There are many opportunities for the enterprise software industry in 2023. Organizations across industries have moved to a teleworking model that has spurred enterprise technology spending and the proliferation of services such as digital collaboration, cloud security, artificial intelligence, and predictive analytics.
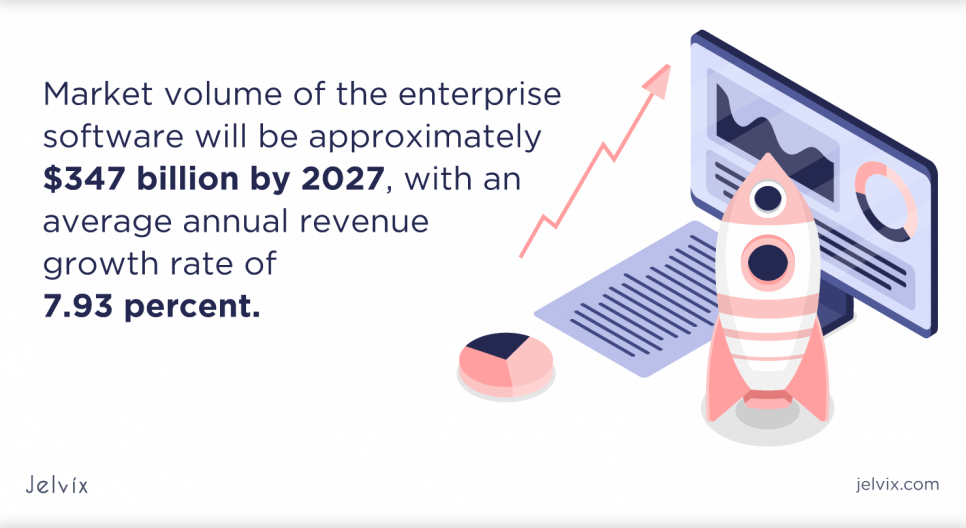
The introduction of innovation has revitalized the enterprise software development market. According to the study, the implementation of digital transformation projects has quickened threefold. The market volume of the enterprise software will be approximately $347 billion by 2027, with an average annual revenue growth rate of 7.93 percent.
Large organizations have complex processes that involve many people. And business growth is usually accompanied by an increase in the amount of data that must be administered.
Therefore, enterprises that recognize the importance of involving technology to provide better control place high demands on the software to manage these processes. They need a special toolkit called enterprise software. And these are all severe tools explicitly designed for big business. So, what is the meaning of enterprise software? Read on to find out more.
What is Enterprise Software?
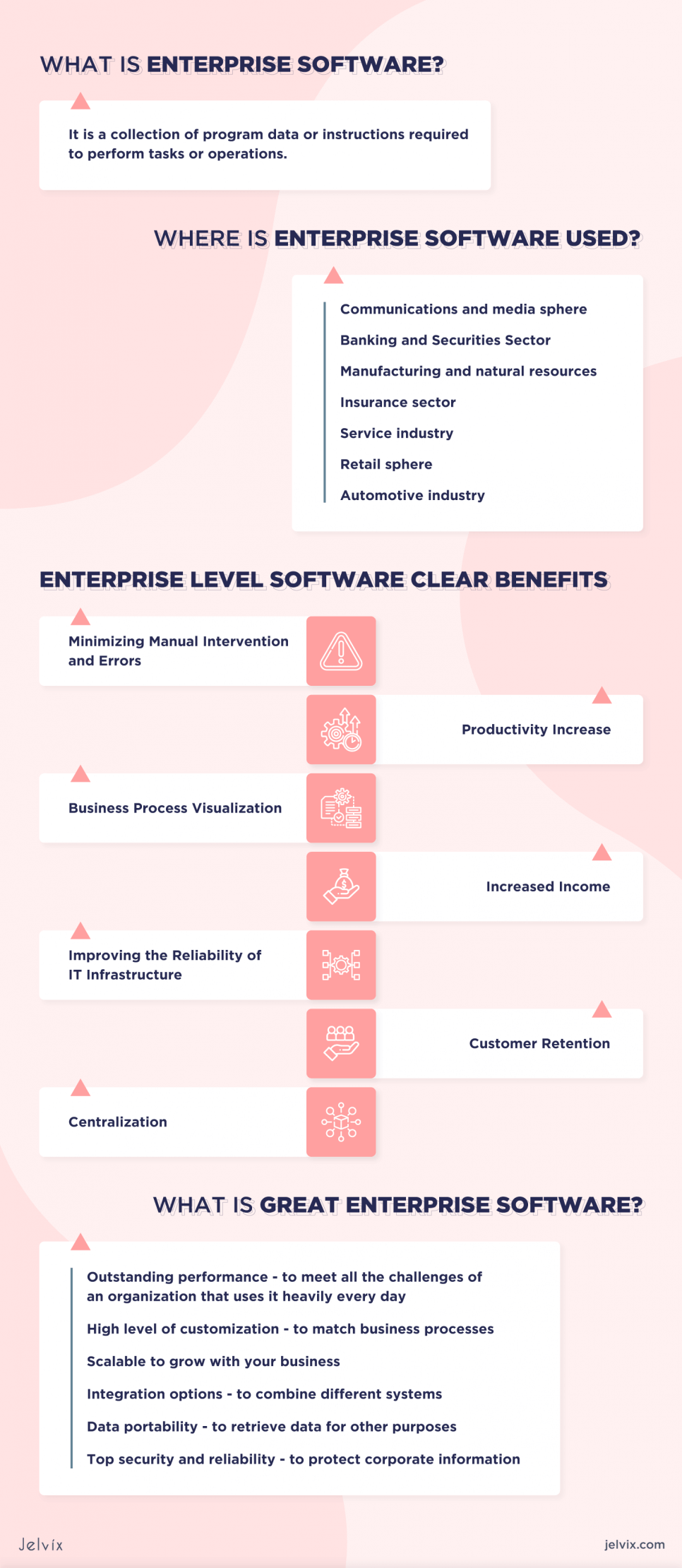
Let’s start with a broad definition of software. It is a collection of program data or instructions required to perform tasks or operations. It’s classified into three categories:
- System software is at the heart of the application software. It is responsible for managing hardware components, submitting and controlling essential non-task-related functions.
- Programming software is a kit of tools for developers to write programs.
- Application software is developed to perform specific tasks. Therefore, it takes on daily and particular tasks that the user wants to solve.
