Every day, businesses are faced with a multitude of risks and potential dangers. Therefore, to help their organizations successfully sail through turbulent waters, business leaders have to devise ways to manage risks efficiently. For many businesses, risk management is part of their daily business operations, but the tactics for managing risks differ between businesses.
Traditionally, risks were handled within each business unit where they occurred; however, this method has proven inefficient in large organizations with multiple departments. Therefore, for business growth and efficiency in the workplace, this fragmented approach to risk management has been superseded by a more effective and holistic risk management strategy: ERM.
What Does ERM Mean?
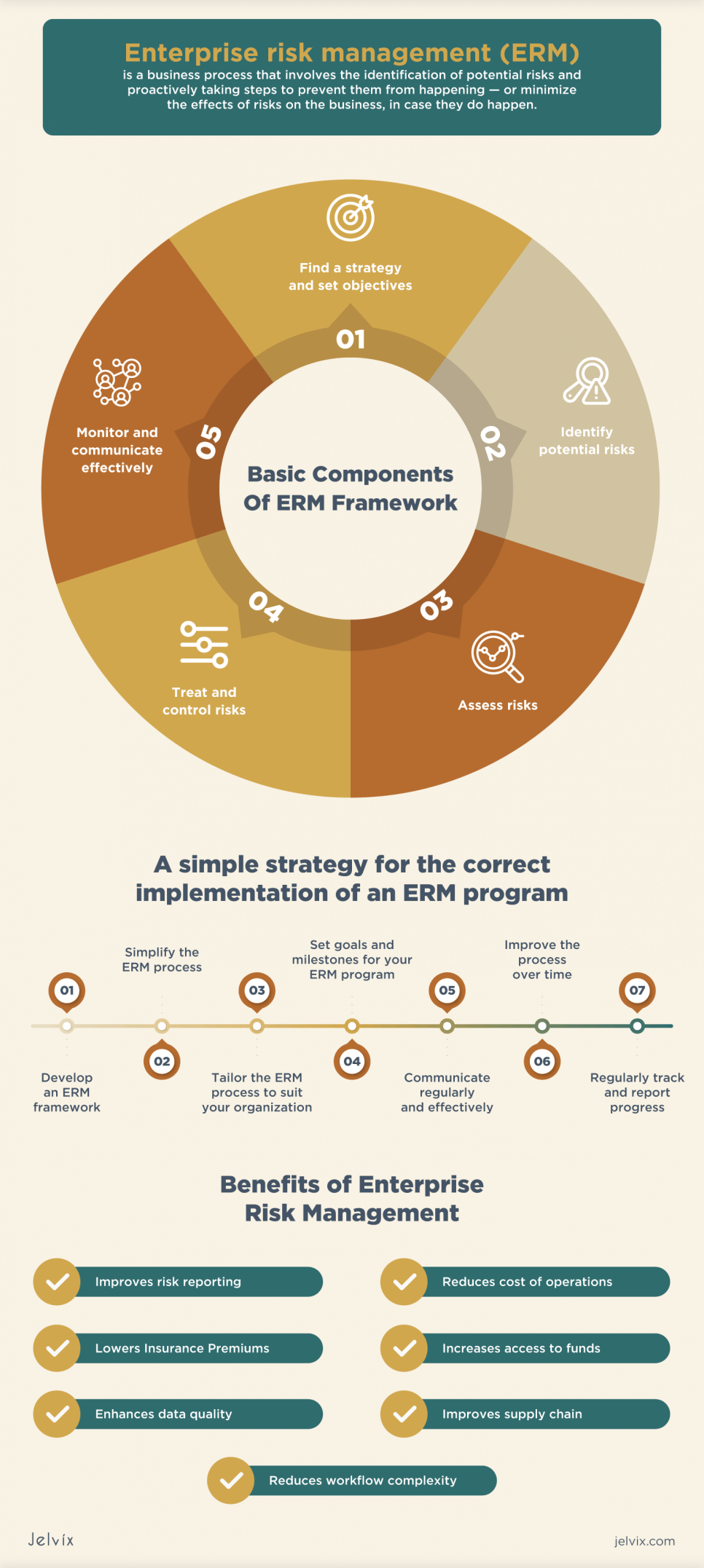
Enterprise risk management (ERM) is a business process that involves the identification of potential risks and proactively taking steps to prevent them from happening — or minimize the effects of risks on the business in case they do happen.
