Take a quick look at your phone—how many health apps do you see? Maybe you have one that tracks your daily steps, another that reminds you to drink water, or even one that logs your workouts. Now imagine these apps doing even more: managing chronic conditions, scheduling doctor appointments, or offering real-time advice based on your data. This is the world of mobile health app development.
So, what is mHealth? This term covers all sorts of mobile delivery of health services and data capture using devices such as smartphones, tablets, and smartwatches. It’s an integral component of eHealth, which leverages technology to improve the provision of health care.
These apps collect clinical data, transmit health information to physicians, monitor real-time vitals, and connect patients to care using telemedicine. The mHealth also reinforces its role in medical staff training and sharing of medical expertise. It’s a technology-enabled approach to making health care smarter, faster, and more accessible.
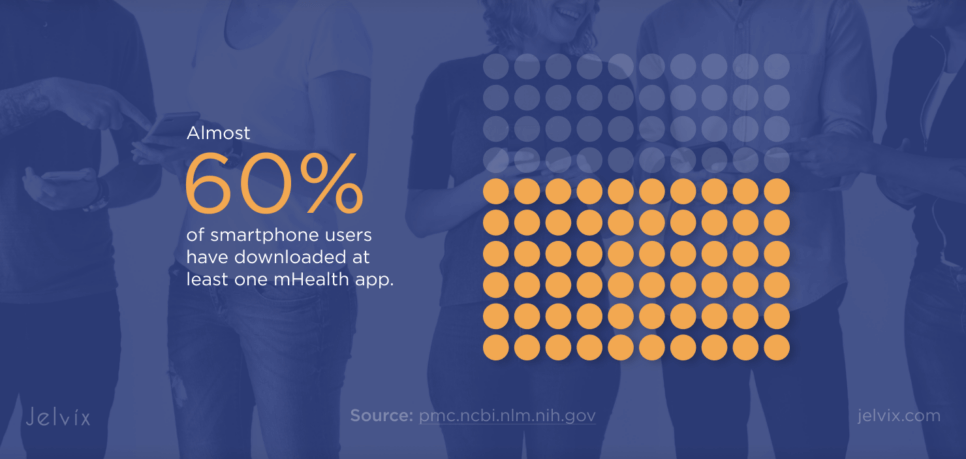
The numbers wring out a powerful story. The most recent figures suggest that the market value of global mHealth apps was $32.42 billion in 2023 and is projected to compound annually at a growth rate of 14.9% between 2024 and 2030. More than 350,000 mHealth apps are available in app stores worldwide and range from applications that help patients control chronic diseases to those that help them achieve fitness goals. Even more remarkable, almost 60% of smartphone users have downloaded at least one mHealth app, and these tools have embedded themselves in many aspects of our lives.
Why are mobile health apps so popular? For one, chronic health problems like diabetes and heart disease are on the rise, making tools like these more essential than ever. Couple that with the move toward digital solutions—online consultations, instant monitoring, and AI-generated health advice—and the reason for the demand’s explosion becomes clear. In this article, we’re delving deeper into mobile health apps, discovering their benefits, features, and leading innovations and what makes them a must-have for modern healthcare.
