doesn’t mind supporting developing AR apps for both Android and iOS. ARCore three key technologies for ‘embedding’ virtual content into real environments: motion tracking, environmental recognition, and lighting recognition.
A 3D model created via ARCore can react to the changes in the lighting volume and even generate shades. Smartphone movements don’t affect the situation of the model in space in any way. A proprietary camera is used to define the parameters of physical objects and horizontal surfaces. In such a manner, created objects are being automatically ‘attached’ to tabletops, floors, and other environmental surfaces.
ARCore is supported by the following platforms:
- Android 7.0+,
- iOS 11+,
- Android NDK,
- Unity для Android,
- Unity для iOS,
- Unreal Engine.
Using this SDK allows:
- tracking the phone’s motion and its position relative to the surrounding objects;
- estimating the lighting to adjust it on the virtual objects;
- understanding the environment by detecting the surfaces, and their size and location;
- placing texts or virtual objects in a certain spot and sharing them with other app users;
- working with Java/OpenGL, Unreal and Unity;
- creating 3D objects with Tilt Brush and Blocks VR building tools.
Pricing: free
5. MaxST
MaxST AR SDK is yet another powerful framework for mobile software developers that increasingly grows in popularity. It is based on five major components:
- Image Tracker – recognizes and tracks planar circuits of an image. It supports three tracking modes: Normal (standard mode), Extended (for tracking all objects in the field of camera’s vision), and Multi (for tracking up to three objects).
- Instant Tracker – identifies a flat surface in the camera’s field of vision to place a 3D object over it.
- Visual SLAM – creates and saves three-dimensional maps that are autonomously scaled and extended beyond the fringes of the initial frame (which happens along with the movement of the camera from place to place).
- Object Tracker – loads map files and put AR objects over them.
- QR/Barcode Scanner – recognizes ‘pre-programmed’ QR-codes and barcodes.
MaxST is compatible with platforms, such as:
- Android,
- iOS,
- Windows, and
- Mac OS.
MaxST comes in two different SDKs: one is the 2D toolkit used for tracking images, and the other one is the 3D toolkit created for scanning and recognizing the surrounding environment. The latter one is more interesting for us in terms of the topic, so let’s take a look at its key features:
- tracking the surroundings and mapping the environment;
- scanning QR codes and barcodes;
- tracking multiple targets at the same time (up to 3 items);
- physics engine effect to create more realistic experiences;
- occlusion effect – screening the virtual object by a real one fully or partially;
- integration with Unity (although MaxST works only with the 32-bit Unity Editor version).
Pricing: free (with watermarks) + paid subscription
6. EasyAR
EasyAR is an Asian solution for creating AR apps that is heavily underappreciated by most developers. As opposed to many other tools, the solution doesn’t feature a built-in object manager. Instead, objects are identified by recreating initially predefined 3D models. Targets are generated in runtime.
Working with EasyAR, you will have to write more code than in case of most other tools, as well as go through project formatting in Unity in a bit different way. However, all this allows for building utterly flexible solutions. The only significant con of this tool is that there is no accessible documentation and tutorials on it.
EasyAR is compatible with:
- Android,
- iOS,
- UWP,
- Unity Editor,
- Windows, and
- Mac OS.
The tool enables developers to:
- recognize images;
- identify 3D objects;
- perceive environments;
- recognize clouds;
- employ Smart Glass;
- record the screen;
- transfer files to cloud storage;
- export, import, and integrate assets.
Pricing: free (requires a generated key).
7. Kudan
Kudan is a SLAM tool from Chinese creators, which is similar in many features to Vuforia, being its direct competitor. On the other hand, it supports only two major platforms: iOS and Android. This can limit the developer’s capabilities to some extent. Using SLAM technology, Kudan allows recognizing simple images and 3D objects, providing simple database generation in the Unity editor.
Kudan-based solutions will be supported only by:
- iOS,
- Android.