Business risks come in many different forms, and the ERM process is essentially an ongoing process with methods that address the potential events that represent risks to the accomplishments of a business.
Enterprise risk management will often comprise holistic and strategic plans that take into account every part of an enterprise. Rather than approach potential business risks within an organization separately in each individual department, ERM takes a holistic approach to addressing risks from the management level and includes every part of the enterprise.
Being a risk-based approach to managing a business, ERM focuses on all forms of business risks, including financial, economic, legal compliance, security and fraud, operational, competitive reputational and publicity, strategic, etc. This ensures that the capital, earnings, assets, and interests of the business stakeholders, including owners, investors, employees, customers, are protected.
When organizations develop enterprise risk management strategies, they often look to:
- Identify the potential risks associated with critical business processes;
- Discover the risks that pose the most threat to key business objectives and strategies;
- Determine a response strategy for diminishing the possibility of risks or lessening the magnitude of impact on the business;
- Monitor and measuring processes using established metrics.
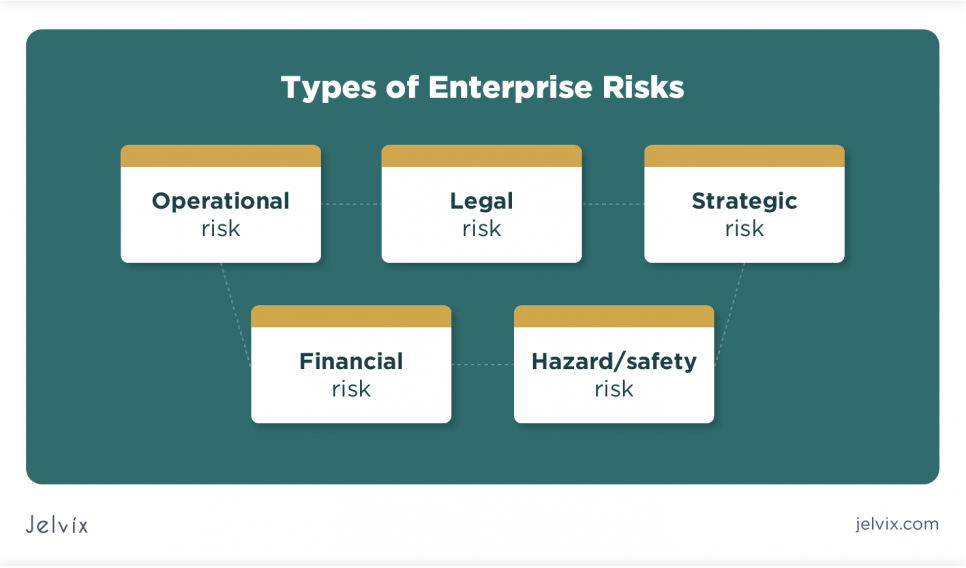
Types of Enterprise Risks
Enterprise risks come in different forms, and every organization faces varying degrees of risks. Therefore, the success of businesses most often hinges on how effectively they recognize and manage risks, and even more important is maintaining a healthy balance between being risk-aggressive and risk-averse.
