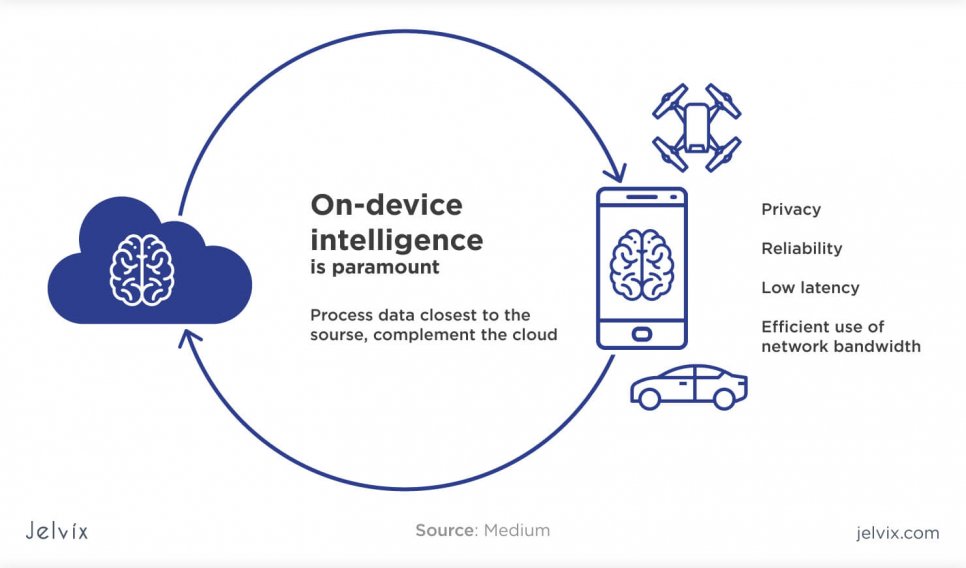
One of the most widespread trends is cloud computing — the form of data storage and processing where files are stored on remote data centers and can be accessed anytime and from any device. However, cloud computing is not the only form of distributed computing. Now, many businesses opt in favor of edge computing.
Edge computing definition
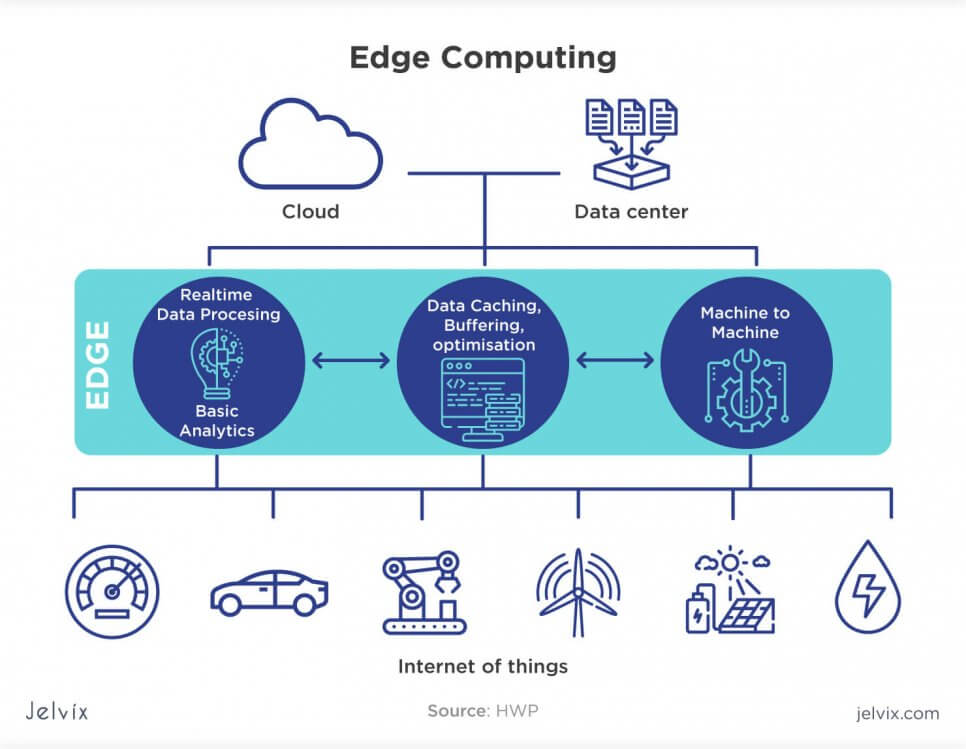