We can classify application software into two types: applications used by individuals or by wider user groups of large companies or enterprises. Enterprise definition is vital in this case. In this context, “enterprise” means a large corporation with an international presence, a charitable foundation, or other large organizations with many processes.
Given the number of people involved in such organizations, single-user PC apps are not enough in this case.
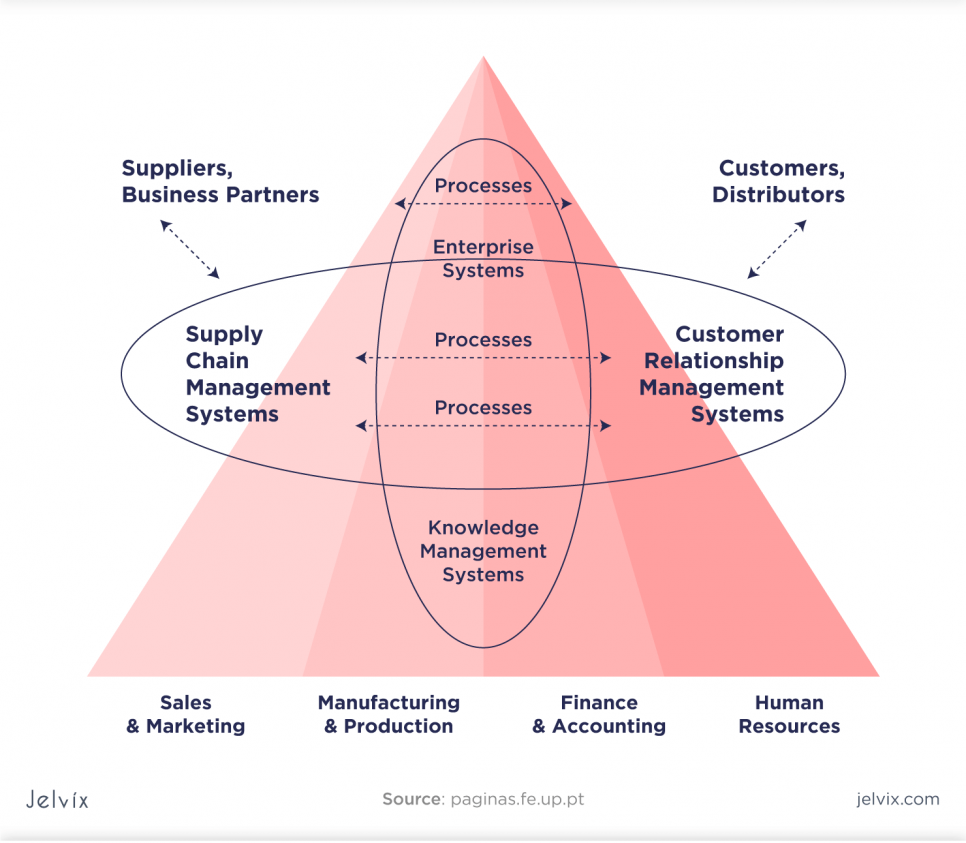
Enterprise Systems (or ES) are large-scale software packages capable of maintaining information flows, data analysis, business processes, and reporting in complex organizations. It is an essential element of a computer information system that provides business-oriented tools to meet the needs of any large organization.
Standard ES is associated with Enterprise Application Software Systems. They can also be customized, tailor-made solutions designed to support the needs of a particular organization.
Enterprise Software Tasks
The primary activities inherent in enterprise software are:
- Display, processing, and storage large volumes of heterogeneous data;
- Support and/or automation processes that rely on this data.
ES comprises a set of computer programs that have:
- Development tools for creating applications that are unique to your organization;
- Tools for modeling organizational processes;
- Base business applications.
Enterprise software is usually centrally managed and shares a common interface with other systems. The services provided perform business functions to solve corporate problems and unite all company departments, even if they work separately. ES’s goal is to speed up business processes, improve efficiency, productivity, transparency, and, as a result, drive revenue growth for the company.
Where is Enterprise Software Used?
The spheres are pretty extensive, but, according to BusinessWire, it is most actively used in:
- Communications and media sphere;
- Banking and Securities Sector;
- Manufacturing and natural resources;
- Insurance sector;
- Service industry;
- Retail sphere;
- Automotive industry.
What is An Enterprise Application?
The term itself is rather broad, but in this context, it is a valuable software tool included in an enterprise software package. Let’s look at the chief characteristics that distinguish an enterprise-grade application.
The critical parameter is locked (non-dynamic) code, which is more expensive because it requires configuration, maintenance, and support. But the principal thing is the difference in internal engineering.
An enterprise application (EA) grants a much deeper level of architectural consideration of development and commissioning (in the language of the software developer, this state is called “production”). In other words, it will be rated for speed, scalability, and any broken and dirty data streams.
In addition, an EA can offer a much deeper and more granular level of auditing. This provides more accurate data validation for business reports related to profit and loss and may also be subject to regulations.
Also, EA often proffers higher levels of reliability, broader end-to-end encryption and is likely to undergo rigorous quality assurance and testing to increase stability. In addition, it is often pre-configured to meet the requirements of a secure production environment.
What are Enterprise Software Examples and Functions?
We categorize enterprise software according to its business function. Each type of EA can be held as a “system” because of its integration with the company’s business processes.
This list contains customer relationship management systems and billing tools, and industrial applications for various industries. As part of its many functions, it constantly updates modern corporate applications with new technological developments.