Here are some of the most common enterprise risks that businesses have to deal with;
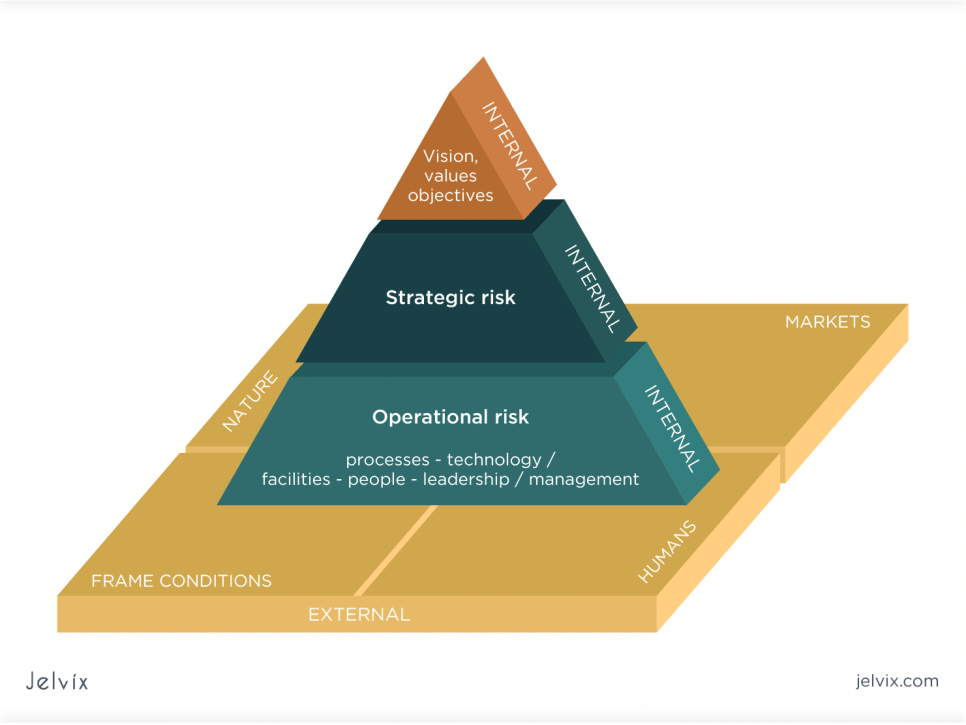
- Operational risk: this is a type of enterprise risk that arises due to failed internal processes. Operational risks can either be due to technical failures, mismanagement, or failure in the model application.
- Legal risk: this is a type of risk associated with legal proceedings and lawsuits against an organization.
- Strategic risk: this refers to the events (both internal and external) that hinder the possibility of an organization to achieve its goals and objectives.
- Financial risk: this is a type of risk that involves the loss of business revenue. Any risk involved with financing and financial transactions is classified as a financial risk.
- Hazard/safety risk: this type of risk is associated with accidents and potential sources of harm in a workplace. It can be either physical, biological, chemical, etc. If it poses any sort of danger to the personnel, then it’s a hazard or safety risk.
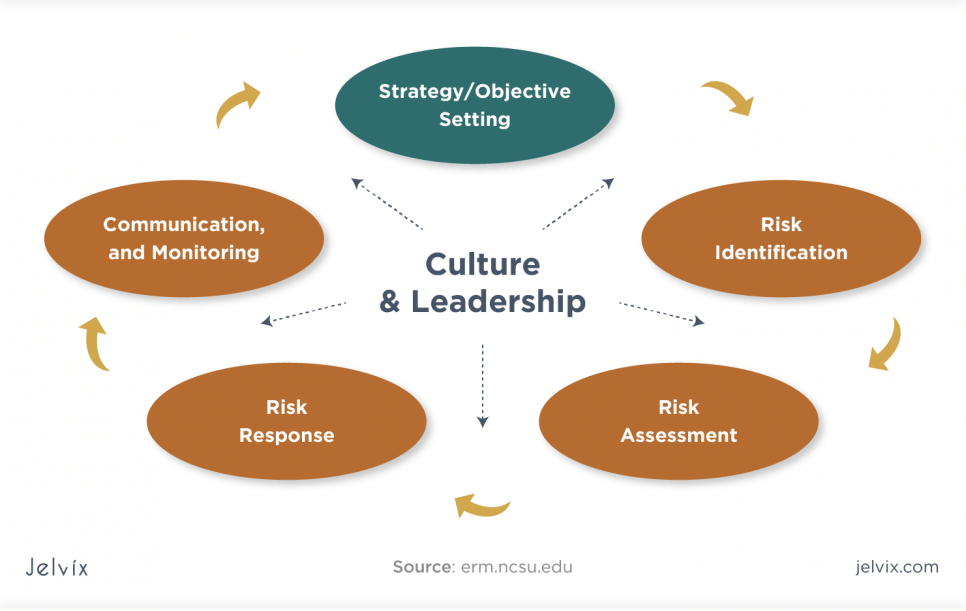
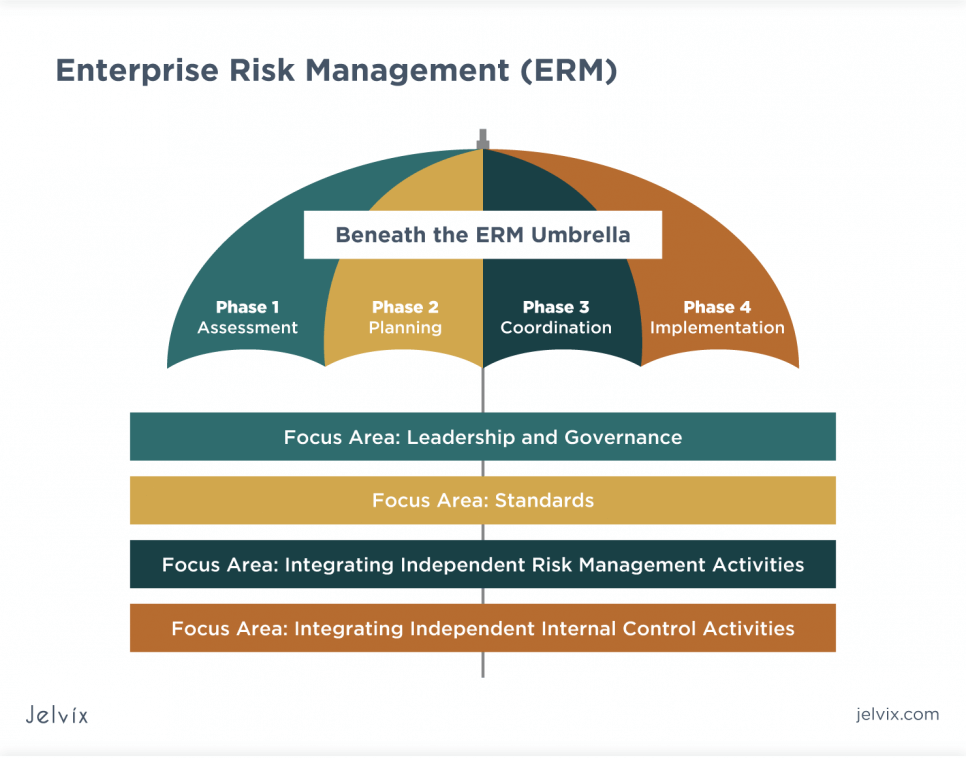
Basic Components of the ERM Framework
There are different approaches to risk management, and each one of them has its specific standards and guidelines. While risk management standards remain fairly the same across different platforms, the practices tend to be more streamlined, focusing on the objectives and values of specific organizations.
A robust enterprise risk management model for any organization will factor in all potential risks, including the ability of the business to properly handle certain risks. However, a business can only achieve a risk-conscious management style by incorporating a viable ERM framework into the organization’s values.
The adoption and practice may be tailored to align with the company’s vision, but the basic framework and processes remain mostly unchanged. Here are the basic components of most enterprise risk management frameworks:
Find a strategy and set objectives: the first step in defining an ERM framework is to clearly understand your objectives as an organization to find a risk management strategy that perfectly aligns with the company’s objectives and values.
