When we talk about healthcare solutions, the narrative centers around interoperability. And no, it’s not just a 2024 trend but rather a foundational principle. With medical technologies and platforms racing ahead, the ability for these systems to talk to each other has shifted from a “nice-to-have” to a “must-have.”
The core of healthcare has always been and always will be, patient care. But what does that look like today? It’s a complex of digital interactions, interconnected systems, and devices that function collaboratively. Interoperability stitches these pieces of IoT-based remote patient monitoring systems together, ensuring the creation of a seamless vision of data.
We’re here for those healthcare institutions standing at the crossroads, wondering how to dive into this interconnected future. Jelvix offers a structured approach to amplify your interoperability game, emphasizing next-gen tools, including telehealth and remote patient monitoring.
Why is Interoperability Important in Healthcare?
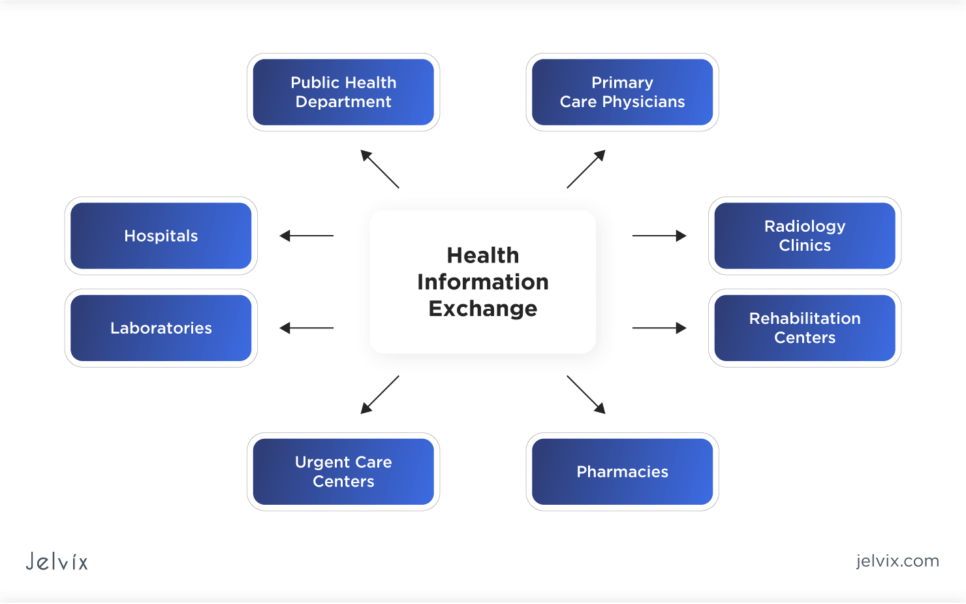
Interoperability in healthcare is straightforward in its ambition and yet complex in its execution. It’s about different systems — whether wearables on a patient’s wrist or advanced electronic health record (EHR) systems in major hospitals — talking to each other, sharing data, and making that data accessible to those who need it.
Imagine a scenario where healthcare data doesn’t just reside in isolated silos but moves with a patient-centered focus. A world where information flows without friction across different platforms, EHR systems, and software applications securely and instantly. That’s the essence of healthcare interoperability.
However, reality presents its own set of challenges. Building these bridges of communication between myriad touchpoints isn’t just about the technical aspects; it’s about streamlining protocols, fostering collaboration, and breaking down long-standing institutional barriers. While individual connections might be forged — say, between a patient monitor and an EHR system — the broader vision of total, holistic interoperability remains a work in progress for many.
Challenges to Achieving Interoperability in Healthcare
Achieving seamless integration and functionality in health systems is challenging, especially for entities still adapting to EHR or grappling with the nuances of HIPAA compliance. A survey from the Center for Connected Medicine reveals a disconnect: while there’s a growing momentum towards embracing interoperability, fewer than 40% of U.S. providers indicate they’ve effectively implemented systems that permit seamless health data sharing across organizations.