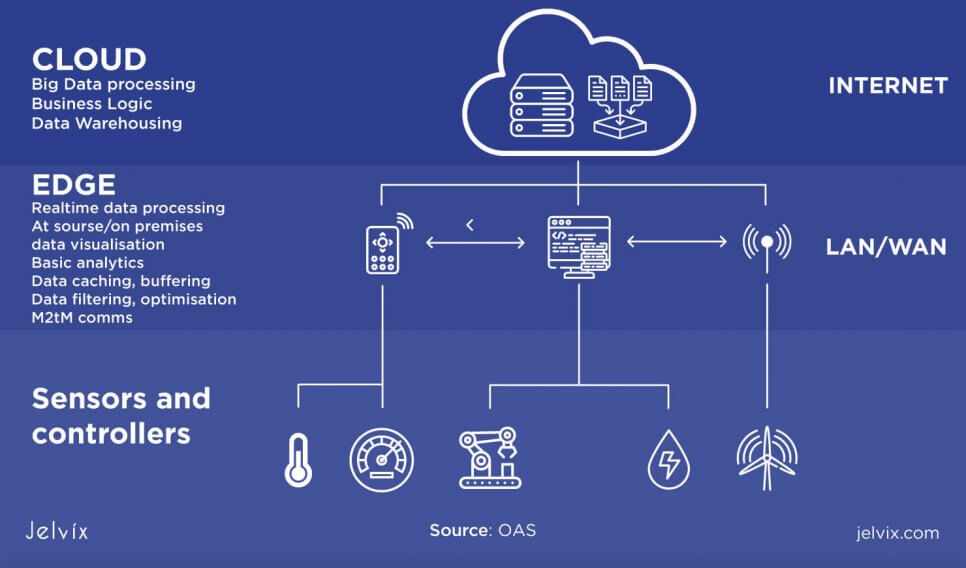
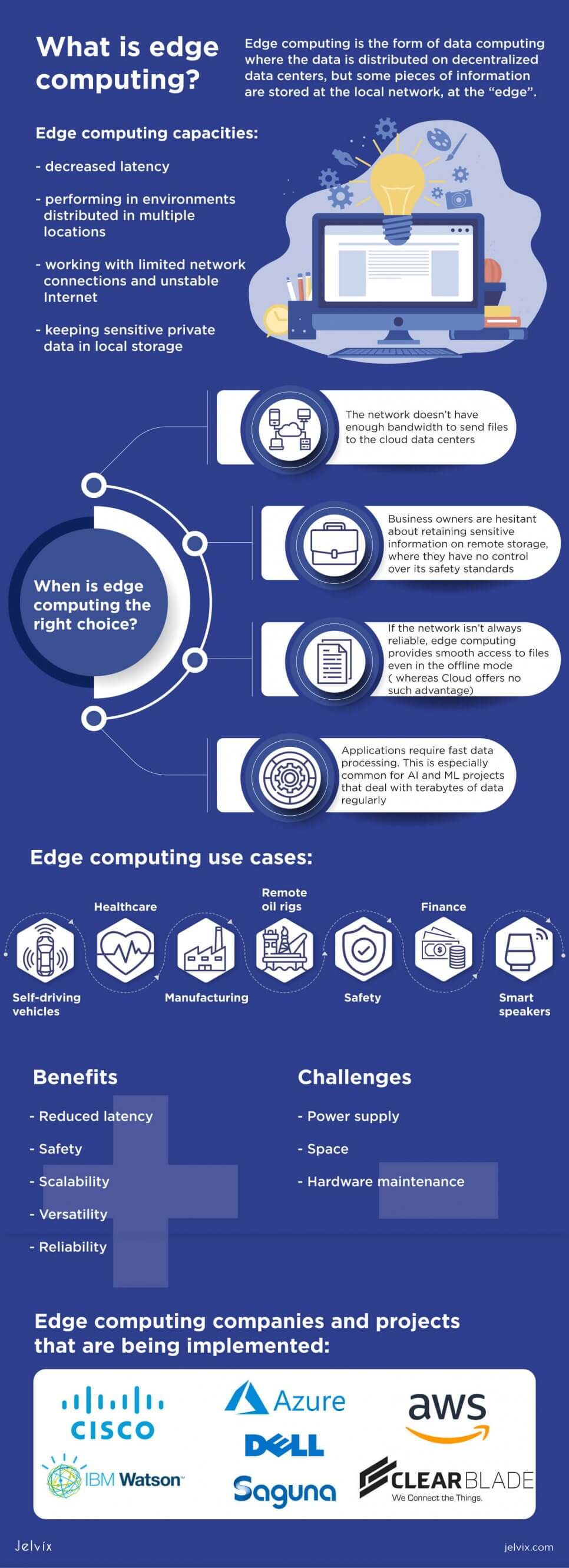
Edge computing is the form of data computing where the data is distributed on decentralized data centers, but some pieces of information are stored at the local network, at the “edge”. Traditional cloud solutions save data to remote centers, whereas edge network keeps these files in local storage where they can be easily accessed and used.