Identify potential risks: a clear understanding of every single risk you face as a business is imperative. You can tackle a problem that you are aware of and understand; this also applies to risk management. Make a comprehensive list of all the risks you face as an organization, from the most to the very least threatening; this will better clarify the company’s risks.
In addition to this, an organization should also estimate its risk tolerance (the maximum level of risk the organization can handle) and risk appetite (the level of risk a business is willing to pursue).
Assess risks: next is to assess every individual risk that has been identified. One of the major importance of enterprise risk management is that it aids in differentiating the risks a company can control from those it has no control over. This helps with resource allocation and better risk management.
Treat and control risks: following the identification and assessment of risks, there must be a decision on how these organization threats should be approached and managed appropriately. The major objective of a robust ERM framework is to be deliberate about managing risks. Nothing is left to chance. Every action from risk avoidance to mitigation and acceptance must be decided upon by management.
Monitor and communicate effectively: since risks are distributed among various business departments, it becomes imperative that the management communicate ways to manage potentially risky events to each department proactively. Communicating and coordinating between different departments is essential for the success of ERM.
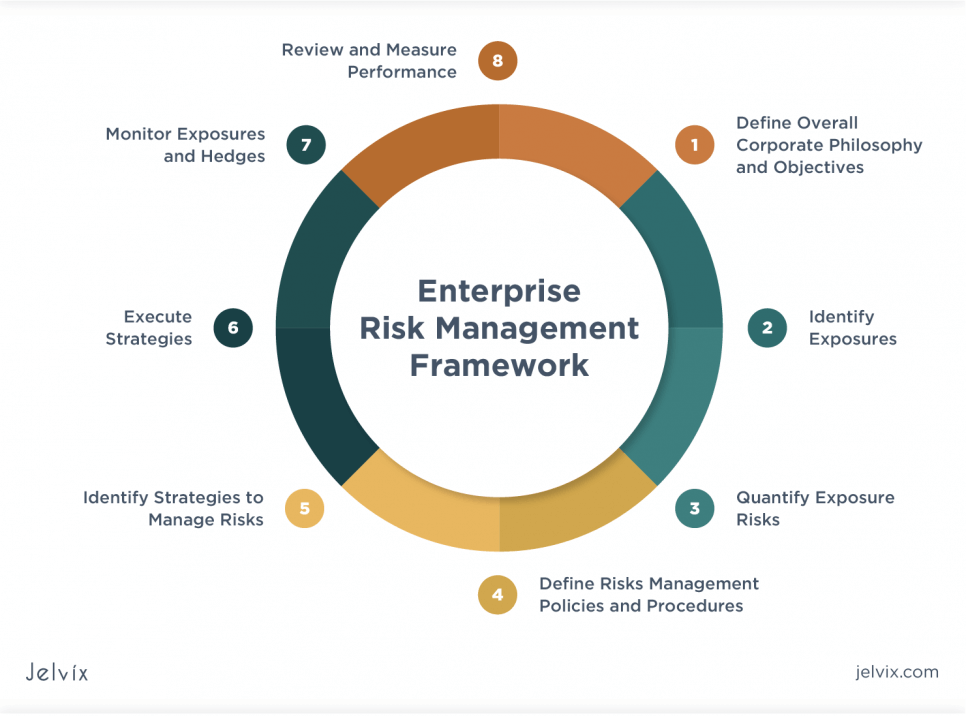
Strategies for Implementing an Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) Program
It’s not unusual for an organization to struggle with implementing an ERM program because not only is the process difficult, but keeping track of the efficacy of the ERM program over a period of time can be a major challenge. However, the process can be less difficult if you have a map with clear strategies on how the implementation process should be approached. Here’s a simple strategy for the correct implementation of an ERM program.