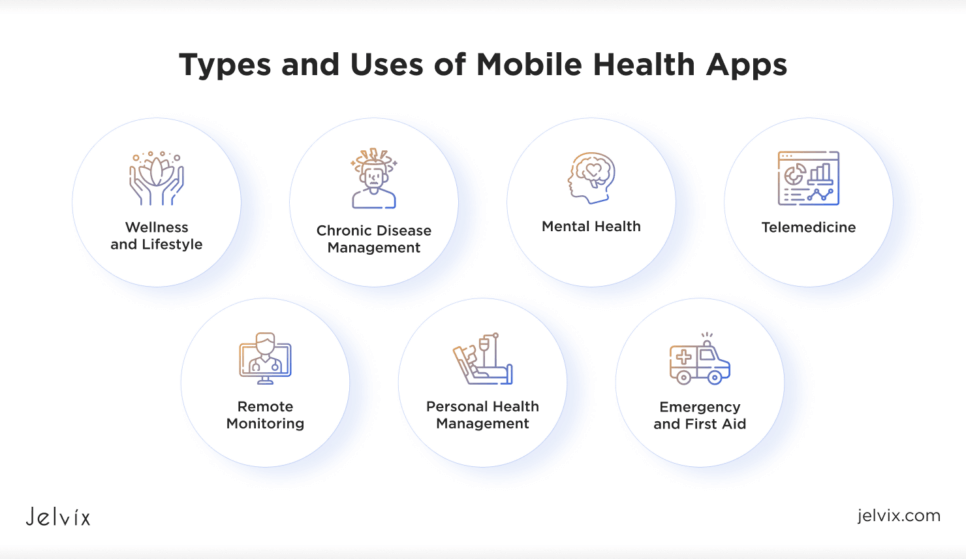
Types and Uses of Mobile Health Apps
Mobile health applications, used by end-users and healthcare providers take many forms and fill many needs. Whether they help individuals stay fit or give doctors the tools to monitor their patients remotely, these tools change healthcare in the most practical ways. Let’s decompose the primary categories of mHealth apps and look at how they make a strong impact.
Wellness and Lifestyle Apps
These apps help users maintain healthier habits and improve their overall well-being:
- Fitness and Exercise: Log workouts, track activity, and monitor goals.
- Diet and Nutrition: Aid with meal planning, calorie counting, and food consumption tracking.
- Sleep Tracking: Analyze sleep patterns, identify disturbances, and provide tips to improve them.
- Meditation and Mindfulness: Include guided meditations and exercises for stress relief.
- Women’s Health: Track menstrual cycles, fertility, and pregnancy milestones.
- Smoking Cessation and Substance Abuse: Offer tools and resources to quit smoking and manage dependencies.
Chronic Disease Management Apps
These tools help users manage ongoing health conditions:
- Diabetes Management: Track glucose levels, insulin doses, and carbohydrate intake.
- Heart Disease: Monitor blood pressure and heart rate while offering lifestyle tips.
- Asthma and Respiratory: Manage symptoms and medications and track air quality.
- Cancer Care: Organize treatment schedules and side effect management.
- Arthritis and Pain Management: Log pain levels, provide therapy exercises, and send medication reminders.
Mental Health Apps
Bringing mental health support closer to users:
- Stress and Anxiety Relief: Include relaxation techniques and mood tracking.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Help identify and adjust negative thought patterns.
- Teletherapy: Connect users to licensed therapists for online counseling.
Telemedicine Apps
Facilitate remote healthcare access:
- Virtual Doctor Visits: Provide video consultations for non-urgent issues.
- Symptom Checkers: Use AI to suggest possible diagnoses.
- Medication Delivery: Enable prescription orders and doorstep delivery.
Remote Monitoring Apps
Ensure continuous care through real-time data sharing:
- Wearable Integration: Sync with fitness devices to track health metrics.
- Home Monitoring: Help caregivers track the health and safety of elderly patients.
Personal Health Management Apps
Streamline healthcare routines:
- Medical Records Management: Store and share personal health records easily.
- Appointment Scheduling: Send reminders for appointments and medications.
Emergency and First Aid Apps
Provide immediate guidance and assistance:
- First Aid: Offer step-by-step instructions for emergencies.
- Location-Based Emergency Services: Connect users with nearby emergency resources.
Mobile health apps are as diverse as the challenges they aim to solve. Whether they promote better sleep, support chronic disease management, or enable telemedicine, there’s a tool for almost every healthcare need. In addition to catering to different needs, mobile health solutions have many other benefits.
Benefits of mHealth App Development
mHealth app development greatly benefits all parties involved in the healthcare system, including improved care accessibility and workflow optimization. Let’s examine these applications’ primary advantages for businesses, providers, and patients.
For Patients
- Convenience and Accessibility. The days of waiting rooms for every little thing are over. mHealth apps make doctors available on the screen, allow people to track medications, and even generate alerts for routine check-ups. They’re a lifeline for those in rural areas or people with chronic conditions.
- Personalized Care. These apps don’t just serve generic advice. They provide personalized insights through wearables and real-time data. From blood sugar management to heart rate monitoring, mHealth tools help patients stay informed and in control.