In cloud computing, requests for data deployment are sent to the data centers, processed there, and only then returned to the local network. Edge computing doesn’t need this request loop — the request is answered immediately, with no need to receive permission from a remote data center. Local devices can deploy data offline with a lower amount of required bandwidth traffic.
What is the network edge?
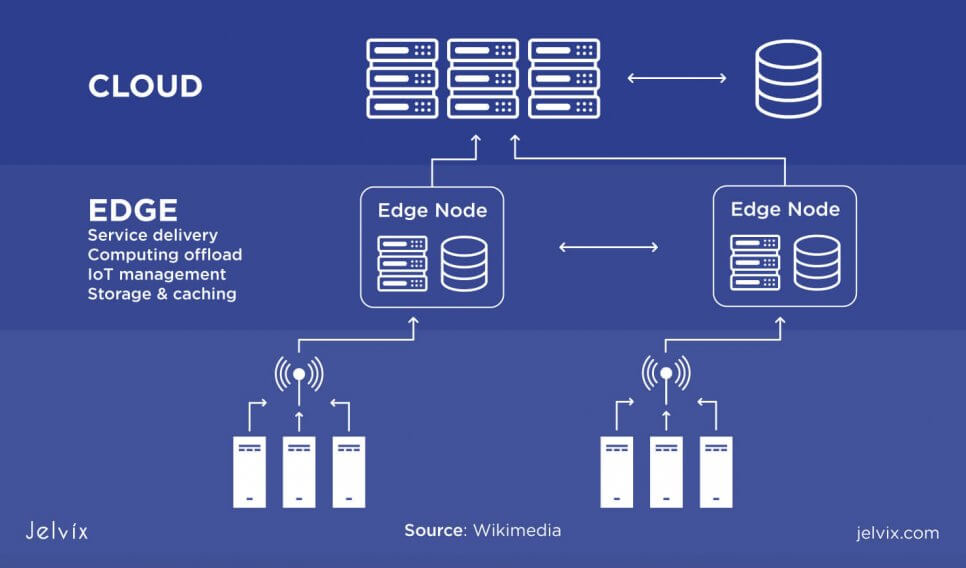
If the enterprise connects its network to a third-party provider, it’s called a network edge. In such a case, the network has several segments that rely on the infrastructure of various providers. Some data can be stored on the wireless LAN, other bits of information — on the corporate LAN, whereas others would be distributed to private centers.
The network edge is a combination of local storage and third-party remote storage. It’s the spot where the enterprise-owned network connects to the third-party infrastructure, the most distant point of the network — quite literally, its edge.
Edge computing capacities
Edge computing is similar to Cloud — it also offers decentralized storage rather than keeping the information in the single-center, but additionally, it provides unique benefits. Let’s take a look at key capacities of edge computing, as opposed to other decentralized computing methods.
Decreased latency
Cloud computing solutions are often too slow to handle multiple requests from AI and Machine Learning software. If the workload consists of real-time forecasting, analytics, and data processing, cloud storage won’t deliver fast and smooth performance.
The data has to be registered in the center, and it can be deployed only after permission from the center. Edge computing, on the other hand, engages local processors in processing data, which decreases the workload for remote storage.
Performing in distributed environments
An edge network connects all points of the network, from one edge to another. It’s a tried-and-proven way to enable the direct data transfer from one distant storage to another without concerning data centers. The data can quickly reach the opposite ends of the local network and do it much faster than a cloud solution would.
Working with limited network connection, unstable Internet
Edge computing allows processing data in the local storage with in-house processors. This is useful in transportation: for instance, trains that use the Internet of Things for communication don’t always have a stable connection during their transit. They can reach data from local networks when they are offline, and synchronize the processes with data centers once the connection is back up.