Develop an ERM Framework
Determining the appropriate enterprise risk management framework to use is often the very first step in ERM implementation programs. To find an ERM model that perfectly suits your organization may require that you develop your own internal ERM framework, or you can choose a standardized ERM model and tailor it to suit your business.
Simplify the ERM Process
One of the objectives of ERM models is to minimize complexity; therefore, it’s imperative that you keep the ERM process as simple as possible. Enterprise risk management can quickly get complex, and the unfamiliar concept can be difficult for some members of your team to digest.
Therefore, this simplification of the entire process is crucial. Here, the goal should be to get everyone on your team to fully comprehend the process, think of graphics that describe it, and highlight its importance.
Tailor the ERM Process to Suit Your Organization
An ERM process that suits an organization has to compliment the values of the organization, as well as align with the goals and objectives of the business. The whole essence of a risk management process is to add value to your business, and this can only be achieved with an ERM program that is tailored to fit the needs of your business.
This is why it’s important to develop a unique ERM system that is in agreement with the culture, values, and habits of your organization to stand a better chance of meeting your risk management needs.
Set Goals and Milestones for Your ERM Program
When a business first implements an enterprise risk management program, it’s important to start small, pick a single relevant goal, and tackle it first. By starting small and picking a single objective, organizations can understand the process better and appreciate how the solution is working for the business.
A controlled ERM program is very important because it helps team members to understand the process better, how it’s progressing, what is working, and what needs to be improved. This also provides some form of positive reinforcement for the team and ensures they stay motivated, which is all you need to incorporate risk awareness and risk management into the organization’s culture.
Communicate Regularly and Effectively
Implementing an enterprise risk management process cannot be successful without proper and effective communication among all stakeholders and employees. One of the easiest ways to ensure the success of your ERM program is by regularly and effectively communicating the risk information to all parties involved, including the board of directors, all levels of management, and employees.
Unity and trust between team members will facilitate sharing ideas and information that can improve the process and help achieve the desired results.
Improve the Process Over Time
ERM processes are never static. They are rather dynamic and undergo a lot of changes and adjustments along the way. In order for an organization to effectively sustain an ERM program for a period of time, it has to constantly tweak and improve the process to serve the organization better. Setting goals and objectives, measuring results, and receiving feedback from team players help in the enhancement of ERM processes.
Regularly Track and Report Progress
It’s essential for every step of the ERM process to be documented, recorded, and reported regularly, as this is the only way to actively determine any form of progress.
By creating a progress report and giving regular updates, an organization will not only be able to measure the progress of the process but will also be able to determine the impact of the ERM program on their business. And this will also give insights into how the risk management program and business operations can be improved.
Benefits of Enterprise Risk Management
Enterprise risk management holds a lot of benefits for businesses. And it’s important to note that any organization looking to break new grounds needs an efficient ERM system in place. Efficient risk management solutions go beyond mitigating risks.
Whether a company wants to enhance workflow processes, reduce reporting time or secure more capital, a sturdy and effective ERM system can be the way to go. Here are some of the benefits a business can reap from implementing an effective ERM system.
Improves Risk Reporting
A robust ERM system allows for more streamlined risk reporting across different departments in an organization. By employing an automated template system and a single ERM software system that is streamlined for different business units, risk data reporting becomes consolidated and automatically reported. Thus, eliminating the need for slower and error-prone manual processes.
Reduces Cost of Operations
An efficient ERM program will help to improve the approach and tools used for risk management. This, in turn, will eliminate delays and redundant risk reporting processes, thus improving efficiency and resource allocation for risk management.
Lowers Insurance Premiums
For a company with a robust risk management system will help reduce the premium cost of insurance because the insurer will be confident that the ERM system can tackle the majority of risks the company faces.
Increases Access to Funds
Companies with a robust ERM system are more likely to raise funds and meet their financial obligations. This is because, with an efficient risk management system in place, investors and credit lending institutes will more likely finance their enterprise.
Enhances Data Quality
By automating and improving underlying data recording and collection processes, powerful ERM systems enhance data quality. Thus, making high-quality data available within a much shorter time.
