You’d be surprised at how many companies have ineffective or no security programs and remain vulnerable to hackers, insider threats, and ransomware!
Corporate organizations are at the top of the list of businesses targeted by cyberattacks. Not only do they have large amounts of data and IT resources that attackers can take advantage of, but a successful breach of a well-known enterprise is more prestigious in the hackers’ world. Small businesses face just as many risks because they underestimate the importance of security systems and processes. But even if an enterprise spends a lot on security, that doesn’t mean they can’t be hacked. The diversity and complexity of enterprise IT systems can, sometimes, make them an easier target.
So the question is, what can you do as a business owner to ensure the enterprise’s security in 2023? This article explores corporate security challenges and describes practices for building a more secure corporate environment.
Why is Enterprise Security Important?
Large corporate systems regularly face various threats to information security — from external interference and destruction of protection tools’ functionality to the theft of data by employees.
The larger the corporate network is, the more difficult it is to ensure the enterprise’s security regarding the integrity of its data. Every entry point, including remote users and their network permissions, is an opportunity for cyberattackers.
Cloud computing also complicates cybersecurity strategies. Whether it’s a hybrid cloud or a public cloud, attackers have yet another way to attack in the form of a cloud service provider. And incorrect settings in the cloud infrastructure lead to serious data leaks without much effort from attackers. Also, unprotected data storages and data lakes can become the target for attackers. Companies could lose up to $4.24 million due to stolen records or leaked information.
By the way, cyber threats do not come only from outside. Insider threats are also quite a troublesome problem for organizations. Aggregate permissions, unnecessary high-level permissions, and deleted users with active accounts are issues that can lead to data leakage because of phishing or social engineering. According to a recent Ponemon Institute study, the average cost of an insider hack has risen 31% to $11.45 million. That is why enterprises need to build their security strategy based on the characteristics of the system and the threats it faces.
However, Conference Board studies have shown that security management in most large companies is often decentralized, with responsibilities grouped into three separate blocks:
- Physical security (protection of personnel, goods, and amenities);
- IT security (protection of data and communications);
- Risk management (insurance and other financial matters).
Many enterprise security systems require collecting and analyzing data in various places and formats. This combination means that sharing information and responding to security issues can be difficult from a security perspective.
Current Challenges in Corporate Security
To develop a strong security convergence strategy and improve security, enterprises need to know the issue they are facing. As the technologies we use every day become more sophisticated, so do the methods used to gain unauthorized access to data and spaces.
- External hacking attempts. These include malicious attempts by third parties to obtain information, data, or physical access. Phishing, social engineering, and IoT hacking are examples of threats to enterprise security from external sources. Data centers are no longer the only primary target for hackers; peripherals such as corporate security cameras are increasingly vulnerable to these incidents.
- Internal security incidents. Employees of the organization perpetrate a surprising number of enterprise security incidents. Issues such as property theft, vandalism, data theft are major security vulnerabilities, and businesses must be vigilant to prevent them. A survey conducted by Fortinet found that fraud (55%), monetary gain (49%), and intellectual property theft (44%) are the top three causes of insider threats. Insider Threat Survey shows finance (41%), customer access (35%), and R&D (33%) are most vulnerable to cyberattacks.
- Accidental employee breaches. Inadequate security policies, insecure networks, and outdated security systems are just a few examples of how spontaneous security breaches can occur.
- Third-party risks. As organizations adopt more manageable software and technology, the risk of hacking among vendors, suppliers, and contractors increases. If third-party providers do not adhere to the same security standards that you expect from your organization, your data and information will be vulnerable.
- Limited visibility and incident response. Not knowing what’s going on in the workplace is a major safety omission in today’s world. When hacks and data leaks occur within minutes, every second lost is worth your organization.
These challenges require an effective corporate security strategy and a regular review to ensure effectiveness. It is important because cybercriminals are constantly improving their methods.
What is Meant by Enterprise Security?
Enterprise security refers to the process which is used by an organization to protect its information assets (data, servers, workstations, storage, networks, applications, etc.) from breaches of confidentiality, integrity, or availability.
