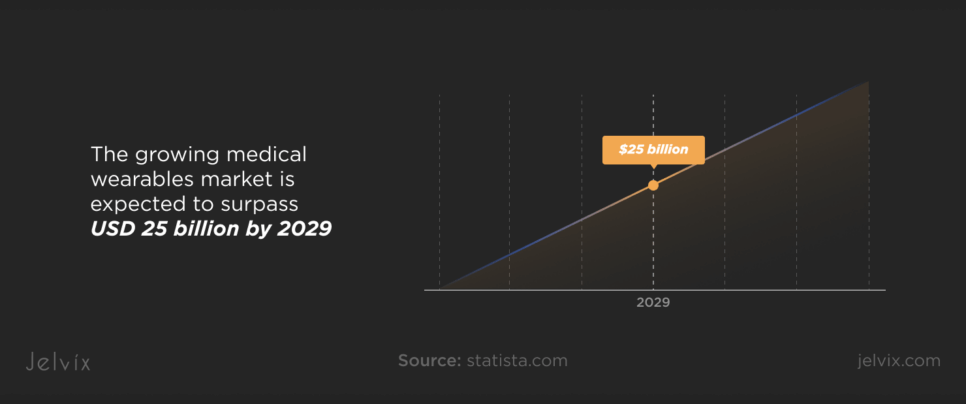
As healthcare becomes more precise and personalized, providers must know more about patients, including data about each possible health metric and condition. This need is confirmed by the growing medical wearable market, which is expected to surpass USD 25 billion by 2029.
Wearable tech in healthcare, especially when combined with AI, can help clinics catch problems early and run more efficiently. But rolling them out isn’t always easy. Privacy rules, high costs, and tech accessibility are real challenges.
If you want to enhance care at your clinic by personalizing treatments with the help of wearable devices, read this article. You’ll find out about key trends in wearable tech, ways to resolve integration-related concerns, and advice on addressing socioeconomic barriers and accessibility challenges.
Integrating Wearable Medical Devices with IoMT Solutions
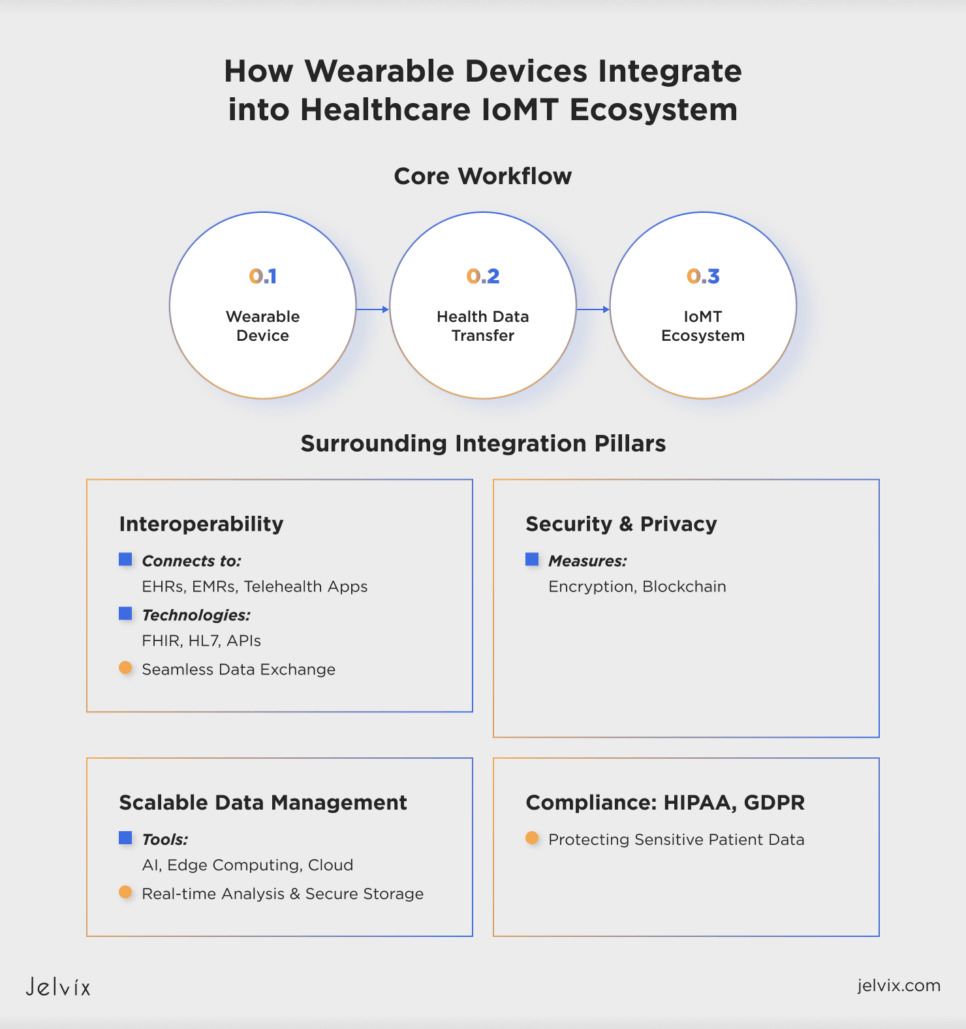
To help doctors get real-time and accurate insights, wearable tech must integrate well with existing IoT in healthcare.
