In a healthcare landscape where patient safety is critical, concerns over patient identification loom large. Misidentification of patients poses challenges due to factors like misspellings, address changes, and name variations. According to the PSQH report, patient record-matching accuracy can drop to 80% within a care setting and as low as 50% across organizations sharing electronic health information.
Addressing patient misidentification presents a critical opportunity for healthcare providers to enhance patient safety and reduce medical errors. For identity management solution vendors, offering innovative technologies positions them as valuable partners in ensuring accurate patient identification.
If you’re a vendor having doubts about what tech stack to offer or a healthcare provider struggling with patient identification errors, this article is for you. Keep reading to find out what dangers patient misidentification may pose, ways to correct those errors, and types of identity technologies to implement.
Why Wrong Patient Identification Is a Critical Issue
While technology has transformed healthcare operations, patient identification hurdles persist. Inefficiencies, outdated processes, and the complexity of managing diverse patient data contribute to the ongoing challenge of ensuring accurate identification. The consequences of patient misidentification can be severe, including compromised patient safety, medical errors, and challenges in delivering effective and personalized healthcare.
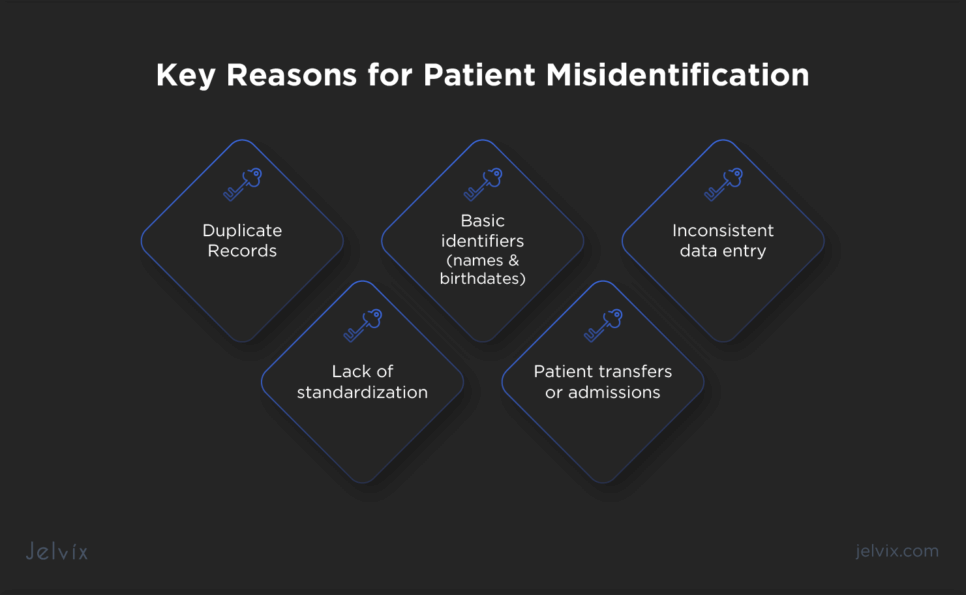
Key Reasons for Patient Misidentification
Patient misidentification can occur through various mechanisms, often stemming from system inconsistencies and human errors. Understanding these factors is crucial for implementing effective prevention strategies:
- Duplicate records: the creation of duplicate patient records, often caused by system glitches or incomplete integration of healthcare databases, can lead to confusion, misidentification, and extra costs (up to $1,000 per duplicated record and about $95 to correct the information);
- Basic identifiers: healthcare systems relying solely on basic identifiers like names and birthdates are more susceptible to misidentification. The lack of robust biometric authentication or unique patient identifiers increases the risk of errors;
- Inconsistent data entry: inaccuracies during data entry contribute to patient misidentification, especially in manual record-keeping systems;
- Lack of standardization: inconsistencies in naming conventions, identification protocols, and data formats across different healthcare systems and facilities can result in misidentification during information exchange;
- Patient transfers or admissions: during patient transfers between departments or facilities, as well as during admission processes, miscommunication or inadequate verification procedures can lead to errors in patient identification.
Why Prevent Patient Misidentification: Real-Life Stories
The consequences of patient misidentification can be grave, leading to severe consequences for both patients and healthcare providers. Examining real-life examples of incident reports in healthcare may help prevent identification issues.
An incident report by Patient Safety Network states that two patients of similar age and with similar head and facial injuries were mixed up in the emergency department. Orders for CT scans were mistakenly performed under the wrong patient’s name leading to incorrect results in both patients’ charts. Additionally, a CT of the abdomen and pelvis, intended for patient A, was performed on patient B. Only upon realizing the inconsistencies did the ED team correct the error by appropriately carrying out the necessary CT scan on Patient A and relabeling all results accurately.