Whereas traditional cybersecurity protects digital assets locally, corporate security secures data in transit across the connected network, servers, and end-users. Because this protection is enterprise-wide, it further focuses on the legal and cultural requirements for protecting data assets owned by an organization’s user base.
What is Corporate Security Responsible for?
Its goal is to ensure a unified approach to security by complying with the strategies, standards, and policies defined by the corporate security.
Security Strategies
An organization’s security strategy highlights the security issues and addresses them. Thus, the effective security incident response may include a security control center (SOC) to provide full incident response services.
Security Policies
Developing security management policies that require employees to adhere to best practices is one step towards making environments and data more secure. For example, policies might specify that multi-factor authentication must be used on company-owned devices and that storage devices must remain local to mitigate certain types of risk.
Security Standards
The Security Systems Standards Policy is important for documenting your company’s specific security hardware and software standards. This policy could allow your organization to manage security systems holistically, and it is especially important for companies with multiple locations.
Security Assessments
By understanding the organization’s current security state, Enterprise IT Security can identify any gaps in security controls. These gaps can then be allocated to the appropriate security groups, and the risk owner can initiate effective risk mitigation actions.
Security assessments come into play when parts of an organization are assessed for compliance, typically when systems or services are built, but it can also happen periodically, such as annually.
Corporate security also includes enterprise security risk management (ESRM).
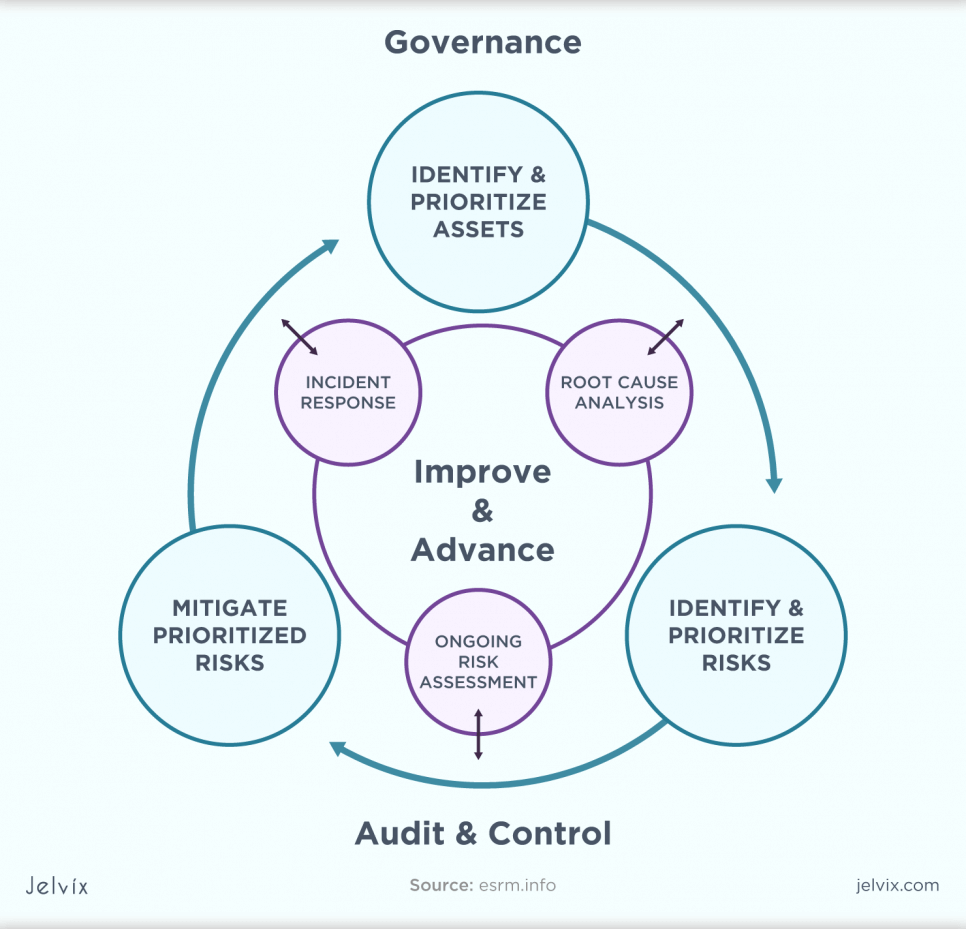
What is ESRM?