Technologies such as artificial intelligence, voice technology, chatbots, or the Internet of Things make it easier for large organizations to operate as efficiently as possible. Let’s inspect the most common systems.
Project Management
Since many employees are now working remotely, these applications are the basis for the entire team’s work. An enterprise project management application aids co-workers in collaborating more effectively, no matter where they are.
Project management apps summarize all active projects. They allow team members to dive into specifics and stay on top of upcoming tasks and their details to keep up with the schedule.
When used correctly, project management apps help you stay as productive as possible and ensure that processes and procedures are transparent and efficient for any task or initiative.
Enterprise Resource Planning
We can put this type at the top of the list of enterprise applications since it is used all over the place. Earlier, ERP solutions were implemented mainly by large corporations. Now, these systems can serve small companies and even startups.
It is probably wrong to call an ERP an application since it is a complete integrated management process of the key business processes in an organization. And to implement such a process, various technologies are used.
The modern ERP system has gone far beyond its original functions. It now includes a complete set of integrated components that provide modern enterprises with the tools necessary to optimize operations.
The system can be integrated with other enterprise management software solutions, including Business Intelligence, supply chain management, CRM, financial information, point of sale data, etc.
Using ERP software, organizations can track both their resources and the statuses of business events. This facilitates the exchange of data between departments of the organization and external stakeholders and provides a comprehensive view of the essential processes. Due to a unified data warehouse and control of access points, the ERP software is reliably protected from data breaches.
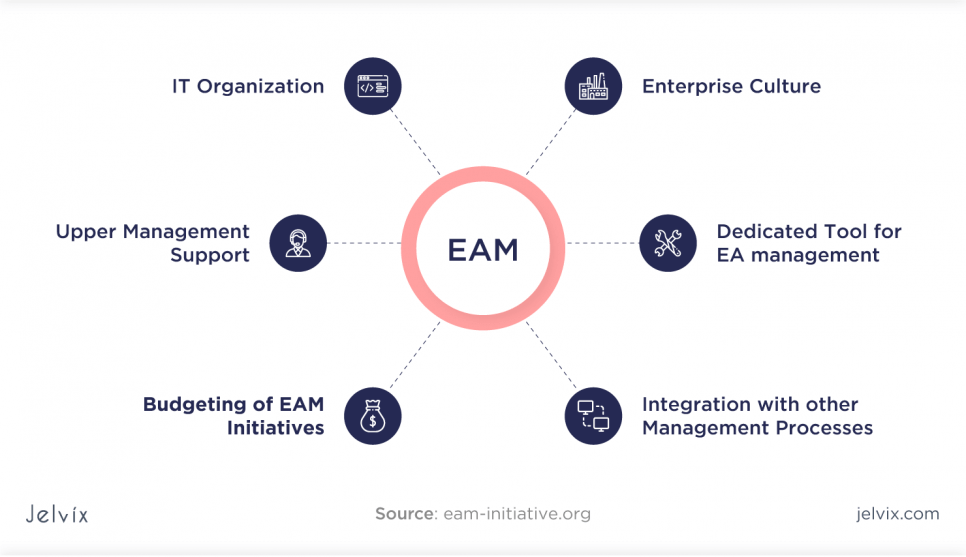
Enterprise Asset Management
This solution permits organizations to track and manage the life cycles of their assets. Asset management software aims to lengthen the life of assets and, therefore, increase revenues. Tracking tasks such as required maintenance or compliance with standards facilitated this. EAM systems include the following features:
- Inventory and material flow management;
- Maintenance management;
- Repair and overhaul or MRO;
- Asset lifecycle management.
Personnel Management
In large organizations, the HR department deals with many employees. Its tasks include hiring, firing, vacations, promotions, PTOs, etc.
Moreover, HR professionals need to consider complex labor laws in carrying out these tasks. Failure to comply with laws or untimely changes to documentation can cause severe financial and legal aftermaths. Thus, most businesses should have specialized HR software.