Ensuring Interoperability with Other Systems
Wearable devices must connect with other medical systems like telemedicine apps, EHRs, and EMRs. To achieve this, it’s better to use proven data formats like FHIR and HL7 for seamless data exchange and APIs for processing vast amounts of data on the go.
Addressing Security and Privacy
Wearables track and collect vast amounts of sensitive information about patients, and providers need to take serious safety measures to protect this data from leaks. Consider using encryption to protect patient information and blockchain tech to prevent tampering, and stay compliant with HIPAA and GDPR for patient privacy.
Managing Large-Scale Data with AI and Cloud
Healthcare providers generate about 137 terabytes of data daily, and a lot of this data comes from wearables. AI tech can help analyze this information, edge computing reduces processing delays, and cloud storage ensures secure and timely access.
Types of Data Collected by Health Monitoring Devices and the Ways AI Helps Analyze It
To get a comprehensive picture of a patient’s health, wearables need to track various types of metrics. AI health solutions help catch up this data by identifying patterns, detecting early health risks, and making care more personalized.
Common Types of Data Collected by Wearables
Medical tracking devices monitor health indicators like heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen levels, body temperature, sleep patterns, physical activity, and glucose levels. However, advanced AI-powered devices can also track ECG readings, stress levels, and hydration for more detailed health monitoring.
The Role of AI in Data Analysis
AI tools can sort through huge volumes of data, spot patterns, and highlight trends that would be easy to miss manually. They also help clean and organize messy data, which is a big part of real-world analysis. Data processed with AI becomes more readable, helping businesses spot operational risks and assisting doctors in catching early signs of illness.
Key Advantages and Disadvantages of Wearable Technology in Healthcare
RPM devices can greatly assist doctors and help them ensure timely care. But like any other tech, they can harm if misused.
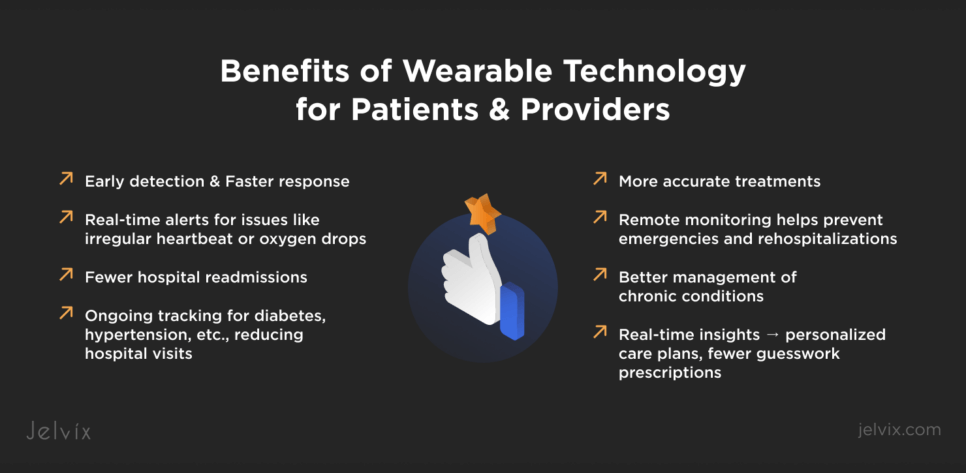
Benefits of Wearable Technology in Healthcare for Patients and Providers
Many healthcare professionals see the bright side of using wearables to treat patients.