It is a strategic approach to security management that links the organization’s security practices to its overall strategy using accepted risk management principles. The essence of ESRM, and the key to realizing business value from a risk-based approach to security, is that security professionals and asset owners share responsibility for security. Understanding your organization, its mission, needs, and priorities are the essence of the ESRM lifecycle.
ESRM lifecycle
- Definition, understanding, and prioritization of enterprise assets;
- Identification and prioritization of risks;
- Reduction of priority risks;
- Continuous improvement.
First, organizations can focus on the most costly vulnerabilities by organizing and prioritizing risks. If risk reduction is more expensive than risk acceptance, the organization may leave it vulnerable or give it a low priority.
Note! Experts recommend developing a risk register and reviewing and updating it regularly. Keeping this document dynamic and up-to-date will create a more efficient and prepared organization.
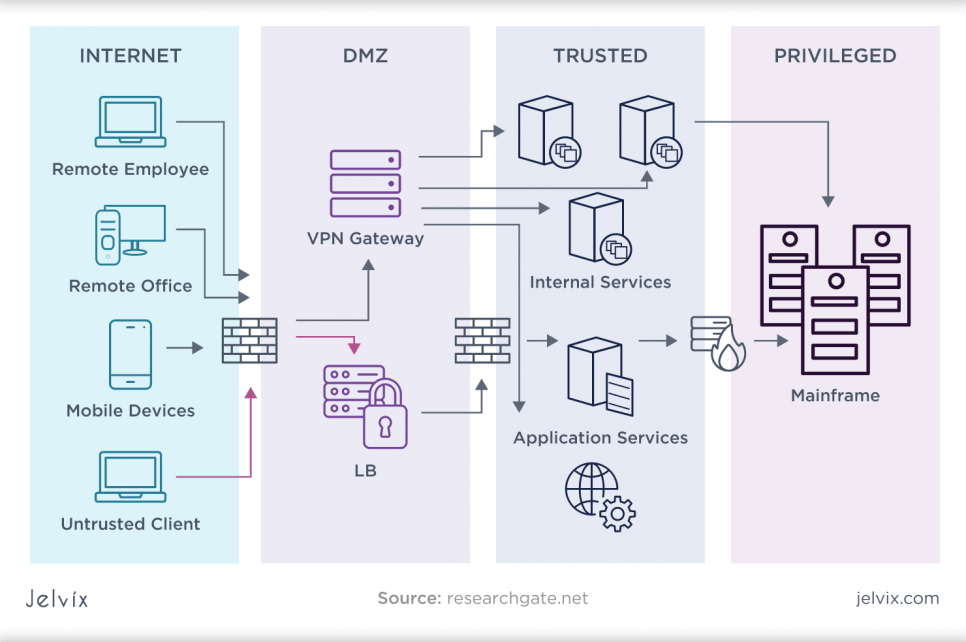
What is enterprise security architecture and design?
The main definition of security architecture is a systematic approach to improving enterprise network security and reducing risk. Security architecture refers to the existing systems, processes, and tools to prevent or mitigate attacks. However, design refers to how the security architecture is built. An enterprise security architecture is a holistic design that helps the various parts of the security infrastructure work together.
Companies of all sizes have a security architecture, whether or not they intentionally design it. Any technology solution must consider this security architecture and design.
If a company has the right tools and resources but does not use them correctly, it will likely not get the expected results. For instance, one part of the IT infrastructure may be less secure than another due to inconsistent security tools.
With these insights in mind, an enterprise security architecture relies on various implementation concepts. These include security domains, levels of trust, multi-layer networks, planning tools that consider different areas or parts of business processes, and security systems. Security engineers work from these principles to provide a functional enterprise security architecture that ensures that business resources are up and running well in the field to support end-to-end security.
What is an enterprise security platform?
Given the complexity of enterprise environments, it is impossible to secure an enterprise through manual processes. Enterprise organizations should strive to implement solutions that can automatically collect and analyze security-related data, whether log data, software source code, configuration files or anything else.
