Compliance and security – these two terms are often used together (sometimes even interchangeably) and may sound like a broken record for businesses. However, in the context of increasing numbers of data breaches, the safety and privacy of information are among the main concerns for businesses of any size.
According to Statista, the number of data breaches in 2022 reached 819 cases and affected over 58 million people in the US only. This quantity only stresses the importance of implementing data protection measures and following compliance regulations for businesses.
However, even though the lines between IT compliance and security may seem blurred for many business owners, these two are not the same thing. Understanding the differences between these notions is crucial for making important decisions related to company data protection.
In this article, we define both terms, outline the similarities and differences between compliance and security, and determine what’s more important for your organization.
What is Compliance in Information Technology?
IT compliance represents a range of activities maintained by an organization and geared towards following a set of regulatory standards and guidelines imposed by a third-party entity. As a rule, compliance standards encompass meeting industry regulations, government policies, security frameworks, and customer contractual terms.
In the current business environment, IT compliance is more important than ever before. The growing popularity of electronic data exchange and storage in the financial, retail, and healthcare sectors made it an obligatory condition for the proper management of business information.
IT security compliance standards define what kind of information it is and how it is gathered, stored, protected, accessed, and processed. Therefore, if an organization is compliant, it meets some level of information protection requirements. Yet, it is necessary to remember that compliance doesn’t replace security measures.
Experts differentiate internal and external compliance. Internal compliance is centered on the policies, regulations, and best practices set by the organization itself. On the other hand, external compliance presupposes following the guidelines set by legislative or industry organizations to protect the personal information of the customer or end-user.
From a business perspective, data security compliance brings the following benefits:
- It helps businesses avoid penalties and fines. Failing to conform to laws and regulations imposed by a third-party entity may lead an organization to severe penalties and fines.
- It helps to build a positive business reputation. Conforming compliance guidelines ensures that your brand uses sensitive customer information in the right way. It all results in a significantly higher degree of customer trust in your business.
- It improves data management in your company. By following compliance standards, companies gain the chance to reorganize their data management processes, audit the existing data systems, and get rid of information and files that, with time, have become irrelevant or of no value for their business.
Yet, achieving compliance may be a daunting task for an organization. Here are several challenges the businesses may face:
- Maintaining multiple compliance regulations may cause conflicts among the regulations themselves and the company’s policies and regulations.
- International presence forces the company to comply with the regulations of each country in which it operates.
- The business may lack financial and human resources to maintain IT security compliance.
Who’s Responsible for IT Compliance?
Ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and legal requirements is a complicated process, requiring the involvement of qualified staff to make it happen. Therefore, more and more companies these days hire third-party consultants or create a specific department to implement and maintain a consistent compliance strategy.
As a rule, a typical compliance department includes:
- Chief Compliance Officer (CCO). This person is responsible for the work of the compliance department. In addition, the CCO reports to the enterprise executives about all updates and issues concerning compliance activities and risks.
- The compliance department usually encompasses a team of compliance officers. They are responsible for developing and implementing the compliance program, overseeing and managing risks, coordinating reporting channels for compliance issues, organizing regular reviews and audits, and scheduling compliance training for employees.
- Chief Technology Officer (CTO) is responsible for all the aspects of the applied technology framework and infrastructure, including its compliance and security.