Business Intelligence
This type of software aids companies in analyzing data kits from varied sources and generating actionable insights. Applications use comparative, data mining, and innovative statistical algorithms to determine patterns and make detailed predictions.
Business intelligence systems use different graphs, charts, and tables to visualize trends and patterns in complex data. Supplementary features that may be available in BI software include:
- Data visualization;
- Document management;
- Analytics;
- Big data integration;
- Decision-making services;
- Analytical processing online.
Email Marketing Systems
To grow and develop, organizations need to find new customers while continually maintaining the interest of existing ones. Therefore, implementing a suitable email marketing system is the best way to gain access to the tools you need to manage client preferences.
Apps and tools enable you to automate communication via mail, social media, SMS, and/or digital advertising; and easily segment customer lists to build targeted marketing campaigns. As a result, the technology is helping to improve the accuracy and effectiveness of campaigns dramatically, enabling marketing teams to achieve ambitious goals.
Accounting Software
This type of enterprise software management comprises sets of financial management tools that simplify handling monetary information and various accounting processes. Enterprise applications centralize and automate financial operations across the entire organization. Some of the most commonly used features of accounting software include:
- General ledger;
- Budgeting;
- Payment statement;
- Debt on accounts;
- Accounts payable;
- Cost management.
- Fixed assets;
- Tax reporting.
Customer Relationship Management
A competent sales approach and positive customer relationships are crucial elements of any business. To achieve these goals, CRM software is used. It includes all the tools you need to personalize sales tactics and strengthen relationships. These are:
- Contact management;
- Sales automation tool;
- Lead management;
- Tracking customer interaction;
- Database management;
- Marketing and Campaign Management.
Business Process Management
It is a tool for automating corporate processes, the principle of which is based on modeling, automation, management, and optimization methodologies. BPM software provides:
- Effective planning;
- Data entry controlling and app errors;
- Minimizing costs and implementing a business strategy;
- Converting manual processes to electronic;
- Ensuring integration and scaling;
- Creation of an understanding of business data;
- Improving the efficiency of the everyday job processes;
- Changing management according to requirements, laws, regulations.
Supply Chain Management
This system allows you to simplify and control the production process from when the order is placed to the moment the package is delivered to the buyer’s doorstep. Most often, SCMs are custom-designed and based on the needs of a particular enterprise. From a supply chain perspective, SCM systems are divided into two blocks:
- Planning – scheduling, forecasting solutions, supply chain design, simulation of various situations, analysis of operations progress.
- Execution – tracking and verifying logistics execution, supplier management, sourcing and procurement, order processing, and more.
SCM software is used to manage activities such as ordering materials, production management, sales order management, machine and distribution management. SCMs can be independent or a part of an ERP system.
Enterprise Level Software Clear Benefits
Enterprise software used to be associated with something slow, cluttered, and difficult to use, especially when compared to today’s lightweight and flexible applications.
But now, corporate software is no worse than consumer software, as it combines modern methods and development tools. This comprises maximal automation, formulating automated testing and release management strategies, and leveraging Agile and DevOps. Well, the decisive factor is the complete transparency of the software delivery process.
Enterprise apps successfully automate day-to-day tasks, deepen customer relationships, and drive the company’s bottom line through efficiency gains or direct revenue. There are some more specific benefits that deserve special mention.
Minimizing Manual Intervention and Errors
Manual data entry often leads to errors that can affect performance and require resources to clean up the system. However, corporate software systems automate the collection and movement of data in such a way, which reduces the risk of any system bugs.
Productivity Increase
Improved performance is one of the fundamental benefits of implementing ES. Automation saves time, which can then be used for more critical tasks.
Business Process Visualization
Typically, enterprise software involves custom reports or data visualizations to help organizations conduct meaningful analyses and identify bottlenecks in internal workflows. For example, reports will allow you to visualize various processes, such as customer retention, accounts receivable, or on-time delivery.
Increased Income
Increasing profits is essential for any business. And the purpose of enterprise software is to help organizations take the steps and actions to increase revenue. For example, business intelligence programs enable enterprises to calculate operational bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
Product lifecycle management oversees the correct development of the product by regulatory requirements. As a result, the costs of the company’s resources are reduced.