Also, these intelligent technologies should include systems that automate processes and operations in the enterprise, including security. For example, enterprise tools such as SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) platforms automate threat monitoring and management, software updates, compliance reporting, and more.
SIEM platforms can be implemented locally and managed by the enterprise’s IT security team or purchased as a managed security service provider, offering dedicated personnel to monitor, update, and maintain the service.
Software and hardware for information security
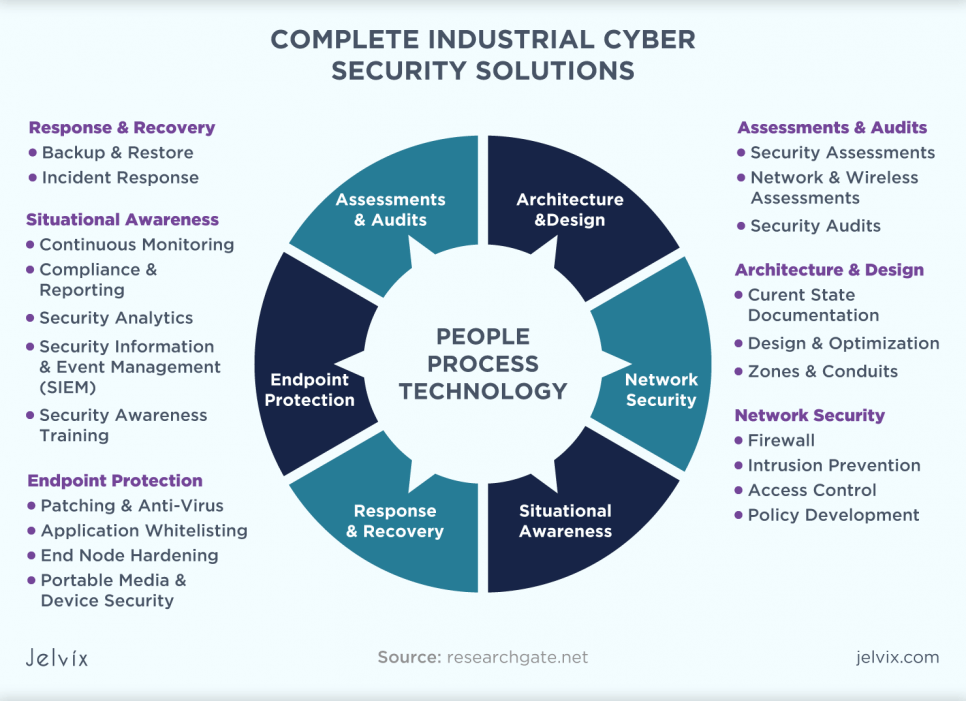
The current working paradigm for corporate security best practices is to apply all available industry practices for physical security, firewalls, encryption, anti-fraud, intruder detection, WAF, antivirus, etc. Here is a list of software tools required to ensure the safety of the company:
- firewalls that restrict the transition from one protected sector to another;
- antivirus tools to detect all new security threats;
- trusted boot tools;
- Intrusion detection tools;
- means of cryptographic protection.
Besides these, enterprises should implement:
- network health monitoring systems;
- vulnerability monitoring systems;
- SIEM programs to detect information security incidents and notify the security service about them;
- DLP systems to keep data leakage from the protected information area and limit access to highly confidential resources.
Best Practices of Corporate Security
Most organizations know they need some level of cybersecurity to protect data from intruders but don’t know how to plan and implement it. Therefore, planning, deployment, maintenance, and improvement should be delegated to experts to avoid mistakes. They recommend the following best practices for strengthening your corporate security:
Take a risk-based approach to security
A good risk assessment helps avoid any unpleasant moments, such as fines for non-compliance with regulatory requirements, the cost of eliminating potential leaks and violations, and losses from the absence or inefficiency of processes.
Tip: Identify cybersecurity flaws and make the necessary adjustments. Also, keep an eye out for new hacking techniques using databases and frameworks, such as MITER ATT&CK for enterprises. A detailed risk assessment can help you prioritize security measures and ensure your strategy is best for your company’s profits.