“Wearable sensors give us an opportunity to identify health problems at an early phase, allowing for timely intervention”, emphasizes Wei Gao, Assistant Professor of Medical Engineering at Caltech.
If you decide to adopt wearable tech, expect faster and more accurate health data monitoring and a more prompt reaction to emergencies.
Early Detection and Faster Response to Health Issues
It’s much simpler to detect conditions like irregular heartbeats or dips in oxygen levels with the help of remote monitoring devices. This allows doctors to intervene in time and prevent more significant health issues. This kind of quick action can also save lives.
Better Management of Chronic Conditions
Routine health tracking becomes more convenient with wearables, especially for people suffering from conditions like diabetes or high blood pressure. On the other side, doctors can monitor vital metrics in real time and adjust medications, preventing patients from visiting a hospital too often.
More Accurate Treatments
Thanks to wearables, doctors can get real-time insights into a patient’s health trends instead of relying only on occasional checkups. This helps them fine-tune medications, spot patterns, and create treatment plans that fit a patient’s routine.
Fewer Hospital Readmissions
By tracking health remotely, doctors can catch problems early and adjust care before a hospital visit is needed. This helps patients recover faster and stay out of the hospital longer.
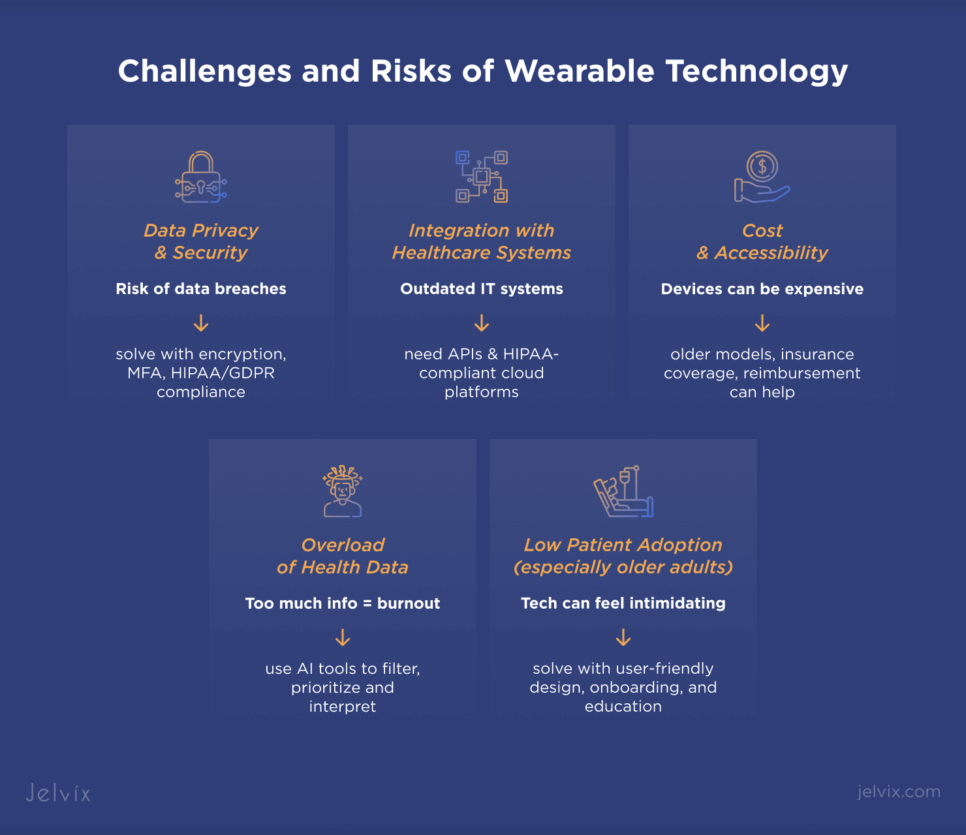
Common Challenges of Wearables and Ways To Overcome Them
Although wearable technology is considered beneficial for patients and doctors, it comes with challenges like security, integration, and implementation costs.