The situation could have been worse if they hadn’t recognized the issue on time. The patients, receiving inaccurate CT scan results, might have undergone unnecessary and potentially harmful treatments based on incorrect medical information.
Another case states that a 21-year-old woman was discovered wearing an ID band belonging to a 60-year-old male during an EKG. The ID band had been mistakenly placed on her wrist by a triage nurse. Had the wristband gone unnoticed, the young woman’s health condition could have been under threat because of medical procedures intended for an older man.
Both cases underscore the importance of accurate patient identification in healthcare settings to prevent errors and ensure patient safety.
How Correct Patient Identification Helps Achieve Your Strategic Goals
Accurate patient identification is a fundamental pillar for achieving business goals in healthcare. The ability to correctly identify patients not only impacts immediate care delivery but also plays a pivotal role in shaping the broader objectives of healthcare organizations.
Enhanced Patient Safety
Accurate patient identification significantly reduces the risk of medical errors, ensuring that each patient receives the right care, medications, and treatments. This directly aligns with the strategic goal aimed at elevating patient safety and minimizing adverse events, reinforcing trust in healthcare delivery.
Data Accuracy
Accurate patient identification ensures reliable health data. Strategic initiatives, like data-driven decision-making and outcomes analysis, depend on precise patient information for better healthcare delivery and continuous improvement.
Efficient Care Delivery
By streamlining patient identification processes, healthcare providers can enhance operational efficiency. Quick and accurate identification facilitates seamless workflows, reducing time spent on administrative tasks and allowing healthcare professionals to focus on delivering timely and effective care.
Patient Experience Enhancement
Accurate identification is integral to personalized and patient-centered care. This aligns with strategic goals aimed at improving the overall patient experience, fostering trust, and ensuring that patients feel recognized and valued within the healthcare system.
Compliance with Regulatory Standards
Meeting regulatory requirements, such as the ones outlined by HIPAA, is a strategic imperative for healthcare organizations. Precise patient identification supports compliance efforts, safeguarding patient privacy and avoiding potential legal consequences.
Effective Health Management
For organizations aspiring to enhance population health management, accurate patient identification is paramount. It ensures that health data is appropriately aggregated and analyzed, enabling targeted interventions and improved outcomes across diverse patient populations.
Interoperability and Information Exchange
As healthcare systems strive for increased clinical interoperability, accurate patient identification becomes pivotal. It enables seamless information exchange between disparate systems contributing to comprehensive and connected healthcare delivery.
Financial Sustainability
Correct patient identification contributes to billing accuracy and reimbursement processes. Healthcare organizations can achieve financial sustainability by preventing revenue loss due to errors in patient identification and associated billing procedures.
Employing Strategies to Minimize Patient Misidentification
Patient misidentification poses significant risks to both individual health outcomes and the overall efficiency of healthcare systems. However, there are effective strategies that healthcare providers can employ to minimize the occurrence of patient misidentification incidents and ensure patient safety.
1. Implement Identification Protocols
Implement standardized protocols across all healthcare touchpoints for patient identification. These protocols should include thorough verification of patient details, such as name, date of birth, and medical record number, ensuring consistency in the data entry process, and minimizing errors.
2. Conduct Staff Training
Invest in comprehensive training programs for healthcare staff involved in patient identification processes. Equip staff members with the knowledge and skills required to follow established protocols, recognize potential pitfalls, and address misidentification issues promptly. Ensure that staff members are proficient in using identification technologies and understand the potential consequences of misidentification errors.
3. Integrate Technology
Leverage technology solutions to automate and streamline patient identification. Biometric authentication, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, offers a highly accurate and unique method of verifying a patient’s identity. This technology eliminates the need for manual entry or traditional identifiers, reducing the risk of errors associated with these methods. Also, explore the implementation of two-factor authentication to strengthen the overall security of the identification process.
4. Establish Audits and Reviews
Implement routine audits and reviews of patient identification processes. Regular assessments help identify weaknesses, assess the effectiveness of implemented strategies, and allow for continuous improvement in minimizing misidentification incidents. Audits should focus on evaluating the adherence to identification protocols, the effectiveness of technology integration, and the identification of any recurring issues that require targeted improvement.
5. Collaborate Incident Reporting
Encourage a culture of incident reporting where healthcare staff can report potential misidentification incidents without fear of repercussions. Collaboration ensures a collective effort in addressing misidentification incidents and fostering a culture of continuous improvement and prevention. Collaborative reporting helps identify systemic issues and enables proactive measures to prevent future occurrences.
Explore the essentials of EHR implementation to boost healthcare efficiency, patient outcomes, and data security.
6. Engage Patients and Their Families
Recognize the role of patients and their families in the identification process. Actively involve them in verifying personal information and ensuring that the data in their health records is accurate. Patient engagement not only empowers individuals but also adds an extra layer of verification to the identification process, contributing to a more comprehensive and accurate patient identification system.