IT compliance & GRC
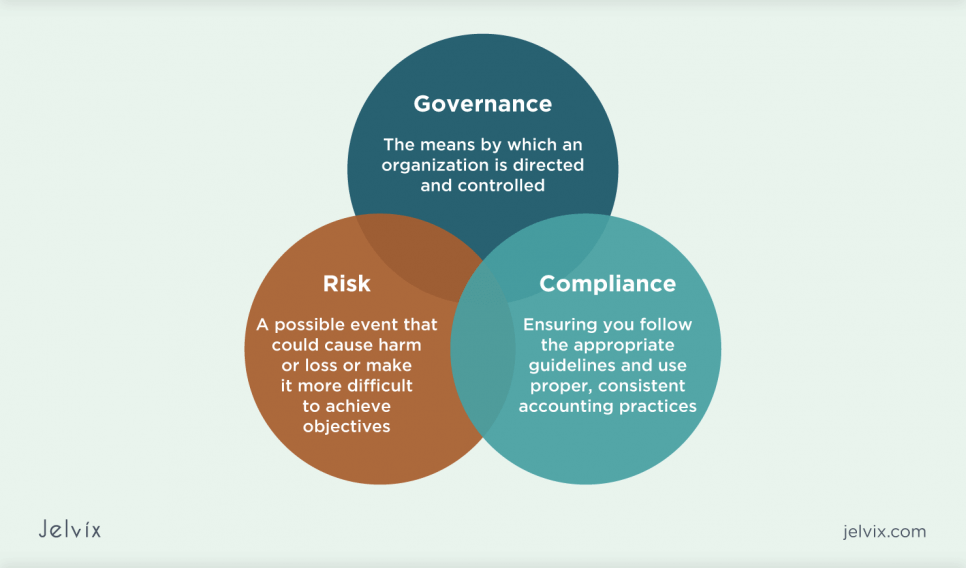
Compliance is only one of the levels of the greater strategy implied to help organizations manage risks, maintain internal governance, and follow the regulations. This strategy is summed up under the acronym “GRC,” which stands for:
- Governance – aimed at ensuring that the organization is directed and controlled in accordance with its business goals;
- Risk – geared towards identification, assessment, and addressing any possible risks which can harm the organization’s activities;
- Compliance – ensuring that an organization is following proper legal and regulatory guidelines.
Еxamples of Common IT Compliance Standards
The regulations and laws that a company should comply with usually depend on geographical location, industry, and other factors. In most cases, they may be subdivided into:
- Generally applicable guidelines apply to all businesses that operate in a certain jurisdiction, irrespective of the industry the businesses belong to.
- Sector-specific regulations apply to businesses belonging to a certain industry.
Some of the most common IT security compliance standards include:
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) is aimed at safeguarding the privacy and safety of customer information in the European Union;
- CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) controls how businesses collect and use the personal information of California residents;
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) represents an IT compliance standard regulating how medical organizations should safeguard patients’ sensitive information;
- SOX (Sarbanes-Oxley Act) is geared towards regulating the transparency and disclosure of financial data;
- PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) is a set of regulations created by credit card companies to protect customers’ credit card information;
- ISO 27000 Family is a set of standards for managing information safety created by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). The standards cover the issues connected to network security, risk management storage, cybersecurity, etc.
What is Security in Information Technology?
IT security (also referred to as information or data security) represents a set of policies, measures, and tools used by organizations to safeguard their business data. The main purpose of IT security procedures is to prevent unauthorized access, theft, misuse, or modification of business data.
Implementing security compliance measures yields a range of benefits for businesses, including:
- Increased productivity. Cyberthreats or computers infected with viruses can slow down and even stop work in the organization for a certain time. Efficient information protection measures accompanied by security training for employees allow enhancing data protection and ensuring that staff works with data in the right way.
- Boosts customer trust. In the digital age, confidentiality and protection of personal information are of core importance for customers. If your business proves to safeguard its customers’ information effectively, it will bring more trust to your company and make them more loyal to your brand.
- Protects your business from financial losses. The business reputation is not the only thing that is affected when the business is attacked. In fact, data breaches often lead to sales losses and paying fines claimed by regulators and customers.
As with any other process, implementing IT security measures may be challenging for companies that lack trained staff, have a limited budget, are deficient in appropriate tools to automate controls and audit their effectiveness.
Who’s Responsible for IT Security?
Everyone involved in business operations and deals with data is responsible for the safety of business information. Unfortunately, experience demonstrates that the biggest data safety risks are not hackers but employees. According to Stanford University research, nine out of ten (or 88%) data breaches result from employees’ errors.
To implement the best information protection practices, maintain a consistent level of risk awareness and security training among your employees, the company needs a team of information security professionals. Organizations usually either hire an in-house team of IT security officers or rely on third-party experts that offer security services and consultations.