Kudan is quite interesting in terms of functionality, featuring:
- tools for creating high-quality 3D graphics;
- marker-based tracking and geolocation definition;
- support of various smartphone camera sensors;
- cloud SLAM system with distributed map generation;
- camera re-localization;
- map scaling;
- map separation and integration, etc.
Pricing: there is a free version for testing apps and license priced at $1,230.
8. ARToolKit
ARToolKit is a package of open-source libraries for developing augmented reality apps based on marker recognition. This is an offspring of DAQRI and quite a popular tool that has loads of corresponding tutorials on YouTube.
The main principle of ARToolKit’s performance is that it processes graphic data received from the mobile camera in the runtime mode guided by the initially known square object markers. After that, the objects are displayed on the smartphone screen with the consideration of their location in space.
With ARToolKit, you can create solutions for the following platforms:
- iOS,
- Android,
- Windows,
- Linux,
- SGI,
- MAC OS X.
Even though this is a well-thought-out solution for beginners (it doesn’t have well-thought-out documentation with good use cases as of yet, though), its functionality is pretty impressive even for experienced AR software creators:
- processing of both 2D and 3D images;
- support of OpenGL specification jointly with GLUT libraries;
- tracking of camera position and orientation;
- code for markers’ identification that employs a simple black square as a basic graphic object;
- support of absolutely any kind of square marker templates;
- simple camera calibration code, etc.
Select a corresponding version of this tool for your particular platform.
Pricing: freeware product.
9. ARmedia
ARmedia is a cross-platform framework for developing software based on 3D model tracking that’s available in both freeware and paid versions. ARMedia is a product by Italian creators which isn’t that popular among wide audiences yet (which doesn’t make it worse than any existing option, though).
As for the capabilities, the tool can identify not only flat images but also complex three-dimensional ones. Thus, ARmedia efficiently handles even large objects with a complex geometrical form.
ARMedia is compatible with the following platforms:
- iOS,
- Android,
- Windows и
- Flash.
In terms of functionality, we can specify:
- an ability to create markers in real-time mode (although, you’ll have to use a plugin for Google SketchUp to do that);
- activation of one of the world’s most perfected 3D trackers from Inglobe Technologies;
- an ability to develop apps for smart glasses;
- multilevel processing of data received through GPS, gyroscope, accelerometer, and magnetometer;
- an ability to manage apps via the cloud.
All in all, this is a very efficient tool that just isn’t as promoted as Vuforia or Wikitude as of yet.
Pricing: there are both freeware and paid versions (the paid costs 249 Euros).
10. DeepAR.ai
This is the last but not the least SDK on our list of the best tools for AR development. The DeepAR company was established in 2015 in the UK. Up to date, its main solution is widely known in the AR developer community. DeepAR can be considered a perfect solution for creating three-dimensional face masks and lenses (e.g., for Snapchat). It also features a patented motion face tracking algorithm and supports unique FX solutions.
DeepAR is compatible with platforms, such as:
- iOS,
- Android,
- Windows,
- WebGL.
Among the major features of DeepAR are:
- recognition of faces and particular facial features in real-time mode (it happens very fast: over 68 facial points can be identified in 1 second with the 60 frames per second speed of recognition);
- precise visualization of images for smartphones with moderate specifications;
- tracking of shifting face positions with the consideration of lighting and degree;
- cross-platform
- cross-platform rendering engine;
- integration with Maya, Blender, and similar solutions.
Pricing: the exact price can be requested.
Let's discuss which IT outsourcing trends will change the industry.