- Empowerment Through Data. Individuals are in the driver’s seat when their medical records and health stats are just a click away. This enables patients to make informed choices and collaborate more effectively with their doctors, improving outcomes.
For Healthcare Providers
- Streamlined Workflows. mHealth apps automate scheduling or data entry, allowing providers to spend less time on administrative tasks.
- Remote Monitoring and Early Intervention. Apps that allow doctors to monitor patients remotely can detect problems before they become emergencies. For example, a heart monitor app could alert a doctor when a patient’s heart is beating irregularly. This type of preemptive action can save lives and limit hospital visits.
- Enhanced Patient Engagement. Interactive care plans and telemedicine features keep providers connected to their patients, effectively building patient trust and keeping patients on treatment.
For Businesses
- New Growth Avenues. The booming mHealth market offers limitless business opportunities. Whether focused on fitness-conscious consumers or chronic-care tools, the demand for precision solutions is increasing.
- Reduce Costs, Improve Service. Digitizing processes such as appointments, billing, and follow-ups reduces costs while enhancing user experience. Businesses need not incur the overhead of traditional infrastructure to deliver excellent care.
- Data Drives Innovation. Aggregated data from apps can reveal trends and potential. Companies can leverage these insights to enhance existing products, create new services, and understand customers’ wants.
At its core, mHealth is making healthcare simpler, faster, and more effective for everyone involved. Whether it’s helping patients stay healthy, giving doctors better tools, or opening up new business opportunities, the advantages of mobile health technology are clear—and they’re only growing.
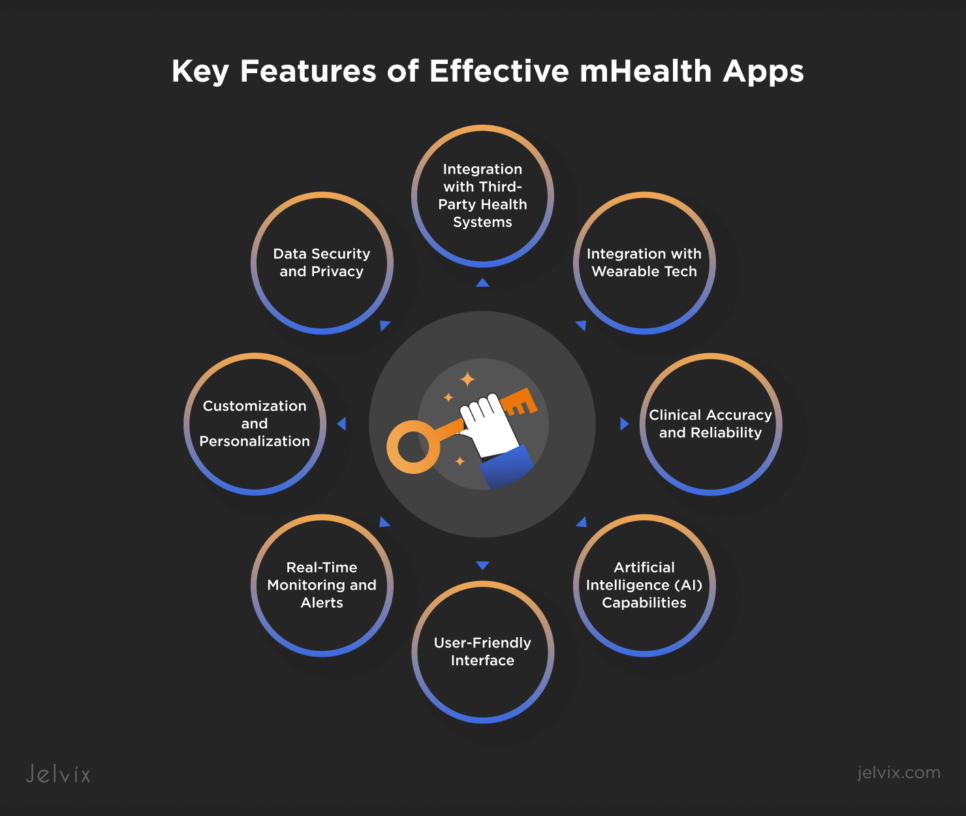
Key Features of Effective mHealth Apps
What would make a mobile health app effective? It’s not all about having the latest technology but making sure it is practical, secure, and of value to users and healthcare providers alike. These are the essential features of a successful mHealth app:
- User-Friendly Interface. A successful app should be intuitive and cater to tech audiences of varying skill levels. A simple, clear design that is super easy to navigate means users stay engaged and easily find the needed features, improving both use rates and outcomes.