Data Security and Privacy Risks
Wearables collect sensitive health data, which makes them a desirable target for cyberattacks. For this reason, providers need to implement strong encryption, multi-factor authentication, and compliance with HIPAA and GDPR.
Integration with Healthcare Systems
Many hospitals use outdated IT systems that don’t connect well with wearable devices. Solutions like APIs, cloud-based IoMT platforms, and HIPAA-compliant cloud storage can help ease and secure data exchange with EHRs and various medical software.
Discover how smart API integration in healthcare streamlines data exchange, enhances interoperability, and improves care coordination.
Cost and Accessibility Barriers
Wearables can be expensive for both hospitals and patients. If you want to adopt them but can’t afford to spend a lot, consider older and more affordable models, seek insurance coverage, and look for reimbursement options to make this tech more accessible.
Managing Large Data Volumes
Huge amounts of medical data collected by wearables can overwhelm medical professionals. To help them analyze patient info, opt for AI-powered analytics tools that filter and process raw data, turning it into helpful insights.
Patient Adoption and Compliance
Some patients, especially older people, may struggle with using remote monitoring devices. Choose solutions with user-friendly designs, simple onboarding, and clear education to improve their adoption by patients.
AI and Wearable Technology in Healthcare: Impacting Doctor-Patient Relationships
Wearable devices can be more helpful for your clinic than you might think, as, beyond health monitoring, they help doctors talk to patients and spot their health concerns. As a result, care becomes more personalized.
AI and wearable devices are changing how doctors and patients interact. Instead of relying only on in-person visits, medical workers now have access to real-time health data that shows what’s happening between appointments. This helps doctors make informed decisions. It also means patients don’t need to explain everything from memory because the data’s already there.
At the same time, having that constant stream of information can make care feel more connected. Patients stay more engaged, and doctors can offer support earlier, not just when something goes wrong.
Still, it’s important to balance tech with real conversation. Data is helpful, but it doesn’t replace trust or understanding. The best results come when AI supports the relationship, not replaces it.
Preventative Healthcare with Wearable Health Monitoring Devices
Wearables can play a big role in spotting health issues early and helping people avoid long-term conditions. These devices track key health data daily, giving both patients and doctors a clearer view of what’s happening before symptoms even appear.
Use wearables to monitor things like heart rate, blood pressure, sleep quality, or blood oxygen levels. This kind of real-time tracking helps catch warning signs early and supports better decisions around care. It also encourages users to stay active, manage stress, and follow healthier habits, which results in preventing chronic diseases like diabetes and hypertension.
Emerging Trends in Wearable Tech and AI in Healthcare Future
Modern wearable technology goes far beyond smartwatches and fitness trackers, and AI-backed innovations help enhance real-time health monitoring and personalized care.