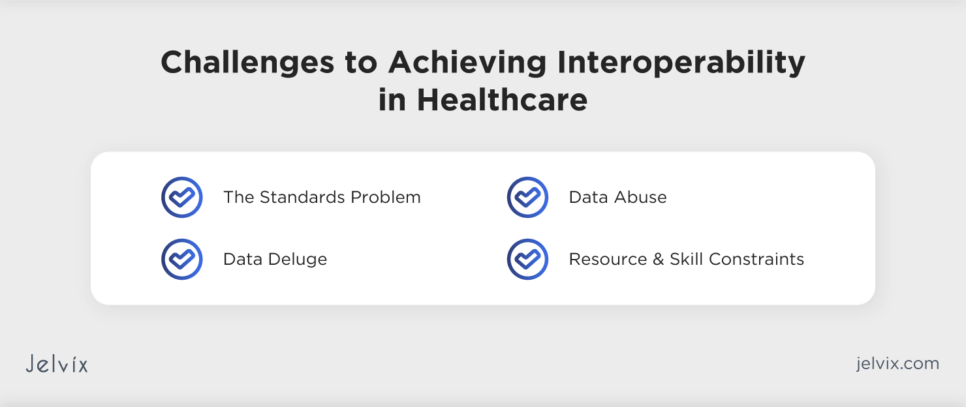
This dichotomy underscores the inherent challenges the sector grapples with. Let’s dive into some of the most pressing ones.
Challenge #1 — The Standards Problem
Certainly, the intent behind establishing standards in healthcare interoperability is to create a common ground for all players involved. However, when these standards increase, each embodying different methodologies and requirements, the outcome isn’t always as streamlined as hoped. Medical practices and hospitals face a labyrinth of protocols which, instead of simplifying processes, can sometimes complicate them further.
This is evident in the case of message formats, FHIR protocols, and EHR interoperability guidelines. The variability in these standards across different countries leads to a lack of uniformity, presenting a real challenge for healthcare providers trying to ensure consistent and secure data exchange. The disparate regulations often result in fragmented applications and can stand in the way of achieving true interoperability in the healthcare sector.
Challenge #2 — Data Deluge
Interoperability isn’t just about transferring data; it’s about efficiently managing an immense volume of information. The sheer quantum of information can be daunting, from EHR/EMR records to IoT-driven data and intricate hospital systems. To effectively manage this data surge, there’s a pressing need for robust data integration tools and analytics solutions tailored to the healthcare sector.
Challenge #3 — Data Abuse
The dark underbelly of the drive towards interoperability is the emergence of practices like information blocking. Some entities see this as an opportunity for monetization, levying fees for access to critical health data. Another roadblock comes from insurance companies that often need to be more open about sharing health data. Ideally, a provider should be able to access comprehensive patient histories, including prior treatments, through claim records. Unfortunately, this remains a challenge due to the hesitancy of many insurers.
Challenge #4 — Resource and Skill Constraints
Interoperability isn’t just a technological shift; it’s a cultural one. Many healthcare entities, especially smaller clinics, face budgetary constraints that make the initial investment in interoperable systems daunting. And even when the financial aspect is addressed, there’s the human element. Proper training is paramount to ensure all stakeholders, from clinicians to administrative staff, are adept at leveraging the capabilities of these systems. This is not a short-term commitment but a sustained effort.
Let's check why choose healthcare IT services by Jelvix.
How to Achieve Interoperability in Healthcare with RPM
Interoperability in healthcare stands at the juncture where technology meets patient care. Different information systems, devices, and applications can connect, share, and seamlessly interpret data. But the million-dollar question remains: How do we ensure this in the complex world of healthcare? One promising avenue is Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM).