- Data Security and Privacy. Strong data protection is non-negotiable, given that sensitive health information is at stake. It includes encryption, user authentication, and compliance with healthcare regulations such as HIPAA or GDPR. This enhances user trust and protects their information from data breaches.
- Integration with Wearable Tech. Wearables (fitness trackers, smartwatches) broaden the app’s functionalities thanks to instant health data: heart rate, activity levels, glucose readings, etc. Also, seamless integration enables users to track their health continuously and share data with healthcare providers for more effective care delivery.
- Customization and Personalization. Apps that can tailor individual settings (e.g., setting personal health goals, customizing notifications, adjusting privacy controls) also increase user satisfaction.
- Clinical Accuracy and Reliability. No mHealth application can afford to provide wrong information. Particularly, symptom checkers, treatment trackers, and health tips must be validated by professionals so that they are not harmful and are reliable.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts. Apps with built-in real-time monitoring can track important metrics like heart rate or blood sugar and send alerts to users or their healthcare providers when needed. This minimizes the need for regular in-office visits and provides early recognition when a problem occurs.
- Integration with Third-Party Health Systems. EHRs and other health systems should be synchronized with mHealth apps to ensure seamless care. This allows users and providers to access up-to-date medical information across platforms, ensuring consistency in care.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Capabilities. AI-powered features enhance the user experience with personalized recommendations, symptom tracking, and even virtual coaching. These intelligent tools improve engagement and outcomes by tailoring health plans to individual needs
From making usability easier to guaranteeing security and accuracy, each characteristic meets a fundamental demand in the healthcare industry. Users and the larger healthcare ecosystem benefit greatly from mHealth apps that incorporate these components, as most of the best healthcare apps do.
Top 10 Revolutionary mHealth Apps
MyFitnessPal
What’s the app for?
MyFitnessPal is your meal-tracking and goal-setting companion. Whether you’d like to count calories, track nutrients, or record workouts, this app makes it easy and helps you stay accountable.
Useful Features:
- Food diary;
- Barcode scanner for easy tracking;
- Exercise and activity monitoring;
- Personalized meal plans;
- Water and macro tracking.
Who might be interested?
MyFitnessPal is an invaluable resource for anyone trying to lose weight, improve the quality of their diet, or track their macros. It can also serve as an excellent tool for establishing long-term habits. Gym enthusiasts and health-conscious beginners will find it helpful.
Headspace
What’s the app for?
Headspace’s primary aim is to improve mental health through meditation and mindfulness, and it has proven successful. Guided programs and exercises help address stress, improve concentration, and build healthier habits.
Useful Features:
- Guided meditation sessions;
- Mindful breathing exercises;
- Sleep and relaxation tools;
- Progress tracking;
- Courses for managing stress and anxiety.
Who might be interested?
This app is perfect for busy professionals, students, or anyone looking to add a touch of calm to their daily routine. It’s ideal for those new to meditation or seeking a structured approach to mindfulness.
Fitbit
What’s the app for?
Fitbit goes beyond just a fitness tracker; it is a whole health monitoring system that aids its users in being active enough, tracking their sleep, and monitoring heart health.
Useful Features:
- Activity and sleep tracking;
- Heart rate monitoring;
- Calorie burn calculator;
- Personalized fitness plans;
- Smartphone notifications.
Who might be interested?
Fitbit is perfect for active people, fitness novices, and anyone wanting scientific health information. It’s also beneficial for those who need to monitor heart health or achieve long-term fitness goals.
mySugr
What’s the app for?
mySugr simplifies diabetes management by providing an easy way to track blood sugar levels, insulin doses, and carb intake—all in one place.