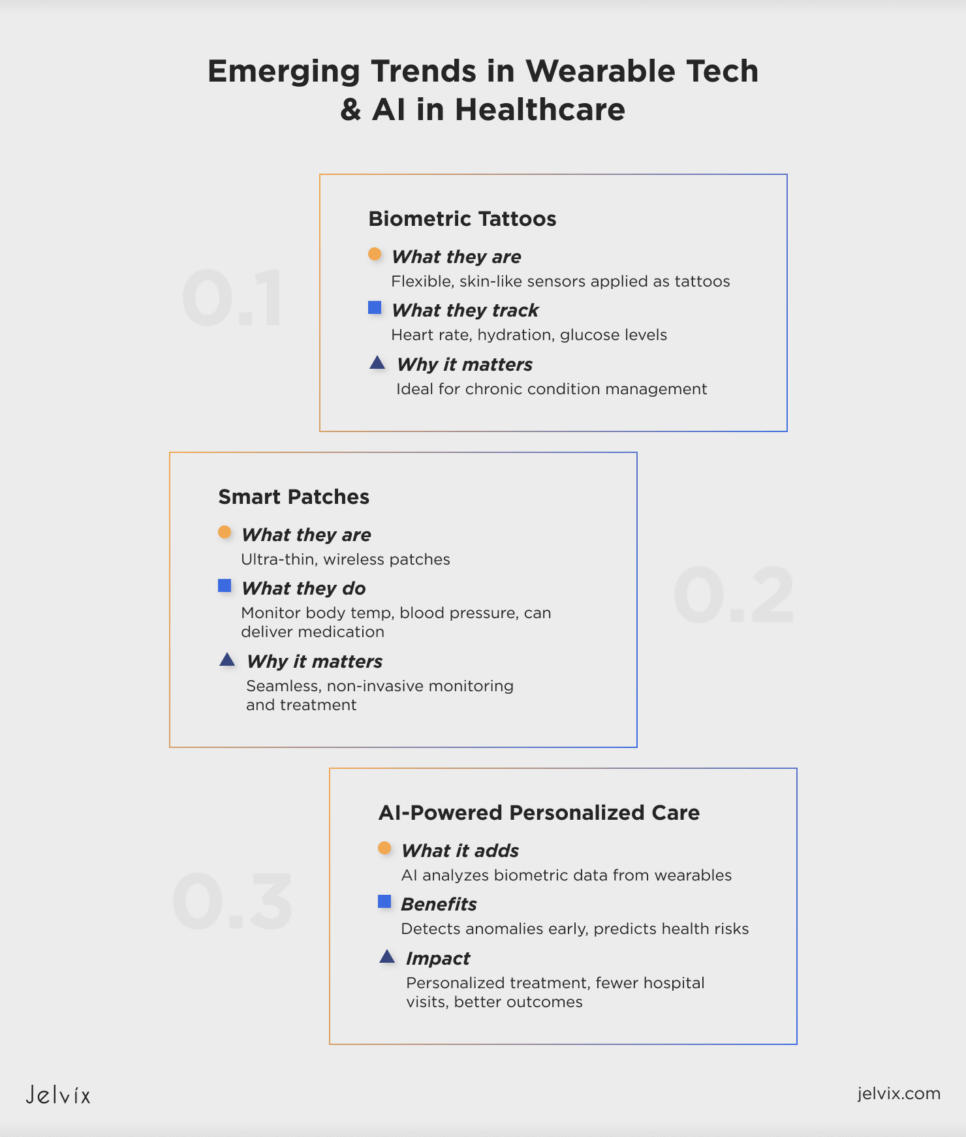
Biometric Tattoos: Real-Time Health Tracking
Biometric tattoos are one of the newest digital health trends that use flexible and skin-adhering sensors to monitor heart rate, hydration levels, and glucose. Unlike traditional wearables, they provide continuous data tracking, becoming a perfect choice for patients with chronic conditions.
Smart Patches: Non-Invasive Monitoring
Smart patches are ultra-thin wireless devices that track biomarkers like body temperature and blood pressure. Some even deliver medication through the skin, offering a seamless way to manage treatments and monitor conditions.
AI-Driven Insights for Personalized Care
AI enhances these innovations by analyzing biometric data, detecting abnormalities, and predicting health risks. This allows doctors to tailor treatments and intervene early, reducing hospital visits and improving patient outcomes.
Ethics and Privacy Concerns in Healthcare Wearable Devices
While AI-driven insights improve care, there’s a fine line between helpful monitoring and excessive surveillance. Patients should have control over their data, with clear policies on how their information is used and shared.
There’s also the issue of consent. People need to know what’s being tracked, how it’s used, and who has access to it. Making that clear up front helps avoid confusion and keeps the relationship between patients and providers transparent.
Inspiring Real-World Wearable Technology Examples
Wearable technology is already making a significant impact on healthcare, helping patients manage chronic conditions, improving diagnostics, and enhancing treatment outcomes. Here are real-life examples of how wearables are transforming patient care.
Detecting Heart Conditions
Apple Watch’s ECG feature has helped detect atrial fibrillation (AFib) in users, alerting them to irregular heart rhythms before symptoms appear. Many cases have led to early diagnosis and timely medical intervention, reducing the risk of stroke and other complications.