Understanding RPM: More Than Just Monitoring
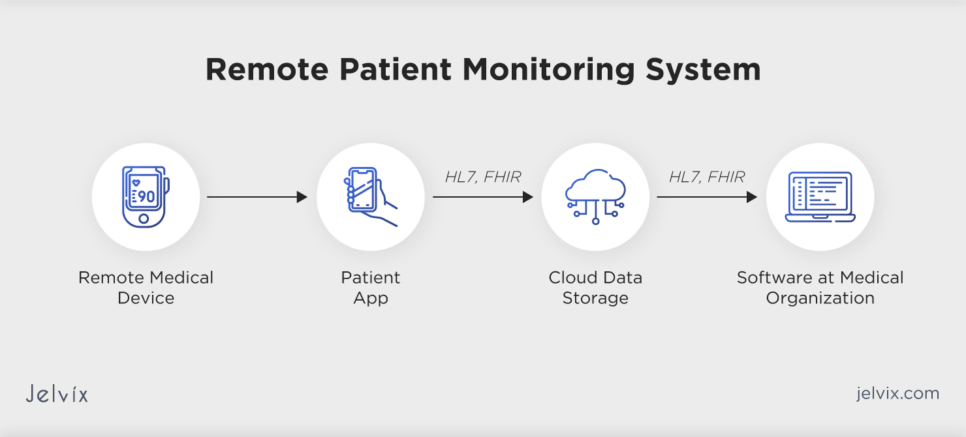
Remote Patient Monitoring is not merely about watching over patients from a distance. Its comprehensive system involves collecting, transmitting, and timely analyzing patient health data from various sources.
- Data Collection: At the heart of remote patient monitoring lies an array of devices – wearable tech, at-home equipment, and specialized tools. They’re not just passive devices; they’re proactive, ceaselessly gathering crucial health metrics. These instruments are the silent custodians of real-time patient health, from routine vital signs like heart rate and blood pressure to specialized measurements such as glucose or respiratory rates.
- Data Transmission: After gathering this wealth of information, the next challenge is conveying it. It’s a journey that demands both speed and security. Leveraging networks like cellular and Wi-Fi and even specialized health communication channels, the emphasis is on zero data loss. Every beat, breath, and blood sugar level must be relayed to healthcare professionals without compromise.
- Data Analysis and Intervention: Data, when left uninterpreted, loses its value. But it becomes a compass in the hands of healthcare professionals equipped with cutting-edge analytical platforms. By sifting through this data, they can identify deviations from the norm. It’s not just about detecting issues but taking proactive steps. Sometimes, it could mean tweaking a treatment plan; other times, it might necessitate a direct medical response. At each stage, robust security protocols are vital to protect sensitive health information, thereby upholding patient trust and maintaining the highest standards of care. Devices and Technologies Underpinning Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
A fusion of technologies has shaped the landscape of Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM), each bringing its weight to the overarching goal: improved patient care. A comprehensive look into remote patient monitoring devices examples and technologies is essential to understand their full potential.
1. Centralized Remote Monitoring Infrastructure
This IoT-based remote patient monitoring system architecture bridges the medical instruments capturing health metrics to the medical professionals overseeing patient care. It’s essential to note that the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) approves only specific wireless, non-intrusive instruments for remote patient oversight. This ensures that each instrument meets stringent criteria for safety, effectiveness, and cybersecurity. Among the devices that have received such approval are digital thermometers, electrocardiograms (ECGs), tools for cardiac assessment, monitors for respiration rate, audiometers, electroencephalograms (EEGs), and pulse oximeters.
2. Patient-Dedicated Mobile Application
This application interfaces directly with the patient, collating information from wearable tech and sensors. Once gathered, it then relays this information to medical practitioners. Given its role in dealing with sensitive medical data, this application must adhere to rigid standards: It must align with HIPAA guidelines, leverage BLE for device-to-device data transfer, and ensure secure integrations.
3. Digital Data Repository
This is essentially a cloud-based storage system that amasses the raw health metrics sourced from patient applications. However, not all systems mandate a separate storage space; certain configurations facilitate direct device-to-cloud transfer, negating the need for an exclusive patient application.
4. Medical Facility Web Application
In alignment with patient applications, medical applications also engage with electronic health data, thus necessitating compliance with HIPAA directives. Enhanced functionality demands that a hospital’s Electronic Medical Records (EMR) system synergizes seamlessly with the RPM platform, typically achieved using a FHIR-based API. Typically, applications tailored for medical facilities boast features like decision-making modules, data analysis, alerts, and comprehensive reporting.