As a rule, the IT security team consists of:
- Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) whose main responsibilities include creating and maintaining the organization’s security architecture, reporting to executives about the security status, real-time threats or issues, and coordinating the IT security department.
- IT security department usually comprises a team of information security officers (also known as information security analysts). They usually take care of real-time identification, analysis, and prevention of risks and threats, perform regular audits and ensure that staff receives regular security training.
Information Security vs Cybersecurity: What’s the Difference?
IT security and cybersecurity are so closely intertwined that most people think they are the same notion. Yet, there is still a small distinction between them.
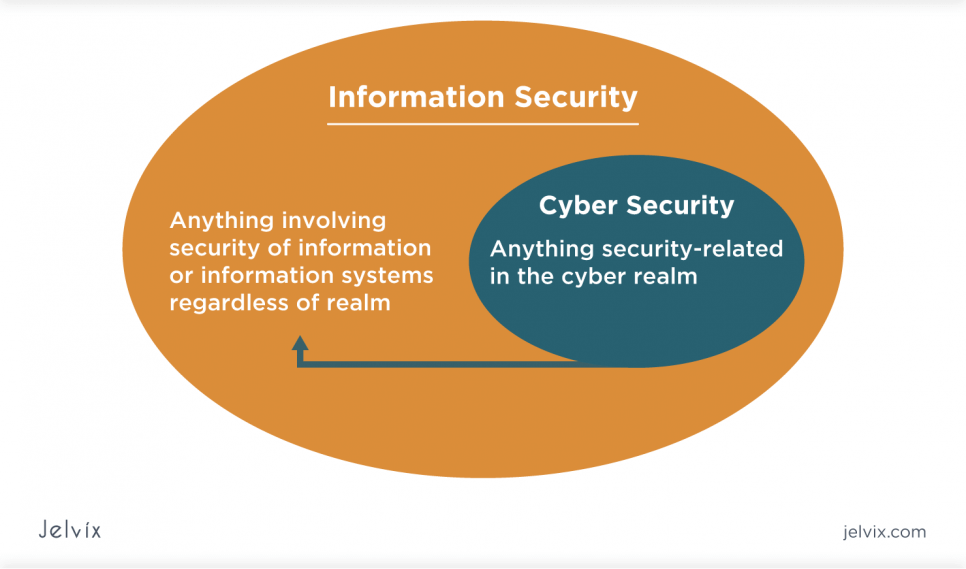
IT security encompasses a range of processes aimed at safeguarding an organization’s sensitive data and information systems from being accessed by unauthorized third parties. IT security is concerned with all types of data used by a company – be it electronic records or paper-based documents.
Cybersecurity, on the other hand, is centered on protecting the organization’s information from online threats. Since more and more companies adopt cloud computing technologies, networks, and servers, the risk of falling victim to malware, phishing, or other cyberattacks is also rising. Cybersecurity compliance allows businesses to protect their electronic data by implementing preventive technologies.
In practice, both processes are focused on keeping the information safe. However, cybersecurity is only a subset of the IT security strategy, as the latter covers all the data involved in business operations.
Learn more about role of AI and ML in CyberSecurity.
What IT Security Areas to Focus On
Successful information security compliance strategy usually implies controlling and safeguarding four main areas related to data storage and transfer: users, data, application, and network. Let’s take a look at each of them.
- User-Level Security aims to ensure that corporate information is accessed only by authorized users aware of the organization’s information protection policies.
- Data Security is focused on keeping sensitive information safe during processing, transition, and storage processes. This vector usually involves control over how the information is used by internal (executives, employees) and external users (business partners, customers).
- Application Security implies safeguarding software applications from intrusions. Among the best practices in this area, the experts differentiate the implementation of firewalls and encryption that ensure that unauthorized users won’t access the application.
- Network Security involves safeguarding an organization’s network infrastructure from unauthorized access, data theft, or other threats. Network security procedures refer to the use of hardware and software solutions that control network use and accessibility.