Improving the Reliability of IT Infrastructure
Another advantage of corporate systems is their increased reliability compared to small IT solutions. This means that systems will have more “uptime” and virtually no “downtime.”
Customer Retention
Keeping existing customers and attracting new customers is one of the main tasks of enterprises. And it is corporate software that is best suited to increase customer conversion.
Centralization
Instead of many programs or several sandbox applications, only one software is used. All employees have access to a shared and up-to-date database, so the company does not have problems with data duplication.
Limitations of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
Implementing corporate software is associated with high financial and time costs because it must be adapted precisely to your needs, and employees must undergo special training. In addition, software of this size requires constant development and regular maintenance.
However, the benefits of effective process planning at all levels and across all departments outweigh these drawbacks in the long run.
Let's find out enterprise data warehouses’ purpose and examine the difference between database and data warehouse.
What is Great Enterprise Software?
As your company grows and its business processes become more complicated, so do the software requirements used to manage these processes. Since almost everything can be automated nowadays, it will not be difficult to fulfill these requirements. All that remains is to choose an enterprise software solution that will meet the needs of your business.
Several defining characteristics are inherent in quality software. Which of the following does enterprise software include?
- Outstanding performance – to meet all the challenges of an organization that uses it heavily every day;
- High level of customization – to match business processes;
- Scalable to grow with your business;
- Integration options – to combine different systems;
- Data portability – to retrieve data for other purposes;
- Top security and reliability – to protect corporate information.
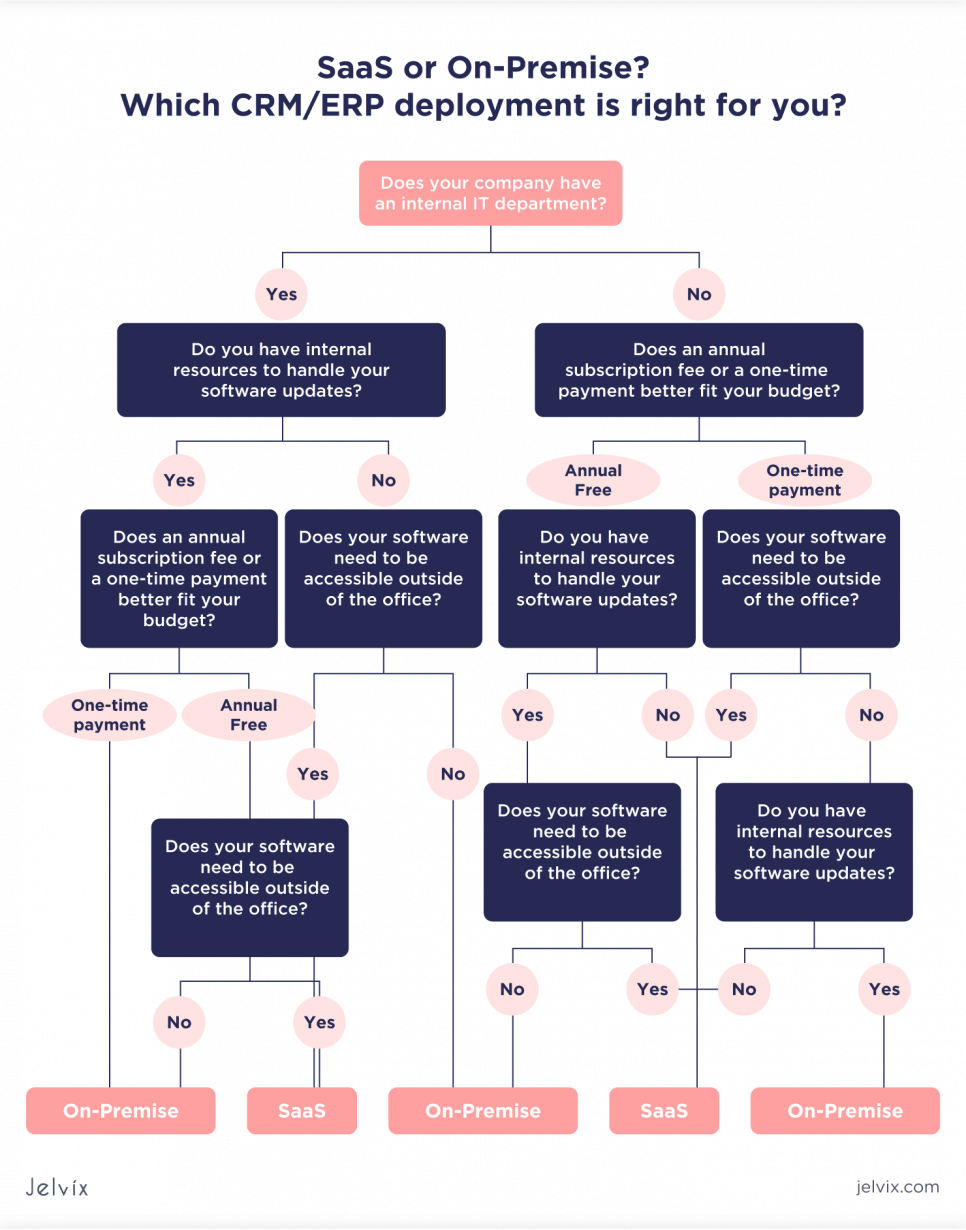
Differences Between SaaS and ES Solutions
Software as a service (SaaS) is notable for being leased and hosted in the cloud. In addition, multiple tenants can use SaaS solutions: that is, numerous enterprises are working on a single database.
While SaaS provides versatile and cost-effective access to software that proposes specific actions, its drawbacks can include security concerns and database maneuvering. And for configuration, enterprise solutions have an edge.