The edge computing service provides a balance between traditional offline data storage, where the information doesn’t leave the local network, and a fully decentralized solution, where nothing is stored on the local drive.
Here, sensitive information can be stored remotely, whereas data that needs to be urgently available regardless of the state of Internet connection can be accessed on the edges of networks.
Keeping sensitive private data in local storage
Some businesses prefer to avoid sharing their sensitive private data with remote data storage. The safety of information then depends on providers’ reliability, not on the enterprise itself. If you don’t have a trusted cloud storage vendor, edge processing provides a compromise between classical centralized and fully decentralized.
Those companies that don’t trust confidential information to third-party providers can send sensitive files to the edge of their networks. This allows companies to have full control over their security and accessibility.
Cloud vs Edge computing
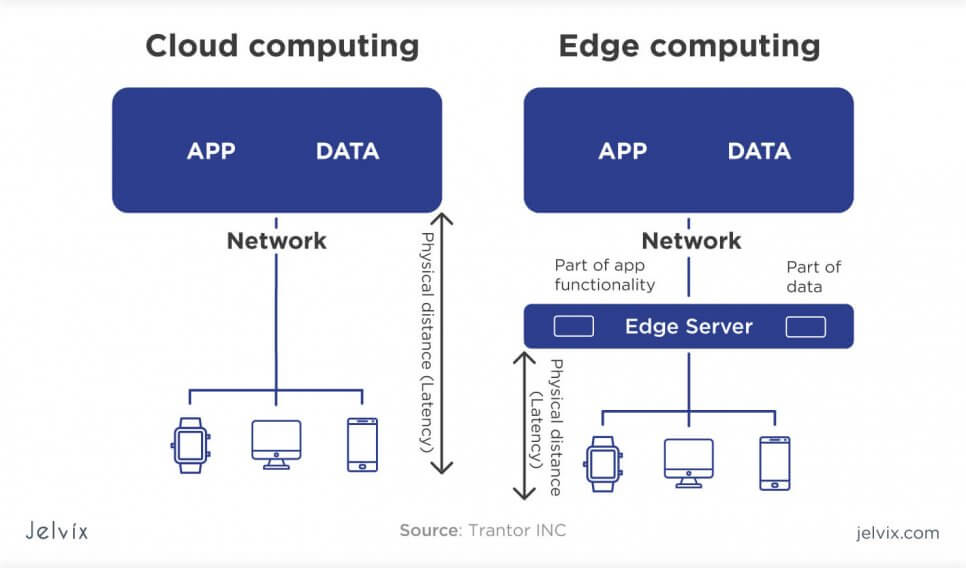
Cloud and edge computing are similar by their key purpose, which is to avoid storing data at the single center and instead distribute it among multiple locations. The main difference is that cloud computing prefers using remote data centers for storage, while edge computing keeps making partial use of local drives.
That said, edge computing also uses remote servers for the majority of stored data, but there is a possibility to decide what data you’d rather leave on the drive.
Edge computing is an excellent backup strategy in the following scenarios:
- The network doesn’t have enough bandwidth to send files to the cloud data centers.
- Business owners are hesitant about retaining sensitive information on remote storages, where they have no control over its storage and safety standards;
- If the network isn’t always reliable, edge computing provides smooth access to files even in the offline mode (because files are stored locally, whereas Cloud offers no such advantage).
- Applications require fast data processing. This is especially common for AI and ML projects that deal with terabytes of data regularly. It would be a waste of time to run each file through data storage when an edge application offers an immediate response from the local network.
Practically, edge computing wins over Cloud in all cases where communications tend to be unstable. When there is a chance that a connection will disappear, but there is still a need for real-time data, edge computing offers a solution.
Cloud computing, on the other hand, has its own unique advantages that can be limited by the edge’s attachments to the local network.
- No need to invest in securing local networks. If the company doesn’t have established security practices and a professional support team, preparing local storages to accommodate sensitive edge data will require a lot of time and resources.
- It’s easier to store large datasets. Edge computing is great if companies don’t need to save all the information that they collect. However, if insights are supposed to be stored long-term, local networks will not be physically able to accommodate large data sets on a regular basis — sooner or later, the data would have to be deleted. This is why the majority of big data projects use Cloud: it allows storing large amounts of data with no limitations, even if it requires the sacrifice of the computing speed.