Improves Supply Chain
A solid risk management system is instrumental in improving the supply chain and inventory. It also estimates future demands and ensures that necessary steps are taken to reach more markets.
Reduces Workflow Complexity
One of the key objectives of an ERM program is to reduce the complexity and intricacy associated with a company’s workflow system. This is important because the less complex business operations and workflow systems are, the more efficient and productive the employees tend to be.
Challenges in Implementing ERM
Although an enterprise risk management program holds tremendous benefits for an organization, there are a number of things that can pose a bottleneck for the successful ERM implementation in an organization. And some of these challenges include:
- Problems with finding or developing the perfect ERM framework that is consistent with the core values of your business;
- Ignoring organizational culture and core values while implementing an ERM program;
- Lack of adequate resources (such as financial constraint) and qualified ERM personnel, such as an experienced Chief Risk Officer (CRO) and a dedicated risk management team;
- Lack of a clearly defined ERM framework and implementation strategy, or misinterpretation of the implementation instructions by the ERM team;
- Inefficient communication of the risk management processes and risk information between team players and all parties involved;
- Deviating from the laid down ERM procedure and policies to satisfy some trivial business goal.
Let's take a look at the definition of EMM and its components, determine the benefits of its implementation, and the industry use cases.
How Does Traditional Risk Management Differ from Enterprise Risk Management?
Traditional risk management and enterprise risk management are two different ways in which an organization can manage risks. While these two concepts have a number of things in common, they vary greatly in their approaches and how they tackle enterprise risks. Here, we discuss some of the obvious differences between TRM systems and ERM systems:
Insurable vs Non-Insurable
One of the key differences between enterprise risk management (ERM) and traditional risk management (TRM) is that the latter focuses on risks that can be insured, while the former covers any form of risk that can hinder a company’s progress.
For instance, TRM will take care of accidents in the workplace, such as fire hazards, which can be covered by insurance. At the same time, ERM will tackle more explosive risks like a data breach or slander.
Reactive vs Proactive
Traditional risk management is more reactive in its nature. It only takes effect after an unpleasant incident has occurred.
While on the other hand, ERM is a more proactive risk management system because its aim is to identify potential risks and operations that are potentially risky and determine how best to minimize the probability of such risks occurring, and how to quickly mitigate the impact of such risks if they do occur.
Siloed-Approach vs Holistic-Approach
TRM is a more basic risk management approach when compared to ERM because it occurs within individual business units. In this type of fragmented risk management, business leaders focus only on risks that matter to their individual departments, with no concerns on how the whole enterprise will be affected.
However, an ERM system is holistic and all-inclusive because when looking at risks, it views the business as a single entity, bringing all the various departments as one.
With this approach, an ERM system is able to identify and prioritize the risks that will have the most impact on the business, and possibility prevent the business from achieving its goals and objectives.
Standardized vs Adaptable
TRM is a more common system in the business. Therefore, it follows preset standards. In contrast, ERM also has a certain standard, but it’s much more dynamic because it can be adapted to the objectives of an organization. Adaptability is a very important aspect of risk management since no two businesses have exactly the same risks, objectives, culture, or management style.
Risk-Averse vs Risk-Taking
Risks are not all bad. In fact, they are sometimes necessary to achieve a significant level of business growth. Taking risks is something businesses need to embrace with caution, which is what ERM systems thrive to achieve.
An ERM system will enable organizations to identify risks that should be completely avoided and those that hold opportunities for growth and expansion. However, TRM is risk-averse and only views risks as channels for potential losses.
Conclusion
The global business environment is changing rapidly, and each new change brings new forms of risks to tackle. And even more importantly, business leaders are expected to have strategies and solutions for addressing each new problem. In this case, enterprise risk management comes to the rescue with insights into potential risks and workable solutions for preventing them before they occur.
Need a qualified team?
Scale your development capacity with top-level expertise and resources.