5. Remote Patient Monitoring Devices
In health technology, we’ve witnessed an uptick in integrating smart, connected tools designed to measure a wide array of health indicators meticulously. This ranges from basic vital statistics, such as body temperature and blood pressure, to more intricate measures like the constituents of sweat. Once these measurements are taken, they are swiftly transmitted to a cloud-based server dedicated to remote patient monitoring, ensuring patients are observed in real-time.
To put it simply, building an all-encompassing remote patient monitoring system is multi-faceted. But when done effectively, it amalgamates tech with healthcare, leading to superior patient care results.
Key RPM Features to Consider
By incorporating the right features, you can set the stage for a platform that stands out in the rapidly evolving healthcare tech landscape. Based on our experience in developing telehealth remote patient monitoring solutions, we see the point of adding the following functions:
This table presents a broad array of features that can be integrated into an RPM system, ranging from fundamental functionalities to specialized features catering to niche requirements.
Steps to Integrate a Remote Patient Monitoring System in Your Operations
Here’s a straightforward guide on the steps you can adopt to incorporate RPM software within your operational structure seamlessly:
Put Data Safety First
Complying with HIPAA is essential, but as someone dealing with electronic health records, the onus of any data breach falls on you. To ensure thorough data protection, consider the following measures:
- Data Encryption: All transmitted data should be encrypted to prevent unauthorized access;
- Restrict Data Accessibility: Access to patient data should be reserved solely for certified medical professionals;
- Robust User Verification: Strong passwords and multi-factor authentication are highly recommendable to adopt;
- Regular Data Backup: Duplicating the patient’s information to a cloud lessens the chances of data loss due to unexpected system glitches;
- Regular Risk Assessments: Consistently evaluating your system helps to identify and address potential vulnerabilities;
- Data Retention Protocols: Proper strategies for storing and disposing patient information ensure compliance;
- System Updates: Regular updates of RPM systems aid in counteracting emerging security threats.
Ensure all internal processes align with HIPAA prerequisites before RPM integration.
Align with Local and Global Regulations
Digital healthcare regulations differ from one region to another. For domestic operations, adhere to local standards. For global functionalities, familiarize yourself with international stipulations.
For the US, the regulations conclude:
- HIPAA: Focuses on the privacy and security of health information;
- FDA: Regulates certain RPM devices for safety and efficacy;
- FCC: Manages wireless communication technologies in RPM tools;
- CMS: Dictates Medicare and Medicaid reimbursable RPM solutions;
- State-Specific Laws: Some states have extra regulations for telemedicine and RPM.
For the EU, these comprise:
- GDPR: Manages personal data protection.
- MDR & IVDR: Supervises medical and in vitro diagnostic devices.
- Directive 93/42/EEC: Sets safety standards for medical equipment.
- ePrivacy Regulation: Protects electronic communication data
Emphasize Interoperability
Seamless communication across your healthcare systems is crucial. To ensure compliance with healthcare interoperability regulations:
- Identify applicable interoperability standards;
- Review current systems for inconsistencies;
- Design a comprehensive interoperability strategy;
- Align your plans with the necessary functionalities;
- Facilitate data exchange within and beyond your RPM system;
- Implement standards such as HL7 FHIR;
- Ensure data adheres to standard terminologies;
- Establish consent management processes;
- Incorporate auditing and testing tools.
Clearly Define Your Requirements
Before venturing into RPM integration, clarify your expectations from the software. Understand the challenges it will address and its ultimate value proposition. This clarity will enable smoother adjustments to your current business processes and facilitate initial discussions with technology partners.
Structure Development and Integration
Consider a phased approach when integrating RPM into your business. Determine the sequence of incorporation — what modules to integrate first, next, and so on. This structured method ensures a smoother transition and minimizes disruptions.
RPM platform development is more than just creating a piece of software, it’s about reshaping healthcare dynamics. This process and the features you incorporate can make or break the success of the platform.
Here’s a concise guide on how we approach the development of an IoT-based system for remote patient monitoring, ensuring it is effective but also resonates with its end-users.