Conclusion
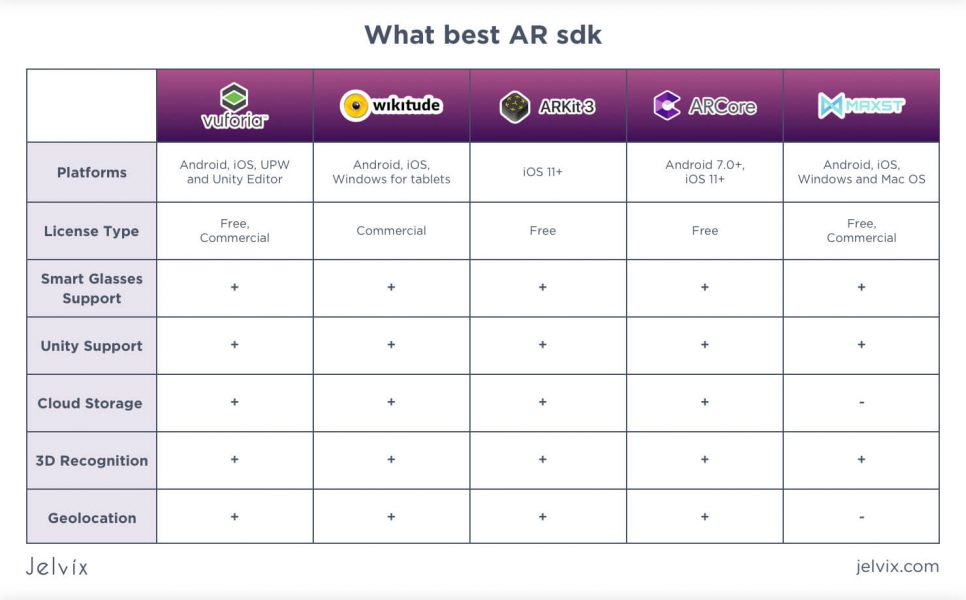
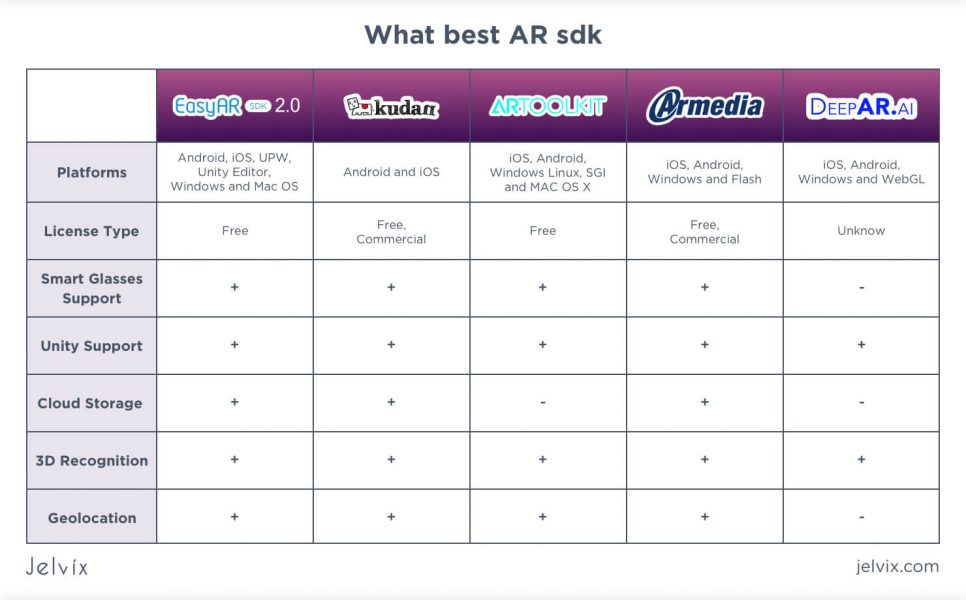
Are you confused about which AR SDK to choose? Fear not – we have prepared a comparison chart with all the main things you may need to know about the best tools for AR development to make your choice. Take a look:
If you are still uncertain how to choose the AR toolkit that would be the perfect fit for developing your app, we suggest you turning to professionals for advice. Do you have the idea that will blow people’s minds? Reach out to us to make the first step towards your success.
Need a certain developer?
Use our top talent pool to get your business to the next level.