Examples of Common IT Security Measures
Information security compliance measures embrace techniques used to safeguard data, networks, and applications from malicious attacks. Among the best security practices identified by experts are:
- Data encryption. This procedure relies on encoding data stored on the servers and transmitted online in a way that it can be decoded only with a special key. In this way, businesses can protect their data from thefts, ransomware, and other cyberattacks.
- Firewall implementation. Browsing the internet without firewalls is not secure. The firewall is used to monitor and filter incoming and outgoing traffic on your network. By examining data packets based on previously set security rules, firewalls protect your data from viruses, malware, and hackers.
- Regular backups. A good backup strategy is the best measure against data loss and ransomware attacks. By performing a backup, you ensure that you can count on duplicated files if there’s a need to restore information.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA). The practice of setting up multi-factor authentication protects data from unauthorized access. This authentication method requires a user to pass two or more verification steps to gain access to the information stored in the application, device, or online account.
Comparing IT Security vs IT Compliance: Similarities and Differences
In certain lights, IT security and compliance represent the two procedures that overlap. As a rule, it may happen when compliance standards of the industry require a high level of information security. So, in what areas do these two overlap?
Some of the key similarities of IT compliance and IT security include:
- Both reduce a range of risks. Maintaining compliance and security practices in your company helps minimize the likelihood of data breaches, leaks, and losses that may harm your reputation and lead to severe penalties and fines.
- Both are important for building customer trust. Suppose it becomes public that the company is not compliant with industry guidelines or has suffered from a data breach. In that case, this company inevitably appears to be in the center of a PR catastrophe within a matter of hours.
Therefore, adopting compliance standards and security measures doesn’t only lessen the risks of facing cyberattacks. It also demonstrates to your customers that your company cares about their data privacy. It builds trust and confidence in your brand in the eyes of your clients.
Yet, in many cases, compliance strategies exist separately from security measures. Therefore, being compliant for a business under such circumstances does not guarantee that it is secure and protected from malicious actors and vice versa.
The key differences that separate IT compliance from IT security are:
- Different types of enforcement
IT security compliance standards and regulations are imposed by external organizations. They require a company to meet at least a minimum standard to pass the compliance audit.
IT security, on the contrary, is mostly an internal initiative. The security measures that a company can implement do not have any limits and may go far above the required minimum compliance standard.
- Different types of losses
Ignoring regulatory standards can lead to fines, penalties, and sanctions, which, in fact, can presuppose mainly financial losses. Failing to implement effective security measures may result, on the other hand, in both financial and data losses.
- Different nature of procedures
When compared with IT compliance, implementing IT security is a more evolving procedure. Once a business has reached the minimum compliance with regulations, there’s no necessity for change, except for the occasions when the compliance regulation is updated or modified.
In contrast, IT security needs are permanently evolving along with the emergence of new threats and attack strategies. Therefore, to keep the business information protected, the security department has to keep its fingers on the pulse and be aware of all new security risks, measures, and tools.
Compliance or Security – What’s More Important?
“Should we invest in security or compliance?” – this is one of the most common questions that business owners ask. Our answer is that companies should try to achieve both.
IT compliance and IT security are the two intertwined processes that go hand-in-hand. Failing to meet one of them creates a lot of serious risks for your company that may even destroy your business.
By concentrating solely on adhering to IT security compliance standards, you make your business vulnerable to cyberattacks and data loss. If the focus is only on security, you open your business to potential audit risks and penalties. Therefore, the best scenario is to implement both compliance and security in your IT infrastructure.
Final Thoughts
In modern reality, finding the balance of compliance and security is of core importance for protecting sensitive information. However, achieving compliance and security is a thorny mission full of tricky tasks. Both processes require establishing strong governance frameworks, choosing relevant policies and protective measures.
If your company needs strong IT compliance and IT security strategies and you don’t know where to start, Jelvix experts are always ready to help. Drop us a line to get a free consultation and map out your path to meeting compliance and security requirements.
Need a qualified team?
Access the talent pool to scale your team capacity.