Ways to Prevent Patient Identification Errors
Traditional methods to prevent patient identification errors typically involve reliance on manual processes and traditional identifiers, such as name, date of birth, and medical record numbers. While these methods have been common, they are prone to human error, and inconsistencies, and may contribute to misidentifications.
In contrast to solutions powered by data stack technologies, traditional approaches lack the robustness and accuracy needed to ensure foolproof patient identification in the complex healthcare environment. However, we recommend that you combine multiple tech solutions listed below to enhance patient safety.
Preventing Patient Misidentification with Identity Management Solutions
If you’re an identity management software vendor you know that deploying advanced identity management solutions with patient-matching algorithms can be a good idea for healthcare organizations. These solutions use sophisticated algorithms to cross-reference patient data, improving accuracy and reducing the risk of misidentification.
Master Patient Index (MPI)
An MPI serves as a centralized repository that consolidates and manages patient demographic data from various sources. It facilitates accurate patient matching across the healthcare ecosystem. By serving as a comprehensive database, an MPI ensures that each patient’s identity is consistently maintained and accurately linked to their health records. This centralized approach minimizes differences, aiding in error-free patient identification.
Biometric Identification
In 2022, the healthcare biometrics market reached USD 6.07 billion, with a projected value of approximately USD 30.08 billion by 2032. This means that biometric identification is already widely used as a way to prevent patient misidentification. Indeed, biometric solutions, such as fingerprint, palm vein, or face recognition, provide highly accurate patient identification, reducing the risk of errors associated with traditional identifiers.
Biometric identification ensures that the unique physical characteristics of each patient become their personal identifier. This significantly reduces the chances of misidentification, providing a robust and reliable method for accurate patient matching.
Patient ID Wristbands
Deploying patient ID wristbands with unique identifiers helps match patients with their electronic health records (EHR) throughout their healthcare journey. A secure hospital wristband serves as a tangible link between the patient and their electronic records. This physical identifier ensures continuous and reliable matching, especially during transitions between different healthcare settings. Regular checks and confirmations ensure that the details on the wristband consistently match the patient’s identity.
Two-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication (2FA) enhances patient identification security by requiring users to provide two different authentication factors. This often involves something the user knows (password) and something they possess (smart card, mobile device). By requiring multiple forms of verification, two-factor authentication significantly reduces the likelihood of unauthorized access or identity errors, contributing to more robust patient identification.
Data Standardization
Adopting standardized data formats and coding systems across healthcare entities promotes consistent patient identification practices and reduces mismatching of patient records. Standardizing data formats ensures that patient information follows a uniform structure, reducing variations that could lead to identification errors. This approach streamlines data exchange and promotes accuracy across healthcare systems. Note that data standardization requires collaboration and agreement on standardized formats among healthcare stakeholders.
Data Governance and Quality Management
Robust data governance and quality management practices ensure that patient data remains accurate and reliable. By setting clear policies and continuously monitoring data quality, healthcare organizations can prevent misidentification and maintain the integrity of patient information.
Health Information Exchange
HIE enables seamless data sharing and standardized patient identification practices across healthcare providers. It aims at reducing duplicate records, enhancing care coordination, and improving patient matching accuracy. Integrating with HIE platforms ensures standardized and consistent patient identification practices across diverse healthcare providers, reducing the risk of duplicate records and enhancing overall matching accuracy. It’s important to note that an additional check should be conducted to prevent the inadvertent inclusion of incorrect data from another system, reinforcing the commitment to data accuracy and patient safety.
Incident Management Explained: How to Prevent Harm in Healthcare
Incident management in healthcare is a systematic way of handling situations that may harm patients or compromise their safety. This structured process involves identifying, responding to, and resolving incidents. By adopting proactive incident management strategies healthcare organizations address patient misidentification issues efficiently, minimize harm, and continuously enhance patient safety practices.
Incident Management Process Steps to Take in 2024
The proactive and structured process of healthcare incident management involves a sequence of steps that help address issues promptly and efficiently.
Step 1. Identification
The process begins with identifying incidents through various channels, including staff reports, patient feedback, or system alerts. Consider establishing clear criteria for recognizing incidents related to patient misidentification.
Step 2. Reporting
Encourage a culture of reporting by creating a straightforward and accessible system for staff to report incidents. Ensure that incident reports capture essential details such as the nature of the incident, the individuals involved, and the potential harm caused.
Step 3. Prioritization
Classify incidents based on severity and prioritize them for investigation and resolution. High-priority incidents that pose an immediate risk to patient safety should be addressed promptly.
Step 4. Investigation
Conduct a thorough investigation into the root causes of the incident. Use methodologies like root cause analysis (RCA) to understand the contributing factors, including process failures, communication breakdowns, or technology glitches.