The enterprise software is wholly owned by the company, hosted on the physical servers of the organization, and uses a computer network to connect users – employees of the company. Large companies use servers, storage systems, and associated software as the basis for their IT infrastructure. These systems can provide the highest level of transaction execution and data security.
Out-of-the-Box vs. Custom: How To Choose Enterprise Software
Managing an organization is not a simple task and requires smooth business processes, thorough planning, efficient control, automation, and much more.
Every enterprise faces a tough choice: implementing a ready-made corporate tool or creating a custom solution based on existing processes. Both options have their nuances. We offer you an easy way to determine if existing solutions can meet your company’s requirements. It comprises six steps:
- Set goals you want to achieve.
- Interview the staff who will use the new tool.
- Together, make a list of the required corporate system features.
- Distribute functions according to their importance to your organization.
- Compare the list of desired features with the features of specific solutions.
- After analyzing the result, you will see if a particular system can meet the needs of your enterprise. Now all you have to do is calculate the budget and create an action plan for software implementation.
If ready-made systems cover less than 60% of the company’s requirements, it is worth choosing a solution created according to an individual template. And on the path to custom software, the first stage is finding reliable enterprise developers. It is always better to bet on a vendor who has already developed this type of software.
Conclusion
Enterprise apps boost digital transformation, creating a foundation for innovation for customers and industries. Companies that want to be competitive must keep in step with the dynamic software development industry. One way to gain a decisive advantage is to invest in enterprise-grade applications.
The right software stack speeds up ROI for individuals and industry giants alike. It can be customized, updated, scaled, reused, extended, and secured. Our company can offer all of these.
Jelvix provides a full range of IT services: from IT consulting to development, testing, and further product support. Our portfolio of products and platforms covers a variety of industries and functional areas and comprises intelligent software solutions that can transform your business.
We will quickly and flexibly develop enterprise-level software that will be fully adapted to your business processes now and in the future. If you are looking for a unique, innovative, and customizable enterprise solution, and you are unsure how and where to start, feel free to contact us at any moment!
Need a qualified team?
Extend your development capacity with the dedicated team of professionals