Useful Features:
- Personalized logging;
- Blood glucose graphs;
- Bolus calculator for insulin doses;
- Integration with glucose meters;
- Motivating challenges.
Who might be interested?
This application is suitable for diabetics who need an easy, paperless way to track their health. It can also be helpful to caregivers or healthcare providers who support people with diabetes.
Talkspace
What’s the app for?
Talkspace provides users access to licensed therapists who conduct online therapy sessions, a convenient approach to resolving issues related to mental health from almost anywhere.
Useful Features:
- Virtual therapy sessions;
- Text, voice, and video communication;
- Licensed therapists across specialties;
- Privacy and confidentiality tools.
Who might be interested?
This app is perfect for those seeking professional mental health support without the hassle of traditional appointments. It is convenient for those who have to cope with anxiety, depression, or relationship issues.
UpToDate
What’s the app for?
UpToDate provides healthcare professionals with evidence-based resources for making informed clinical decisions quickly.
Useful Features:
- Clinical guidelines and pathways;
- Disease and drug reference tools;
- Patient education materials;
- Medical calculators.
Who might be interested?
Healthcare providers, medical students, and researchers will find UpToDate invaluable for quick, reliable answers to complex clinical questions.
ZocDoc
What’s the app for?
ZocDoc simplifies booking medical appointments by connecting users with healthcare providers based on availability and reviews.
Useful Features:
- Real-time doctor availability;
- Patient reviews and ratings;
- Appointment reminders;
- Insurance compatibility check.
Who might be interested?
Busy professionals, parents, and anyone needing quick access to healthcare services will appreciate ZocDoc’s convenience.
Ada Health
What’s the app for?
Ada Health helps users assess symptoms and provides personalized recommendations for managing their health or seeking professional care.
Useful Features:
- Symptom checker;
- Health insights and reports;
- Personalized health advice;
- Integration with health records.
Who might be interested?
This app is great for individuals who want to understand their health better or need guidance on whether to see a doctor.
BetterHelp
What’s the app for?
BetterHelp provides online counseling with licensed therapists, making therapy more accessible and flexible for users worldwide.
Useful Features:
- Secure Messaging;
- Video and phone therapy sessions;
- Licensed therapists for various mental health issues;
- Flexible scheduling.
Who might be interested?
Individuals seeking confidential, convenient mental health support for issues like stress, anxiety, or relationships will benefit from BetterHelp.
Medisafe
What’s the app for?
Medisafe helps users manage their medications by sending reminders and tracking doses, ensuring adherence to treatment plans.
Useful Features:
- Medication reminders;
- Caregiver support;
- Reports on adherence trends;
- Integration with wearable devices.
Who might be interested?
This app is perfect for individuals managing multiple medications or caregivers helping loved ones stay consistent with their treatments.
How To Build a Mobile Health App: Step-by-Step Guide
A mobile health application is more than just written code; it addresses important healthcare issues through accessible, safe, and scalable solutions. A plan-deploy cycle where each phase is designed carefully to meet users’ expectations, regulatory requirements, and standards of technical excellence will be in order. Here is the way to start.
Planning and Research
Every mHealth app triumph begins with thorough research and an unmistakable plan.
- Define the Problem and Target Audience: Identify the healthcare problem your app will solve. Are you targeting patients managing chronic diseases, fitness enthusiasts, or healthcare providers needing better workflow tools?
- Do Competitive Analysis: Look for competing healthcare apps and determine where your app fits. Identify gaps in features, usability issues, or unmet user needs. You may find a niche that needs filling.
- Establish Goals and Requirements: Clash with a comprehensive development roadmap. Include core app functions (symptom tracking, teleconsultations), nonfunctional needs like security regulations in other areas of healthcare, such as HIPAA or GDPR, and protocols for encryption.
- The Right Tech Stack: Finally, what programming languages or frameworks should you use? Swift or Kotlin are used for native development, and React Native is used for cross-platform approaches.
Design and Development
After you come up with an idea, it’s time to turn concepts into prototypes and features that work:
- Wireframes and UX/UI Design: Fire up your wireframes to sketch the application’s layout and how users flow through it. Create a user-friendly interface with logical progressions—intuitive navigation, accessible design, etc. Tools like Figma or Adobe XD can help refine the design process.