Case Study of Telehealth Solution with RPM Module
We, at Jelvix, recently collaborated with a top US clinic, improving life for people with disabilities, to revolutionize how healthcare is delivered. This clinic, committed to overcoming accessibility barriers, sought to create a state-of-the-art remote care model. Their goal was clear: provide extensive healthcare to patients with mobility challenges without them needing to visit the clinic frequently.
Our mission was to make this innovative idea of a patient remote monitoring system a reality. We developed a custom telehealth solution, deeply integrated with medical IoT, featuring a sophisticated remote monitoring system. This technology empowers patients to monitor their vital signs and relay this information to their doctors. In our blog article, you can read about the difference between telehealth vs virtual health solutions.
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) System Development Process
Throughout the project, we worked hand-in-hand with the client, moving together through pivotal stages to achieve the desired results. These crucial steps included:
- Discovery Phase: During the discovery phase, we partnered with the client to understand their vision and needs, shaping prototypes that matched their goals. Next, in the business analysis, we pinpointed essential features to shape a telemedicine solution that met the client’s precise objectives.
- Initial Design: This step centered on molding the overall structure and designing an easy-to-navigate user interface for the telemedicine platform. We poured our energy into devising an approachable, simple-to-use interface, keeping in mind those who might be less tech-savvy or have mobility issues.
- Estimation and Road Mapping: With transparency in mind, we laid out a thorough development plan for the client, complete with timeframes, necessary resources, and projected expenses. This roadmap aimed to give our client a comprehensive view, assisting them in making well-informed choices.
- Software Development: Diving into the development phase, we adopted a cyclical, bi-weekly approach. Prioritizing efficiency and excellence, our team rolled out progressive versions of the solution within a quarter of a year. Throughout this journey, we kept the communication lines open with the client, adjusting based on their insights and evolving requirements.
- Rigorous Testing: In the testing stage, our focus shifts to meticulously scrutinizing every aspect of the telemedicine platform. Stringent tests are conducted to ensure that both the functionality and the integrated wearable technologies perform flawlessly. We emulate real-world scenarios, verifying that the system is not only robust but also intuitively aligns with user expectations.
- Wearable Tech Integration: During software development, we seamlessly connected the telemedicine platform with various wearable gadgets. This integration allowed users to effortlessly monitor vital stats and relay this information to their healthcare professionals, boosting the efficiency of remote health monitoring and promoting data-driven care decisions. We require thorough documentation and usage guidelines to understand the full scope of the device’s capabilities and any potential limitations.
In essence, this collaboration was about building a telehealth solution that mixed technological innovation with genuine patient-centric care, and we achieved that in spades.
Estimating the Cost of Developing Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) Software
The cost dynamics for developing remote patient monitoring tools span a wide range, driven by multiple factors. These include the depth of features desired, software complexity, the skill set and locale of the development team, compliance with medical regulations, and the set project timelines.
Industry insiders suggest that RPM system cost is largely dependent on the scope and sophistication of the features involved. However, this pricing bracket is merely indicative. The actual outlay will predominantly depend on the distinct requirements and objectives of each project.
For a detailed financial assessment of product development, Jelvix offers expert consultation. Our in-house business strategists, in tandem with technical experts, provide a meticulous cost analysis, aiding you in prioritizing essential features.
In conclusion, while the initial investment might seem substantial, the potential for improved patient outcomes, streamlined healthcare processes, and long-term cost savings can make RPM software development a sound investment for healthcare providers.
Achieving Interoperability in Healthcare with Jelvix
Dealing with interoperability can be quite a headache, but with our expertise, we can simplify this process. Our commitment lies in optimizing the productivity of medical teams and enriching patient experiences, recognizing the specific needs of small to medium clinics.
We regard healthcare interoperability as essential for improving care standards. Be it software for remote monitoring, hospital management systems, or feature-rich telehealth solutions, our emphasis is on seamless integration. Our designs will align with your existing infrastructure, facilitating effortless data sharing. We keep up with the latest standards like FHIR so your software functions seamlessly and meets all the compliance checkboxes. Thinking of taking your healthcare system’s interoperability up a notch? We’re just a call away.
Leverage RPM to Improve Your Patient Outcomes
We are ready to develop an efficient remote patient monitoring solution for your healthcare organization.