- Easy to deploy on multiple devices and software. Information, stored on the cloud, isn’t limited to particular hardware. Provided that a user has an Internet connection, the data can be accessed any time and from any device, as soon as the access requirements were met.
Edge computing focuses on providing stable and fast performance across the entire enterprise. It can’t store large amounts of data because local networks have size limitations, but the performance is smoother.
Use cases of edge computing
Edge computing can be applied to any industry. Whenever there is a need for a consistent data stream, edge computing can provide fast and uninterrupted performance. Let’s examine industries where edge computing can be most useful.
Self-driving vehicles
Autonomous vehicles need to make data-based decisions incredibly fast. There is no time for an urgent request to be sent to the cloud data centers and then returned to the local network if a pedestrian is running in front of the car. An edge service doesn’t send a request back to the cloud, and decisions can be made much faster. Also, edge computing IoT provides a real-time data stream even when the vehicle is offline.
Healthcare
Healthcare software requires real-time data processing regardless of the quality of the Internet connection. The device should be able to access a patient’s history immediately and with no errors. Edge computing can function online, and, just like in autonomous vehicles, it provides a fast response from the server, because it’s located directly on the local network.
Manufacturing
Manufacturers can use edge computing to control big networks and process multiple data streams simultaneously. If the industrial equipment is distributed among multiple locations, edge computing will provide fast connections between all devices at all points of the network. Again, the data stream doesn’t depend on the quality of the Internet connection.
Remote oil rigs
Some industries use software that functions with low or absent bandwidths. Synchronizing data is quite difficult in such conditions. If environmental factors, location, or accidents can disrupt the Internet connection, edge computing provides a solution. The rig can receive information from the local network, and back it up to the cloud as soon as the connection is back.
Safety
Whenever there is a need for immediate security response, edge computing architecture is a better alternative to traditional cloud solutions. The requests are processed directly at the network without being processed at the data center. It allows security providers to promptly answer threats and predict risks in real-time.
Finance
Edge computing can be used with smartphone IoT and AI applications as an enabler of real-time data updates. Users will be able to control their financial history, get documentation, and view operations even if they are offline because the key information is stored on their device’s local network.
Smart speakers
Speakers should process the user’s input immediately to perform requested operations. Again, they should preferably be independent of the bandwidth quality. Edge computing provides stable data storage and fast response to users’ commands.
Advantages of edge computing
After we’ve analyzed the most common technology applications and compared it to cloud solutions, it’s time to summarize the key benefits of the technology.
Reduced latency
Edge computing can deliver much faster performance because the data doesn’t have to travel far to be processed. When the information is located closer to its network, it will be processed much faster. In certain industries, like transportation or healthcare, even a second of delay can lead to multi-million damage.
Also, reduced latency provides a faster user experience to end-users, which helps to retain the audience.
Safety
Despite removing data from the local central storage, cloud computing architecture is still centralized. Even if companies use multiple remote storages, the data still goes to data centers, even if there are several of them.
If something happens to the center due to the power outage or security attack, the enterprise will be deprived of data. Edge computing allows companies to keep some of their control over data by storing the key pieces of information locally.
Scalability
Edge computing allows storing increasing amounts of data both in remote centers and on the edges of networks. If at some point, the local network can no longer accommodate all the collected data, the enterprise can transfer some of the files reserved on the remote storage. The local network, in this case, is left for files that are crucial for a team’s operation. The secondary data is sent to data centers.
Versatility
Edge computing finds a balance between traditional centralized cloud data storage and local storage. Companies can focus both on the speed of the performance and send some data to the edges of the network.
The other portion of data can be transferred to data centers — this allows working with large data centers. In a way, enterprises can benefit from the best practices of local and remote data storage and combine them.
Reliability
Edge computing minimizes the chances that a technical issue on the third-party network will compromise the operations of the entire system. Also, locally-stored portions of data can be accessed even if the solution is offline and synchronized in the data storage as soon as the connection is back. Edge computing increases enterprises’ independence and minimizes risks associated with power outages and security issues.
Let's discuss which IT outsourcing trends will change the industry.
Challenges of edge computing
Despite the versatility of the technology, it’s obvious that edge computing isn’t a perfect computing form. Several crucial challenges need to be addressed before the enterprise can fully switch to this storage method.
Power supply
Technically, edge computing can process data at any location on the planet because it doesn’t require an Internet connection. However, practically, this concept is often made impossible by the lack of power supply.