- Front-End Development: Build the user-facing side of the app, ensuring responsiveness and smooth interactions. Employ Flutter or Angular to guarantee seamlessness across devices.
- Back-end Development: Establish the app’s server, database, and APIs for secure data storage and transmission. Process complex healthcare data using solid backend languages like Node.js, Python (Django), or Java (Spring Boot).
- Functionality Integration: Incorporate essential features like real-time monitoring, wearable device coordination, appointment scheduling, and secure messaging. Use APIs and SDKs (e.g., Apple HealthKit, Google Fit) for third-party devices and platform interoperability.
Testing and Deployment
Numerous tests must be run on an application designed for healthcare to ensure its reliability and meet industry standards.
- Functional Testing: Test each feature to ensure it works properly. For example, simulate user interactions such as monitoring vital signs or arranging appointments to pinpoint and fix bugs.
- Performance Testing: Test the app’s responsiveness and load time under different conditions. Use tools like Apache JMeter or Appium to see if it is scalable, stable, and working well.
- Security Testing: Ensure all applications pass regulation testing for health care, including encrypting data, using secure API connections, and properly handling user authentication. Close loopholes to keep data safe.
- Usability Testing: When designing an interface, allow real users—both patients and consultants—to give feedback and make adjustments. Then, proceed with the design based on their comments.
- Deploy and Monitor: After your software passes all the tests, launch it in outlets like the Apple App Store or Google Play. Observe for sudden changes in user behavior, track your performance in metrics so you can troubleshoot any problems that arise, and offer additional functions to improve the total User Experience gradually.
When developing a mobile health app, technical know-how, familiarity with the healthcare sector, and a user-first approach are necessary. By adhering to a methodical strategy, you can develop a solution that satisfies user needs and distinguishes itself in the crowded mHealth market.
Discover how we created a custom physical therapy app that enhances communication between therapists and patients, making it easy to share exercise videos and track progress on any device.
Investing in a Mobile Health App
The numbers do not lie. By 2030, the global mHealth market will be worth over $100 billion. This growth is fueled by increasing smartphone adoption, widespread internet connectivity, and a shift toward preventive and personalized healthcare.
However, beyond the figures, mHealth apps also face many urgent healthcare difficulties. They bridge the gap in the accessibility of medical services, and by remote monitoring, they keep hospital readmissions down; they give patients the power to manage their health effectively. For businesses, the apps offer new revenue streams, chances for innovation, and opportunities to create value in a space that is not yet fully developed but is growing rapidly.
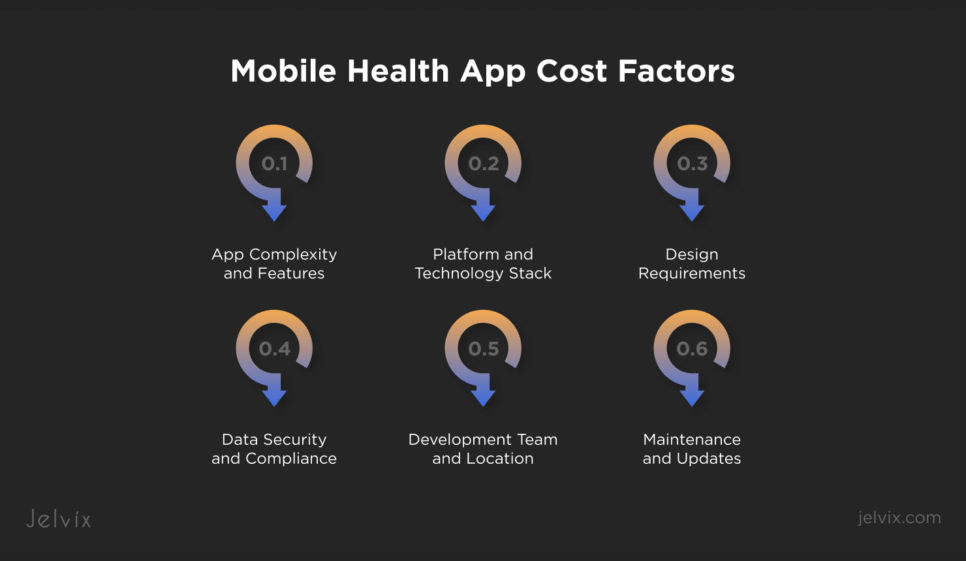
Many variables are involved in developing a healthcare app, ranging from complexity to design requirements. A typical mobile health app can cost anywhere from $30,000 to $300,000, depending on the app’s scope and features:
- App Complexity and Features: Basic apps with limited features, like appointment reminders, fall on the lower end of the cost spectrum. Apps that offer features like real-time monitoring, an AI-driven symptom checker, or integration with wearables are more expensive due to the longer development time and resource allocation.