Protect data at rest and in transit
Determine the data assets that need to be encrypted and develop a security strategy for them. Encryption must scale across your network and protect data workloads in dynamic and distributed cloud environments. Remember to monitor the performance of your encryption implementations.
Tip: Next-generation firewalls (NGFW) can focus on existing threats and new zero-day attacks. NGFW can protect against a wider range of cybercriminals by using artificial intelligence to isolate further attacks. For this, Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) is used, which checks both basic information about where the data packet came from and what is inside. You can install Web Application Firewalls, which add an extra layer of protection to Web Forms to prevent cross-site scripting and MySQL injection attacks.
Install strong identity and access controls
Any system that demands a password before granting access should also be secure, especially because when logging in, an attacker can use their access to elevate their privileges or navigate to other areas of the network to compromise them. It may require the use of multi-factor authentication measures and the restriction of individual access rights to specific systems to reduce the risk of data leakage and network intrusions because of human error or malicious intent.
Tip: Use the principle of least privilege, which gives users only the limited access they need to do their job. Using biometrics as one of the best practices for enterprise data security provides stronger authentication than passwords and SMS verification.
Invest in the best security software
High-quality security software typically includes protections such as SIEM platform, robust antivirus, malware detection, and external hard drives for data backup. All of these tools must be kept up –to –date. The best antivirus and anti-malware programs are only as good as their latest patches. The National Cybersecurity Center in the UK estimates that over 80% of hacks are indirectly caused by outdated software.
Tip: Make sure your team knows to set up dashboards, connect to the appropriate logs, and update the configuration as your network changes. No platform can provide all the customization you want out –of –the –box.
Develop robust disaster recovery and mitigation plan
It is an important risk mitigation strategy that can be very costly to ignore. In the event of a data breach, ransomware attack, or natural disaster that damages your network, a disaster recovery plan will help your business recover quickly and easily from the loss.
Tip: Back up your data. It is one of the best information security practices that has become increasingly relevant in recent years. With ransomware, having a complete and up-to-date backup of all your data can be lifesaving for your business. Ensure that backups are carefully protected, encrypted, and updated frequently. It’s also important to divide backup responsibilities between multiple people to mitigate internal threats.
Train your employees on cybersecurity measures
Personnel can act as a reliable first line of defense against cyberthreats that target the human factor. On the other hand, employees who are not security savvy can become weak links in a security chain that is otherwise equipped with enterprise security solutions.
Tip: Make sure there are no weak links within your company. It’s good to educate employees to detect phishing emails, avoid clicking on suspicious web links or email attachments, and create more secure passwords.
Involve senior management in the development of an enterprise security strategy
The security review should extend to the executive level, where you should make the risk management decisions. CEOs and executive management must understand their corporate security decisions’ legal, financial, cultural, and technological implications. Cyber threats should not be considered or attributed to IT; it is a business problem that should become a business affair.
Tip: Initiate meetings, presentations, and demonstrations to see the benefits of a strategic approach to managing security. Explain to management that it is in their best interest to implement defenses throughout the organization because they are as invested in risk management and information security as everyone in the IT team.
Create a security team or outsource
A recent ISSA study shows that 60% of organizations suffer from a shortage of qualified employees. High demand makes hiring and retaining experienced and highly skilled cybersecurity professionals extremely difficult and expensive. Companies that cannot afford to invest in the best are more vulnerable to attacks and slower to recover from attacks.
Tip: Consider outsourcing necessary security tasks such as security monitoring, threat detection, and troubleshooting to dedicated teams of external security experts. Outsourcing is one of the best ways to get the best specialists at an affordable price.
Output
Cybersecurity threats continue to multiply, and you have no choice but to invest time, effort, and, of course, money to keep your company safe.
Ask yourself this question: what have you done to protect your business? And if you feel you haven’t done enough, contact the Jelvix corporate security experts. We’ll help you protect your digital infrastructure from multifaceted threats, manage risk, and thrive in a transforming world.
Need a qualified team?
Access the talent pool to scale your team capacity.