If a device is cut off from the stable electricity source, it won’t be able to process data in the local network. This challenge can be answered by implanting alternative energy production means (solar panels) and accumulators.
Space
Local networks require hardware to function. This poses the first problem: not all companies have physical space to store servers. If there aren’t enough local servers, the edge computing will not be able to accommodate a lot of data. Hence, if your goal is to store large masses of data long-term (like for the big data technology), cloud computing is a more feasible option.
Hardware maintenance
On the one hand, edge computing provides more control over the way your data is stored and processed. On the other hand, the enterprise needs to take responsibility for monitoring and repairing local servers, invest in maintenance, and deal with the outages. With cloud computing, this task is fully outsourced to the server provider.
Security
Technically, edge computing can be a lot more secure than cloud computing because you don’t have to entrust sensitive information to the third-party provider. In reality, this is only possible if the enterprise invests in securing its local network. You need to get a professional IT security partner that will monitor the safety of your local network and assure safe data transfers from one edge to another.
Examples of edge computing companies
Global technology players joined the edge computing trend a long time ago. There are already many services that can be used by enterprises to implement edge computing in their data storage. Let’s take a look at edge computing use and projects that are being implemented by big organizations.
Siemens
The company launched the Industrial Edge solution, the platform where manufacturers can analyze their machine’s data and its workflow instantly. The non-essential information is transferred to the cloud, which reduces latency on the local network.
Crucial bits are stored at the edge of the network – locally, on the hardware. If there’s an issue with an Internet connection, industrial companies still can keep track of their productivity, detect technical issues, and prevent downtimes.
Saguna
It’s an edge computing provider that offers an infrastructure for edge computing implementation. The company created Open-RAN, the set of tools that help build, deploy, and secure edge computing stores. The tools allow companies to set up low-latency data transfers and secure sensitive information.
ClearBlade
ClearBlade uses the Internet of Things and edge computing to allow enterprises to set up edge computing across multiple devices. If a business has a ready IoT edge device, developers can transfer it to edge storage by using Clear Blade’s development and security tools.
Cisco
Cisco offers a set of communication tools for implementing edge computing, compatible with 4G and 5G connectivity. Businesses can connect their services to the Cisco Network Service Orchestrator to store data, collected by their software, on the edge of the local network and Cisco’s data centers.
IBM
IBM’s IoT platforms and Artificial Intelligence tools support edge computing as one of many possible computing options. Right now, the company’s research is focused on building networking technology that connects multiple edge networks with no WiFi connection
Dell EMC
Dell has been actively investing in the Internet of Things ever since the opening of an IoT division in 2017. The company now adapts edge computing to store data from its IoT edge devices. Dell developed a custom set of specialized instruments: Edge Gateways, PowerEdge C-Series servers, and others.
Amazon
Amazon has already proven to be one of the most stable and powerful cloud computing providers. AWS is the best cloud solution on the market right now. It’s only natural that the company takes an interest in edge computing as well. Lambda@Edge, a service developed by Amazon, allows processing data offline without contacting AWS data centers.
Microsoft
Microsoft has the potential to revolutionize edge computing the way Amazon revolutionized the cloud. The company currently holds more than 300 edge patents and invests in developing multiple IoT infrastructure. The most prominent example is their IoT Azure service, a package of tools and modules for implementing edge computing in IoT projects.
Conclusion
The demand for automation and the Internet of Things keep growing, and devices need to deal with real-time data and produce immediate outputs. When industries like healthcare and autonomous transportation start investing in automation, new data processing challenges arise.
Even a second of delay can make a life-or-death difference and lead to multi-million economic and reputational damage. Under such conditions, it’s imperative to have a reliable data processing technology that can answer offline requests and deliver prompt responses.
Shifting data storage from cloud data centers closer to the network allows reducing operation costs, delivering faster performance, and working with low bandwidth. These benefits can potentially solve multiple issues for IoT, healthcare, AI, AR — any field and technology that requires fast real-time data processing.
You can implement edge computing into your enterprise operations right now and access these benefits. It’s possible with an experienced tech partner who knows how to set up data transfers, secure local networks and connect systems to edge storage.
At Jelvix, we help companies to secure their data storage and find the optimal computing solution. Contact our experts to find out if your project can benefit from edge computing, and if so, start working on the infrastructure.
Need a qualified team of developers?
Boost your business capacity with the dedicated development team.