- Platform and Technology Stack: Native application development for iOS or Android costs much less than developing an application using cross-platform frameworks. Technologies such as AI, blockchain, and IoT devices will raise development costs, but they add significantly to the overall value of your project.
- Design Requirements: A user-friendly, intuitive interface requires skilled designers and extensive testing. Custom designs and animations may increase costs but improve engagement and retention.
- Data Security and Compliance: Enhanced security measures like encryption, secure APIs, and compliance frameworks, which increased costs. However, these measures are necessary to protect sensitive health data from prying eyes.
- Development Team and Location: Hiring an experienced development team in North America or Western Europe cost more than outsourcing to regions like Eastern Europe or Asia
- Maintenance and Updates: After the launch, additional costs can include server maintenance, bug fixes, feature updates, and support (for users). Typically, this adds on about 15-20% of the original development costs annually.
So, with all the nuances, is it worth the investment? Absolutely. With proper planning, a well-executed mHealth app can provide long-term value. It reduces the cost of treating patients, improves their health outcomes, and establishes your company as an innovative player in this fast-growing market. The trick is to understand the user requirements, develop a scalable and regulatory-compliant solution, and stay agile in the industry’s changing trends.
Challenges in mHealth Development
One of the biggest challenges in mHealth development is complying with regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, or FHIR, which uphold user data protection and privacy. Yet these constraints are complex and constantly changing, meaning developers must design applications with compliance in mind from day one.
To avoid breaking those rules, the integration of secure data storage, encrypted communication, and access control points should be addressed in the early design stages. At best, working with legal experts or employing developers familiar with healthcare regulations ensures that your app will meet standards without limiting its functionality. In addition to regular monitoring and updating procedures (as necessary), ensure that the software conforms to law changes.
With mHealth apps handling highly sensitive user information, data security is another critical concern. A cyberattack, data leak, or security breach can destroy user trust and bring heavy penalties. Balancing strong security measures with user-friendly design adds more complexity.
End-to-end encryption, multi-factor authentication, and secure APIs are all viable ways to protect user data. Conduct regular vulnerability testing, such as penetration and code reviews, to identify and fix potential weaknesses. Design simple, intuitive authentication flows to ensure a seamless user experience.
Developing an m-health application involves complex technology, from real-time data aggregation and the interoperability of wearable devices to ensuring smooth functionality across multiple platforms. These advanced features require skilled developers and significant financial investment, especially for startups or smaller businesses.
To reduce costs, start with an MVP (Minimum Viable Product) that concentrates on the core features. Use open-source frameworks like React Native or Flutter to build cross-platform apps efficiently. Collaborate with experienced development teams to develop scalable solutions. Maintain a clear roadmap for future updates. Cloud-based infrastructure also slashes operational costs and enhances scalability.
By carefully addressing these concerns, developers can create mHealth applications that are secure, compliant, easy to use, and versatile. With the right approach, these applications can overcome obstacles and greatly influence healthcare.