Diabetes Management
Dexcom’s CGM system tracks blood glucose levels in real time, helping diabetes patients manage their condition more effectively. The device sends alerts when glucose levels are too high or too low, allowing for timely action and reducing the risk of complications.
Remote Patient Monitoring
The BioButton is a medical-grade wearable that monitors temperature, respiratory rate, and heart rate for remote patient monitoring. It has been used in post-surgery recovery and COVID-19 monitoring, helping doctors track patients without frequent hospital visits.
Addressing Neurological Disorders
Wearables like Empatica’s Embrace detect seizures in epilepsy patients by monitoring electrical activity and physiological responses. The device can send emergency alerts to caregivers, improving response times and patient safety.
Managing Large Patient Groups with Wearable Devices
Wearable health devices can alert medical staff when something’s wrong, like a sudden drop in oxygen levels or an irregular heartbeat. In emergency situations, that quick response can be critical and even life-saving.
These devices also help providers monitor large groups of patients more efficiently. Instead of checking in manually, doctors and nurses can track health data in real time and get notified if anything needs attention. This makes care more responsive and helps medical teams stay focused on the patients who need them most.
How To Integrate Data from Wearable Devices into Existing Systems
Connecting wearable health data to your current systems takes more than just syncing devices. It also means keeping that data secure, accessible, and easy to use across diverse platforms. That’s where technologies like blockchain, encryption, and secure APIs can assist your efforts.
Blockchain helps create a tamper-proof record of health data, so only authorized users can access or change it. It also makes audit trails easier to manage, which is useful for compliance.
On the practical side, secure APIs let wearable devices send data directly to existing platforms without rebuilding everything from scratch. Cloud services help store and scale that data, and AI tools can filter and organize it so providers see what actually matters. The key is to make integration smooth while keeping patient data safe and easy to use.
The Role of Patient Engagement in Adopting Wearable Technology in Healthcare
Even the best wearable tech won’t make a difference if patients don’t actually use it. Engagement is a big part of whether these devices help or just collect dust.
Many patients, especially older adults, may find new technology intimidating. Wearables with simple interfaces, intuitive apps, and easy setup increase user confidence and daily engagement. Providing clear onboarding, tutorials, and customer support also helps improve adoption rates.
To boost adoption, the experience has to be simple and meaningful. That means easy setup, clear health goals, and feedback patients can understand. When people see how wearables connect to their daily routines or help avoid doctor visits, they’re more likely to stick with them.
Education also plays a role. If patients understand what’s being tracked and why it matters, they’re more likely to stay involved and use the data to make better choices.
Learn how we helped our client build a remote patient monitoring solution that improves chronic care, reduces readmissions, and enables real-time patient insights.
Cost Implications and Accessibility of Wearable Devices in Healthcare
While wearable technology helps make care more proactive, providers still need to address the challenges of their cost and accessibility.
Many advanced wearables, such as smartwatches and biometric patches, are expensive, making them unaffordable for some patients. Limited insurance coverage and reimbursement options further restrict access. Expanding health insurance policies to include wearable devices and offering subsidized programs can help bridge this gap.
Lower-income patients often lack access to wearable tech due to high upfront costs and the need for smartphones or internet connectivity. Manufacturers and healthcare providers can improve accessibility by offering lower-cost models, rental programs, or partnerships with public health initiatives.
Wearables should be designed for diverse users, including seniors and those with disabilities. User-friendly interfaces, voice commands, and accessibility features make these devices easier to use. Expanding availability in clinics, pharmacies, and telehealth services can also help more people access wearable technology.
How Jelvix Helps Develop and Adopt Wearable Technology for Healthcare
Wearable technology allows medical entities to enable real-time monitoring, early disease detection, and personalized treatment plans. However, challenges like data security, system integration, and cost barriers must be addressed to maximize their impact.
At Jelvix, we specialize in developing secure, scalable, and AI-powered healthcare solutions, including wearable tech. If you need to build an RPM tool from scratch or want to implement a ready-made solution, our experts can help. Reach out for a personalized consultation based on your unique clinical needs and business goals.
Turn complex goals into actionable results.
Gain full control and flexibility with a dedicated development team tailored to your needs.