Step 5. Documentation
Document all aspects of the incident investigation, including findings, corrective actions, and recommendations for improvement. This documentation serves as a valuable resource for continuous improvement and future incident prevention.
Step 6. Communication
Keep stakeholders informed throughout the incident management process. Communicate with affected patients, healthcare staff, and relevant departments to ensure transparency and build trust.
Step 7. Corrective Action
Implement corrective actions based on the investigation’s findings. These actions may involve process changes, additional staff training, technology upgrades, or policy revisions to prevent similar incidents from recurring.
Step 8. Monitoring and Evaluation
Continuously monitor the effectiveness of corrective actions and evaluate their impact on preventing future incidents. Regularly review incident trends and adjust strategies as needed to address emerging risks.
Step 9. Learning and Training
Extract lessons learned from each incident to inform ongoing staff training and education programs. Use incidents as opportunities to enhance the organization’s overall awareness of patient safety and the importance of accurate identification.
Step 10. Prevention Strategies
Develop and implement proactive strategies to prevent incidents before they occur. This may involve leveraging technology, refining processes, and fostering a culture of patient safety throughout the healthcare organization.
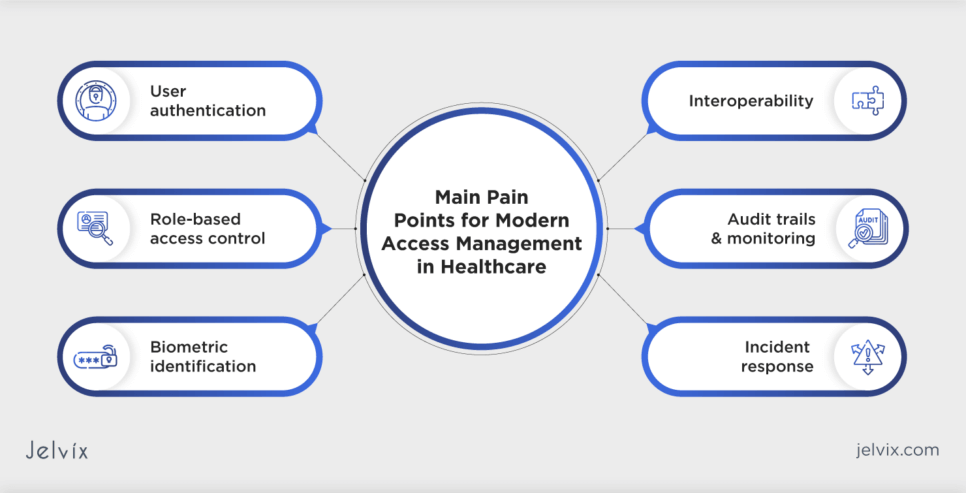
Top Pain Points For Modern Access Management in Healthcare
Modern access management in healthcare plays a crucial role in preventing patient misidentification and ensuring the integrity of patient data. The challenges associated with access management directly impact the accuracy, security, and privacy of patient information.
Here’s how modern access management is interconnected with addressing patient misidentification:
- User authentication: implementing robust user authentication measures is fundamental to modern access management. By ensuring that only authorized healthcare professionals can access patient data, the risk of misidentification and unauthorized access is significantly reduced;
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): modern access management often incorporates RBAC, defining user roles and permissions. This helps tailor access to patient records based on job responsibilities, minimizing the chances of errors related to misidentification and unauthorized data access;
- Biometric identification: advanced access management solutions may include biometric authentication methods such as fingerprints or facial recognition. Integrating biometrics enhances patient identification accuracy, reducing the risk of errors associated with traditional identifiers;
- Audit trails and monitoring: access management systems with robust audit trail capabilities enable healthcare organizations to monitor user activities. Timely detection of unusual access patterns or attempts can prevent patient misidentification incidents and enhance overall system security;
- Interoperability: modern access solutions facilitate interoperability, enabling seamless data exchange between different healthcare systems. A unified patient record accessible through interoperable systems reduces the likelihood of misidentification across diverse platforms;
- Incident response: in the event of a misidentification incident, access management systems play a role in incident response. Timely detection and corrective actions, facilitated by access management tools, help mitigate the impact of patient misidentification.
How Jelvix Improves Patient Identification
At Jelvix, we understand the importance of correct patient identification and also realize the outcomes of errors in it. As a technology-backed company, we help our clients improve patient care by implementing remote patient monitoring software solutions into their healthcare ecosystem.
We focus on seamless integration with EHR systems, creating a unified and interoperable healthcare environment. By bridging the gap between identity management and EHR, we streamline patient data access while maintaining accuracy and security.
Healthcare providers who seek innovative solutions to enhance patient identification accuracy and identity management solutions vendors who look for strategic collaborations are welcome to reach out to our managers. Let’s discuss your specific needs and efficient ways to cover them.