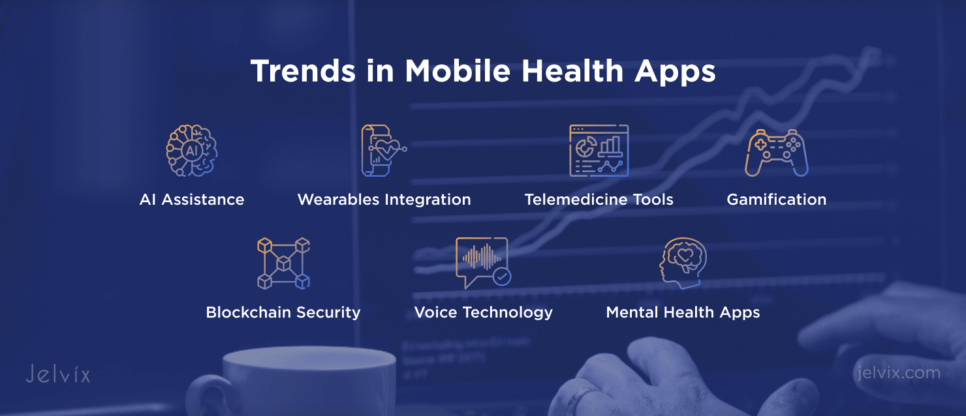
Trends in Mobile Health Apps
Smart technologies are continually emerging and driving the Mobile Health force, providing solutions that are more convenient. Here are some development trends that will shape the future of applications for mHealth:
- AI uses the experience to help people by giving practical exercise guidance, taking charge of their medicine regimen, or receiving a professional help to manage chronic disease through telemedicine. Features like virtual assistants and symptom checkers can significantly improve accuracy and allow timely interventions.
- Wearable devices like smartwatches and glucose monitors integrate with apps, enabling real-time tracking and automated data sharing with healthcare providers. IoT expands connectivity for seamless health monitoring.
- Telemedicine apps simplify access to care through video consultations and innovative tools, such as virtual reality (VR) for therapy and augmented reality (AR) for surgeries.
- Gamification in healthcare. Apps use challenges, rewards, and leaderboards to motivate users in fitness, therapy, and chronic disease management.
- Blockchain secures sensitive data with decentralized, tamper-proof storage, ensuring privacy and transparency for users.
- Voice technology simplifies and enhances symptom reporting, appointment scheduling, and medication tracking, making apps accessible to seniors and users with disabilities.
- AI chatbots, mood trackers, and VR therapy sessions make mental health apps more effective and accessible.
These trends push mHealth apps beyond their traditional limits and change healthcare into a more closely connected, secure, personalized experience. With advancements like AI personalization and blockchain security, mHealth tools are becoming suitable for every patient and health provider. Businesses that adopt them are not only keeping up but are setting new standards for how Healthcare service is accessed and managed.
Conclusion
To stay ahead regarding the future of mHealth means one thing: looking forward to embracing cutting-edge technologies and shifting our focus to user-centric solutions. Partner with Jelvix’s mobile app developers and leverage our expertise to bring your vision to life. We have years of production experience and are ready to help you create an app that meets industry demands and simultaneously exceeds user expectations! Together, let’s create a healthier tomorrow now.
FAQ
Can mHealth Apps Be Integrated with Wearable Devices?
Indeed, many mHealth applications are designed to work well with wearable technology, such as smartwatches and activity trackers. Through these interfaces, apps may gather health data in real-time, such as blood pressure, heart rate, and activity levels, giving users a more complete experience.
How Do mHealth Apps Improve Patient-Doctor Communication?
mHealth apps frequently include features like telemedicine, secure messaging, and appointment booking, facilitating communication between patients and medical professionals. Some apps also offer remote monitoring, which allows medical professionals to monitor patient’s progress and modify treatments as necessary.
How Are AI and Machine Learning Used in mHealth Apps?
AI and machine learning are increasingly used in mHealth apps for symptom analysis, predictive analytics, personalized health recommendations, and automated appointment scheduling features. These technologies improve patient outcomes and app functionality.
Can mHealth Apps Function Offline?
Some mHealth apps have offline capabilities for medication tracking or fitness logging, syncing data when the app reconnects to the internet. However, many mHealth apps depend on internet connectivity for real-time updates and communication.
How Do mHealth Apps Help in Chronic Disease Management?
Through symptom tracking, medication reminders, and lifestyle recommendations, mHealth apps help manage chronic illnesses. Numerous apps also make remote monitoring possible, enabling medical professionals to modify therapies in response to real-time data.
Need a qualified team of developers?
Reach new business objectives with the dedicated team of professionals.